The Universe - The Cosmos
Universe is all of time and space and its contents. It includes planets, moons, minor planets, stars, black holes, galaxies, the contents of intergalactic space, and all matter and energy. The universe is all existing matter and space considered as a whole. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from sub-atomic particles to entire galactic filaments. A particular sphere of activity, interest, or experience. The portion of the universe that can be seen by humans is approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter at present, but the total size of the universe is not known. Cosmos is an alternative name for the universe or its nature or order. Usage of the word cosmos implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. Cosmology is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos.
 The photo on the right is not a
selfie. It is just an artist rendition of what our
milky way galaxy would look like if it were
seen from another galaxy.
The photo above is not to make you feel
insignificant, it is only for
reference and
scale. Think of it as a
scale in your mind.
Depending on your
field of view, you would have to be around
100,000 light years away to see this Galaxy using the naked human
eye. And as you got closer, it would almost disappear because of the
tremendous amount of space there is between
everything, like with atoms. The
universe is so large that the
earth in comparison is smaller than a grain of sand or a speck of
dust. But even with the earth and humans being so tiny, there are things
still a lot smaller than us that we can't even see. We are simultaneously
really big and really small at the same time. Sizes (nano)
- Pyramid of Complexity.
The photo on the right is not a
selfie. It is just an artist rendition of what our
milky way galaxy would look like if it were
seen from another galaxy.
The photo above is not to make you feel
insignificant, it is only for
reference and
scale. Think of it as a
scale in your mind.
Depending on your
field of view, you would have to be around
100,000 light years away to see this Galaxy using the naked human
eye. And as you got closer, it would almost disappear because of the
tremendous amount of space there is between
everything, like with atoms. The
universe is so large that the
earth in comparison is smaller than a grain of sand or a speck of
dust. But even with the earth and humans being so tiny, there are things
still a lot smaller than us that we can't even see. We are simultaneously
really big and really small at the same time. Sizes (nano)
- Pyramid of Complexity.The Scale of the Universe from Big to Small (youtube) - The Scale of the Universe from Small to Big (youtube) - Animation illustrates in real time the journey of a photon of light emitted from the surface of the sun and traveling across a portion of the solar system, from a human perspective.
NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) - The Scale of the Universe - Interactive (manual control scale)
Galaxies - Space - Black Holes - Earth - Planets - Moon - Stars - Sun - Solar System - Magnetics - Gravity - Dimensions - Round - Extra Terrestrial - ET - Space Aliens - Probes - Space Station - Space Shuttle - Space Travel - Satellites - Asteroids - Telescopes - Time - Space - Dark Matter - Radiation - Cosmology - Science - Physics - Plasma
“If you want to find the secrets of the universe, think in terms of energy, frequency and vibration.” - Nicola Tesla.
Geological time scale is a scale that divides up the history of Earth into scientifically meaningful periods.
Timeline of our Universe
13.7 Billion Years Ago
Around 14 billion years ago in earth time, it is believed that our Universe began. We are not sure if it was the first time or even the beginning of time? Time Line of the Universe - Chronology of the Universe (wiki) - Detailed Logarithmic Timeline (wiki) - Shape of the Universe - Photo (image) - Seeing the Beginning of Time 4k (youtube) - Big Bang - Creationism - Matter (conservation of mass) - Universe was denser and smoother in the beginning. Low Entropy - Time - Dating.
After 250 or 400 Million Years Later
Around 300 million years after the universe was created, stars, blackholes and galaxies started to form. Reionization marks the point at which the hydrogen in the Universe became ionized. Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ion is an Atom or a molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving the atom or molecule a net positive or negative electrical charge. Ions can be created, by either chemical or physical means, via ionization. Galaxies had already formed 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang. Subaru/XMM-Newton Deep Field.
GN-z11 high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major, and is currently the oldest and most distant known galaxy in the observable universe - 13.4 billion years old. Galaxy z8 GND 5296 is 13.1 billion years old, only about 700 million years younger than the universe. Methuselah Star HD 140283 is one of the oldest stars known.
After 9 Billion Years
Around 9 billion years after the universe was created, the Sun in our Solar System is formed, which was around 4.7 Billion years ago earth time. (Did life start a few billion years before us in another galaxy, or in our own galaxy?)
4.5 Billion Years Ago
Earth is formed, around 200 million years after our star formed. Earth day then was only 6 hours long. Mostly Molten Rock. Theia collided with another planetary-mass object, Gaia (the early Earth) around 4.51 billion years ago. That was when the Moon Formed, the Moon was twice as close then it is now causing 10,000 ft. tides. Age of the Earth is approximately 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This dating is based on evidence from radiometric age-dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples. The Earth has over 4 billion years left in its life, but humans only have around a billion years left before we have to find a new home. We might have even less time if we don't start making improvements.
Scientists find evidence that overturns theories of the origin of water on Earth. A research team demonstrated that the material which built our planet was far richer in hydrogen than previously thought. The findings support the theory that the formation of habitable conditions on Earth did not rely on asteroids hitting the Earth. Using a rare type of meteorite, known as an enstatite chondrite, which has a composition analogous to that of the early Earth around 4.55 billion years ago, they have found a source of hydrogen which would have been critical for the formation of water molecules.
4 Billion Years Ago
The lunar cataclysm when asteroids bombarded the earth and moon. The late heavy bombardment is a hypothesized event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years or Ga ago, at a time corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. During this interval, a disproportionately large number of asteroids are theorized to have collided with the early terrestrial planets in the inner Solar System, including Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Since 2018, the existence of the Late Heavy Bombardment has been questioned.
Earliest evidence of freshwater on Earth 4 billion years ago, 5 hundred million years earlier than previously thought. By examining the age and oxygen isotopes in tiny crystals of the mineral zircon, it found that unusually light isotopic signatures as far back as four billion years ago. Such light oxygen isotopes are typically the result of hot, fresh water altering rocks several kilometres below Earth's surface.
3.5 Billion Years Ago
One Billion Years since the Birth of Earth.
Single Cell Micro-Organisms start to form on earth. Stromatolite life from 3.7 billion years ago when Earth’s skies were orange and its oceans green. Pyramid of Complexity - Primordial Soup - Carbon Dating.
Timeline of Evolutionary History of Life (wiki)
Atmospheric Pressure was about half of what it is today.
3.2 Billion Years Ago
Great Oxygenation Event. Was this the first Extinction? Oxygen is what makes the sky blue, molecules in the air scatter blue light from the sun more than they scatter red light. New type of Green Algae produced O2, which created the Ozone Layer that protected life from damaging UV Rays and gave life a chance to progress. Free oxygen is oxygen that isn't combined with other elements such as carbon or nitrogen. Olivine (wiki) - Organisms Change - Atmosphere.
3 Billion Years Ago
1.5 Billion Years since the Birth of Earth - 2.4 billion years ago, oxygen in the atmosphere suddenly increased by about 10,000 times in just 200 million years. Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy synthesizes sugars from carbon dioxide, releasing oxygen as a waste product. 2.4 – 2.3 billion years ago First rock evidence of atmospheric oxygen. 2.7 billion years ago Cyanobacteria were the first oxygen producers. Ocean organisms and primitive animals start to evolve. Marine Biology.
Boring Billion or the Mid Proterozoic and Earth's Middle Ages, is the time period between 1.8 and 0.8 billion years ago (Ga) spanning the middle Proterozoic eon, characterized by more or less tectonic stability, climatic stasis, and slow biological evolution. It is bordered by two different oxygenation and glacial events, but the Boring Billion itself had very low oxygen levels and no evidence of glaciation.
Over 2 Billion Years Go By....yada yada yada...and then....
Between 685 and 800 million years ago, multicellular organisms began to appear in all of Earth's oceans during what's known as the Avalon explosion, 33 million years earlier than the Cambrian explosion. During this era, sea sponges and other bizarre multicellular organisms replaced small single-celled amoeba, algae and bacteria, which until then, had had run of the planet for more than 2 billion years. Oxygen didn't catalyze the swift blossoming of Earth's first multicellular organisms. The Avalon explosion resulted in a rapid increase in organism diversity. Many of the animals and plants from the Avalon are found living in deep marine environments and the Flinders Ranges. The first stages of the Avalon explosion were observed through comparatively minimal species.
715 - 810 Million Years Ago the first mushrooms evolved. Neurons.
700 - 550 Million Years Ago, in the late Proterozoic, oxygen levels in the oceans and atmosphere increased dramatically. By 600 million years ago, the oxygen in the atmosphere reached about one-fifth of today’s level (21 percent). Ediacaran period spans 94 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period that was 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 541 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon.
Snowball Earth is when the Earth's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen and was completely covered in ice, sometime earlier than 650 Mya or million years ago during the Cryogenian period.
Earth was a giant snowball 700 million years ago and Geoscientists have proposed that an all-time low volcanic carbon dioxide emissions triggered a 57-million-year-long global Sturtian ice age. Sturtian Glaciation was a worldwide glaciation during the Cryogenian Period when the Earth experienced repeated large-scale glaciations. As of January 2023, the Sturtian glaciation is thought to have lasted from c. 717 Ma to c. 660 Ma, a time span of approximately 57 million years. It is hypothesised to have been a Snowball Earth event, or contrastingly multiple regional glaciations, and is the longest and most severe known glacial event preserved in the geologic record, after the much earlier Huronian glaciation.
600 Million Years Ago
3.9 Billion Years since the Birth of Earth, and 2.9 Billion Years since microorganisms formed.
Multicellular Organisms appear that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organisms, which is an organism that consists of only one cell. Cell Division. Multicellularity has evolved independently at least 46 times. Algae.
Choanoflagellate are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals.
Protein Domain is a conserved part of a given protein sequence and (tertiary) structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain.
Around 600 million years ago, a thin Ozone Layer Formed that was capable of protecting life from harmful wavelengths of UV radiation (wavelengths between 200-300 nm).
Oldest known species of swimming jellyfish identified. 505-million-year-old swimming jellyfish from the Burgess Shale highlights diversity in Cambrian ecosystem.
Avalon Explosion is named from the Precambrian faunal trace fossils discovered on the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland, eastern Canada, is a proposed evolutionary radiation of prehistoric animals about 575 million years ago in the Ediacaran period, with the Avalon explosion being one of three eras grouped in this time period.
500 Million Years Ago
Cambrian Explosion. Prior to the Cambrian explosion, most organisms were simple, composed of individual cells occasionally organized into colonies. Over the following 70 to 80 million years, the rate of diversification accelerated by an order of magnitude and the diversity of life began to resemble that of today. Almost all the present phyla plants (Asterids - Verbena) appeared during this period, with the exception of Bryozoa, which are a phylum of aquatic invertebrate animals who made its earliest known appearance later, in the Lower Ordovician. First Plants colonize Earth around 500 million years ago. Intelligent Design.
450 Million Years Ago
Plants. First land plants occurs in the Ordovician, in the form of fossil spores. Land plants began to diversify in the Late Silurian, from around 430 million years ago, and the results of their diversification are displayed in remarkable detail in an early Devonian fossil assemblage from the Rhynie chert. This chert, formed in volcanic hot springs, preserved several species of early plants in cellular detail by petrification. Paleozoic is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 541 to 251.902 million years ago, Phanerozoic covers 541 million years to the present. Timeline of Plant Evolution (wiki) - Photosynthesis.
Horseshoe Crab are marine arthropods invertebrates of the family Limulidae, suborder Xiphosurida, and order Xiphosura.
Living Fossil is an extant taxon that closely resembles organisms otherwise known only from the fossil record. As a rule, to be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade.
Carbon Dating (measuring how old things are).
450-million-year-old organism finds new life in Softbotics. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University's College of Engineering used fossil evidence to engineer a soft robotic replica of pleurocystitids, a marine organism that existed nearly 450 million years ago and is believed to be one of the first echinoderms capable of movement using a muscular stem.
400 Million Years Ago
Insects.
Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period 358.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, 298.9 Mya. The name Carboniferous means "coal-bearing".
Hangenberg Event is a bioevent that occurred at the end of the Famennian epoch (late Devonian) associated with the Late Devonian extinction (roughly 358.9 ± 0.4 million years ago).
Bioevent is an event recognised in a sequence of sedimentary rocks, where there is a significant change in the biota as recorded by assemblages of fossils over a relatively short period of time. It has been defined as "short-term (hours or days to kyrs) locally, regionally, or interregionally pervasive changes in the ecological, biogeographical, and/or evolutionary character of biotas that are isochronous or nearly so throughout their range". Bioevents either relate to diversification of a particular fossil group or a reduction, these may equate to speciation events or extinction events, or may only represent migration. Records of the appearance and disappearance of particular taxa at a single locality are insufficient to define a bioevent.
Late Devonian Extinction was one of five major extinction events in the history of the Earth's biota. A major extinction, the Kellwasser event, occurred at the boundary that marks the beginning of the last phase of the Devonian period, the Famennian faunal stage (the Frasnian–Famennian boundary), about 375–360 million years ago. Overall, 19% of all families and 50% of all genera became extinct. A second, distinct mass extinction, the Hangenberg event, closed the Devonian period.
250 Million Years Ago
Permian Extinction, which caused Extinction of 95% of all living species? (Animals - Plants)
Peter Ward: Earth's Mass Extinctions (youtube)
(14 °F rise in temperature)
Earth took up to 10 million years to recover.
A footprint of a reptile-like creature called an Isochirotherium, an ancestor of dinosaurs and crocodiles that roamed the area 230 million years ago, was discovered in early April by a person out walking in Olesa de Montserrat, 40 kilometers (25 miles) north of Barcelona, Northeastern Catalonia in the Iberian Peninsula. Carnian Pluvial Event 230 million years ago it rained for 2 million years.
Violent supernovae 'triggered at least two Earth extinctions'. At least two mass extinction events in Earth's history were likely caused by the 'devastating' effects of nearby supernova explosions, a new study suggests. Researchers say these super-powerful blasts -- caused by the death of a massive star -- may have previously stripped our planet's atmosphere of its ozone, sparked acid rain and exposed life to harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. They believe a supernova explosion close to Earth could be to blame for both the late Devonian and Ordovician extinction events, which occurred 372 and 445 million years ago respectively. Extinction Number Six.
200 Million Years Ago
Mammals Evolve - Dinosaurs Evolved and lived for 180 Million years (over 700 types). Dinosaurs are a diverse group of Reptiles of the clade Dinosauria that first appeared during the Triassic period, which was a geologic period and system which spans 50.9 million years from the end of the Permian Period 252.17 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.3 Mya. The Triassic is the first period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. Earth had 1 Continent, mostly desert, no broad leaf trees, no flowers, Earth spun faster, moon was closer. Pangaea started braking apart about 200 million years ago. Volcanic carbon dioxide emissions helped trigger Triassic climate change 201 million year ago. - Plate Tectonics.
First 'warm-blooded' dinosaurs may have emerged 180 million years ago. The ability to regulate body temperature, a trait all mammals and birds have today, may have evolved among some dinosaurs early in the Jurassic period about 180 million years ago.
125 Million Years Ago
Flowers Evolve, almost 325 million years after plants evolved. Flowers may have bloomed more than 174 million years ago, 264 specimens of 198 individual flowers preserved on 34 rock slabs from the South Xiangshan Formation.
100 Million Years Ago
India broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana and began moving north. Gondwana is the name given to an ancient supercontinent. It is believed to have sutured between about 570 and 510 million years ago (Mya), joining East Gondwana to West Gondwana. Gondwana formed prior to Pangaea, and later became part of it. Continental Drift - Earths Surface - Ancient Rainforest in Antarctica - Research tracks 66 million years of mammalian diversity.
65 Million Years Ago
Dinosaurs go extinct. Dinosaur era lasted from 230 to 66 million years ago.
Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event is also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) extinction, was a mass extinction of some three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth that occurred over a geologically short period of time approximately 66 million years ago. With the exception of some ectothermic species like the leatherback sea turtle and crocodiles, no tetrapods weighing more than 25 kilograms (55 lb) survived. It marked the end of the Cretaceous period and with it, the entire Mesozoic Era, opening the Cenozoic Era that continues today. Recovery Time after Extinction.
Iridium is found in meteorites in much higher abundance than in the Earth's crust.
Mesozoic Era is an interval of geological time from about 252 to 66 million years ago. It is also called the Age of Reptiles.
Dinosaurs: Giants of Patagonia (2014) (Argentinosaur, Giganotosaur 11/25/2014 - 40 min. video).
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs that includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to Ornithomimus velox. Earths Early History.
Dreadnoughtus is a genus of giant titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur containing a single species.
Ant agriculture began 66 million years ago. Ants began farming fungi when an asteroid struck Earth 66 million years ago.
55 Million Years Ago
Grasses evolved. The Evolution of Terrestrial Ecosystems Program or ETE. Earth's land biotas throughout their 400 million year history. Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum was a time period with a more than 5–8 °C global average temperature rise across the event. This climate event occurred at the time boundary of the Paleocene and Eocene geological epochs. The exact age and duration of the event is uncertain but it is estimated to have occurred around 55.5 million years ago. The associated period of massive carbon release into the atmosphere has been estimated to have lasted from 20,000 to 50,000 years. The entire warm period lasted for about 200,000 years. Global temperatures increased by 5–8 °C..
50 Million Years Ago the land mass known as India today, drifted into Asia, the collision created the Himalayas, and is still moving an inch every year. Table Mountain (30 - 50 million years) - Forbidden Archeology (Michael A. Cremo) - Laetoli Footprints (3.7 million years ago). Neogene is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period 23.03 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period 2.58 Mya.
Scientists discover 36-million-year geological cycle that drives biodiversity. Tectonic changes alter sea levels that can create breeding grounds for life.
2.6 Million Years Ago
Paleolithic primitive Stone Tools discovered. Stone Age Begins. Oldowan is the earliest widespread stone tool archaeological industry in prehistory (it is pre-dated by Lomekwian tools at a single site dated to 3.3 million years ago). Oldowan tools were used during the Lower Paleolithic period, 2.6 million years ago up until 1.7 million years ago, by ancient hominids across much of Africa, South Asia, the Middle East and Europe. This technological industry was followed by the more sophisticated Acheulean industry. Bolas throwing weapon made of weights on the ends of interconnected cords, used to capture animals by entangling their legs. Axe is one of the first stone tools used by humans to shape, split and cut wood, to harvest timber, to dig for roots, and to cut animal skin or used as a weapon, and as a ceremonial or heraldic symbol. Before the modern axe, the stone-age hand axe was used from 1.5 million years BP without a handle. It was later fastened to a wooden handle and made of copper, bronze, iron and steel as these technologies developed. 2.9 million years ago along the shores of Africa's Lake Victoria in Kenya roughly, early human ancestors used some of the oldest stone tools ever found to butcher hippos and pound plant material, according to new research.
2 Million years ago, our solar system may have passed through dense interstellar clouds, altering Earth's climate by interfering with the sun's solar wind.
1.3 million years ago, new geological dating places the first European hominids in the south of the Iberian Peninsula.
Ancient Knowledge - Advancement in Tools - Archaeology (culture) - Discovery of Human Antiquity.
2,588,000 to 11,700 Years Ago
Pleistocene - Documentary : Secrets Beneath The Ice In Antarctica HD full (youtube) - Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.588 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today). The informal term "Late Quaternary" refers to the past 0.5–1.0 million years.
Oldest evidence of the controlled use of fire to cook food, researchers report. The remains of a huge carp fish mark the earliest signs of cooking by prehistoric human to 780,000 years ago, predating the available data by some 600,000 years, according to researchers. Fire.
600,000 Years Ago
Homo Sapiens evolved, or were engineered or created or arrived here from another planet around 500 million years ago, or 3 billion years ago? The Day We Learned to Think (youtube).
500,000 Years Ago
Humans - Population Bottleneck is believed to occurred among a group of Australopithecina as they transitioned into the species known as Homo erectus two million years ago. It is believed that additional bottlenecks must have occurred since Homo erectus started walking the Earth, but current archaeological, paleontological, and genetic data is inadequate to give much reliable information about such conjectured bottlenecks. That said, the possibility of a severe recent species-wide bottleneck cannot be ruled out. Recent research shows the extent of climate change was much smaller than believed by proponents of the theory. In addition, coalescence times for Y-chromosomal and mitochondrial DNA have been revised to well above 100,000 years since 2011. Finally, such coalescence would not, in itself, indicate a population bottleneck, because mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome DNA are only a small part of the entire genome, and are atypical in that they are inherited exclusively through the mother or through the father, respectively. Genetic material inherited exclusively from either father or mother can be traced back in time via either matrilineal or patrilineal ancestry.
400,000 Years Ago
Schöningen Spears, four ancient wooden spears found in an opencast mine near the town (Bamford & Henderson 2003). The spears are about 400,000 years old.
Spear thrower weapon use by prehistoric females equalized the division of labor while hunting. The atlatl is a handheld, rod-shaped device that employs leverage to launch a dart, and represents a major human technological innovation used in hunting and warfare since the Stone Age. The first javelins are at least hundreds of thousands of years old; the first atlatls are likely at least tens of thousands of years old.
250,000 Years Before the Present. Hueyatlaco is an archeological site in the Valsequillo Basin near the city of Puebla, Mexico. After excavations in the 1960s, the site became notorious due to geochronologists' analyses that indicated human habitation at Hueyatlaco.
Earthworks are artificial changes in land level, typically made from piles of artificially placed or sculpted rocks and soil. Earthworks can themselves be archaeological features, or they can show features beneath the surface. Earthworks of interest to archaeologists include hill forts, henges, mounds, platform mounds, effigy mounds, enclosures, long barrows, tumuli, ridge and furrow, mottes, round barrows, and other tombs.
100,000 Years Ago
Last Glacial Period occurred from the end of the Eemian interglacial to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago. This most recent glacial period is part of a larger pattern of glacial and interglacial periods known as the Quaternary glaciation extending from c. 2,588,000 years ago to present. The definition of the Quaternary as beginning 2.58 Ma is based on the formation of the Arctic ice cap. The Antarctic ice sheet began to form earlier, at about 34 Ma, in the mid-Cenozoic (Eocene–Oligocene extinction event). The term Late Cenozoic Ice Age is used to include this early phase. Timeline of Glaciation (wiki) - Middle Pleistocene is a subdivision of the Pleistocene Epoch, from 781,000 to 126,000 years ago (781–126 ka). It is preceded by the Calabrian stage, beginning with the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, and succeeded by the Tarantian stage (equivalent ot the Late or Upper Pleistocene), taken as beginning with the last interglacial (MIS 5). Climate Change.
75,000 Years Ago
Toba Catastrophe Theory was a supervolcanic eruption that occurred about 75,000 years ago at the site of present-day Lake Toba in Sumatra, Indonesia. It is one of the Earth's largest known eruptions. The Toba catastrophe theory holds that this event caused a global volcanic winter of six to ten years and possibly a 1,000-year-long cooling episode.
San People are members of various Khoesān-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer groups representing the first nation of Southern Africa, whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho and South Africa.
Recent African Origin of Modern Humans (wiki) - Multistep food plant processing at Grotta Paglicci (Southern Italy) around 32,600 cal B.P.
55,000-year-old mummified body of a Steppe bison was found in the Alaskan tundra in 1979. The skeleton, the skin, the muscles were all in near-impeccable condition. Radiocarbon dating.
Earliest evidence of humans using fire to shape the landscape of Tasmania. Some of the first human beings to arrive in Tasmania, over 41,000 years ago, used fire to shape and manage the landscape, about 2,000 years earlier than previously thought.
23,000 Years Ago
People came from Siberia and East Asia to America.
22,000 Years Ago
The Last Glacial Maximum, the maximum extent of glaciation within the last glacial period 100,000 years ago.
Ice Age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and greenhouse periods, during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the Quaternary glaciation, known in popular terminology as the Ice Age. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed "glacial periods" (or, alternatively, "glacials", "glaciations", "glacial stages", "stadials", "stades", or colloquially, "ice ages"), and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called "interglacials" or "interstadials", with both climatic pulses part of the Quaternary or other periods in Earth's history. In the terminology of glaciology, ice age implies the presence of extensive ice sheets in both northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, we are in an interglacial period—the Holocene. The amount of heat trapping gases emitted into Earth's oceans and atmosphere are predicted to prevent the next glacial period, which otherwise would begin in around 50,000 years, and likely more glacial cycles. History of Agriculture (wiki). Wild grains were collected and eaten from at least 20,000 BC. Sun Solar Wind.
Study reveals our European ancestors ate seaweed and freshwater plants. Researchers say they have found 'definitive' archaeological evidence that seaweeds and other local freshwater plants were eaten in the mesolithic, through the Neolithic transition to farming and into the Early Middle Ages, suggesting that these resources, now rarely eaten in Europe, only became marginal much more recently. 20,000 to 10,000 Before Present.
14,000 Years Ago
Humans' arrive in southern South America, first or second time? Pumapunku - Tiwanaku (Bolivia).
13,000 Years Ago
A prehistoric group of hunter-gathers known as the Clovis people lived in Northern America. Ancient stone carvings in Gobekli Tepe Temple in Turkey suggest that a comet struck Earth around 11,000 B.C..
Younger Dryas Impact Hypothesis or Clovis comet hypothesis posits that fragments of a large (more than 4 kilometers in diameter), disintegrating asteroid or comet struck North America, South America, Europe, and western Asia about 12,800 to 11,700 years ago. Multiple airbursts/impacts produced the Younger Dryas (YD) boundary layer (YDB), depositing peak concentrations of platinum, high-temperature spherules, meltglass, and nanodiamonds, forming an isochronous datum at more than 50 sites across about 50 million km² of Earth’s surface. Some scientists have proposed that this event triggered extensive biomass burning, a brief impact winter and the Younger Dryas abrupt climate change, contributed to extinctions of late Pleistocene megafauna, and resulted in the end of the Clovis culture. The Younger Dryas was named after a flower (Dryas octopetala) that grows in cold conditions and that became common in Europe during this time. The end of the Younger Dryas, about 11,500 years ago, was particularly abrupt.
Meltwater Pulse 1B is the name used by Quaternary geologists, paleoclimatologists, and oceanographers for a period of either rapid or just accelerated post-glacial sea level rise that some hypothesize to have occurred between 11,500 and 11,200 years ago at the beginning of the Holocene and after the end of the Younger Dryas. Meltwater pulse 1B is also known as catastrophic rise event 2 (CRE2) in the Caribbean Sea. Other named, postglacial meltwater pulses are known most commonly as meltwater pulse 1A0 (meltwaterpulse19ka), meltwater pulse 1A, meltwater pulse 1C, meltwater pulse 1D, and meltwater pulse 2. It and these other periods of proposed rapid sea level rise are known as meltwater pulses because the inferred cause of them was the rapid release of meltwater into the oceans from the collapse of continental ice sheets.
11,000 Years Ago
Beringia. The last ice age ended about 11,000 years ago. Next one might be in 100,000 years. Global sea level rose as the vast ice sheets of the last Ice Age melted back, more than 120 meters or 393 feet. This melt-back lasted from about 19,000 to about 6,000 years ago, meaning that the average rate of sea-level rise was roughly 1 meter per century. Post-Glacial Rebound is the rise of land masses after the lifting of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Domestication of Plants.
Theopetra Cave in Greece is a limestone cave located in Theopetra village of Meteora municipality, Thessaly, Greece. The site has become increasingly important as human presence is attributed to all periods of the Middle and Upper Paleolithic, the Mesolithic, Neolithic and beyond, bridging the Pleistocene with the Holocene.
Holocene is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years before present, after the last glacial period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat.
Anthropocene is a proposed geological epoch dating from the commencement of significant human impact on Earth's geology and ecosystems, including, but not limited to, anthropogenic climate change.
10,000 to 5,000 BC
Mesolithic pre-agricultural material in northwest Europe. Gobekli Tepe dates back to the 10th–8th millennium BCE. During the first phase, pre-pottery Neolithic A or PPNA. Circles of massive T-shaped stone pillars were erected, the world's oldest known megaliths. More than 200 pillars in about 20 circles are currently known through geophysical surveys. Each pillar has a height of up to 6 m (20 ft) and a weight of up to 20 tons. They are fitted into sockets that were hewn out of the bedrock. Archaeological site is atop a mountain ridge "Potbelly Hill" in the Southeastern Anatolia Region of modern-day Turkey. The MacCready explosion states that 10,000 years ago humans and their pets and livestock made up 0.1% of terrestrial vertebrate biomass, today it's 98%. Wall of Jericho was a Pre-Pottery Neolithic defensive or flood protection wall suggested to date to approximately 8000 BC. If interpreted as an "urban fortification", the Wall of Jericho is the oldest city wall discovered by archaeologists anywhere in the world. It is built of undressed stones and is located at the archaeological mound known as Tell es-Sultan, in the city of Jericho on the West Bank. The topic of this article is the unique Neolithic-age stone wall, the earliest one of its kind. Other walls, such as contemporary house walls, or later, Bronze age and Iron Age city walls, are only mentioned for the sake of context.
Farming - Supplies - Division of Labor
Early human species benefited from food diversity in steep mountainous terrain. A new study shows that the patchwork of different ecosystems found in mountainous regions played a key role in the evolution of humans. Mountainous regions have enhanced biodiversity because the changes in elevation result in shifts of the climate, providing a range of environmental conditions under which different plant and animal species can thrive. The decrease in topographic adaptation around 1 million years ago roughly coincides with large-scale reorganizations in our climate system, known as the Mid-Pleistocene Transition. It also lines up with evolutionary events such as a recently discovered ancestral genetic bottleneck, which drastically reduced human diversity, and the timing of the chromosome 2 merger in hominins. Whether this is all a coincidence, or whether the intensifying glacial climate shifts contributed to the genetic transitions in early humans, remains an open question.
Feline genetics help pinpoint first-ever domestication of cats. Cat genes reveal how invention of agriculture bonded cats with people in ancient Mesopotamia, leading to worldwide feline migration with humans. Nearly 10,000 years ago, humans settling in the Fertile Crescent, the areas of the Middle East surrounding the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, made the first switch from hunter-gatherers to farmers. They developed close bonds with the rodent-eating cats that conveniently served as ancient pest-control in society's first civilizations. A new study found this lifestyle transition for humans was the catalyst that sparked the world's first domestication of cats, and as humans began to travel the world, they brought their new feline friends along with them.
Hunter-Gatherer social ties spread pottery-making far and wide. Analysis of more than 1,200 vessels from hunter-gatherer sites has shown that pottery-making techniques spread vast distances over a short period of time through social traditions being passed on.
6,000 and 10,000 Years Ago
The OCA2 Gene mutation for Blue Eyes occurred. Before then there were no blue eyes. So we went from having nobody on Earth with blue eyes 10,000 years ago, to now having 20 or 40 percent of Europeans having blue eyes. Blue-eyed humans have a single, common ancestor. Harran was a major ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia whose site is in the modern city Harran, Turkey, 44 kilometers southeast of Şanlıurfa. The location is in the Harran district of Şanlıurfa Province. The archaeological remains are in the ancient Harran, a major commercial, cultural, science and religious center first inhabited in the Chalcolitic Age (6th millennium BCE). Blue-eyed humans have a single, common ancestor. Scientists have tracked down a genetic mutation which took place 6,000-10,000 years ago and is the cause of the eye color of all blue-eyed humans alive on the planet today. Originally, we all had brown eyes, but a genetic mutation affecting the OCA2 gene in our chromosomes resulted in the creation of a "switch," which literally "turned off" the ability to produce brown eyes. The OCA2 gene codes for the so-called P protein, which is involved in the production of melanin, the pigment that gives colour to our hair, eyes and skin. The "switch," which is located in the gene adjacent to OCA2 does not, however, turn off the gene entirely, but rather limits its action to reducing the production of melanin in the iris -- effectively "diluting" brown eyes to blue. The switch's effect on OCA2 is very specific therefore. If the OCA2 gene had been completely destroyed or turned off, human beings would be without melanin in their hair, eyes or skin colour -- a condition known as albinism. Variation in the colour of the eyes from brown to green can all be explained by the amount of melanin in the iris, but blue-eyed individuals only have a small degree of variation in the amount of melanin in their eyes.
4,500 and 2,000 BC
Neolithic - Neolithic Revolution. More humans went from hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, allowing the ability to support an increasingly large population. Ġgantija is a megalithic temple complex from the Neolithic on the Mediterranean island of Gozo. The Ggantija temples are the earliest of the Megalithic Temples of Malta and are older than the pyramids of Egypt. Their makers erected the two Ggantija temples during the Neolithic (c. 3600–2500 BC), which makes these temples more than 5500 years old and the world's second oldest existing manmade religious structures after Göbekli Tepe in present-day Turkey. The Myth of Man the Hunter: Women’s contribution to the hunt across ethnographic contexts. Female Hunters of the early Americas.
3000 BC
Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of bronze, proto-writing, and other early features of urban civilization. From Stone Tools to Metal Tools (metal working).
Clocks Invented - The Babylonians (Iraq today) divided the day into hours and minutes, at that time man started to notice the sun coming up regularly. That's the earliest recorded 365 day year. Humans understood that there were patterns and cycles in life, so humans created tools to help predict those patterns, like Calendars - BC,AD,CE,BCE.
Stonehenge is a ring of standing stones are set within earthworks in the middle of the most dense complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred burial mounds. (3000 BC).
Indus Valley Civilization 3300–1300 BCE, regions of South Asia, extending from what today is northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India.
Pyramids have been built by civilizations in many parts of the world. For thousands of years, the largest structures on Earth were pyramids, which is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single point at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense.
Maya Civilization was a Mesoamerican civilization developed by the Maya peoples, and noted for its hieroglyphic script—the only known fully developed writing system of the pre-Columbian Americas—as well as for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in an area that encompasses southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. This region consists of the northern lowlands encompassing the Yucatán Peninsula, and the highlands of the Sierra Madre, running from the Mexican state of Chiapas, across southern Guatemala and onwards into El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain.
Archery in Andes Mountains dated to 5,000 years ago -- earlier than previous research.
Sumer was the first urban civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia, modern-day southern Iraq, during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze ages, and arguably the first civilization in the world with Ancient Egypt and the Indus Valley. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates, Sumerian farmers were able to grow an abundance of grain and other crops, the surplus of which enabled them to settle in one place. Proto-writing in the prehistory dates back to c. 3000 BC. The earliest texts come from the cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr and date back to 3300 BC; early cuneiform writing emerged in 3000 BC. Modern historians have suggested that Sumer was first permanently settled between c. 5500 and 4000 BC by a West Asian people who spoke the Sumerian language (pointing to the names of cities, rivers, basic occupations, etc., as evidence), an agglutinative language isolate.
Sparta - 900s BC 192 BC. - Agoge was the rigorous education and training program mandated for all male Spartan citizens, except for the firstborn son in the ruling houses, Eurypontid and Agiad. The training involved learning stealth, cultivating loyalty to the Spartan group, military training (e.g., pain tolerance), hunting, dancing, singing, and social (communicating) preparation. The word "agoge" meant rearing in ancient Greek, but in this context generally meant leading, guidance, or training.
Roman Empire was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterized by government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. 27 BC – 395 AD, 395–480 (Western), 395–1453 (Eastern). Rome (wiki) (27 BC–330 AD).
Alexander the Great was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon and a member of the Argead dynasty. He was born in Pella in 356 BC and succeeded his father Philip II to the throne at the age of 20. He spent most of his ruling years on an unprecedented military campaign through western Asia and northeast Africa, and by the age of thirty, he had created one of the largest empires of the ancient world, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered one of history's most successful military commanders. Basileus is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history.
Byzantine Empire also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire and Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, which had been founded as Byzantium). It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Both "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" are historiographical terms created after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire simply as the Roman Empire (Greek: Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia Rhōmaiōn; Latin: Imperium Romanum), or Romania (Ῥωμανία), and to themselves as "Romans".
Angkor Wat is a temple complex in Cambodia and the largest religious monument in the world, with the site measuring 162.6 hectares (1,626,000 m2; 402 acres). It was originally constructed as a Hindu temple of god Vishnu for the Khmer Empire, gradually transforming into a Buddhist temple toward the end of the 12th century. It was built by the Khmer King Suryavarman II in the early 12th century.
Dorset Culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture (500 BCE–1500 CE) that preceded the Inuit culture in Arctic North America.
Norsemen refers to the group of people who spoke what is now called the Old Norse language between the 8th and 11th centuries. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages, and is the earlier form of modern Scandinavian languages.
Stone Spheres of Costa Rica dating back to the Aguas Buenas Period (300–800 CE) and Chiriquí Period (800–1550 CE). (Diquis Spheres or Stone Balls).
Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire eventually stretched from Eastern Europe and parts of Central Europe to the Sea of Japan, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into the Indian subcontinent, Mainland Southeast Asia and the Iranian Plateau; and westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomadic tribes in the Mongol homeland under the leadership of Genghis Khan (c. 1162–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the East with the West, the Pacific to the Mediterranean, in an enforced Pax Mongolica, allowing the dissemination and exchange of trade, technologies, commodities and ideologies across Eurasia. Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia. Its area is roughly equivalent with the historical territory of Outer Mongolia, and that term is sometimes used to refer to the current state. It is sandwiched between Russia to the north and China to the south, where it neighbours the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, although only 37 kilometres (23 mi) separate them. Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia and to China's Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. They also live as minorities in other. Mongoloid is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Southeast Asia, North Asia, Polynesia, and the Americas. Mongolian Idiocy refers to a specific type of mental deficiency, associated with the genetic disorder or lack of education. Because of it's offensive and misleading implications, it's better to say the someone is not accurately understanding themselves or the world around them. Not totally stupid, just stupid in certain ways. Civilizations Collapsed.
Paleontological Research Institution - Utilizing its unique collections, staff, physical facilities and digital presence, the Paleontological Research Institution pursues and integrates education and research, and interprets the history and systems of the Earth and its life to increase knowledge, educate society, and encourage wise stewardship of the Earth.
Archaeologists discover world's oldest wooden structure, Pre-dates Homo sapiens. Half a million years ago, earlier than was previously thought possible, humans were building structures made of wood, according to new research. The research, published in the journal Nature, reports on the excavation of well-preserved wood at the archaeological site of Kalambo Falls, Zambia, dating back at least 476,000 years and predating the evolution of our own species, Homo sapiens.
DNA evidence rewrites story of people buried in Pompeii eruption. The DNA evidence revealed unexpected variations in gender and kinship, revising the story as written since 1748. The genetic data also underlined the cosmopolitan nature of the Roman Empire, showing that Pompeians were mainly descended from immigrants from the eastern Mediterranean.
Horrible Moments in History - 410 A.D. Barbarians sacked Rome - 1348 Peak year of the Black Death - 1644 China's Ming Dynasty collapsed and the Thirty Years' War raged in Europe - 1816 The Year Without A Summer, when a volcanic eruption in Indonesia blocked out the sun - 1838 Trail of Tears - 1862 The darkest year of the Civil War - 1919 The Spanish flu pandemic - 1929 The Wall Street stock market crash - 1944 The Holocaust was at its height - 1968 Assassinations of Martin Luther King Jr. and Robert Kennedy - 1962 The Cuban missile crisis - 2001 The 9/11 attacks - 2016 Donald Trump becomes president - 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic - 2024 Donald Trump becomes president again.
Today - 2025
Since then, for thousands of years, humans have struggled to survive, with many civilizations failing. Even in the last 2000 years, humans are still struggling to survive. Humans have been suffering from wars, diseases, and all kinds of catastrophes. We have made many improvements, but we still have many problems that we have to solve. Luckily, the Earth during the last 5,000 years has been pretty good to us. Except for the regular outbursts from mother nature, we have had no major extinction events like the previous ones, except for the one we are currently in. It's estimated that 106 Billion Humans Have Lived since the beginning, and as of 2011, 94% are Dead. That means over 99 Billion people have lived and died before you were born, 38 billion people have lived and died in the last 1,000 years. So everyone is standing on the Shoulders of Giants, and everyone is Passing the Baton, so please make it a good one.
99.9 Percent of all Species that have existed on Earth, are now Extinct. We are now in the 6th Extinction at an extremely fast rate. Holocene 6th Extinction.
Extinctions are kind of like a computer rebooting and life is hitting the restart button.
Inventions Timeline - Some of our Greatest Inventions and Innovations
Corporate Takeover of America Timeline.
Corporate Takeover of America's Education System.
"You have to have something to show for your life, something significant, something relevant, something positive. And don't worry about the time that was wasted, think about the time that you still have. You don't have to finish, you just have to start, someone else will pick up where you left off, pass your baton forward."
"It's amazing to know that everyone who has lived before 1901 is dead, and in 120 years everyone alive today will be dead. And that's not just 7 billion people dying, it's all the other deaths that happened in those 120 years. If 55 million people die every year, that's almost another 7 billion people gone. We need to get in touch with this reality. Though our lives are temporary, our actions could continue to do damage long after we have died. But if our actions are positive, then life will continually improve, long after we have gone."
Remember that the universe is still young and still evolving. Only eight percent of the potentially habitable planets that will ever form in the universe exist today. So the bulk of possible habitable planets - 92 percent - have yet to be born. We have a very long future ahead us.
And after all that, here you are today....
Historical Geology principles and techniques of geology to reconstruct and understand the geological history of Earth.
Paleontology is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). Time Measuring.
Palaeogeography is the study of historical geography, generally physical landscapes.
History (teaching history) - Big History Project
There is no such thing as stationary, everything is in constant motion, we are in constant motion even when we sleep. Physical stillness is an illusion, but it's an illusion we sometimes need in order to relax and to find peace. But we have to make sure that we fully understand that nothing can be still, things are either getting better, or things are continually getting worse. And in order to continually improve things, we have take necessary actions, actions that are proven to help things get better, if not, then things will continually get worse. I prefer to have things continually improve and get better, it seems natural, so why not take the path of least resistance, it's life's natural path. And we know from History that if you go off the path, then adaptation is no longer available. And we are off the path on a lot of things in our world. We need to get back on the path, and stay connected to life's natural progression. We need to avoid decline and retrograde. We need to stop devolving, We need to stop making things worse, or bad, or unnatural, or abnormal, or unstable. Those directions are nothing but trouble. Don't be fooled into believing that you have fixed a problem, because you may still be headed towards failure.
"We are either progressing or retrograding all the while. There is no such thing as remaining stationary in this life." - James Freeman Clarke.
My Earth Time Scale (At the age of 55 years and 5 months as of April 2016).
If I were born on the planet Mars I would be 28 years old instead of 55.
Since I was born in 1960, my heart has beat over 2 billion times so far after 55 years.
I have traveled 37,094,025,717 miles through the Universe so far.
I have traveled over 32,496,627,730 miles around the Sun so far.
I have traveled over 270,805,235,560 miles through the Milky Way so far.
The Earth has had 270 major eruptions so far in my life.
A Coast Redwood's Tree growth in my lifetime was 70' 10".
Over 2 billion people have died in my lifetime so far at 55.
106 Billion people have lived before I was born.
World Population has increased by 4,378,974,225 in my lifetime in 2015.
In my life there have been 122 solar eclipses so far.
Tectonic plate movement in my lifetime on the East Pacific Rise was 27' 1".
1.4 billion lost acres of forest were destroyed so far in my lifetime in 2015.
In 1960, the earths average temp was 57.2 in 2013, it is now 58.3 Degrees F.
What We Know So Far - Genealogy - Heredity - Blood Line - Generations - History
If you look at the human species as a whole, you can clearly see that we are in our teenage years. We're rebellious, we're trying new things, we're wasteful, we make many mistakes, we're irresponsible, and we are clearly not mature enough to move out on our own.
Time - Measuring Time
Time is a measurement system and a process for learning and a very important tool that helps us plan and predict. Though the timing of cycles, rhythms and development are essential for life, try not to spend to much time thinking about time, because time is just one of the many tools that we have.
What is Time - Schedule - Time Management - Calendars - Scale - History - Stages - Ages - Universe Timeline - Time Travel - Telescopes
Time Scale is a duration of time or the quantity of time, or both. Evolutionary Changes.
Timeline is a way of displaying a list of events in chronological order, sometimes described as a project artifact.
Timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. The term derives from rubber stamps used in offices to stamp the current date, and sometimes time, in ink on paper documents, to record when the document was received. Computer files contain timestamps that tell when the file was last modified, and digital cameras add timestamps to the pictures they take, recording the date and time the picture was taken.
Chronology is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time.
Geologic Time Scale is a system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other Earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships of events that have occurred during Earth's history.
Geologic Record in stratigraphy, paleontology and other natural sciences refers to the entirety of the layers of rock strata. That is, deposits laid down by volcanism or by deposition of sediment derived from weathering detritus (clays, sands etc.). This includes all its fossil content and the information it yields about the history of the Earth: its past climate, geography, geology and the evolution of life on its surface. According to the law of superposition, sedimentary and volcanic rock layers are deposited on top of each other. They harden over time to become a solidified (competent) rock column, that may be intruded by igneous rocks and disrupted by tectonic events.
Period in geology is one of several subdivisions of geologic time enabling cross-referencing of rocks and geologic events from place to place. These periods form elements of a hierarchy of divisions into which geologists have split the Earth's history. Eons and eras are larger subdivisions than periods while periods themselves may be divided into epochs and ages. The rocks formed during a period belong to a stratigraphic unit called a system.
Retrospective means to take a look back at events that already have taken place.
Billion Years is a unit of time on the petasecond scale, more precisely equal to 3.16×1016 seconds (or simply 1,000,000,000). It is sometimes abbreviated Gy, Ga ("giga-annum, 10 to the 9 years"), Byr and variants. The abbreviations Gya or bya are for "billion years ago", i.e. billion years before present. The terms are used in geology, paleontology, geophysics, astronomy, and physical cosmology. The prefix giga- is preferred to billion- to avoid confusion in the long and short scales over the meaning of billion; the postfix annum may be further qualified for precision as a sidereal year or Julian year: 1 Gaj=3.15576×1016 s, 1 Gas=3.15581×1016 s (epoch J2000.0). 1 Gas=1×109 y. Byr was formerly used in English-language geology and astronomy as a unit of one billion years. Subsequently, the term gigaannum (Ga) has increased in usage, with Gy or Gyr still sometimes used in English-language works (at the risk of confusion with Gy as abbreviation for the gray, a unit of radiation exposure). Astronomers use Gyr or Gy as an abbreviation for gigayear.
BCE as an abbreviation for "before the Common (or Current) Era". (Before Christ)
Common Era (CE) is a calendar era that is often used as an alternative naming of the Anno Domini era ("in the year of the Lord"), abbreviated AD. A.D., is used to refer to the years after the birth of Jesus. A.D. used to be "After Death."
Before Present years is a time scale used mainly in geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred.
History of Timekeeping Devices - Clocks - Calendars
Archaeoastronomy is the investigation of the astronomical knowledge of prehistoric cultures and the study of how people in the past have understood the phenomena in the sky, and how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures. A common justification for the need for astronomy is the need to develop an accurate calendar for agricultural reasons. Astronomical alignments are both solar and lunar alignments built into Stonehenge. Solsticial Alignments is a line from the monument center to the "Heelstone" points toward the location of sunrise at the summer solstice (the northernmost sunrise of the year and the longest day of the year). A common source of data for archaeoastronomy is the study of alignments. This is based on the assumption that the axis of alignment of an archaeological site is meaningfully oriented towards an astronomical target. Historical Astronomy (wiki).
We did not invent time, we learned how to understand time and use it to our advantage.
Pattern Recognition - Light - Action Physics
Spacetime is any mathematical model that combines space and time into a single interwoven continuum.
Time of Flight describes a variety of methods that measure the time that it takes for an object, particle or acoustic, electromagnetic or other wave to travel a distance through a medium.
Measuring the Age of Objects - How Old is That?
Radiocarbon Dating is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon (14C), a radioactive isotope of carbon. Carbon-14 dating is based on the fact that radiocarbon is constantly being created in the atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting radiocarbon combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire 14 C by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and from that point onwards the amount of 14 C it contains begins to decrease as the 14 C undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of 14 C in a sample from a dead plant or animal such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone provides information that can be used to calculate when the animal or plant died. The older a sample is, the less 14 C there is to be detected, and because the half-life of 14 C (the period of time after which half of a given sample will have decayed) is about 5,730 years, the oldest dates that can be reliably measured by radiocarbon dating are around 50,000 years ago, although special preparation methods occasionally permit dating of older samples.
Time Travel - Entropy - Decay - Fossils
We can't date the bones, only the place where they were found. Magnetic fingerprint or Paleomagnetism is the record of the Earth's magnetic field in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials and fossils.
Fine-tuning radiocarbon dating could 'rewrite' ancient events.
Radiometric Dating is a technique used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay.
Zircon is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green. Zircon is one of the key minerals used by geologists for geochronology, which is why it has earned the name "Time Lord" because it's so incredibly good at keeping geologic time. The mineral is zircon, and scientists have found bits of it that formed 4.37 billion years ago, not too long after the proto-Earth's epic collision with a Mars-sized object that spawned our moon. Zircon can also give scientists clues about the conditions that existed when that zircon originally got created. Zircon is common in the crust of Earth. It occurs as a common accessory mineral in igneous rocks (as primary crystallization products), in metamorphic rocks and as detrital grains in sedimentary rocks. Large zircon crystals are rare. Because of their uranium and thorium content, some zircons undergo metamictization. Connected to internal radiation damage, these processes partially disrupt the crystal structure and partly explain the highly variable properties of zircon. As zircon becomes more and more modified by internal radiation damage, the density decreases, the crystal structure is compromised, and the color changes. Structurally, zircon consists of parallel chains of alternating silica tetrahedra (silicon ions in fourfold coordination with oxygen ions) and zirconium ions, with the large zirconium ions in eightfold coordination with oxygen ions.
Half-Life of uranium-238 is 4.5 billion years, it decays into redium-226, which in turn decays into redon-222. Redon-222 becomes polonium-210, which then decays into a stable nuclide called lead.
Decay Chain refers to a series of radioactive decays of different radioactive decay products as a sequential series of transformations. It is also known as a "radioactive cascade". Most radioisotopes do not decay directly to a stable state, but rather undergo a series of decays until eventually a stable isotope is reached.
Archaeomagnetic Dating is the study and interpretation of the signatures of the Earth's Magnetic Field at past times recorded in archaeological materials. These paleomagnetic signatures are fixed when ferromagnetic materials such as magnetite cool below the Curie point, freezing the magnetic moment of the material in the direction of the local magnetic field at that time. The direction and magnitude of the magnetic field of the Earth at a particular location varies with time, and can be used to constrain the age of materials. In conjunction with techniques such as radiometric dating, the technique can be used to construct and calibrate the geomagnetic polarity time scale. This is one of the dating methodologies used for sites within the last 10,000 years. The method has been conceived by E. Thellier in the 1930s and the increased sensitivity of SQUID magnetometers has greatly promoted its use.
Paleomagnetism is the study of the record of the Earth's magnetic field in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Magnetic minerals in rocks can lock-in a record of the direction and intensity of the magnetic field when they form. This record provides information on the past behavior of Earth's magnetic field and the past location of tectonic plates. The record of geomagnetic reversals preserved in volcanic and sedimentary rock sequences (magnetostratigraphy) provides a time-scale that is used as a geochronologic tool. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called paleomagnetists. Paleomagnetists led the revival of the continental drift hypothesis and its transformation into plate tectonics. Apparent polar wander paths provided the first clear geophysical evidence for continental drift, while marine magnetic anomalies did the same for seafloor spreading. Paleomagnetic data continues to extend the history of plate tectonics back in time as it can be used to constrain the ancient position and movement of continents and continental fragments (terranes). Paleomagnetism relied heavily on new developments in rock magnetism, which in turn has provided the foundation for new applications of magnetism. These include biomagnetism, magnetic fabrics (used as strain indicators in rocks and soils), and environmental magnetism.
Potassium–Argon Dating, abbreviated K–Ar dating, is a radiometric dating method used in geochronology and archaeology. It is based on measurement of the product of the radioactive decay of an isotope of potassium (K) into argon (Ar). Potassium is a common element found in many materials, such as micas, clay minerals, tephra, and evaporites. In these materials, the decay product 40Ar is able to escape the liquid (molten) rock, but starts to accumulate when the rock solidifies (recrystallizes). The amount of Argon sublimation that occurs is a function of the purity of the sample, the composition of the mother material, and a number of other factors. These factors introduce error limits on the upper and lower bounds of dating, so that final determination of age is reliant on the environmental factors during formation, melting, and exposure to decreased pressure and/or open-air. Time since recrystallization is calculated by measuring the ratio of the amount of 40Ar accumulated to the amount of 40K remaining. The long half-life of 40K allows the method to be used to calculate the absolute age of samples older than a few thousand years. The quickly cooled lavas that make nearly ideal samples for K–Ar dating also preserve a record of the direction and intensity of the local magnetic field as the sample cooled past the Curie temperature of iron. The geomagnetic polarity time scale was calibrated largely using K–Ar dating.
Uranium-Lead Dating is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range. The dating method is usually performed on the mineral zircon. The mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead. Therefore, one can assume that the entire lead content of the zircon is radiogenic, i.e. it is produced solely by a process of radioactive decay after the formation of the mineral. Thus the current ratio of lead to uranium in the mineral can be used to determine its age. The method relies on two separate decay chains, the uranium series from 238U to 206Pb, with a half-life of 4.47 billion years and the actinium series from 235U to 207Pb, with a half-life of 710 million years. Radioactive Decay to Lead. Frequently, the quantity of uranium 238 and lead 206 are measured for radiometric determination of the age of rocks. The half-life with which uranium 238 decays to form lead 206 is 4.46 billion years.
Relative Dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events (i.e., the age of an object in comparison to another), without necessarily determining their absolute age (i.e. estimated age). In geology, rock or superficial deposits, fossils and lithologies can be used to correlate one stratigraphic column with another. Prior to the discovery of radiometric dating in the early 20th century, which provided a means of absolute dating, archaeologists and geologists used relative dating to determine ages of materials. Though relative dating can only determine the sequential order in which a series of events occurred, not when they occurred, it remains a useful technique. Relative dating by biostratigraphy is the preferred method in paleontology and is, in some respects, more accurate. The Law of Superposition, which states that older layers will be deeper in a site than more recent layers, was the summary outcome of 'relative dating' as observed in geology from the 17th century to the early 20th century.
Thermoluminescence Dating is the determination, by means of measuring the accumulated radiation dose, of the time elapsed since material containing crystalline minerals was either heated (lava, ceramics) or exposed to sunlight (sediments). As a crystalline material is heated during measurements, the process of thermoluminescence starts. Thermoluminescence emits a weak light signal that is proportional to the radiation dose absorbed by the material. It is a type of luminescence dating.
Thermochronology is the study of the thermal evolution of a region of a planet. Thermochronologists use radiometric dating along with the closure temperatures that represent the temperature of the mineral being studied at the time given by the date recorded to understand the thermal history of a specific rock, mineral, or geologic unit. It is a subfield within geology, and is closely associated with geochronology. A typical thermochronological study will involve the dates of a number of rock samples from different areas in a region, often from a vertical transect along a steep canyon, cliff face, or slope. These samples are then dated. With some knowledge of the subsurface thermal structure, these dates are translated into depths and times at which that particular sample was at the mineral's closure temperature. If the rock is today at the surface, this process gives the exhumation rate of the rock. Common isotopic systems used for thermochronology include fission track dating in zircon, apatite, titanite, natural glasses, and other uranium-rich mineral grains. Others include potassium-argon and argon-argon dating in apatite, and (U-Th)/He dating zircon and apatite.
Geology - Soil - Core Sample - Forensics
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers or strata, and the layering or stratification. It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has two related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy) and biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy).
Surface Exposure Dating is a collection of geochronological techniques for estimating the length of time that a rock has been exposed at or near Earth's surface. Surface exposure dating is used to date glacial advances and retreats, erosion history, lava flows, meteorite impacts, rock slides, fault scarps, cave development, and other geological events. It is most useful for rocks which have been exposed for between 10 years and 30,000,000 years. Egypt's Pyramids are estimated to be over 10,000 years old using weathering measurements.
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil, and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, water, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs in situ (on site), that is, in the same place, with little or no movement, and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations. Techniques for measuring rock weathering.
Unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented is called a hiatus. It is a kind of relative dating. Great Unconformity is the many unconformities or gaps in time that are observed in geological strata, which is a layer of sedimentary rock or soil, or igneous rock that were formed at the Earth's surface, with internally consistent characteristics that distinguish it from other layers. Hutton's Unconformity is a geological phenomenon that marks the location where rock formations created at different times and by different forces adjoin. The Earth's cycle of supercontinent formation and separation uplifts and erodes incredible extents of rock over long periods of time. And because supercontinent processes, by definition, involve a lot of land, their effects can appear fairly synchronous across the geologic record. However, these processes don't happen simultaneously, as they would in a global event like Snowball Earth. Is the Mystery of Earth's 1.2 Billion Missing Years Solved? | SciShow News (youtube) - Geologists dig into Grand Canyon’s mysterious gap in time - Asteroids.
Beryllium-10 is a radioactive isotope of beryllium. It is formed in the Earth's atmosphere mainly by cosmic ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Beryllium-10 has a half-life of 1.39 × 106 years, and decays by beta decay to stable boron-10 with a maximum energy of 556.2 keV. It decays through the reaction 10Be→10B+e. Light elements in the atmosphere react with high energy galactic cosmic ray particles.
New Method for Dating Pottery. A team has developed a new method to date archaeological pottery using fat residues remaining in the pot wall from cooking using molecular and isotopic evidence. The method means prehistoric pottery can be dated with remarkable accuracy, sometimes to the window of a human life span. Pottery found in Shoreditch, London proven to be 5,500 years old and shows the vibrant urban area was once used by established farmers who ate cow, sheep and goat dairy products as a central part of their diet.
Dendrochronology is the scientific method of dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed. As well as dating them this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmospheric conditions during different periods in history from wood.
Dendroclimatology is the science of determining past climates from trees (primarily properties of the annual tree rings). Tree rings are wider when conditions favor growth, narrower when times are difficult.
Bristlecone Pine or Pinus longaeva is more than 5,000 years old, making it the oldest known individual of any species.
Molecular Clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleotide sequences for DNA, RNA, or amino acid sequences for proteins. The benchmarks for determining the mutation rate are often fossil or archaeological dates. The molecular clock was first tested in 1962 on the hemoglobin protein variants of various animals, and is commonly used in molecular evolution to estimate times of speciation or radiation. It is sometimes called a gene clock or an evolutionary clock.
Nitrogen Isotopes or the ratio of nitrogen-15 to nitrogen-14 (δ15N), are not used for direct "dating" in the sense of determining the absolute age of an object, they are a valuable tool in studying past diets and trophic levels of organisms by analyzing the nitrogen isotopic composition of their remains, as the nitrogen isotope ratio increases with each step up the food chain; essentially providing information about an organism's position in the food web at a specific time period. Key points about nitrogen isotope analysis: Stable isotope: Unlike carbon-14 used in radiocarbon dating, nitrogen isotopes used in analysis are stable, meaning they don't decay radioactively. Trophic level indicator: The higher the δ15N value in an organism's tissue, the higher its trophic level in the food chain. Applications: Paleodietary studies: Examining the nitrogen isotope ratios in ancient human bones to understand their diet and reliance on different food sources. Ecological research: Studying the food web dynamics in different ecosystems by analyzing the nitrogen isotopes of various organisms. Environmental monitoring: Identifying potential sources of nitrogen pollution by analyzing the nitrogen isotope ratios in different environmental samples.
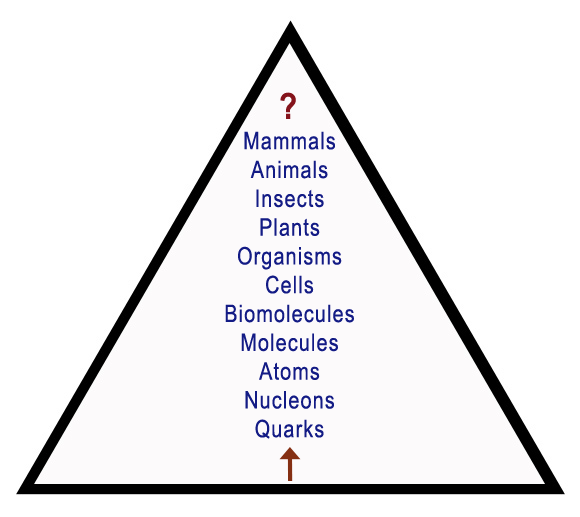
Pyramid of Complexity
Technospher
Mammals
Animals
Insects
Plants
Organisms
Cells
Biomolecules
Molecules
Atoms
Nucleons
Quarks
Tree of Life - Biology Domains - Biosphere - Earth - Building Blocks - Connected - Associations - Time Line of the Universe.
Solar System
 Solar System
is the gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun
and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of those
objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the
planets, with the
remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and
small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that
orbit the Sun indirectly, the moons, two are larger than the smallest
planet, Mercury.
Our Solar System is located in the
Orion
Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the
Milky Way galaxy. The name of our solar system is solar system or Sol
System. The
formation and evolution of our Solar System began 4.6 billion years
ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular
cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the
Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the
planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.
Gravity
Well.
Solar System
is the gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun
and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of those
objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the
planets, with the
remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and
small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that
orbit the Sun indirectly, the moons, two are larger than the smallest
planet, Mercury.
Our Solar System is located in the
Orion
Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the
Milky Way galaxy. The name of our solar system is solar system or Sol
System. The
formation and evolution of our Solar System began 4.6 billion years
ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular
cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the
Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the
planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.
Gravity
Well.
 If the Sun were the size of a
Basketball, the Earth would be the size of a
Sesame Seed.
If the Earth were shrunk down to the size of a Basketball (Radius:
4.69 inches), the Moon would be the size of a
Tennis
Ball (Radius: 1.2768 inches, to be exact) and 23.5 feet away
(238,855.086 miles). The Sun would be a 42.6-foot sphere (source) and
located 1.7 miles away (92 million miles). (figure out the math involved).
If the Sun were the size of a
Basketball, the Earth would be the size of a
Sesame Seed.
If the Earth were shrunk down to the size of a Basketball (Radius:
4.69 inches), the Moon would be the size of a
Tennis
Ball (Radius: 1.2768 inches, to be exact) and 23.5 feet away
(238,855.086 miles). The Sun would be a 42.6-foot sphere (source) and
located 1.7 miles away (92 million miles). (figure out the math involved).
Scaled down Version (image) - To Scale: The Solar System (vimeo) - Scaling - Atom Size - Interesting Tidbits - The Solar System to Scale on a dry lakebed in Nevada (youtube)
Discovery of planet too big for its sun throws off solar system formation models. Researchers report the discovery of a planet more than 13 times as massive as Earth orbiting the "ultracool" star LHS 3154, which itself is nine times less massive than the sun. The mass ratio of the newly found planet with its host star is more than 100 times higher than that of Earth and the sun.
Study of 'polluted' white dwarfs finds that stars and planets grow together. A team of astronomers have found that planet formation in our young Solar System started much earlier than previously thought, with the building blocks of planets growing at the same time as their parent star.
Islands of regularity discovered in the famously chaotic three-body problem. When three massive objects meet in space, they influence each other through gravity in ways that evolve unpredictably. In a word: Chaos. That is the conventional understanding. Now, a researcher has discovered that such encounters often avoid chaos and instead follow regular patterns, where one of the objects is quickly expelled from the system. This new insight may prove vital for our understanding of gravitational waves and many other aspects of the universe. The Three-Body Problem is one of the most famous unsolvable problems in mathematics and theoretical physics.
Planet-forming disks around very low-mass stars are different. The results reveal the richest hydrocarbon composition seen to date in a protoplanetary disk, including the first extrasolar detection of ethane and a relatively low abundance of oxygen-bearing species. By including previous similar detections, this finding confirms a trend of disks around very low-mass stars to be chemically distinct from those around more massive stars like the Sun, influencing the atmospheres of planets forming there.
Planets may start forming before stars even finish growing. Planets start taking shape just a few hundred thousand years after their suns ignite, far earlier than anyone expected.
Eyes on the Solar System - Planetary
Orrery is a mechanical model of the Solar System that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; however, since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead.
Thunderbolts of the Gods (youtube)
Episode 2 Symbols of an Alien Sky: The Lightning Scarred Planet, Mars (youtube)
Mars Scars - Jupiter was once close to Mars - Plasma
Grand Tack - The Resonance Project
Are nearby planets sending radio signals to each other? Scientists use Allen Telescope Array to search for interplanetary communications in the TRAPPIST-1 star system. Plants Communicate with each other.
Could we eavesdrop on communications that pass through our solar system?
Oort Cloud is an extended shell of icy objects that exist in the outermost reaches of the solar system. A theoretical cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from 50,000 to 200,000 AU (0.8 to 3.2 ly). It is divided into two regions: a disc-shaped inner Oort cloud (or Hills cloud) and a spherical outer Oort cloud. Both regions lie beyond the heliosphere and in interstellar space. The Kuiper Belt and the scattered disc, the other two reservoirs of trans-Neptunian objects, are less than one thousandth as far from the Sun as the Oort cloud. Voyager 1&2.
The Oort Cloud | The Solar System's Shell (youtube) - Oct 16, 2020 What lies at the very furthest recesses of the Solar System? Far beyond the orbit of Neptune and the Kuiper Belt, deep into interstellar space, lies a vast, thick shell of icy space debris. We have never seen it directly, but we know it exists- because it is the source of the most distant comets that we see entering the Solar System. Why is it there?
Astronomical Unit or AU is a unit of measurement equal to 149.6 million kilometers, the mean distance from the center of the earth to the center of the sun. One astronomical unit is the approximate mean distance between the Earth and sun. It's about 93 million miles (150 million km), or 8 light-minutes.
Planets
Planet is an astronomical body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.
Earth - Sun - Minor Planets - Moon - Asteroids - Comets
Planetary System is a set of gravitationally bound non-stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consist of bodies such as dwarf planets, asteroids, natural satellites, meteoroids, comets, planetesimals and circumstellar disks. The Sun together with its planetary system, which includes Earth, is known as the Solar System. The term exoplanetary system is sometimes used in reference to other planetary systems. As of 1 February 2019, there are 3,976 confirmed planets in 2,971 systems, with 653 systems having more than one planet. Debris disks are also known to be common, though other objects are more difficult to observe. Of particular interest to astrobiology is the habitable zone of planetary systems where planets could have surface liquid water, and thus the capacity to harbor Earth-like life.
Planetary Science is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), moons, and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes that form them. It studies objects ranging in size from micrometeoroids to gas giants, aiming to determine their composition, dynamics, formation, interrelations and history. It is a strongly interdisciplinary field, originally growing from astronomy and earth science, but which now incorporates many disciplines, including planetary geology (together with geochemistry and geophysics), cosmochemistry, atmospheric science, oceanography, hydrology, theoretical planetary science, glaciology, and exoplanetology. Allied disciplines include space physics, when concerned with the effects of the Sun on the bodies of the Solar System, and astrobiology. Space - Milky Way.
Gas Giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune are the three immense gas giants in the outer solar system, all have atmospheres made up of mostly hydrogen. A gas giant means that it is comprised almost entirely of gas with a liquid core of heavy metals. Since none of the gas giants has a solid surface, you cannot stand on any of these planets, nor can spacecraft land on them. They do have a small rocky and metallic core, but it is buried deep in the core planet. Jupiter is called a failed star because it is made of the same elements (hydrogen and helium) as is the Sun, but it is not massive enough to have the internal pressure and temperature necessary to cause hydrogen to fuse to helium, the energy source that powers the sun and most other stars.
Jovian Planet is also called a giant planet, large gaseous planet like Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, or Neptune.
Giant Planet is any massive planet. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (gases or ices), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. There are four known giant planets in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Many extrasolar giant planets have been identified orbiting other stars. Giant planets are also sometimes called jovian planets, after Jupiter. They are also sometimes known as gas giants. However, many astronomers apply the latter term only to Jupiter and Saturn, classifying Uranus and Neptune, which have different compositions, as ice giants. Both names are potentially misleading: all of the giant planets consist primarily of fluids above their critical points, where distinct gas and liquid phases do not exist. The principal components are hydrogen and helium in the case of Jupiter and Saturn, and water, ammonia and methane in the case of Uranus and Neptune. The defining differences between a very low-mass brown dwarf and a gas giant (~13 MJ) are debated. One school of thought is based on formation; the other, on the physics of the interior. Part of the debate concerns whether "brown dwarfs" must, by definition, have experienced nuclear fusion at some point in their history.
Other Planets in other Solar Systems
Pluto - Pluto's Moon Charon - Pluto Photos - The Year of Pluto - NASA New Horizons (youtube)
Venus when viewed from above its northern polar region, rotates very slowly on its axis clockwise in the opposite direction, with a single revolution taking about 243 Earth days or 5,832 hours and it takes longer to rotate about its axis than any other planet in the Solar System by far. A single day on Venus is around 4 months and its night is 4 months or 116.75 Earth days. The Sun on Venus rises in the west and sets in the east. Venus orbits in a counter-clockwise direction around the Sun and takes 225 Earth days to go all the way around the sun. Venus does not have any moons, a distinction it shares only with Mercury among the planets in the solar system. On Mercury a day lasts 1,408 hours.
Terrestrial Planet is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun, i.e. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Among astronomers who use the geophysical definition of a planet, the Moon, Io and Europa may also be considered terrestrial planets. The terms "terrestrial planet" and "telluric planet" are derived from Latin words for Earth (Terra and Tellus), as these planets are, in terms of structure, Earth-like. These planets are located between the Sun and the asteroid belt. Terrestrial planets have a solid planetary surface, making them substantially different from the larger gaseous planets, which are composed mostly of some combination of hydrogen, helium, and water existing in various physical states.
Tallest Mountains in the Solar System (wiki)
Latest view of Jupiter from NASA’s Juno spacecraft (youtube)
Mars Map that's Perfect everyday Earthlings
Planets that have no stars are called Rogue Planets, there may be billions of rogue planets in the Milky Way.
Curiosity Mars Rover Snaps 1.8 Billion-Pixel Panorama (narrated video) (youtube) - Composed of more than 1,000 images and carefully assembled over the ensuing months, the larger version of this composite contains nearly 1.8 billion pixels of Martian landscape. NASA Curiosity Project Scientist Ashwin Vasavada guides this tour of the rover's view of the Martian surface. This panorama showcases "Glen Torridon," a region on the side of Mount Sharp that Curiosity is exploring. The panorama was taken between Nov. 24 and Dec. 1, 2019. NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Heliocentrism is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the Solar System. Copernican Heliocentrism (wiki) - Momentum - Action Physics.
Why We See the Same Stars Every Night?
Not only does every planet go around the sun in the same counter-clockwise direction, but upwards of 99% of asteroids and other small features do too. The Earth also rotates on its axis in a counter-clockwise direction. And the Earth revolves around the Sun in an counter-clockwise direction. The Sun rotates counter-clockwise. All the other major planets, and most of the minor planets (asteroids) also orbit the Sun in an counter-clockwise direction. Note that this plane of rotation in our solar system does not match up with the overall plane of galactic rotation, which is clockwise. The direction of rotation within individual star systems is largely unaffected by the galaxy, but the systems themselves do all orbit the galactic core in one clockwise direction? Scientists believe that on large scales the Universe is isotropic (the same in all directions). Thus, from our perspective, half of all spiral galaxies should spin clockwise, and half counter-clockwise. A recent analysis of the spin of spiral galaxies confirms this. The public classified over 35,000 spiral galaxies with spins both clockwise and counter-clockwise in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey as part of the Galaxy Zoo project. Scientists published the results in a recent paper and found that the Universe is indeed isotropic - we see the same number of clockwise as counter-clockwise spirals (within the uncertainties).
Frost Line is the boundary between mostly ice-covered objects and mostly rock-covered objects where simple molecules condense. Inside the frost line surfaces exposed to the Sun are warm enough for water ice to melt or sublime readily, leaving exposed rock like our Moon. It marks the clear separation between the terrestrial planets and the gas planets. This particular distance in the solar nebula from the central protostar, is cold enough for volatile compounds such as water, ammonia, methane, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide to condense into solid ice grains. Different volatiles have different condensation temperatures at different partial pressures (thus different densities) in the protostar nebula, so their respective frost lines will differ. The frost line is also known as the snow line or ice line, which is at about 5 AU, which is a bit closer than Jupiter, 700 million km or 434,959,834 miles.
Every Planet was visible in the sky on Dec. 28, 2022. For most of them, you won’t even need a telescope. Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn will all be visible to the naked eye at the same time on Wednesday. As for the remote planets — Uranus and Neptune — hobbyist astronomers can see them with the help of a pair of binoculars or a decent telescope.
Planet Formation
Formation of the Planets. The planets are thought to have formed from the solar nebula, the disc-shaped cloud of gas and dust left over from the Sun's formation. The currently accepted method by which the planets formed is accretion, in which the planets began as dust grains in orbit around the central protostar. Through direct contact, these grains formed into clumps up to 200 metres in diameter, which in turn collided to form larger bodies (planetesimals) of ~10 kilometres (km) in size. These gradually increased through further collisions, growing at the rate of centimetres per year over the course of the next few million years. The inner Solar System, the region of the Solar System inside 4 AU, was too warm for volatile molecules like water and methane to condense, so the planetesimals that formed there could only form from compounds with high melting points, such as metals (like iron, nickel, and aluminium) and rocky silicates. These rocky bodies would become the terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars). These compounds are quite rare in the Universe, comprising only 0.6% of the mass of the nebula, so the terrestrial planets could not grow very large. The terrestrial embryos grew to about 0.05 Earth masses and ceased accumulating matter about 100,000 years after the formation of the Sun; subsequent collisions and mergers between these planet-sized bodies allowed terrestrial planets to grow to their present sizes. When the terrestrial planets were forming, they remained immersed in a disk of gas and dust. The gas was partially supported by pressure and so did not orbit the Sun as rapidly as the planets. The resulting drag and, more importantly, gravitational interactions with the surrounding material caused a transfer of angular momentum, and as a result the planets gradually migrated to new orbits. Models show that density and temperature variations in the disk governed this rate of migration, but the net trend was for the inner planets to migrate inward as the disk dissipated, leaving the planets in their current orbits. The giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) formed further out, beyond the frost line, which is the point between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where the material is cool enough for volatile icy compounds to remain solid. The ices that formed the Jovian planets were more abundant than the metals and silicates that formed the terrestrial planets, allowing the giant planets to grow massive enough to capture hydrogen and helium, the lightest and most abundant elements. Planetesimals beyond the frost line accumulated up to 4 M within about 3 million years. Today, the four giant planets comprise just under 99% of all the mass orbiting the Sun. Theorists believe it is no accident that Jupiter lies just beyond the frost line. Because the frost line accumulated large amounts of water via evaporation from infalling icy material, it created a region of lower pressure that increased the speed of orbiting dust particles and halted their motion toward the Sun. In effect, the frost line acted as a barrier that caused material to accumulate rapidly at ~5 AU from the Sun. This excess material coalesced into a large embryo (or core) on the order of 10 M⊕, which began to accumulate an envelope via accretion of gas from the surrounding disc at an ever-increasing rate. Once the envelope mass became about equal to the solid core mass, growth proceeded very rapidly, reaching about 150 Earth masses ~105 years thereafter and finally topping out at 318 M⊕. Saturn may owe its substantially lower mass simply to having formed a few million years after Jupiter, when there was less gas available to consume. Inner Core.
Birth of a Planet is witnessed by ESO Telescope that sees signs of planet birth. The new images feature a stunning spiral of dust and gas around AB Aurigae, located 520 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Auriga (The Charioteer).
Scientists may have figured out how dust particles can stick together to form planets. In homes, adhesion on contact can cause fine particles to form dust bunnies. Particles under microgravity develop strong electrical charges spontaneously and stick together, forming large aggregates. Although like charges repel, like-charged aggregates form nevertheless, apparently because the charges are so strong that they polarize one another and therefore act like magnets.
Protoplanetary Disk is a rotating circumstellar disk of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, because gases or other material may be falling from the inner edge of the disk onto the surface of the star. This process should not be confused with the accretion process thought to build up the planets themselves. Externally illuminated photo-evaporating protoplanetary disks are called proplyds.
How Newborn Stars prepare for the Birth of Planets. Very young stars, also called protostars, form in clouds of gas and dust in space. The first step in the formation of a star is when these dense clouds collapse due to gravity. As the cloud collapses, it begins to spin -- forming a flattened disk around the protostar. Material from the disk continues to feed the star and make it grow. Eventually, the left-over material in the disk is expected to form planets.
Astronomers reveal a new link between water and planet formation. Researchers have found water vapor in the disc around a young star exactly where planets may be forming. Water is a key ingredient for life on Earth, and is also thought to play a significant role in planet formation. Yet, until now, we had never been able to map how water is distributed in a stable, cool disc -- the type of disc that offers the most favorable conditions for planets to form around stars.
Pebble Accretion is the accretion of objects ranging from centimeters up to meters in diameter onto planetesimals in a protoplanetary disk is enhanced by aerodynamic drag. This drag reduces the relative velocity of pebbles as they pass by larger bodies, preventing some from escaping the body's gravity. These pebbles are then accreted by the body after spiraling or settling toward its surface. This process increases the cross section over which the large bodies can accrete material, accelerating their growth. The rapid growth of the planetesimals via pebble accretion allows for the formation of giant planet cores in the outer Solar System before the dispersal of the gas disk. A reduction in the size of pebbles as they lose water ice after crossing the ice line and a declining density of gas with distance from the sun slow the rates of pebble accretion in the inner Solar System resulting in smaller terrestrial planets, a small mass of Mars and a low mass asteroid belt.
Orbiting - Round and Round We Go - Everything is Spinning
Orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object about a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet about a star or a natural satellite around a planet. Orbits of planets are typically elliptical, and the central mass being orbited is at a focal point of the ellipse. Foucault Pendulum is a simple device conceived in 1851 as an experiment to demonstrate the Earth's rotation. Cycles. Earth's orbit speed around the sun is 19 miles per second. Centrifugal Force - Gravity Well.
Orbital Plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) and of an orbiting celestial body at two different times/points of its orbit. The orbital plane is defined in relation to a reference plane by two parameters: inclination (i) and longitude of the ascending node (Ω). By definition, the reference plane for the Solar System is usually considered to be Earth's orbital plane, which defines the ecliptic, the circular path on the celestial sphere that the Sun appears to follow over the course of a year. In other cases, for instance a moon or artificial satellite orbiting another planet, it is convenient to define the inclination of the Moon's orbit as the angle between its orbital plane and the planet's equatorial plane.
Accretion is the accumulation of particles into a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter, typically gaseous matter, in an accretion disk. Most astronomical objects, such as galaxies, stars, and planets, are formed by accretion processes. Rings of Saturn (wiki).
Orbital Resonance occurs when two orbiting bodies exert a regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of two small integers. The physics principle behind orbital resonance is similar in concept to pushing a child on a swing, where the orbit and the swing both have a natural frequency, and the other body doing the "pushing" will act in periodic repetition to have a cumulative effect on the motion. Orbital resonances greatly enhance the mutual gravitational influence of the bodies, i.e., their ability to alter or constrain each other's orbits. Under some circumstances, a resonant system can be self-correcting and thus stable. Examples are the 1:2:4 resonance of Jupiter's moons Ganymede, Europa and Io, and the 2:3 resonance between Pluto and Neptune. Unstable resonances with Saturn's inner moons give rise to gaps in the rings of Saturn. The special case of 1:1 resonance between bodies with similar orbital radii causes large solar system bodies to eject most other bodies sharing their orbits; this is part of the much more extensive process of clearing the neighborhood, an effect that is used in the current definition of a planet. A binary resonance ratio in this article should be interpreted as the ratio of number of orbits completed in the same time interval, rather than as the ratio of orbital periods, which would be the inverse ratio. Thus, the 2:3 ratio above means that Pluto completes two orbits in the time it takes Neptune to complete three. In the case of resonance relationships among three or more bodies, either type of ratio may be used (whereby the smallest whole-integer ratio sequences are not necessarily reversals of each other), and the type of ratio will be specified.
Orbital Period is the time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object, and applies in astronomy usually to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars.
Elliptic Orbit not centered, rounded like an egg. Angular Parameters of Elliptical Orbit (image)
Circular Orbit is the orbit at a fixed distance around any point by an object rotating around a fixed axis.
Spinning Motion (action physics) - Angular Momentum - Centrifugal Force (action physics)
Orbital Mechanics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft.
Orbiting Satellites - Moons - Orbiting Asteroids - Stars - Torus - Helix
Rotate is to turn on or around an axis or a center.
Atomic Orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom.
Orbital Inclination is the acute (smaller) angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of an object in orbit around another object.
 Ecliptic
is the mean
plane of the apparent path in the Earth's sky that the Sun
follows over the course of one year; it is the basis of the ecliptic
coordinate system. This plane of reference is coplanar with
Earth's orbit
around the Sun (and hence the Sun's apparent path around Earth). The
ecliptic is not normally noticeable from Earth's surface because the
planet's rotation carries the observer through the daily cycles of sunrise
and sunset, which obscure the Sun's apparent motion against the background
of stars during the year. Ecliptic is the
great circle representing the apparent annual path of the sun. The plane
of the Earth's orbit around the sun, which makes an angle of about
23
degrees with the equator. North Pole.
Ecliptic
is the mean
plane of the apparent path in the Earth's sky that the Sun
follows over the course of one year; it is the basis of the ecliptic
coordinate system. This plane of reference is coplanar with
Earth's orbit
around the Sun (and hence the Sun's apparent path around Earth). The
ecliptic is not normally noticeable from Earth's surface because the
planet's rotation carries the observer through the daily cycles of sunrise
and sunset, which obscure the Sun's apparent motion against the background
of stars during the year. Ecliptic is the
great circle representing the apparent annual path of the sun. The plane
of the Earth's orbit around the sun, which makes an angle of about
23
degrees with the equator. North Pole. The shape of Earth's orbit, or eccentricity, and the wobble in its rotation, or precession, favored hotter conditions at the onset of the The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum and that these orbital configurations together may have played a role in triggering the event. The eccentricity of an elliptical orbit is a measure of the amount by which it deviates from a circle.
Earth is revolving around the solar system’s center of mass, also known as its barycenter. This is the balancing point around which the combined mass of every object in the solar system is evenly distributed. Due to the planets’ constant motion, this point is always shifting. Because the Sun has over 99% of the solar system’s total mass, the barycenter of the solar system is located near its surface, and sometimes within the Sun itself. But when the barycenter is outside the Sun, our planet is just orbiting an empty spot in space.
Planets of our solar system rotate around the sun at different speeds. Deferent and Epicycle meaning circle moving on another circle, was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the Moon, Sun, and planets. In particular it explained the apparent retrograde motion of the five planets known at the time. Secondarily, it also explained changes in the apparent distances of the planets from Earth.
Light will reach Pluto at different times in its orbit. At perihelion: 14,800 seconds (4 hours, 6 minutes, 40 sec). At aphelion: 24,617 seconds (6 hours, 50 minutes, 17 sec). Average: 19,680 seconds (5 hours, 28 minutes).
Richard Feynman giving an elementary demonstration of why planets orbit in ellipses. Feynman's Lost Lecture.
Orbital Decay is a process that leads to gradual decrease of the distance between two orbiting bodies at their closest approach (the periapsis) over many orbital periods. These orbiting bodies can be a planet and its satellite, a star and any object orbiting it, or components of any binary system. Orbits do not decay without some friction-like mechanism which robs energy from the orbital motion. This can be any of a number of mechanical, gravitational, or electromagnetic effects. For bodies in a low Earth orbit, the most significant effect is the atmospheric drag. If left unchecked, the decay eventually results in termination of the orbit when the smaller object strikes the surface of the primary; or for objects where the primary has an atmosphere, the smaller object burns, explodes, or otherwise breaks up in the larger object's atmosphere; or for objects where the primary is a star, ends with incineration by the star's radiation (such as for comets), and so on. Collisions and mergers of two stellar-mass objects usually produce cataclysmic effects; see stellar collision and gamma-ray burst. Due to atmospheric drag, the lowest altitude above the Earth at which an object in a circular orbit can complete at least one full revolution without propulsion is approximately 150 km (90 mi). Satellites.
Proper Motion is the astronomical measure of the observed changes in apparent positions of stars in the sky as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System compared to the imaginary fixed background of the more distant stars.
Earth and Venus Orbit (image)
 Apparent Retrograde Motion is the apparent motion of a
planet in a direction opposite to that of other bodies within its system,
as observed from a particular vantage point. Direct motion or prograde
motion is motion in the same direction as other bodies.
Apparent Retrograde Motion is the apparent motion of a
planet in a direction opposite to that of other bodies within its system,
as observed from a particular vantage point. Direct motion or prograde
motion is motion in the same direction as other bodies.Retrograde and Prograde Motion is motion in the direction opposite to the movement of something else and the contrary of direct or prograde motion. This motion can be the orbit of one body about another body or about some other point, or the rotation of a single body about its axis, or other phenomena such as precession or nutation of the axis. In reference to celestial systems, retrograde motion usually means motion which is contrary to the rotation of the primary, that is, the object which forms the system's hub.
Planetary Migration occurs when a planet or other stellar satellite interacts with a disk of gas or planetesimals, resulting in the alteration of the satellite's orbital parameters, especially its semi-major axis. Planetary migration is the most likely explanation for hot Jupiters, extrasolar planets with jovian masses, but orbits of only a few days.
Celestial Mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles of physics (classical mechanics) to astronomical objects, such as stars and planets, to produce ephemeris data.
Tidal Force is a force that stretches a body towards and away from the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomena, including tides, tidal locking, breaking apart of celestial bodies and formation of ring systems within the Roche limit, and in extreme cases, spaghettification of objects. It arises because the gravitational field exerted on one body by another is not constant across its parts: the nearest side is attracted more strongly than the farthest side. It is this difference that causes a body to get stretched. Thus, the tidal force is also known as the differential force, as well as a secondary effect of the gravitational field. In celestial mechanics, the expression tidal force can refer to a situation in which a body or material (for example, tidal water) is mainly under the gravitational influence of a second body (for example, the Earth), but is also perturbed by the gravitational effects of a third body (for example, the Moon). The perturbing force is sometimes in such cases called a tidal force (for example, the perturbing force on the Moon): it is the difference between the force exerted by the third body on the second and the force exerted by the third body on the first.
Occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden by another object that passes between it and the observer. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks from view (occults) an object in the background. In this general sense, occultation applies to the visual scene observed from low-flying aircraft (or computer-generated imagery) when foreground objects obscure distant objects dynamically, as the scene changes over time.
Spin-Orbit Interaction is an interaction of a particle's spin with its motion. The first and best known example of this is that spin–orbit interaction causes shifts in an electron's atomic energy levels due to electromagnetic interaction between the electron's spin and the magnetic field generated by the electron's orbit around the nucleus. This is detectable as a splitting of spectral lines, which can be thought of as a Zeeman Effect due to the internal field. A similar effect, due to the relationship between angular momentum and the strong nuclear force, occurs for protons and neutrons moving inside the nucleus, leading to a shift in their energy levels in the nucleus shell model. In the field of spintronics, spin–orbit effects for electrons in semiconductors and other materials are explored for technological applications. The spin–orbit interaction is one cause of magnetocrystalline anisotropy.
Solar System's Motion through Space: The Resonance Project / Nassim Haramein (youtube) - Interesting Theory's
The Helical Model - Our Solar System is a Vortex (youtube)
The Helical Model - our Galaxy is a Vortex (youtube)
The above videos are not totally accurate, but for all intensive purposes, it's good enough for now.
Torus - Torus Spacetime Manifold (youtube)
Helix is a type of smooth space curve, i.e. a curve in three-dimensional space. It has the property that the tangent line at any point makes a constant angle with a fixed line called the axis. Vortex.
Wobble
 Axial Tilt
also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis
and its orbital axis, or, equivalently, the angle between its equatorial
plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination.
Earth.
Axial Tilt
also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis
and its orbital axis, or, equivalently, the angle between its equatorial
plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination.
Earth.Axial Precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In particular, it can refer to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation, which, similar to a wobbling top, traces out a pair of cones joined at their apices in a cycle of approximately 26,000 years. Through each 26,000-year cycle, the direction in the sky to which the Earth's axis points goes around a big circle. The period of one complete cycle of the equinoxes around the ecliptic, or about 25,800 years". A more precise figure of 25,772 years is currently accepted. Great Year is the period of one complete cycle of the equinoxes around the ecliptic, or about 25,800 years. Binary Star.
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. The rate of precession at 1 degree per 72 years. Momentum.
Age of Aquarius is an astrological term denoting either the current or forthcoming astrological age, depending on the method of calculation. Astrologers maintain that an astrological age is a product of the earth's slow precessional rotation and lasts for 2,160 years, on average (26,000-year period of precession / 12 zodiac signs = 2,160 years). There are various methods of calculating the length of an astrological age. In sun-sign astrology, the first sign is Aries, followed by Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces, whereupon the cycle returns to Aries and through the zodiacal signs again. Astrological ages, however, proceed in the opposite direction ("retrograde" in astronomy). Therefore, the Age of Aquarius follows the Age of Pisces. The 5th Dimension - Age of Aquarius - 1969 (youtube).
Galaxies - Milky Way
 Galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars,
stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter in the
Universe. There are at least 2 trillion galaxies
in the observable universe.
Galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars,
stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter in the
Universe. There are at least 2 trillion galaxies
in the observable universe. Satellites - Telescopes - Locating Planets
Galaxy Zoo helps to classify Galaxies - The Zooniverse is a collection of web-based citizen science projects that use the efforts and abilities of volunteers to help researchers deal with the flood of data that confronts them.
Astronomers discover 49 new galaxies in under three hours. An international team of astronomers has discovered 49 new gas-rich galaxies using the MeerKAT radio telescope in South Africa.
Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our solar system. The Milky Way is a combination of smaller galaxies that were absorbed over billions of years. Our galaxy contains 200–400 billion stars, with at least 50 billion planets, 500 million of which could be located in the habitable zone of their parent star.
We have estimated the size of our galaxy to be around 125,000 light years in diameter. But the latest evidence may bring that size to almost 150,000 light-years in size. The Milky Way's black hole is 26,000 light years away.
Space - Dark Matter
Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with 4 galactic arms. Our solar system is on the edge of a small arm called the orion arm. The milky way is estimated to be about 13.2 billion years old.
New evidence of how and when the Milky Way came together. Aging individual stars helped date an early merger event, including the merger with a key satellite galaxy. Using relatively new methods in astronomy, the researchers were able to identify the most precise ages currently possible for a sample of about a hundred red giant stars in the galaxy. The study also used a spectroscopic survey, called APOGEE, which provides the chemical composition of stars -- another aid in determining their ages. With this and other data, the researchers were able to show what was happening when the Milky Way merged with an orbiting satellite galaxy, known as Gaia-Enceladus, about 10 billion years ago.
Two of the Milky Way's earliest building blocks identified. Astronomers have identified what could be two of the Milky Way's earliest building blocks: Named 'Shakti' and 'Shiva', these appear to be the remnants of two galaxies that merged between 12 and 13 billion years ago with an early version of the Milky Way, contributing to our home galaxy's initial growth. The new find is the astronomical equivalent of archeologists identifying traces of an initial settlement that grew into a large present-day city.
Milky Way churns out Seven New Stars Per Year, Scientists Say with enough dust and gas to make billions more.
Starburst Galaxy is one undergoing an exceptionally high rate of star formation, as compared to the long-term average rate of star formation in the galaxy or the star formation rate observed in most other galaxies. Some galaxies make only one star a year.
Newly discovered adolescent star Gaia 17bpi seen undergoing 'growth spurt'. Star Formation burst in the Milky Way 2-3 billion years ago. More than 50 percent of the stars that created the galactic disc may have been born. Star formation seems to happen in cycles.
Astronomers' theory of how galaxies formed may be upended. New research questions standard model. The standard model for how galaxies formed in the early universe predicted that the James Webb Space Telescope would see dim signals from small, primitive galaxies. But data are not confirming the popular hypothesis that invisible dark matter helped the earliest stars and galaxies clump together. Instead, the oldest galaxies are large and bright, in agreement with an alternate theory of gravity.
Hubble finds a black hole igniting star formation in a dwarf galaxy. The connection between the black hole and a neighboring star forming region located 230 light-years from the black hole, is an outflow of gas stretching across space like an umbilical cord to a bright stellar nursery. The region was already home to a dense cocoon of gas when the low-velocity outflow arrived. Hubble spectroscopy shows the outflow was moving about 1 million miles per hour, slamming into the dense gas like a garden hose hitting a pile of dirt and spreading out. Newborn star clusters dot the path of the outflow's spread, their ages also calculated by Hubble. This is the opposite effect of what's seen in larger galaxies, where material falling toward the black hole is whisked away by surrounding magnetic fields, forming blazing jets of plasma moving at close to the speed of light. Gas clouds caught in the jets' path would be heated far beyond their ability to cool back down and form stars. But with the less-massive black hole in Henize 2-10, and its gentler outflow, gas was compressed just enough to precipitate new star formation. Hubble Examines a Star-Forming Chameleon.
Our sun was born in a giant gas cloud cluster alongside with thousands of other stars, with each star being a little different or very different than our sun. Some stars stay together as binaries, but the stars gravitational influence and gravitational perturbations can make the stars disperse and force stars to spread out and drift apart. Conservation - Star Formation.
Dwarf Galaxies that are less evolved have bigger regions of star factories, with higher rates of star formation. In these relatively pristine dwarf galaxies, massive stars--stars about 20 to 200 times the mass of our sun--collapse into black holes instead of exploding as supernovae. But in more evolved, polluted galaxies, like our Milky Way, they are more likely to explode, thereby generating a collective superwind. Gas and dust get blasted out of the galaxy, and star formation quickly stops.
Plasma - Cosmic Winds - Lifespan of Atoms
But what shuts down star formation in galaxies? Galaxies originally form when large clouds of hydrogen gas collapse and are converted into stars, if you remove that gas, the galaxy cannot grow further.
Milky Way's graveyard of dead stars found,
once massive suns that have since collapsed into black holes and neutron stars.
Astronomers spot oldest 'dead' galaxy yet observed. A galaxy that suddenly stopped forming new stars more than 13 billion years ago has been observed by astronomers. Using the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have spotted a 'dead' galaxy when the universe was just 700 million years old, the oldest such galaxy ever observed.
Astronomers discover newborn galaxies with the James Webb Space Telescope.
Radcliffe Wave is the nearest coherent gaseous structure in the Milky Way, dotted with a related high concentration of interconnected stellar nurseries. It stretches about 8,800 light years. It runs with the trajectory of the Milky Way arms, and lies at its closest (the Taurus Molecular Cloud) at around 400 light-years and at its farthest about 5000 light-years (the Cygnus X star complex) from the Sun, always within the Local Arm (Orion Arm) itself, spanning about 40% of its length and on average 20% of its width. Its discovery was announced in January 2020 and its proximity surprised astronomers.
Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy is an elliptical loop-shaped satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It contains four globular clusters, with the brightest of them – NGC 6715 (M54) – being known well before the discovery of the galaxy itself in 1994. Sgr dSph is roughly 10,000 light-years in diameter, and is currently about 70,000 light-years from Earth, travelling in a polar orbit (an orbit passing over the Milky Way's galactic poles) at a distance of about 50,000 light-years from the core of the Milky Way (about one third of the distance of the Large Magellanic Cloud). In its looping, spiraling path, it has passed through the plane of the Milky Way several times in the past. In 2018 the Gaia project of the European Space Agency showed that Sgr dSph had caused perturbations in a set of stars near the Milky Way's core, causing unexpected rippling movements of the stars triggered when it moved past the Milky Way between 300 and 900 million years ago.
The Milky Way has Satellite Galaxies with their own Satellites. Drawing from data on those galactic neighbors, a new model suggests the Milky Way should have an additional 100 or so very faint satellite galaxies awaiting discovery. Is the Milky Way an ‘outlier’ galaxy? Studying its ‘siblings’ for clues.
Satellite Galaxy is a smaller companion galaxy that travels on bound orbits within the gravitational potential of a more massive and luminous host galaxy (also known as the primary galaxy). Satellite galaxies and their constituents are bound to their host galaxy, in the same way that planets within our own solar system are gravitationally bound to the Sun. While most satellite galaxies are dwarf galaxies, satellite galaxies of large galaxy clusters can be much more massive. The Milky Way is orbited by about fifty satellite galaxies, the largest of which is the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Massive Galaxies are Still Forming. NASA’s Galaxy Evolution Explorer has spotted what appear to be massive “baby” galaxies in our corner of the universe. Previously, astronomers thought the universe’s birth rate had dramatically declined and only small galaxies were forming. If these galaxies are indeed newly formed, then this implies parts of the universe are still hotbeds of galaxy birth. There are three-dozen bright, compact galaxies that greatly resemble the youthful galaxies of more than 10 billions years ago. These new galaxies are relatively close to us, ranging from two to four billion light-years away. They may be as young as 100 million to one billion years old. The Milky Way is approximately 10 billion years old. NASA’s Galaxy Evolution Explorer is an orbiting ultraviolet space telescope launched on April 28, 2003, and operated until early 2012.
Staggering structure in 19 nearby spiral galaxies (2024)
Galaxy Formation and Evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have generated the variety of structures observed in nearby galaxies. Galaxy formation is hypothesized to occur from structure formation theories, as a result of tiny quantum fluctuations in the aftermath of the Big Bang. The simplest model in general agreement with observed phenomena is the Lambda-CDM model—that is, that clustering and merging allows galaxies to accumulate mass, determining both their shape and structure.
Distant colliding galaxy dying out as it loses the ability to form stars. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have seen a galaxy ejecting nearly half of its star-forming gas. This ejection is happening at a startling rate, equivalent to 10,000 Suns-worth of gas a year. The team believes that this event was triggered by a collision with another galaxy.
Discovery of massive early galaxies defies prior understanding of the universe. Using the first dataset released from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, the international team of scientists discovered objects as mature as the Milky Way when the universe was only 3% of its current age, about 500-700 million years after the Big Bang. The telescope is equipped with infrared-sensing instruments capable of detecting light that was emitted by the most ancient stars and galaxies. Essentially, the telescope allows scientists to see back in time roughly 13.5 billion years, near the beginning of the universe as we know it.
Does the farthest galaxy away from earth see only stars in one direction, with one direction seeing nothing but a black abyss? GN-z11 is currently the oldest and most distant known galaxy in the observable universe reported as 13.4 billion light-years, just 400 million years after the Big Bang. The farthest star ever observed, a bright dot 9 billion light-years away
If Light from a Galaxy is 14 Billon years old, that means if you go there now, it may not be there. It's been traveling for 14 billion years and it will not be in the same place or even look the same as it did 14 billon years ago. Space Time.
Astronomers detect most distant fast radio burst to date. European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in a galaxy so far away that its light took eight billion years to reach us. The FRB is also one of the most energetic ever observed; in a tiny fraction of a second it released the equivalent of our Sun's total emission over 30 years.
Star Explodes in the Milky Way Galaxy about once every 50 years. Supernovas.
Catching a GLIMPSE of the Milky Way (youtube) - Huelux (video)
The Milky Way as You’ve Never Seen It Before – AMNH SciCafe (youtube)
The Center of the Milky Way Tastes Like Raspberries. Astronomers reported that Sagittarius B2, a dust cloud at the center of the Milky Way, includes the molecule ethyl formate, which is one of the compounds behind the flavor of raspberries and the scent of rum. Is the Milky Way Galaxy the center of the Universe?
Monoceros Ring is a long, complex, ringlike filament of stars that wraps around the Milky Way three times.
Our solar system orbits around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy at an average velocity of 828,000 km/hr. But even at that high rate, it still takes us about 230 million years to make one complete orbit around the Milky Way. The Milky Way is moving at a rate of 552 to 630 km per second, being pushed away from the local void at 600,000 mph with respect to this local co-moving frame of reference sideways stellar motion.
Our solar system travels at 447,000 MPH and takes 250 Million years to complete one Galactic Rotation. Galaxy Rotation Curve of a disc galaxy (also called a velocity curve) is a plot of the orbital speeds of visible stars or gas in that galaxy versus their radial distance from that galaxy's centre.
Galactic Year is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. Estimates of the length of one orbit range from 225 to 250 million terrestrial years. The Solar System is traveling at an average speed of 828,000 km/h (230 km/s) or 514,000 mph (143 mi/s) within its trajectory around the galactic center, a speed at which an object could circumnavigate the Earth's equator in 2 minutes and 54 seconds; that speed corresponds to approximately one 1300th of the speed of light. Shedding light on Galaxies’ Rotation Secrets.
The earth takes one day to rotate, spins 1,050 MPH and travels 67,000 miles per hour. Earth orbits the Sun once every 366.26 times it rotates about its own axis, which is equal to 365.26 Solar Days. The Sun is moving 486,000 Mph.
Halo Stars or outer disk stars, are the stars bordering the outer reaches of Segmentum Obscurus. Galactic Halo extends beyond the main, visible component.
Time-Laps Video of Space at Night shows Rotation of Earth
Great Attractor is a gravitational anomaly in intergalactic space at the center of the Laniakea Supercluster that reveals the existence of a localised concentration of mass tens of thousands of times more massive than the Milky Way.
Higgs Boson (Hadron Collider)
Galactic Coordinate System - Celestial Navigation - Google Sky - Telescopes
Galaxy Rotation Curve is a plot of the orbital speeds of visible stars or gas in that galaxy versus their radial distance from that galaxy's centre. It is typically rendered graphically as a plot.
Dwarf Galaxy is a small galaxy composed of up to several billion stars, a small number compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars.
Antlia 2 or Ant 2 is a low-surface-brightness dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way at a galactic latitude of 11.2°. It spans 1.26° in the sky just southeast of Epsilon Antliae. The galaxy is similar in size to the Large Magellanic Cloud, despite being 10,000 times fainter. Antlia 2 has the lowest surface brightness of any galaxy discovered and is ~ 100 times more diffuse than any known ultra diffuse galaxy. It was discovered by the European Space Agency's Gaia spacecraft in November 2018. It has an extremely low density as well as a perfect hiding place in the Zone of Avoidance, behind the shroud of the Milky Way’s disc–a region full of dust and an overabundance of bright stars near the galactic center. This is what we call a ghost of a galaxy.
Oddball Galaxy NGC 1052-DF2, doesn't have a noticeable central region, or even spiral arms and a disk, typical features of a spiral galaxy.
 The photo on the right, in about 4 Billion years from now, the
Galaxy Andromeda and the
Milky Way will come in contact with each other to form one big Galaxy.
But the chance of even two stars colliding is
negligible because of the huge distances between the stars. The
Andromeda Galaxy,
2.5 million light-years from Earth, contains about 1 trillion stars and the Milky
Way contains about 300 billion. In order to see this image above would
mean that Andromeda Galaxy is still around 100,000 light years away.
Andromeda and Milky Way Collision (wiki) -
Motion
Gif of Galaxies Colliding.
The photo on the right, in about 4 Billion years from now, the
Galaxy Andromeda and the
Milky Way will come in contact with each other to form one big Galaxy.
But the chance of even two stars colliding is
negligible because of the huge distances between the stars. The
Andromeda Galaxy,
2.5 million light-years from Earth, contains about 1 trillion stars and the Milky
Way contains about 300 billion. In order to see this image above would
mean that Andromeda Galaxy is still around 100,000 light years away.
Andromeda and Milky Way Collision (wiki) -
Motion
Gif of Galaxies Colliding.There are about 50 Galaxies that we know of Circling the Milky way.
Laniakea Supercluster is the galaxy supercluster that is home to the Milky Way and approximately 100,000 other nearby galaxies.
Supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups, which is among the largest-known structures of the cosmos. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy cluster (that contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Laniakea Supercluster with approximately 100,000 other nearby galaxies. This supercluster spans over 500 million light-years, while the Local Group spans over 10 million light-years. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Virgo Supercluster (wiki) - Great Attractor.
Coma Cluster is a large cluster of galaxies that contains over 1,000 identified galaxies.
Globular Cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. Globular clusters, which are found in the halo of a galaxy, contain considerably more stars and are much older than the less dense galactic, or open clusters, which are found in the disk. The galactic halo is an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy which extends beyond the main, visible component. Several distinct components of galaxies comprise the halo: the galactic spheroid (stars). the galactic corona (hot gas, i.e. a plasma). the dark matter halo. The distinction between the halo and the main body of the galaxy is clearest in spiral galaxies, where the spherical shape of the halo contrasts with the flat disc. In an elliptical galaxy, there is no sharp transition between the body of the galaxy and the halo.
Magellanic Clouds are two irregular dwarf galaxies visible from the southern hemisphere; they are members of the Local Group and are orbiting the Milky Way galaxy. Because they both show signs of a bar structure, they are often reclassified as Magellanic spiral galaxies. The two galaxies are: Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), approximately 160,000 light-years away. Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), approximately 200,000 light years away.
Close look at the ATLASGAL image of the plane of the Milky Way (youtube)
In around 1.2 million years from now a star will come close to ours.
There are 52 stellar systems beyond our own Solar system that currently lie within 5.0 parsecs (16.3 light-years) of the Sun. These systems contain a total of 63 stars, of which 50 are red dwarfs, by far the most common type of star in the Milky Way. Much more massive stars, such as our own, make up the remaining 13. In addition to these "true" stars, there are 11 brown dwarfs (objects not quite massive enough to fuse hydrogen), and 4 white dwarfs (extremely dense objects that remain after stars such as our Sun exhaust all fusable hydrogen in their core and slowly shed their outer layers while only the collapsed core remains). Despite the relative proximity of these objects to Earth, only nine (not including the Sun) are brighter than 6.5 apparent magnitude, the dimmest magnitude visible to the naked eye from Earth. All of these objects are located in the Local Bubble, a region within the Orion–Cygnus Arm of the Milky Way. Based on results from the Gaia telescope's second data release from April 2018, an estimated 694 stars will possibly approach the Solar system to less than 5.0 parsecs (16 light-years) over the next 15 million years. Of these, 26 have a good probability to come within 1.0 parsec (3.3 light-years) and another 7 within 0.5 parsecs (1.6 light-years). This number is likely much higher, due to the sheer number of stars needed to be surveyed; a star approaching the Solar System 10 million years ago, moving at a typical Sun-relative 20–200 kilometers per second, would be 600–6,000 light years from the Sun at present day, with millions of stars closer to the Sun. The closest encounter to the Sun so far predicted is the low-mass orange dwarf star Gliese 710 / HIP 89825 with roughly 60% the mass of the Sun. It is currently predicted to pass 19,300 ± 3,200 astronomical units (0.305 ± 0.051 light-years) from the Sun in 1.280+0.041−0.039 million years from the present, close enough to significantly disturb our Solar System's Oort cloud. The easiest way to determine stellar distance to the Sun for objects at these distances is parallax, which measures how much stars appear to move against background objects over the course of Earth's orbit around the Sun. As a parsec (parallax-second) is defined by the distance of an object that would appear to move exactly one second of arc against background objects, stars less than 5 parsecs away will have measured parallaxes of over 0.2 arcseconds, or 200 milliarcseconds. Determining past and future positions relies on accurate astrometric measurements of their parallax and total proper motions (how far they move across the sky due to their actual velocity relative to the Sun), along with spectroscopically determined radial velocities (their speed directly towards or away from us, which combined with proper motion defines their true movement through the sky relative to the Sun). Both of these measurements are subject to increasing and significant errors over very long time spans, especially over the several thousand-year time spans it takes for stars to noticeably move relative to each other.
Quantum Fluctuation is the temporary change in the amount of energy in a point in space. This allows the creation of particle-antiparticle pairs of virtual particles.
Galactic bubbles are more complex than imagined. Fresh look at old data reveals novel details about galactic formation. Astronomers have revealed new evidence about the properties of the giant bubbles of high-energy gas that extend far above and below the Milky Way galaxy's center.
Fermi Bubbles are two enormous orbs of gas and cosmic rays that tower over the Milky Way. Fermi bubbles are two large structures in gamma-rays above and below the Galactic center. They are associated with the microwave haze around the Galactic center discovered in the WMAP data and recently confirmed in the Planck data.
eRosita Bubbles are about two times the size of the Fermi bubbles and are expanded by the wave of energy, or a shockwave.
Local Bubble is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbors and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Solar System), the neighboring G-Cloud, the Ursa Major moving group (the closest stellar moving group) and the Hyades (the nearest open cluster). It is estimated to be at least 1000 light years in size, and is defined by its neutral-hydrogen density of about 0.05 atoms/cm3, or approximately one tenth of the average for the ISM in the Milky Way (0.5 atoms/cm3), and one sixth that of the Local Interstellar Cloud (0.3 atoms/cm3).
Galactic Magnetic Field is a weak but pervasive magnetic field that permeates our galaxy, the Milky Way. It is composed of two main components: a large-scale, ordered component that follows the structure of the galaxy (like its spiral arms), and a smaller-scale, random component. This field plays a crucial role in the dynamics and evolution of the galaxy, influencing star formation, gas distribution, and the behavior of cosmic rays. The Galactic magnetic field is generally weak, about 100 times weaker than Earth's magnetic field. Scientists use various techniques to study the magnetic field, including analyzing polarized radio waves, synchrotron radiation, and dust polarization. Role in Galaxy Evolution and Star Formation: The magnetic field can help remove angular momentum from collapsing gas clouds, facilitating the formation of stars. Gas Dynamics: It influences the movement and distribution of gas and dust in the interstellar medium, potentially affecting the formation of spiral arms and other galactic structures. Cosmic Rays: Magnetic fields help confine and guide cosmic rays, which are high-energy particles that originate from various sources in the galaxy. Galaxy Evolution: The magnetic field's interaction with gas and other components of the galaxy can play a role in the overall evolution and shape of the galaxy. Human Body Magnetic Field.
Magnetic Fields are present throughout space, originating from celestial objects like planets, stars, and galaxies, and also existing in the large-scale interstellar medium. These cosmic magnetic fields are not just local phenomena but are coherent on galactic and intergalactic scales, playing a significant role in shaping the structure and dynamics of the universe despite often being much weaker than Earth's magnetic field.
Circumgalactic Medium is a massive multiphase gas reservoir that resides within the virial radius of their galaxies. The evolution of galaxies is directly linked to the gas reservoirs surrounding them.
"I was given something wonderful, something that changed me forever. A vision of the universe." Quote from the 1997 Film "Contact".
Astronomy - Universe Studies
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It applies mathematics, physics, and chemistry, in an effort to explain the origin of those objects and phenomena and their evolution. The objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, galaxies, and comets; while the phenomena include supernovae explosions, gamma ray bursts, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally all astronomical phenomena that originate outside Earth's atmosphere is within the preview of astronomy. A related but distinct subject, physical cosmology, is concerned with the study of the Universe as a whole. Ask an Astronomer at Cornell University - The National Radio Astronomy Observatory.
Astronomical is something that relates to the science of astronomy. Something inconceivably large.
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of the solar system and our galaxy, the Milky Way. Calendars - Astronomical Clock.
Observable Universe are only the things that we can see with our eyes or detect using our instruments. There are things that we can't see or detect. We can theorize about all the things that are beyond our perception and beyond our comprehension, but we can't be sure or be positive about things that we can't see or detect. All we can do is build better instruments and keep educating ourselves so that we keep building on all the knowledge and information that we have accumulated so far. We will continue to discover new things and advance and develop, but only if we keep asking questions and continue to look for answers to our questions. Learning is the path, learning is the way, learning is what we do to be the best that we can be. So what's next? Everything.
Observable Universe is a spherical region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. There are at least 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe has a spherical volume (a ball) centered on the observer. Every location in the universe has its own observable universe, which may or may not overlap with the one centered on Earth.
Observational Astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments. As a science, the study of astronomy is somewhat hindered in that direct experiments with the properties of the distant universe are not possible. However, this is partly compensated by the fact that astronomers have a vast number of visible examples of stellar phenomena that can be examined. This allows for observational data to be plotted on graphs, and general trends recorded. Nearby examples of specific phenomena, such as variable stars, can then be used to infer the behavior of more distant representatives. Those distant yardsticks can then be employed to measure other phenomena in that neighborhood, including the distance to a galaxy. Galileo Galilei turned a telescope to the heavens and recorded what he saw. Since that time, observational astronomy has made steady advances with each improvement in telescope technology.
Tiny1: The World's Smallest Astronomy Camera - Worlds Most Powerful 3.2-Gigapixel Digital Camera.
Astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, solar astronomy, the origin or evolution of stars, or the formation of galaxies. Related but distinct subjects like physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Astronomers usually fall under either of two main types: observational and theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate models of things that cannot be observed. Because it takes millions to billions of years for a system of stars or a galaxy to complete a life cycle, astronomers must observe snapshots of different systems at unique points in their evolution to determine how they form, evolve, and die. They use these data to create models or simulations to theorize how different celestial objects work. Further subcategories under these two main branches of astronomy include planetary astronomy, galactic astronomy, or physical cosmology.
Stargazer is a physicist who studies astronomy. Someone who is not distracted by a busy world.
Uranologist is a physicist who studies astronomy.
Archaeoastronomy, ethnoastronomy or cultural astronomy, are concerned with humankind's perceptions and understanding of astronomical phenomena, throughout human history and among all cultures. Archaeoastronomy is the interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary study of how people in the past "have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures.
Astrology is the study of the movements and relative positions of celestial objects as a means for divining information about human affairs and terrestrial events.
Horoscope is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth.
Asterism is a popularly known pattern or group of stars that can be seen in the night sky. This colloquial definition makes it appear quite similar to a constellation, but they differ mostly in that a constellation is an officially recognized area of the sky, while an asterism is a visually obvious collection of stars and the lines used to mentally connect them; as such, asterisms do not have officially determined boundaries and are therefore a more general concept which may refer to any identified pattern of stars. This distinction between terms remains somewhat inconsistent, varying among published sources. An asterism may be understood as an informal group of stars within the area of an official or defunct former constellation. Some include stars from more than one constellation. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just few stars to more complex collections of many bright stars. They are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. For example, the asterisms known as The Plough (Charles' Wain, the Big Dipper, etc.) comprises the seven brightest stars in the International Astronomical Union (IAU) recognised constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, whose recognised constellation is Crux.
Constellation is a group of stars that forms an imaginary outline or pattern on the celestial sphere, typically representing an animal, mythological person or creature, a god, or an inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many have changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Others were limited to a single culture or nation. Constellations are human constructs to make sense of the night sky and use star positions as a way to navigate and to measure time. Some say the Sun is the only star that does not belong to a constellation. The Sun travels through the 13 constellations along the ecliptic, the 12 of the Zodiac and Ophiuchus. The Sun is a G-type main-sequence star or G2V. The Sun is currently in the constellation of Capricornus. The current Right Ascension of The Sun is 21h 57m 03s and the Declination is -12° 29' 41” (topocentric coordinates computed for the selected location: Greenwich, United Kingdom). The current magnitude of The Sun is -26.77 (JPL). If viewed from the surface of this planet, the Sun would appear to be part of the Cassiopeia constellation.
Celestial is of the sky or relating to the sky, or inhabiting a divine heaven. Extraterrestrial - Celestial Sphere.
Spherical Astronomy is the branch of astronomy that is used to determine the location of objects on the celestial sphere, as seen at a particular date, time, and location on Earth. It relies on the mathematical methods of spherical geometry and the measurements of astrometry. This is the oldest branch of astronomy and dates back to antiquity. Observations of celestial objects have been, and continue to be, important for religious and astrological purposes, as well as for timekeeping and navigation. The science of actually measuring positions of celestial objects in the sky is known as astrometry. The primary elements of spherical astronomy are coordinate systems and time. The coordinates of objects on the sky are listed using the equatorial coordinate system, which is based on the projection of Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere. The position of an object in this system is given in terms of right ascension (a) and declination (d). The latitude and local time can then be used to derive the position of the object in the horizontal coordinate system, consisting of the altitude and azimuth. The coordinates of celestial objects such as stars and galaxies are tabulated in a star catalog, which gives the position for a particular year. However, the combined effects of precession and nutation will cause the coordinates to change slightly over time. The effects of these changes in the movement of Earth are compensated by the periodic publication of revised catalogs. To determine the position of the Sun and planets, an astronomical ephemeris (a table of values that gives the positions of astronomical objects in the sky at a given time) is used, which can then be converted into suitable real-world coordinates. The unaided human eye can detect about 6000 stars, of which about half are below the horizon at any one time. On modern star charts, the celestial sphere is divided into 88 constellations. Every star lies within a constellation. Constellations are useful for navigation. Polaris lies close to due north to an observer in the northern hemisphere. This star is always at a position nearly over the North Pole.
Astrophotography is a specialized type of photography for recording photos of astronomical objects, celestial events, and large areas of the night sky. Astrophotography.
Astronomical Symbols are symbols used to represent astronomical objects, theoretical constructs and observational events in astronomy. The earliest forms of these symbols appear in Greek papyri of late antiquity.
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that employs the principles of physics and chemistry "to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space.
Plasma Physics is one of the four fundamental states of matter, the others being solid, liquid, and gas. A plasma has properties unlike those of the other states.
Constellation is formally defined as a region of the celestial sphere, with boundaries laid down by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The constellation areas mostly had their origins in Western-traditional patterns of stars from which the constellations take their names.
Telescopes - Star Navigation - Age of Aquarius
Space Adventures - Science Websites - Science Education
Nikola Tesla - Wireless Energy
Physical Cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate.
Cosmos is the universe regarded as a complex and orderly system; the opposite of chaos.
Cosmology is the study of the origin, evolution, and eventual fate of the universe. Physical cosmology is the scholarly and scientific study of the origin, large-scale structures and dynamics, and ultimate fate of the universe, as well as the scientific laws that govern these realities.
Star Date is the public education and outreach arm of the University of Texas McDonald Observatory. Our radio program airs daily on more than 300 stations, and our popular bimonthly astronomy magazine is the perfect sky watching companion for amateur astronomers or anyone interested in celestial events and space exploration. We also offer astronomy resources to teachers, the media, and the public.
Universe
Universe is all of time and space and its contents. It includes planets, moons, minor planets, stars, blackholes, galaxies, the contents of intergalactic space, and all matter and energy. The size of the entire Universe is unknown. The size of the Universe is estimated to be around 46.5 billion light-years and its diameter about 28.5 gigaparsecs (93 billion light-years, 8.8×1026 metres or 2.89×1027 feet). Age: 13.799±0.021 billion years. Diameter: 8.8×1026 m (28.5 Gpc or 93 Gly). Density (of total energy): 9.9×10-27 kg/m3. Mass (ordinary matter): 1.5 × 10 to the power of 53 kg. Universe Basics (PDF) - Timeline.
250 million years after the Big Bang the Universe started to form. Astronomers have used observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) to determine that star formation in the very distant galaxy MACS1149-JD1 started at an unexpectedly early stage, only 250 million years after the Big Bang. This discovery also represents the most distant oxygen ever detected in the universe and the most distant galaxy ever observed by ALMA or the VLT.
Wendy Freedman: This new telescope might show us the beginning of the universe (video)
The most distant galaxy ever seen ' UDFj-39546284 is about 13.2 billion Light Years from Earth. The galaxy dated back to a time just 480 million years after the big bang.
Giant Galaxies die from the inside out: Star formation shuts down in the centers of elliptical galaxies first.
Stupendous is something great in size, force or extent as to elicit awe. Colossal.
Big is something above average in size, number, quantity, magnitude or extent. Significant. On a grand scale. In a major way. Very intense. Loud and firm. Marked by intense physical force. Conspicuous in position or importance.
Entropy - Black Holes - Multiverse
Charting the Slow Death of the Universe is an international team of astronomers studying more than 200,000 galaxies has measured the energy generated within a large portion of space more precisely than ever before. They confirm that the energy produced in a section of the Universe today is only about half what it was two billion years ago and find that this fading is occurring across all wavelengths from the ultraviolet to the far infrared. Is the Universe slowly dying or expanding?
Universe Era Stages: Inflationary era preceded and set up the hot Big Bang. Primordial Soup era was from the start of the hot Big Bang until the final transformative nuclear & particle interactions occur in the early Universe. Plasma era was from the end of non-scattering nuclear and particle interactions until the Universe cools enough to stably form neutral matter. Dark Ages era was from the formation of neutral matter until the first stars and galaxies reionize the intergalactic medium of the Universe completely. Stellar era was from the end of reionization until the gravity-driven formation and growth of large-scale structure ceases, when the dark energy density dominates over the matter density. Dark Energy era is the final stage of our Universe, where the expansion accelerates and disconnected objects speed irrevocably and irreversibly away from one another.
Universe Photos
M60-UCD1 Dwarf Galaxy with Black hole 5 times bigger then the Milky Way (image)Elephant-4214115 (image)
Butterfly Nebula (image)
Colliding Galaxies Leave a Trail of Stars (NGC 4676) (image)
Whirlpool Galaxy (M51) (image)
Spiral Galaxy NGC 7714 (image)
Cats Eye Nebula Dying Star (image)
Galaxy Pair Arp 87 (image)
Antennae Galaxies NGC 4038 NGC 4039 (image)
MyCn18 (image)
Sombrero Galaxy (M104) (image)
Astrophotography is photography of astronomical objects, celestial events, and areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object was the moon taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, astrophotography has the ability to image objects invisible to the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is done by long time exposure since both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum light photons over these long periods of time. Photography revolutionized the field of professional astronomical research, with longtime exposures recording hundreds of thousands of new stars and nebulae that were invisible to the human eye, leading to specialized and ever-larger optical telescopes that were essentially big cameras designed to record light using photographic plates. Astrophotography had an early role in sky surveys and star classification but over time it has given way to more sophisticated equipment and techniques designed for specific fields of scientific research, with image sensors becoming just one of many forms of sensor. Today, astrophotography is mostly a subdiscipline in amateur astronomy, usually seeking aesthetically pleasing images rather than scientific data. Amateurs use a wide range of special equipment and techniques.
Telescopes - Space Observation Tools
Telescope is a magnifier of images of distant objects. Telescope is an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe and focus on distant objects, or various devices used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century, by using glass lenses. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy.
Optical Telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. There are three primary types of optical telescope: Refractors, which use lenses (dioptrics). Reflectors, which use mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric Telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrors.
Depth Perception - Light Bending
Refracting Telescope is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope design was originally used in spy glasses and astronomical telescopes but is also used for long focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes the refracting telescope has been superseded by the Reflecting Telescope which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece. Telescopes to Buy (amazon) - Microscopes.
A telescope is like a time machine. You see distant stars and galaxies as there once were and not as we see them now. But at the same time, looking at stars may not be seeing back in time, because time does not have the same meaning when measuring light years or the speed of light. Our perception of time may be something totally different and time itself may not be what it is to humans on earth. Time may be something totally unimaginable. What you see is not what you get. Planet Hunting - Satellites.
 Photo on the Right is the
Big Dipper
changing over time, from 100,000 BCE to present-day to 50,000 CE to 100,000 CE.
Space.
Photo on the Right is the
Big Dipper
changing over time, from 100,000 BCE to present-day to 50,000 CE to 100,000 CE.
Space.Why do we see the same stars every night?
Most Distant Astronomical Objects List (wiki).
Galileo Galilei (February 5th, 1564 – January 8th, 1642).
The Universe Looks like One Large Experiment, someone has tried all kind of things and is still trying all kind of things. Not every planet has life and not every star gives life, but you can still learn something from all these different outcomes.
Earthsky has daily updates on your cosmos and world.
Worldwide Telescope Web Client - Home
Hubble Telescope - Cosmic Journeys - Hubble: Universe in Motion (youtube)
James Webb Telescope (100 times stronger than hubble)
Spitzer Telescope
X-Ray Telescoped
Radio Telescopes
Infrared Astronomy
Laser Guided Telescope (image)
Synoptic Survey Telescope
European Southern Observatory
Faulkes Telescope
Stratospheric Observatory Infrared Astronomy (wiki)
Fermi Gamma-Ray (wiki)
Meade LX 800
Celestron
Sloan Digital Sky Survey (wiki)
S.D.S.S.
Millimeter Telescope
The heart of world's largest solar telescope begins to beat. The world's largest solar telescope has reached an important milestone. The data published now were obtained during the technical commissioning of the instrument. The world's largest solar telescope, the U.S. National Science Foundation Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope in Hawaii, has reached an important milestone. After almost 15 years of preparation, the German instrument for the Inouye Solar Telescope, the Visible Tunable Filtergraph, has now taken its first images. The imaging spectro-polarimeter was developed and built at the Institute for Solar Physics in Freiburg Germany. The Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Göttingen Germany is a partner in the project.
Open Source Virtual Telescope and Interactive Universe Images for Students and the General Public.
Astrophotography is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects invisible to the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is done by long time exposure since both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over these long periods of time.
 Lens
in optics
is a transmissive
optical device that
focuses or disperses a
light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single
piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of
several
simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are
made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished
or moulded to a desired shape. A lens can
focus light to form an image,
unlike a prism, which refracts light without
focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation
other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses,
electron lenses,
acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.
Optical Engineering.
Lens
in optics
is a transmissive
optical device that
focuses or disperses a
light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single
piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of
several
simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are
made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished
or moulded to a desired shape. A lens can
focus light to form an image,
unlike a prism, which refracts light without
focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation
other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses,
electron lenses,
acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.
Optical Engineering.Bending Light - Polarized - Illusions
Eyepiece is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. The objective lens or mirror collects light and brings it to focus creating an image. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece. An eyepiece consists of several "lens elements" in a housing, with a "barrel" on one end.
Adaptive Optics is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of wavefront distortions: it aims at correcting the deformations of an incoming wavefront by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array. Satellites.
Active Optics is a technology used with reflecting telescopes developed in the 1980s, which actively shapes a telescope's mirrors to prevent deformation due to external influences such as wind, temperature, mechanical stress. Without active optics, the construction of 8 metre class Telescopes is not possible, nor would telescopes with segmented mirrors be feasible.
Geometrical Optics describes light propagation in terms of rays. The ray in geometric optics is an abstraction useful for approximating the paths along which light propagates under certain circumstances. The simplifying assumptions of geometrical optics include that light rays: propagate in straight-line paths as they travel in a homogeneous medium. Bend, and in particular circumstances may split in two, at the interface between two dissimilar media. Follow curved paths in a medium in which the refractive index changes. May be absorbed or reflected. Geometrical optics does not account for certain optical effects such as diffraction and interference. This simplification is useful in practice; it is an excellent approximation when the wavelength is small compared to the size of structures with which the light interacts. The techniques are particularly useful in describing geometrical aspects of imaging, including optical aberrations.
Alhazen's Problem is a problem in geometrical optics first formulated by Ptolemy in 150 AD. It is named for the 11th-century Arab mathematician Alhazen (Ibn al-Haytham) who presented a geometric solution in his Book of Optics. The algebraic solution involves quartic equations and was found only as late as 1965, by Jack M. Elkin. The problem comprises drawing lines from two points in a circle meeting at a third point on its circumference and making equal angles with the normal at that point. Thus, its main application in optics is to solve the problem, "Given a light source and a spherical mirror, find the point on the mirror where the light will be reflected to the eye of an observer." This leads to an equation of the fourth degree.
Image Sensors - Lens Flare
Eyes in the Skies (looking inward - environmental monitoring)
Manned Orbiting Laboratory was a 963 military reconnaissance space plane. - National Reconnaissance Operations Center
Almaz program was a highly secretive Soviet military space station program where 3 crewed military reconnaissance stations were launched between 1973 and 1976.
Microscopes (looking inward)
MEMS Chips get Metalenses. Combining metasurface lenses with MEMS technology could add high-speed scanning and enhance focusing capability of optical systems. Lens technologies have advanced across all scales, from digital cameras and high bandwidth in fiber optics to the LIGO instruments. Now, a new lens technology that could be produced using standard computer-chip technology is emerging and could replace the bulky layers and complex geometries of traditional curved lenses. Researchers have developed a device that integrates mid-infrared spectrum metalenses onto MEMS. Scanning Electron Micrograph.
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance-era mathematician and astronomer, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at the center of the universe, in all likelihood independently of Aristarchus of Samos, who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. (February 19, 1473 – May 24, 1543).
Sidereus Nuncius or the Starry Messenger, is a short astronomical treatise or pamphlet published in New Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published scientific work based on observations made through a telescope, and it contains the results of Galileo's early observations of the imperfect and mountainous Moon, the hundreds of stars that were unable to be seen in either the Milky Way or certain constellations with the naked eye, and the Medicean Stars (later Galilean moons) that appeared to be circling Jupiter.
Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer. He is a key figure in the 17th-century scientific revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae. These works also provided one of the foundations for Newton's theory of universal gravitation. (Born December 27, 1571 Died November 15, 1630).
Light Pollution - I Can't See all the Stars
Light Pollution is the presence of anthropogenic and artificial light in the night environment. It is exacerbated by excessive, misdirected or obtrusive uses of light, but even carefully used light fundamentally alters natural conditions.
International Dark-Sky Association works to protect the night skies from artificial light that interferes with seeing the stars at night. 7th designated Dark Sky Sanctuary.
Olbers's Paradox or the dark night sky paradox, is an argument in astrophysics and physical cosmology that says that the darkness of the night sky conflicts with the assumption of an infinite and eternal static universe. In the hypothetical case that the universe is static, homogeneous at a large scale, and populated by an infinite number of stars, any line of sight from Earth must end at the surface of a star and hence the night sky should be completely illuminated and very bright. This contradicts the observed darkness and non-uniformity of the night.
Olbers's paradox is a fallacy. It assumes that our atmosphere is perfectly clear and that light pollution or the sun and moon have no effect on our vision. Apollo 8 astronaut witnessed a star filled sky when he was between the sun and moon. He said that it was so bright that he could not identify any constellations because there were so many stars that were so equally bright, that it was impossible to see any patterns of constellations. He said that he never saw so many stars in his life. There for, the dark night sky is relative.
Globe at Night is an international citizen-science campaign to raise public awareness of the impact of light pollution.
Space Travel 1 of 5 HQ - The Universe (youtube)
There are more stars in space than there are grains of sand on every beach on Earth. Telescopes.
Seeing Stars
 It seems that we see the same Stars
every Night, well almost. If you only look at the stars at the same
time at night and at the same time of year and in the same direction,
it
will seem like you see the same stars all the time. You need to see
time-lapse photos of the night sky to better
understand our planet, our solar system and our galaxy. The night sky in winter looks different than the summer.
We see constellations at different times of the year - spring, summer,
fall, & winter. This occurs because the Earth is orbiting the Sun. In
winter, we see the constellation Orion in the south at night and during
the day the Sun is in the sky with the constellation Scorpius. In summer,
we see the opposite (we see Scorpius at night and Orion is in the sky
during the day). This is why you cannot see Orion or any one constellation
all year long, except for constellations in the northern circumpolar sky,
which include Auriga, Camelopardalis, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Draco, Lynx,
Perseus, Ursa Major, and Ursa Minor. These constellations are always
visible in the night sky of the Northern Hemisphere.
Peripheral vision.
It seems that we see the same Stars
every Night, well almost. If you only look at the stars at the same
time at night and at the same time of year and in the same direction,
it
will seem like you see the same stars all the time. You need to see
time-lapse photos of the night sky to better
understand our planet, our solar system and our galaxy. The night sky in winter looks different than the summer.
We see constellations at different times of the year - spring, summer,
fall, & winter. This occurs because the Earth is orbiting the Sun. In
winter, we see the constellation Orion in the south at night and during
the day the Sun is in the sky with the constellation Scorpius. In summer,
we see the opposite (we see Scorpius at night and Orion is in the sky
during the day). This is why you cannot see Orion or any one constellation
all year long, except for constellations in the northern circumpolar sky,
which include Auriga, Camelopardalis, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Draco, Lynx,
Perseus, Ursa Major, and Ursa Minor. These constellations are always
visible in the night sky of the Northern Hemisphere.
Peripheral vision.
 Celestial Sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large
radius, concentric with Earth. All objects in the observer's sky can be
thought of as projected upon the inside surface of the celestial sphere,
as if it were the underside of a dome or a hemispherical screen. The
celestial sphere is a practical tool for spherical astronomy, allowing
observers to plot positions of objects in the sky when their distances are
unknown or unimportant. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being
projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be
centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of
the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing
location. The celestial sphere is a practical tool for spherical
astronomy, allowing astronomers to specify the apparent positions of
objects in the sky if their distances are unknown or irrelevant. In the
equatorial coordinate system, the celestial equator divides the celestial
sphere into two halves: the northern and southern celestial hemispheres.
Celestial Sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large
radius and is concentric to Earth.
Relative - Star
Navigation.
Celestial Sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large
radius, concentric with Earth. All objects in the observer's sky can be
thought of as projected upon the inside surface of the celestial sphere,
as if it were the underside of a dome or a hemispherical screen. The
celestial sphere is a practical tool for spherical astronomy, allowing
observers to plot positions of objects in the sky when their distances are
unknown or unimportant. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being
projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be
centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of
the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing
location. The celestial sphere is a practical tool for spherical
astronomy, allowing astronomers to specify the apparent positions of
objects in the sky if their distances are unknown or irrelevant. In the
equatorial coordinate system, the celestial equator divides the celestial
sphere into two halves: the northern and southern celestial hemispheres.
Celestial Sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large
radius and is concentric to Earth.
Relative - Star
Navigation.Celestial Equator is a great circle on the imaginary celestial sphere, in the same plane as the Earth's equator. In other words, it is a projection of the terrestrial equator out into space. As a result of the Earth's axial tilt, the celestial equator is inclined by 23.4° with respect to the ecliptic plane.
Circumpolar Star is a star that, as viewed from a given latitude on Earth, never sets (that is, never disappears below the horizon), due to its proximity to one of the celestial poles. Circumpolar stars are therefore visible from said location toward nearest pole for the entire night on every night of the year (and would be continuously visible throughout the day too, were they not overwhelmed by the Sun's glare).
Copernican Principle states that humans are not privileged observers of the universe on the Earth or in the Solar System. If one assumes the Copernican principle and observes that the universe appears isotropic or the same in all directions from the vantage point of Earth, then one can infer that the universe is generally homogeneous or the same everywhere (at any given time) and is also isotropic about any given point. These two conditions make up the cosmological principle. In practice, astronomers observe that the universe has heterogeneous or non-uniform structures up to the scale of galactic superclusters, filaments and great voids. It becomes more and more homogeneous and isotropic when observed on larger and larger scales, with little detectable structure on scales of more than about 200 million parsecs. However, on scales comparable to the radius of the observable universe, we see systematic changes with distance from Earth. For instance, galaxies contain more young stars and are less clustered, and quasars appear more numerous. While this might suggest that Earth is at the center of the universe, the Copernican principle requires us to interpret it as evidence for the evolution of the universe with time: this distant light has taken most of the age of the universe to reach Earth and shows the universe when it was young. The most distant light of all, cosmic microwave background radiation, is isotropic to at least one part in a thousand.
Principle of Locality states that an object is only directly influenced by its immediate surroundings. A theory which includes the principle of locality is said to be a "local theory". This is an alternative to the older concept of instantaneous "action at a distance". Locality evolved out of the field theories of classical physics. The concept is that for an action at one point to have an influence at another point, something in the space between those points (such as a field, wave, or particle) must carry (i.e. "mediate") the action. To exert an influence, something must travel through the space between the two points, carrying the influence.
Image of the Angle our Solar System as it Travels through the Milky Way - Triangulation.
Ecliptic - Earth's Orbit - Sun
Planisphere is a star chart analog computing instrument in the form of two adjustable disks that rotate on a common pivot. It can be adjusted to display the visible stars for any time and date. It is an instrument to assist in learning how to recognize stars and constellations. The astrolabe, an instrument that has its origins in Hellenistic astronomy, is a predecessor of the modern planisphere. The term planisphere contrasts with armillary sphere, where the celestial sphere is represented by a three-dimensional framework of rings. Planisphere - How to read a Celestial Planisphere Chart.
Using Stars to Navigate (sextant)
Uncle Milton Star Theatre Pro (amazon)
Portable Planetariums - Digital Education
Spitz Inc - DIY Star Projector
The number of stars are estimated to be around is 300,000,000,000,000,000,000,000. That is 300 Sextillion.
Star Chart is a map of the night sky. Astronomers divide these into grids to use them more easily. They are used to identify and locate astronomical objects such as stars, constellations and galaxies. They have been used for human navigation since time immemorial. Note that a star chart differs from an astronomical catalog, which is a listing or tabulation of astronomical objects for a particular purpose. Tools utilizing a star chart include the astrolabe and the planisphere. Spatial Intelligence.
The Night Sky - Starry Maps - Stelvision
Apps for Star Names and Locations - Starwalk Cell Phone App - Space Junk App - Sky Guide App: View Stars Night or Day - Apps (store)
The Sun Moves too, everything moves together. Asteroids
The star is known as WISE J072003.20-084651.2, or Scholz's star. Today, it's 20 light-years away from us in the constellation Monoceros. But in a study published by Astrophysical Journal Letters, researchers say it passed right by us at a distance of 5 trillion miles (8 trillion kilometers, or 52,000 astronomical units, or 0.8 light-years). No other star has been known to come that close. A different star called HIP 85605 might make a dangerous pass through the Oort Cloud 240,000 to 470,000 years from now.
Coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view the corona of the Sun, but a new class of conceptually similar instruments (called stellar coronagraphs to distinguish them from solar coronagraphs) are being used to find extrasolar planets and circumstellar disks around nearby stars.
Star Location Resources - In The Sky - Google Sky - Earth Sky - Planetarium - Sky and Telescope - Clear Dark Sky - The European Space Agency (ESA) - Eyes in Space - Hayden Planetarium - Night Sky Network - Star Count - Galaxy Zoo - Starry Night Software Store - Exploration NASA - Stellarium - Time and Date Astronomy
NASA YouTube Channel (videos)
Galactic Center of Milky Way Rises over Texas Star Party (youtube)
Cosmic Distance Ladder is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are "close enough" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity. The ladder analogy arises because no single technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.
Standard Ruler is an astronomical object for which the actual physical size is known. By measuring its angular size in the sky, one can use simple trigonometry to determine its distance from Earth. In simple terms, this is because objects of a fixed size appear smaller the further away they are. Measuring distances is of great importance in cosmology, as the relationship between the distance and redshift of an object can be used to measure the expansion rate and geometry of the Universe. Distances can also be measured using standard candles; many different types of standard candles and rulers are needed to construct the cosmic distance ladder.
Redshift is a phenomenon where electromagnetic radiation (such as light) from an object undergoes an increase in wavelength. Whether or not the radiation is visible, "redshift" means an increase in wavelength, equivalent to a decrease in wave frequency and photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light. Neither the emitted nor perceived light is necessarily red; instead, the term refers to the human perception of longer wavelengths as red, which is at the section of the visible spectrum with the longest wavelengths. Examples of redshifting are a gamma ray perceived as an X-ray, or initially visible light perceived as radio waves. The opposite of a redshift is a blueshift, where wavelengths shorten and energy increases. However, redshift is a more common term and sometimes blueshift is referred to as negative redshift. There are three main causes of red (and blue shifts) in astronomy and cosmology: Objects move apart (or closer together) in space. This is an example of the Doppler effect. Space itself expands, causing objects to become separated without changing their positions in space. This is known as cosmological redshift. All sufficiently distant light sources (generally more than a few million light years away) show redshift corresponding to the rate of increase in their distance from Earth, known as Hubble's Law. Gravitational redshift is a relativistic effect observed due to strong gravitational fields, which distort spacetime and exert a force on light and other particles. Knowledge of redshifts and blueshifts has been used to develop several terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns. Redshifts are also seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects. Its value is represented by the letter z.
Astronomers have discovered that there is a vast wall across the southern border of the local cosmos. The South Pole Wall, as it is known, consists of thousands of galaxies — beehives of trillions of stars and dark worlds, as well as dust and gas — aligned in a curtain arcing across at least 700 million light-years of space. It winds behind the dust, gas and stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, from the constellation Perseus in the Northern Hemisphere to the constellation Apus in the far south. It is so massive that it perturbs the local expansion of the universe. But don’t bother trying to see it. The entire conglomeration is behind the Milky Way, in what astronomers quaintly call the zone of avoidance.
Zone of Avoidance is when viewing space from Earth, the attenuation, interstellar dust, and stars in the plane of the Milky Way (the galactic plane) obstruct the view of around 20% of the extragalactic sky at visible wavelengths. As a result, optical galaxy catalogues are usually incomplete close to the galactic plane. Many projects have attempted to bridge the gap in knowledge caused by the Zone of Avoidance. The dust and gas in the Milky Way cause extinction at optical wavelengths, and foreground stars can be confused with background galaxies. However, the effect of extinction drops at longer wavelengths, such as the infrared, and the Milky Way is effectively transparent at radio wavelengths. Surveys in the infrared, such as IRAS and 2MASS, have given a more complete picture of the extragalactic sky. Two very large nearby galaxies, Maffei 1 and Maffei 2, were discovered in the Zone of Avoidance by Paolo Maffei by their infrared emission in 1968. Even so, approximately 10% of the sky remains difficult to survey as extragalactic objects can be confused with stars in the Milky Way. Projects to survey the Zone of Avoidance at radio wavelengths, particularly using the 21 cm spin-flip emission line of neutral atomic hydrogen (known in astronomical parlance as HI), have detected many galaxies that could not be detected in the infrared. Examples of galaxies detected from their HI emission include Dwingeloo 1 and Dwingeloo 2, discovered in 1994 and 1996 respectively.
Galactic Plane is the plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms galactic plane and galactic poles usually refer specifically to the plane and poles of the Milky Way, in which Planet Earth is located. Some galaxies are irregular and do not have any well-defined disk. Even in the case of a barred spiral galaxy like the Milky Way, defining the galactic plane is slightly imprecise and arbitrary since the stars are not perfectly coplanar.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copernican_heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting around it in circular paths, modified by epicycles, and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model displaced the geocentric model of Ptolemy that had prevailed for centuries, which had placed Earth at the center of the Universe.
Geocentric Model is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under the geocentric model, the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets all orbit Earth. The geocentric model was the predominant description of the cosmos in many ancient civilizations, such as those of Aristotle in Classical Greece and Ptolemy in Roman Egypt. Two observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe: First, from anywhere on Earth, the Sun appears to revolve around Earth once per day. While the Moon and the planets have their own motions, they also appear to revolve around Earth about once per day. The stars appeared to be fixed on a celestial sphere rotating once each day about an axis through the geographic poles of Earth. Second, Earth seems to be unmoving from the perspective of an earthbound observer; it feels solid, stable, and stationary. Greek astronomer and mathematician Aristarchus of Samos (c. 310 – c. 230 BC) developed a heliocentric model placing all of the then-known planets in their correct order around the Sun. The ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century, when Johannes Kepler postulated that orbits were heliocentric and elliptical (Kepler's first law of planetary motion). In 1687 Newton showed that elliptical orbits could be derived from his laws of gravitation.
Copernican Heliocentrism model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting around it in circular paths, modified by epicycles, and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model displaced the geocentric model of Ptolemy that had prevailed for centuries, which had placed Earth at the center of the Universe.
Earth
 Earth
was formed about 4.54 billion years ago. The
third planet from
the Sun, the densest planet in the
Solar System,
the largest of the Solar System's four
terrestrial planets, and the only astronomical object known
to accommodate life. During one orbit around the Sun,
Earth rotates about its own axis 366.26 times, creating
365.26 solar days or one sidereal
year. The Earth has
5 Directions of Motion, Wobble, Spin, Orbit around the Sun,
Orbit around the
Galaxy, and
moving through space in the
same direction as
our Galaxy. Earth's Circumference: 24,901.46 miles or 40,075.017
km. Radius: 3,959 mi. Area: 196.9 million mi².
Mass: 5.972 ×
10^24 kg. Distance from Sun: 92.96 million mi.,
Earth is
Biosphere 1.
Subterranean Biosphere.
Earth
was formed about 4.54 billion years ago. The
third planet from
the Sun, the densest planet in the
Solar System,
the largest of the Solar System's four
terrestrial planets, and the only astronomical object known
to accommodate life. During one orbit around the Sun,
Earth rotates about its own axis 366.26 times, creating
365.26 solar days or one sidereal
year. The Earth has
5 Directions of Motion, Wobble, Spin, Orbit around the Sun,
Orbit around the
Galaxy, and
moving through space in the
same direction as
our Galaxy. Earth's Circumference: 24,901.46 miles or 40,075.017
km. Radius: 3,959 mi. Area: 196.9 million mi².
Mass: 5.972 ×
10^24 kg. Distance from Sun: 92.96 million mi.,
Earth is
Biosphere 1.
Subterranean Biosphere.The length of an Earth day has grown by 1.8 milliseconds per century. Age of the Earth (timeline).
Planet Sizes (youtube) - Video 2 - Google Earth - Countries by Land Size (image)
Geodesy is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's geometric shape, orientation in space and gravitational field.
Earth Science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical and chemical constitution of Earth and its atmosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields. DIY Science.
Giga Pan - Planet Earth's Northern Hemisphere (youtube)
Solar System - Eclipse - Atmosphere - Weather - Wind - Storms - Rain - Lightning - Climate - Seasons - Oceans - Earthquakes - Volcanoes - Fire - Aurora
Future of the Earth can be extrapolated based upon the estimated effects of several long-term influences. These include the chemistry at Earth's Surface, the rate of cooling of the planet's interior, the gravitational interactions with other objects in the Solar System, and a steady increase in the Sun's luminosity. An uncertain factor in this extrapolation is the ongoing influence of technology introduced by humans, such as climate engineering, which could cause significant changes to the planet. The current Holocene extinction is being caused by ignorance and the effects may last for up to five million years. In turn, ignorance may result in the extinction of humanity, leaving the planet to gradually return to a slower evolutionary pace resulting solely from long-term natural processes.
Beneath the Surface of Planet Earth
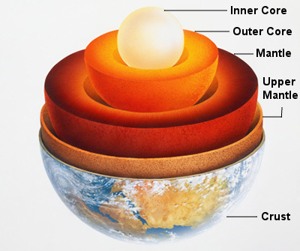 Planetary
Core consists of the innermost layer(s) of a planet; which may be
composed of solid and liquid layers. Cores of specific planets may be
entirely solid or entirely liquid. In the Solar System, core size can
range from about 20% (Moon) to 85% of a planet's radius (Mercury).
Gas
Giants also have cores, though the composition of these are still a matter
of debate and range in possible composition from traditional stony/iron,
to ice or to fluid metallic hydrogen. Gas giant cores are proportionally
much smaller than those of terrestrial planets, though theirs can be
considerably larger than the Earth's nevertheless; Jupiter has one 10–30
times heavier than Earth, and exoplanet HD149026 b has a core 67 times the
mass of the Earth.
Planetary
Core consists of the innermost layer(s) of a planet; which may be
composed of solid and liquid layers. Cores of specific planets may be
entirely solid or entirely liquid. In the Solar System, core size can
range from about 20% (Moon) to 85% of a planet's radius (Mercury).
Gas
Giants also have cores, though the composition of these are still a matter
of debate and range in possible composition from traditional stony/iron,
to ice or to fluid metallic hydrogen. Gas giant cores are proportionally
much smaller than those of terrestrial planets, though theirs can be
considerably larger than the Earth's nevertheless; Jupiter has one 10–30
times heavier than Earth, and exoplanet HD149026 b has a core 67 times the
mass of the Earth.Navigation - Latitude - Topology - Topography Map - Oceans
Earth's Inner Core is the innermost geologic layer of the Earth. It is primarily a solid ball with a radius of about 1,220 kilometres (760 miles), which is about 20% of the Earth's radius and 70% of the Moon's radius. There are no samples of the Earth's core available for direct measurement, as there are for the Earth's mantle. Information about the Earth's core mostly comes from analysis of seismic waves and the magnetic field. The inner core is believed to be composed of an iron–nickel alloy with some other elements. The temperature at the inner core's surface is estimated to be approximately 5,700 K (5,430 °C) or 9806 °F, which is about the temperature at the surface of the Sun. Magnetic Core.
Inner Core Super-Rotation is a theorized eastward rotation of the inner core of Earth relative to its mantle, for a net rotation rate that is faster than Earth as a whole. A 1995 model of Earth's dynamo predicted super-rotations of up to 3 degrees per year; the following year, this prediction was supported by observed discrepancies in the time that p-waves take to travel through the inner and outer core. Seismic observations have made use of a direction dependence (anisotropy) of the speed of seismic waves in the inner core, as well as spatial variations in the speed. Other estimates come from free oscillations of Earth. The results are inconsistent and the existence of a super-rotation is still controversial, but it is probably less than 0.1 degrees per year. When geodynamo models take into account gravitational coupling between the inner core and mantle, it lowers the predicted super-rotation to as little as 1 degree per million years. For the inner core to rotate despite gravitational coupling, it must be able to change shape, which places constraints on its viscosity. Earths inner core rotates in the same direction as the Earth and slightly faster, completing its once-a-day rotation about two-thirds of a second faster than the entire Earth. The Spin of Earth’s Inner Core May Be Changing, Scientists Say.
Magnetic Pole Reversal
How solid rock flows 3,000 kilometers beneath us. Groundbreaking experiments by ETH Zurich have finally revealed that solid rock flows at extreme depths, acting like liquid in motion. This horizontal mantle flow aligns mineral crystals called post-perovskite in a single direction, explaining the seismic behavior.
How Microwaving Grapes Makes Plasma (youtube) - The Sun is the brightest source of radio waves in the sky. The depth to which the radio waves and microwaves can penetrate depends on their exact wavelength.
New evidence for how heat is transported below the sun's surface. Using sound waves, scientists develop findings that challenge standard theories of solar convection. Solar physicists have revealed the interior structure of the sun's supergranules, a flow structure that transports heat from the sun's hidden interior to its surface. The researchers' analysis of the supergranules presents a challenge to the current understanding of solar convection.
Nickel is Crucial for the Earth’s Magnetic Field. Earth's hot core, consisting mainly of iron, is responsible for the 'dynamo effect,' which creates a magnetic field. But with iron alone, this effect cannot be explained. A team of researchers has shown that the theory of the geodynamo has to be revised. It is crucial for the dynamo effect that the earth's core contains up to 20 percent nickel -- a metal, which under extreme conditions behaves quite differently from iron.
 Structure of the Earth
is layered in spherical shells, like an onion. These
layers can be defined
by their chemical and their rheological properties. Earth has an outer
silicate solid crust, a highly viscous
mantle, a liquid outer core that is
much less viscous than the mantle, and a solid inner core. Scientific
understanding of the internal structure of the Earth is based on
observations of topography and bathymetry, observations of rock in
outcrop, samples brought to the surface from greater depths by
volcanoes
or volcanic activity, analysis of the seismic waves that pass through the
Earth, measurements of the gravitational and magnetic fields of the Earth,
and experiments with crystalline solids at pressures and temperatures
characteristic of the Earth's deep interior.
Structure of the Earth
is layered in spherical shells, like an onion. These
layers can be defined
by their chemical and their rheological properties. Earth has an outer
silicate solid crust, a highly viscous
mantle, a liquid outer core that is
much less viscous than the mantle, and a solid inner core. Scientific
understanding of the internal structure of the Earth is based on
observations of topography and bathymetry, observations of rock in
outcrop, samples brought to the surface from greater depths by
volcanoes
or volcanic activity, analysis of the seismic waves that pass through the
Earth, measurements of the gravitational and magnetic fields of the Earth,
and experiments with crystalline solids at pressures and temperatures
characteristic of the Earth's deep interior.There may be a layer of surprisingly fluid rock ringing the Earth at the very bottom of the upper mantle, a new study suggests. Study uses 350-mile-deep earthquake to make elusive measurements of the Earth's layers. The finding was made by measuring the lingering movement registered by GPS sensors on islands in the wake of a deep earthquake in the Pacific Ocean near Fiji. Published Feb. 22 in Nature, the study demonstrates a new method to measure the fluidity of the Earth's mantle.
Deepest Underground Structures. Comparisons represented on a real scale. Mines, caves, cities, tunnels and installations. (youtube)
Solid Earth refers to "the Earth beneath our feet" or terra firma, the planet's solid surface and its interior.
Geography (environment) - Botany - Trees (plants)
Topography World Map (image) - World Map (image) - Satellites
Land Use - Agriculture - Countries - States - Cities
Elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface. Elevation, or geometric height, is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while altitude or geopotential height is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and depth is used for points below the surface.
Seismic Tomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth with seismic waves produced by earthquakes or explosions. P-, S-, and surface waves can be used for tomographic models of different resolutions based on seismic wavelength, wave source distance, and the seismograph array coverage. The data received at seismometers are used to solve an inverse problem, wherein the locations of reflection and refraction of the wave paths are determined. This solution can be used to create 3D images of velocity anomalies which may be interpreted as structural, thermal, or compositional variations. Geoscientists use these images to better understand core, mantle, and plate tectonic processes. Earths inner core layers are not perfect as the diagrams show.
Navigation
Sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument used to measure the angle between any two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to determine the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celestial navigation. The determination of this angle, the altitude, is known as sighting (or shooting) the object, or taking a sight. The Angle, and the time when it was measured, can be used to calculate a position line on a nautical or aeronautical chart. Common uses of the sextant include sighting the sun at solar noon or Polaris at night (in the Northern Hemisphere) to determine latitude. Sighting the height of a landmark can give a measure of distance off and, held horizontally, a sextant can measure angles between objects for a position on a chart. A sextant can also be used to measure the lunar distance between the moon and another celestial object (such as a star or planet) in order to determine Greenwich Mean Time and hence longitude.
Navigation Knowledge (orienteering - finding your way around) - Mapping Tools
Triangulation - Seeing the Same Stars every night
Orientation is a function of the mind involving awareness of three dimensions: time, place and person.
Coordinate is a number that identifies a position relative to an axis.
Celestial Coordinate System is a system for specifying positions of celestial objects: satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and so on. Coordinate systems can specify a position in 3-dimensional space, or merely the direction of the object on the celestial sphere, if its distance is not known or not important.
Geographic Coordinate System is a coordinate system used in geography that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position, and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a two-dimensional map requires a map projection. GPS.
Geographical Pole is either of the two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface. The North Pole lies in the Arctic Ocean while the South Pole is in Antarctica. North and South poles are also defined for other planets or satellites in the Solar System, with a North pole being on the same side of the invariable plane as Earth's North pole. Relative to Earth's surface, the geographic poles move by a few metres over periods of a few years. This is a combination of Chandler wobble, a free oscillation with a period of about 435 days; an annual motion responding to seasonal movements of air and water masses; and an irregular drift towards the 80th west meridian. As cartography requires exact and unchanging coordinates, the averaged locations of geographical poles are taken as fixed cartographic poles and become the points where the body's great circles of longitude intersect. Magnetic Poles.
Topography is the study of the shape and features of the surface of the Earth and other observable astronomical objects including planets, moons, and asteroids. The topography of an area could refer to the surface shapes and features themselves, or a description (especially their depiction in Maps).
Transit Map is a topological map in the form of a schematic diagram used to illustrate the routes and stations within a public transport system—whether this be bus lines, tramways, rapid transit, commuter rail or ferry routes. The main components are color coded lines to indicate each line or service, with named icons to indicate stations or stops.
Cartesian Coordinate System (dimensions)
World Geodetic System is a standard for use in cartography, geodesy, and navigation including GPS or Global Positioning System. It comprises a standard coordinate system for the Earth, a standard spheroidal reference surface (the datum or reference ellipsoid) for raw altitude data, and a gravitational equipotential surface (the geoid) that defines the nominal sea level.
 Latitude are lines of constant latitude, or
parallels,
run
east–west as circles parallel to the
Equator. Specifies the
north–south position of a point on the Earth's surface, which
ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the
poles. Horizontal is
parallel
to or in the plane of the horizon or a base line.
Dimensions.
Latitude are lines of constant latitude, or
parallels,
run
east–west as circles parallel to the
Equator. Specifies the
north–south position of a point on the Earth's surface, which
ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the
poles. Horizontal is
parallel
to or in the plane of the horizon or a base line.
Dimensions.Longitude are meridians (lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. Vertical is straight up and down at right angles (90°) to the plane of the horizon or a base line. (My Home in Danbury, Ct. is 41.3948° North Latitude, 73.4540° West Longitude, Elevation 472).
Searching by Latitude & Longitude.
Decimal degrees or DD: 41.40338, 2.17403
Degrees, minutes, and seconds or DMS: 41°24'12.2"N 2°10'26.5"E. (37°25'19.07"N, 122°05'06.24"W).
Degrees and decimal minutes or DMM: 41 24.2028, 2 10.4418.
Correct: 41.40338, 2.17403
Incorrect: 41,40338, 2,17403.
Date Line is an imaginary line on the surface of the earth following (approximately) the 180th meridian.
Meridian is an imaginary great circle on the surface of the earth passing through the north and south poles at right angles to the equator.
Grid System helps with spacing and page layout and to align screen elements based on columns and rows. Grid is a pattern of regularly spaced horizontal and vertical lines.
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to: Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. Eliminate characteristics of the mapped object that are not relevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of generalization. Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. Orchestrate the elements of the map to best convey its message to its audience. This is the concern of map design. Modern cartography constitutes many theoretical and practical foundations of geographic information systems.
Mercator Projection is a cylindrical standard map projection for nautical purposes because of its ability to represent lines of constant course, known as rhumb lines or loxodromes, as straight segments that conserve the angles with the meridians. Although the linear scale is equal in all directions around any point, thus preserving the angles and the shapes of small objects (which makes the projection conformal), the Mercator projection distorts the size of objects as the latitude increases from the Equator to the poles, where the scale becomes infinite. So, for example, landmasses such as Greenland and Antarctica appear much larger than they actually are relative to land masses near the equator, such as Central Africa.
Map Projection is a systematic transformation of the latitudes and longitudes of locations on the surface of a sphere or an ellipsoid into locations on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections.
Geodetic Datum is a coordinate system, and a set of reference points, used to locate places on the Earth (or similar objects). An approximate definition of sea level is the datum WGS 84, an ellipsoid, whereas a more accurate definition is Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008), using at least 2,159 spherical harmonics.
Spherical Harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations that commonly occur in science. The spherical harmonics are a complete set of orthogonal functions on the sphere, and thus may be used to represent functions defined on the surface of a sphere, just as circular functions (sines and cosines) are used to represent functions on a circle via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by spatial angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a central role in the group theoretic discussion of SO(3).
Large low-shear-velocity provinces or Superplumes are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle (the region surrounding the outer core) of Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave velocities and were discovered by seismic tomography of deep Earth. There are two main provinces: the African LLSVP and the Pacific LLSVP. Both extend laterally for thousands of kilometers and possibly up to 1,000 km vertically from the core–mantle boundary. The Pacific LLSVP has specific dimensions of 3,000 km across and 300 metres higher than the surrounding ocean floor, and is situated over four hotspots that suggest multiple mantle plumes underneath. These zones represent around 8% of the volume of the mantle (6% of Earth). Other names for LLSVPs include superwells, thermo-chemical piles, or hidden reservoirs. Some of these names, however, are more interpretive of their geodynamical or geochemical effects, while many questions remain about their nature.
Tectonic Plates (earthquakes) - Volcanoes (ring of fire)
As the continents mash against each other, their collision gradually slows, but mountain growth has apparently stayed relatively constant from the past to the present. People thought because the Earth is cooling that plate movements would slow down. Continental drift is caused by heat deep in the planet, driving the convection of material in the Earth's Mantle. The eight major and numerous minor tectonic plates on the planet's surface are moved by these convection currents.
Satellites help discover a Jet Stream in the Earth’s Core.
Orogeny refers to forces and events leading to a large structural deformation of the Earth's lithosphere (crust and uppermost mantle) due to the interaction between tectonic plates.
Lithosphere "rocky",or "sphere" is the rigid, outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet or natural satellite that is defined by its rigid mechanical properties.
Soil - Rocks - Geography - Oceans
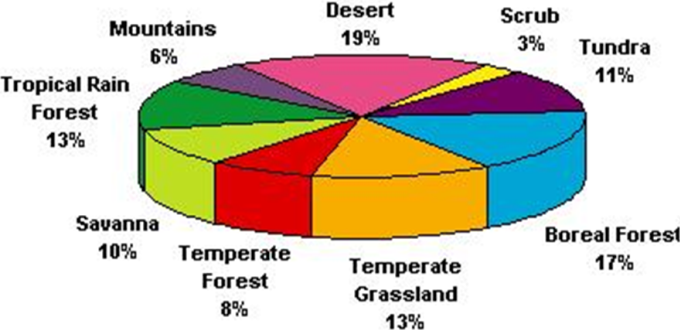 Pedosphere is the
outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of
soil and subject to soil formation
processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, atmosphere,
hydrosphere and
biosphere. The sum total of all
the organisms, soils,
water and air is termed as the "pedosphere". The pedosphere is the skin of
the Earth and only develops when there is a dynamic interaction between
the atmosphere (air in and above the soil),
biosphere (living organisms), lithosphere (unconsolidated regolith and
consolidated bedrock) and
the hydrosphere (water in, on and below the soil). The pedosphere is the
foundation of terrestrial life on this planet. There is a realization that
the pedosphere needs to be distinctly recognized as a dynamic interface of
all terrestrial ecosystems and be integrated into the Earth system science knowledge base.
Pedosphere is the
outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of
soil and subject to soil formation
processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, atmosphere,
hydrosphere and
biosphere. The sum total of all
the organisms, soils,
water and air is termed as the "pedosphere". The pedosphere is the skin of
the Earth and only develops when there is a dynamic interaction between
the atmosphere (air in and above the soil),
biosphere (living organisms), lithosphere (unconsolidated regolith and
consolidated bedrock) and
the hydrosphere (water in, on and below the soil). The pedosphere is the
foundation of terrestrial life on this planet. There is a realization that
the pedosphere needs to be distinctly recognized as a dynamic interface of
all terrestrial ecosystems and be integrated into the Earth system science knowledge base.
Continent is one of several very large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven regions are commonly regarded as continents geopolitically. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example some systems include Eurasia or America as single continents.
Countries - States - Cities
Eurasia is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Located primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two different continents is a historical social construct, with no clear physical separation between them; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or even four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around 55,000,000 square kilometres (21,000,000 sq mi), or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. The landmass contains well over 5 billion people, equating to approximately 70% of the human population. Humans first settled in Eurasia between 60,000 and 125,000 years ago. Some major islands, including Great Britain, Iceland, and Ireland, and those of Japan, the Philippines and Indonesia, are often included under the popular definition of Eurasia, in spite of being separate from the contiguous landmass.
Middle East is a transcontinental region which includes Western Asia (although generally excluding the Caucasus) and all of Egypt (which is mostly in North Africa). The term has come into wider usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The broader concept of the "Greater Middle East" (or Middle East and North Africa) also adds the Maghreb, Sudan, Djibouti, Somalia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and sometimes even Central Asia and Transcaucasia into the region. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The history of the Middle East dates back to ancient times, with the geopolitical importance of the region being recognized for millennia. Several major religions have their origins in the Middle East, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Arabs constitute the majority ethnic group in the region, followed by Turks, Persians, Kurds, Azeris, Copts, Jews, Assyrians, Iraqi Turkmen, and Greek Cypriots. The Middle East generally has a hot, arid climate, with several major rivers providing irrigation to support agriculture in limited areas such as the Nile Delta in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates watersheds of Mesopotamia (Iraq, Kuwait, and eastern Syria), and most of what is known as the Fertile Crescent. The most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Iran, and Turkey, while Saudi Arabia is the largest Middle Eastern country by area. Most of the countries that border the Persian Gulf have vast reserves of crude oil, with monarchs of the Arabian Peninsula in particular benefiting economically from petroleum exports.
Oceania is a geographic region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia. Spanning the eastern and western hemispheres, Oceania has a land area of 8,525,989 square kilometres and a population of over 47 million.
Asia is Earth's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the Eastern and Northern Hemispheres. It shares the continental landmass of Eurasia with the continent of Europe and the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. Southeast Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the regions that are geographically south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent and north-west of Australia.
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It comprises the westernmost part of Eurasia and is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. However, Europe is generally accorded the status of a full continent because of its great physical size and the weight of history and tradition. Eastern Europe is the eastern part of the European continent.
Russia is a transcontinental country located in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. Covering an area of 17,125,200 square kilometres (6,612,100 sq mi), it is the largest country in the world by area, spanning more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area, stretching eleven time zones, and bordering 16 sovereign nations. The territory of Russia extends from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Black Sea and the Caucasus in the south. With 146.7 million inhabitants living in the country's 85 federal subjects, Russia is the most populous nation in Europe and the ninth-most populous nation in the world. Russia's capital and largest city is Moscow; other major urban areas include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Kazan and Chelyabinsk.
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area. With 1.3 billion people as of 2018, it accounts for about 16% of the world's human population.
North America is a continent entirely within the Northern Hemisphere and almost all within the Western Hemisphere. In can also be described as a northern subcontinent of the Americas, or America, in models that use fewer than seven continents. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean, and to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea.
South America is a continent in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It may also be considered a subcontinent of the Americas, which is how it is viewed in most of Europe and the Spanish and Portuguese-speaking regions of the Americas. The reference to South America instead of other regions (like Latin America or the Southern Cone) has increased in the last decades due to changing geopolitical dynamics (in particular, the rise of Brazil).
Antarctica is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic South Pole and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle, and is surrounded by the Southern Ocean. At 14,200,000 square kilometres (5,500,000 square miles), it is the fifth-largest continent and nearly twice the size of Australia. At 0.00008 people per square kilometre, it is by far the least densely populated continent. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice that averages 1.9 km (1.2 mi; 6,200 ft) in thickness, which extends to all but the northernmost reaches of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Interesting information about the Earth
Did you know that if the earth were the size of a Billiard Ball, it would be as smooth as a billiard ball. High and Low Areas of Earth Chart (image). If the Sun was the same size as a Basketball.
If you took all the water on earth and put it into a ball, the ball would be half the size of the Moon, around 860 miles in diameter. About 71 percent of the Earth's surface is water-covered, and the oceans hold about 96.5 percent of all Earth's water. Water also exists in the air as water vapor, in rivers and lakes, in icecaps and glaciers, in the ground as soil moisture and in aquifers, and even in you and your dog.
A Day on Earth is actually 23 Hours and 56 Minutes and 4.1 Seconds long. (spinning on its axis 1,000 mph at the equator).
Sidereal Time is a time-keeping system that astronomers use to locate celestial objects. Using sidereal time it is possible to easily point a telescope to the proper coordinates in the night sky. Briefly, sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars" rather than the Sun.
23.5 Degrees North Latitude (Axial Tilt)
Leap Second is a one-second adjustment that is occasionally applied to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) in order to keep its time of day close to the mean solar time, or UT1. Without such a correction, time reckoned by Earth's rotation drifts away from atomic time because of irregularities in the Earth's rate of rotation. Since this system of correction was implemented in 1972, 27 leap seconds have been inserted, the most recent on December 31, 2016 at 23:59:60 UTC.
On Mercury, a day is two years long. Time Management.
The Earth is slowing at a rate of 4.7×10−4 miles per second every 100 years due to tidal forces of the moon. Earth's Rotation (wiki)
The Moon is currently moving away from the Earth at about 3.8 centimeters per year.
Earths Inner Core is about the same temperature as the surface of the Sun, approximately 5700 K (5430 °C).
Navigation (how to find your way around planet earth) - Geography
The earth is not perfectly Round. Ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scaling's.
Geodesy is the measurement and representation of the Earth (or any planet), including its gravitational field, in a three-dimensional time-varying space. Geodesists also study geodynamical phenomena such as crustal motion, tides, and polar motion. For this they design global and national control networks, using space and terrestrial techniques while relying on datums and coordinate systems.
Historia Da Terra (Earth Story with Aubrey Manning, History of our Planet) - Earth Story: Video 1.The age of the Earth (1 of 6 ) (youtube)
Seasons - Solstice - Equinox
 Solstice
is an astronomical event that occurs twice each year, once in June and
once in December as the Sun reaches its highest or lowest excursion relative to
the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. The seasons of the year are
directly connected to both the solstices and the equinoxes. After the
winter solstice the sun shines a little longer each day about 2 minutes
and 7 seconds. Orbit - Precession.
Solstice
is an astronomical event that occurs twice each year, once in June and
once in December as the Sun reaches its highest or lowest excursion relative to
the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. The seasons of the year are
directly connected to both the solstices and the equinoxes. After the
winter solstice the sun shines a little longer each day about 2 minutes
and 7 seconds. Orbit - Precession.Equinox occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September. It is the moment at which the center of the visible Sun is directly above the equator. In the Northern Hemisphere, the March equinox is called the vernal or spring equinox while the September equinox is called the autumnal or fall equinox. In the Southern Hemisphere, the reverse is true. The vernal equinox falls on March 19 nationwide this year in 2020. It's the earliest start to spring since 1896. Every fourth year, we add a leap day to the calendar on February 29, which gets us almost back in sync with the Earth's orbit. The leap day turns back the clock on the time of the equinox, nearly resetting the approximately 6-hour annual leap forward from the previous three years. leap day we observe every four years would fix things if the length of a year were exactly 365.25 days. But remember, the actual length is closer to 365.24 days. So the leap day intended to get us back in sync with the Earth's solar orbit doesn't quite do it. And that discrepancy shows up in the time of the equinox, which gets about 45 minutes earlier every leap year. Next year, the spring equinox will return to March 20 in much of the country (remember, it moves 6 hours later each year). But spring will begin on March 19 every leap year for the rest of this century, and the time of the spring equinox in non-leap years will move earlier and earlier. By the end of the century, the spring equinox will fall on March 19 most years. Eventually, in 2100, we'll skip a leap year as we did in 1900 and the time of the equinox will move later again.
Earth Rotation & Revolution around a moving Sun (youtube)
Tropic of Cancer, also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is currently 23°26′13.2″ (or 23.437°) north of the Equator. It is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun to its maximum extent.
Tropic of Capricorn is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point on the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be directly overhead. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of Cancer. The Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth. As of 6 August 2017, its latitude is 23°26′13.2″ (or 23.437°) south of the Equator, but it is very gradually moving northward, currently at the rate of 0.47 arcseconds, or 15 metres, per year. Arcsecond is a unit of angular measurement equal to 1/60 of one degree. The angular measure of an object is usually expressed in degrees, arcminutes or arcseconds. Just as an hour is divided into 60 minutes and a minute into 60 seconds, a degree is divided into 60 arcminutes and an arcminute is divided into 60 arcseconds.
Tropics are a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. They are delimited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at 23°26′13.0″ (or 23.43696°) N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at 23°26′13.0″ (or 23.43696°) S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). The tropics include all the areas on the Earth where the Sun contacts the zenith, a point directly overhead, at least once during the solar year (which is a subsolar point). The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics comprise 40% of the Earth's surface area and contain 36% of the Earth's landmass. As of 2014, the region is home to 40% of the world population, and this figure is projected to reach 50% by the late 2030s.
Each zone is 10 degrees F warmer (or colder) than an adjacent zone during an average winter.
Earth's Motion around the Sun, not as simple as I thought (youtube)
Weather - Climate - Air - Wind - Clouds - Rain - Storms - Lightening - Fires - Volcanoes - Earthquakes
Season is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology and hours of daylight. Seasons result from the yearly orbit of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's rotational axis relative to the plane of the orbit. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to go into hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. During May, June, and July, the northern hemisphere is exposed to more direct sunlight because the hemisphere faces the sun. The same is true of the southern hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is the tilt of the Earth that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months which increases the solar flux. However, due to seasonal lag, June, July, and August are the hottest months in the northern hemisphere and December, January, and February are the hottest months in the southern hemisphere.
Seasonality consists of periodic, repetitive, and generally regular and predictable patterns in the levels of a time series. Seasonality can repeat on a weekly, monthly or quarterly basis, these periods of time are structured and occur in a length of time less than a year. Cycle.
Earth's Climate History. Scientists have compiled a continuous, high-fidelity record of variations in Earth's climate extending 66 million years into the past. The record reveals four distinctive climate states, which the researchers dubbed Hothouse, Warmhouse, Coolhouse, and Icehouse. These major climate states persisted for millions and sometimes tens of millions of years, and within each one the climate shows rhythmic variations corresponding to changes in Earth's orbit around the sun.
Atmosphere
Atmosphere is a thin layer of gases surrounding a planet or other material body, that is held in place by earths magnetic field and gravity. An atmosphere is more likely to be retained if its gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low.
Biosphere - Ecosphere - Earth's Spheres - Overview Effect - Our Living Planet From Space (youtube) - NASA
Exosphere: 700 to 10,000 km (440 to 6,200 miles).
Thermosphere: 80 to 700 km (50 to 440 miles). (2,500 °C or 4,530 °F).
Mesosphere: 50 to 80 km (31 to 50 miles). (−143 °C or −225 °F; 130 K).
Stratosphere: 12 to 50 km (7 to 31 miles). UV - Ozone
Troposphere: 0 to 12 km (0 to 7 miles).
Weather - Wind - Lightning - Magnetosphere - Oceans - Pressure
Hydrosphere is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, or minor planet or natural satellite.
Plasmasphere or inner magnetosphere, is a region of the Earth's magnetosphere consisting of low energy or cool plasma. It is located above the ionosphere. The outer boundary of the plasmasphere is known as the plasmapause, which is defined by an order of magnitude drop in plasma density.
States of Matter - Heliosphere - Earths Magnetic Field - Ether - Space
Ionosphere is the ionized part of Earth's upper atmosphere, from about 60 km (37 mi) to 1,000 km (620 mi) altitude, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on the Earth. The region below the ionosphere is called neutral atmosphere, or neutrosphere.
 Troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere, and is also
where all weather takes place. It contains approximately 75% of the
atmosphere's mass and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols.
The average depths of the troposphere are 20 km (12 mi) in the tropics, 17
km (11 mi) in the mid latitudes, and 7 km (4.3 mi) in the polar regions in
winter. The lowest part of the troposphere, where friction with the
Earth's surface influences air flow, is the planetary boundary layer. This
layer is typically a few hundred meters to 2 km (1.2 mi) deep depending on
the landform and time of day. Atop the troposphere is the tropopause,
which is the border between the troposphere and stratosphere. The
tropopause is an inversion layer, where the air temperature ceases to
decrease with height and remains constant through its thickness.
Pressure.
Troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere, and is also
where all weather takes place. It contains approximately 75% of the
atmosphere's mass and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols.
The average depths of the troposphere are 20 km (12 mi) in the tropics, 17
km (11 mi) in the mid latitudes, and 7 km (4.3 mi) in the polar regions in
winter. The lowest part of the troposphere, where friction with the
Earth's surface influences air flow, is the planetary boundary layer. This
layer is typically a few hundred meters to 2 km (1.2 mi) deep depending on
the landform and time of day. Atop the troposphere is the tropopause,
which is the border between the troposphere and stratosphere. The
tropopause is an inversion layer, where the air temperature ceases to
decrease with height and remains constant through its thickness.
Pressure.Tropospheric Ozone is a constituent of the troposphere (it is also an important constituent of some regions of the stratosphere commonly known as the ozone layer). The troposphere extends from the Earth's surface to between 12 and 20 kilometers above sea level and consists of many layers. Ozone is more concentrated above the mixing layer, or ground layer. Ground-level ozone, though less concentrated than ozone aloft, is more of a problem because of its health effects.
Atmospheric Chemistry is a branch of atmospheric science in which the chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere and that of other planets is studied. It is a multidisciplinary approach of research and draws on environmental chemistry, physics, meteorology, computer modeling, oceanography, geology and volcanology and other disciplines. Research is increasingly connected with other arenas of study such as climatology.
We live at the bottom of an ocean of air. Atmospheric Pressure.
Atmospheric Physics is the application of physics to the study of the atmosphere. Atmospheric physicists attempt to model Earth's atmosphere and the atmospheres of the other planets using fluid flow equations, chemical models, radiation budget, and energy transfer processes in the atmosphere (as well as how these tie into other systems such as the oceans).
Atmospheric and Space Scientists investigate atmospheric phenomena and interpret meteorological data, gathered by surface and air stations, satellites, and radar to prepare reports and forecasts for public and other uses.
Atmospheric Escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases or air to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape, operating at different time scales; the most prominent is Jeans Escape, named after British astronomer Sir James Jeans, who described the process of atmospheric loss to the molecular kinetic energy. Hydrogen and Helium are very light gases, so light that Earth's gravity is too weak to hold them. Most of the hydrogen and helium of the early atmosphere escaped into space.
Root-Mean-Square Speed is the measure of the speed of particles in a gas which is most convenient for problem solving within the kinetic theory of gases. It is defined as the square root of the average velocity-squared of the molecules in a gas. Atmosphere of Earth at sea level, by contrast, is packed with about 100 billion billion molecules per cubic centimetre. Wind.
Scientists discover a way Earth's atmosphere cleans itself. Chemist helped shed light on the formation of an air-clearing molecule. Human activities emit many kinds of pollutants into the air, and without a molecule called hydroxide or OH, many of these pollutants would keep aggregating in the atmosphere. OH is a key player in the story of atmospheric chemistry. It initiates the reactions that break down airborne pollutants and helps to remove noxious chemicals such as sulfur dioxide and nitric oxide, which are poisonous gases, from the atmosphere.
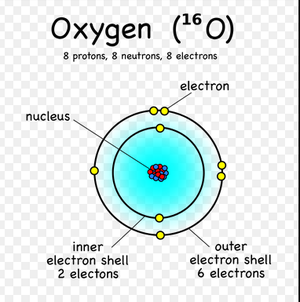 Oxygen is a highly
reactive nonmetal and oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most
elements as well as other compounds. By mass,
oxygen is the third-most
abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.
Oxygen forms a molecule O2 of two
atoms. At standard
temperature and pressure, two atoms of the
element bind to form
dioxygen,
a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula
O2. This is an important part of the
atmosphere and
diatomic oxygen gas constitutes 20.8% of the Earth's
atmosphere. Additionally, as oxides the element makes up almost half of
the Earth's crust. In one atom of oxygen
is 8 protons. In one molecule of oxygen gas, which is O2, 2 times 8 = 16
protons. Molecule of O2 is 0.0005
microns. Oxygen is capable of having 2
Bonds. Carbon 12 Atom.
Oxygen is a highly
reactive nonmetal and oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most
elements as well as other compounds. By mass,
oxygen is the third-most
abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.
Oxygen forms a molecule O2 of two
atoms. At standard
temperature and pressure, two atoms of the
element bind to form
dioxygen,
a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula
O2. This is an important part of the
atmosphere and
diatomic oxygen gas constitutes 20.8% of the Earth's
atmosphere. Additionally, as oxides the element makes up almost half of
the Earth's crust. In one atom of oxygen
is 8 protons. In one molecule of oxygen gas, which is O2, 2 times 8 = 16
protons. Molecule of O2 is 0.0005
microns. Oxygen is capable of having 2
Bonds. Carbon 12 Atom.Air - Every Breath you Take - Geological History of Oxygen (wiki) - Antioxidants - Exercise - Breathing - States of Matter
Dark Oxygen. Metallic nodules on the seafloor produce their own oxygen.
Oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. Oxidation.
The ground state of dioxygen is known as triplet oxygen because it has two unpaired electrons. The first excited state, singlet oxygen, has no unpaired electrons and is metastable, which means it is continuing in its present state of equilibrium unless sufficiently disturbed to pass to a more stable state of equilibrium.
Triplet Oxygen the electron configuration of the oxygen molecule has two electrons occupying two molecular orbitals (MOs) of equal energy (that is, degenerate MOs), therefore remaining unpaired. These orbitals are classified as antibonding and are of higher energy, so the resulting bonding structure between the oxygen atoms is weakened (i.e., is higher in energy)—for instance, it is higher in energy than the bonding in dinitrogen, where the corresponding antibonding orbitals are empty.
Singlet Oxygen is a high-energy form of oxygen. A gas with the formula O2, its physical properties differ only subtly from those of the more prevalent triplet ground state of O2. In terms of its chemical reactivity, however, singlet oxygen is far more reactive toward organic compounds.
Featherweight Oxygen discovery opens window on nuclear symmetry. Oxygen-11 can be produced only in a laboratory. It decays immediately after its creation by emitting two protons, and it can be observed solely through detection of its decay products. Two-proton decay is the most recently discovered nuclear decay channel. Oxygen-11 is the nuclear mirror of lithium-11. Isotopes of Oxygen (wiki).
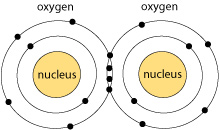 Great Oxygenation Event is when oceanic
cyanobacteria are believed to have become the first
microbes to produce oxygen by
photosynthesis.
Before the GOE, any free oxygen they produced was
chemically captured by dissolved iron or organic matter. The GOE was
the point in time when these oxygen sinks became saturated, at which point
oxygen, produced by the cyanobacteria, was free to escape into the
atmosphere. Oxygen is the byproduct of life intervening in our planet’s
geochemical cycles: harvesting
solar energy to split water molecules,
keeping the hydrogen atoms and reacting them with
CO2 to make
organic food and body parts, but spitting the oxygen back out. In Earth’s
upper atmosphere some of this oxygen, under the influence of
ultraviolet light, is transformed into ozone, O3, which shields
Earth’s surface from deadly ultraviolet, making the land surface
habitable. When it appeared, this shield allowed life to leave the
ocean
and the continents to become green with forests. O2 rendered the once
deadly continents habitable for life.
Great Oxygenation Event is when oceanic
cyanobacteria are believed to have become the first
microbes to produce oxygen by
photosynthesis.
Before the GOE, any free oxygen they produced was
chemically captured by dissolved iron or organic matter. The GOE was
the point in time when these oxygen sinks became saturated, at which point
oxygen, produced by the cyanobacteria, was free to escape into the
atmosphere. Oxygen is the byproduct of life intervening in our planet’s
geochemical cycles: harvesting
solar energy to split water molecules,
keeping the hydrogen atoms and reacting them with
CO2 to make
organic food and body parts, but spitting the oxygen back out. In Earth’s
upper atmosphere some of this oxygen, under the influence of
ultraviolet light, is transformed into ozone, O3, which shields
Earth’s surface from deadly ultraviolet, making the land surface
habitable. When it appeared, this shield allowed life to leave the
ocean
and the continents to become green with forests. O2 rendered the once
deadly continents habitable for life.Oxygen Depletion - Global Warming
Dissolved Oxygen - Joseph Priestley (wiki)
 There is more oxygen in forests and in
green areas than there is in deserts and in cities. Air would
also be cleaner and more humidified in forests and in other
green areas like near waterfalls. Cities have less oxygen
because there are
less trees
and more pollution. There is also more oxygen at lower altitudes
and less oxygen at higher altitudes. The arctic and Antarctic
regions have the highest oxygen ratios. Oxygen saturation is
inversely proportional to the temperature of the water and
phytoplankton life is abundant in cold waters. The amount of
oxygen produced by
single cell organisms is way more than that produced by
multicellular
plants.
There is more oxygen in forests and in
green areas than there is in deserts and in cities. Air would
also be cleaner and more humidified in forests and in other
green areas like near waterfalls. Cities have less oxygen
because there are
less trees
and more pollution. There is also more oxygen at lower altitudes
and less oxygen at higher altitudes. The arctic and Antarctic
regions have the highest oxygen ratios. Oxygen saturation is
inversely proportional to the temperature of the water and
phytoplankton life is abundant in cold waters. The amount of
oxygen produced by
single cell organisms is way more than that produced by
multicellular
plants. Global Oxygen Levels are Dropping - CO2 Increasing
Carbon Dioxide in Earth's Atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere currently constituting about 0.04% of CO2.
Keeling Curve is a graph which plots the ongoing change in concentration of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere since 1958.
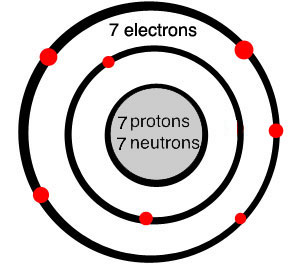 Percent Oxygen in Air (youtube)
- Atoms
Percent Oxygen in Air (youtube)
- AtomsBreathing - Air - Wind
Climate Change - Seasons
Nitrogen is a chemical element with symbol N and Atomic Number 7. The lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. The name comes from the Greek πνίγειν "to choke", directly referencing nitrogen's asphyxiating properties. Fertilizer.
Cosmic Cinema: astronomers make real-time, 3D movies of plasma tubes drifting overhead (youtube)
Weather - Climate
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the lowest level of the atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.
Seasons - Emergencies - Pressure
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences which includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics, with a major focus on weather forecasting, which is made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere at a given place and using meteorology to predict how the atmosphere will change.
World Meteorological Organization - National Weather Service
Global Historical Climatology Network includes daily observations from automated and human-facilitated weather stations across the United States and around the world. The GHCN-Daily dataset includes observations from World Meteorological Organization, Cooperative, and CoCoRaHS networks. If observed, each station dataset includes daily max and minimum temperatures, total precipitation, snowfall, and depth of snow on ground.
Climate is the long-term average of weather, typically averaged over a period of 30 years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, which includes the ocean and ice on Earth. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, and altitude, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents. More generally, the "climate" of a region is the general state of the climate system at that location at the current time. Climates can be classified according to the average and the typical ranges of different variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature and precipitation information and is used in studying biological diversity and how climate change affects it. The Bergeron and Spatial Synoptic Classification systems focus on the origin of air masses that define the climate of a region. Paleoclimatology is the study of ancient climates. Since very few direct observations of climate are available before the 19th century, paleoclimates are inferred from proxy variables that include non-biotic evidence such as sediments found in lake beds and ice cores, and biotic evidence such as tree rings and coral. Climate models are mathematical models of past, present and future climates. Climate change may occur over long and short timescales from a variety of factors; recent warming is discussed in global warming. Global warming results in redistributions. For example, "a 3°C change in mean annual temperature corresponds to a shift in isotherms of approximately 300–400 km in latitude (in the temperate zone) or 500 m in elevation. Therefore, species are expected to move upwards in elevation or towards the poles in latitude in response to shifting climate zones". Climate differs from weather, in that weather only describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a given region. A region's climate is generated by the climate system, which has five components: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere.
Climatology is the scientific study of climate, scientifically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of time.
Temperate Climate is when the temperatures in certain regions are generally relatively moderate, rather than extremely hot or cold, and the changes between summer and winter are also usually moderate. Seasons.
Highest Temperature Recorded on Earth. According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the highest registered air temperature on Earth was 56.7 °C (134.1 °F) in Furnace Creek Ranch, California, located in the Death Valley desert in the United States, on July 10, 1913. The lowest natural temperature ever directly recorded at ground level on Earth is -89.2 °C (-128.6 °F; 184.0 K) at the Soviet Vostok Station in Antarctica on July 21, 1983 by ground measurements.
Microclimate is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. Microclimates can exist near bodies of water which may cool the local atmosphere, or in heavy urban areas where brick, concrete, and asphalt absorb the sun's energy, heat up, and re-radiate that heat to the ambient air: the resulting urban heat island is a kind of microclimate. Another contributing factor of microclimate is the slope or aspect of an area. South-facing slopes in the Northern Hemisphere and north-facing slopes in the Southern Hemisphere are exposed to more direct sunlight than opposite slopes and are therefore warmer for longer periods of time, giving the slope a warmer microclimate than the areas around the slope. The lowest area of a glen may sometimes frost sooner or harder than a nearby spot uphill, because cold air sinks, a drying breeze may not reach the lowest bottom, and humidity lingers and precipitates, then freezes.
Climate Data Online provides free access to NCDC's archive of global historical weather and climate data in addition to station history information. These data include quality controlled daily, monthly, seasonal, and yearly measurements of temperature, precipitation, wind, and degree days as well as radar data and 30-year Climate Normals. Customers can also order most of these data as certified hard copies for legal use.
Volunteers Needed to Unlock Historic Weather Secrets.
"There is no bad weather, just a bad choice of clothes."
Weather Reports - Intellicast Detailed Local Weather Reports in several formats.
BloomSky World's Smartest Weather Camera Station Smartest weather camera station with real-time images, time-lapse & precise weather data.
Portable Weather Stations
NOAA upgrades the U.S. Global Weather Forecast Model. Improved model will boost weather forecasts across the U.S.. Finite-Volume Cubed-Sphere Dynamical Core is a scalable and flexible dynamical core capable of both hydrostatic and non-hydrostatic atmospheric simulations. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory.
The National Ocean Service says that episodes of El Niño and La Niña typically last nine to 12 months but can sometimes stretch for years.
Ventusky animated wind, rain and temperature maps, detailed forecast for your place, data from the best weather forecast models such as GFS, ICON, GEM.
"There is no such thing as bad weather, only different kinds of good weather." John Ruskin (wiki).
Weather Measurements
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible. Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. This effect is calculated in a heat index table or humidex.
Relative Humidity is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor to the equilibrium vapor pressure of water at a given temperature. Relative humidity depends on temperature and the pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is that of dew point. Humidity between 30 to 60 percent is the most comfortable for humans, with indoor humidity ideally between 30 to 50 percent. Other studies suggest that 40% to 60% humidity is a better range being not too dry or not too moist. But humidity benefits depend on your body type, if you have dry skin you may need a higher humid climate, or a lower humid climate if you have asthma.
Dew Point is the temperature at which dew forms and is a measure of atmospheric moisture. Dew Point is the temperature at which air is saturated with water vapor, which is the gaseous state of water. It is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure and water content to reach saturation. A higher dew point indicates more moisture in the air; a dew point greater than 20 °C (68 °F) is considered uncomfortable and greater than 22 °C (72 °F) is considered to be extremely humid. Frost point is the dew point when temperatures are below freezing. The dew point is the temperature at which the moisture (water vapor) in the air begins to condense. The warmer the air is, the more moisture it can hold.
Condense is to change or cause to change from a gas or vapor to a liquid.
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gas phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of Evaporation, which is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs from the surface of a liquid into a gaseous phase that is not saturated with the evaporating substance. Once the air temperature reaches the dew point, fog will form. It also determines whether it will rain or snow. The dew point determines how high the danger is for a grass or brush fire during a dry spell. It affects whether you will have to clean the frost off your windshield in the morning. The dew point determines how uncomfortable you will feel on a warm summer day. When you perspire, the water on your skin evaporates and cools your body, this is your temperature regulating system at work. When the dew point is high, the evaporation rate is very slow because there is so much water vapor in the air, and you don't get the cooling effect from your wet skin. The dew point also affects how you feel when you get out of a pool, lake or the ocean. On those days when the dew point is very low, you will feel cooler than when the dew point is high. This is because when the dew point is low, the water on your skin evaporates faster thus cooling you off. Boil - Water from Air.
Atmospheric Pressure sometimes also called Barometric Pressure, is the pressure exerted by the weight of air in the atmosphere of Earth. The Earth's atmosphere exerts a pressure on the surface. Areas of high and low pressure are caused by ascending and descending air. As air warms, it ascends or travels up leading to low pressure at the surface. As air cools, it descends or travels down leading to high pressure at the surface. In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. Low-Pressure areas have less atmospheric mass above their location, whereas High-Pressure areas have more atmospheric mass above their location. Atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Standard sea-level pressure, by definition, equals 760 mm (29.92 inches) of mercury, 14.70 pounds per square inch, 1,013.25 × 103 dynes per square centimetre, 1,013.25 millibars, one standard atmosphere, or 101.325 kilopascals. When the air pressure drops, so does the mercury level. Atmospheric pressure can also be measured in millibars (mb), with a "bar" being roughly equivalent to one atmosphere of pressure (one atmosphere equals 1.01325 bars). One bar is equivalent to 29.6 in. Hg. A barometer reading of 30 inches (Hg) is considered normal. The term barometric pressure is synonymous with the term air pressure when describing conditions in the atmosphere, and may also be referred to as atmospheric pressure. Like all matter, air is composed of molecules. These molecules have mass and are subjected to the force of Earth’s Gravity. Air pressure is the weight of air molecules pressing down on you. Inhabitants on Earth’s surface bear the weight of all the air molecules in the atmosphere. At higher altitudes, air pressure decreases because there are fewer air molecules pressing down from above compared with the air pressure at sea level. Barometric pressure is measured in millibars (mb) but is often given in inches because older style of barometers measured the height of a column of mercury to indicate air pressure. Normal air pressure at sea level is 1013.2 mb, or 29.92 in. An aneroid barometer measures air pressure by the expansion or contraction of springs, housed in a partial vacuum, in response to changes in air pressure. In older mercury barometers, a column of mercury would rise or fall in response to changes in air pressure. Air pressure is constantly changing due to fluctuations in temperature, which is related to air density. Warm air causes air pressure to rise. When air molecules collide, they exert force on each other. When gas molecules are heated, the molecules move more quickly, and the increased velocity causes more collisions. As a result, more force is exerted on each molecule and air pressure increases. Temperature affects air pressure at different altitudes due to a disparity in air density. Given two columns of air at different temperatures, the column of warmer air will experience the same air pressure at a higher altitude that is measured at a lower altitude in the cooler column of air. Cool temperatures cause air pressure to drop. When gas molecules cool, they move more slowly. Decreased velocity results in fewer collisions between molecules and air pressure decreases. Air density plays a role in the correlation between temperature and pressure because warmer air is less dense than cool air, allowing molecules to have more space to collide with greater force. In cooler air, the molecules are closer together. The proximity results in collisions with less force and lower air pressure. Weather patterns complicate the relationship between barometric pressure and temperature. Meteorologists gather barometric readings and represent them on weather maps with “H” and “L” to indicate areas of high and low pressure. Very cold temperatures can create areas of high air pressure because cold air has greater density and the concentration of molecules can raise the air pressure. An area of higher pressure, H, is called a high-pressure system and generally has a denser air mass where air temperature is cool. These systems often bring warmer temperatures and dry weather. A low-pressure system, L, is an area of less dense air with warmer air temperatures. The lower concentration of molecules causes lower air pressure in these areas. Low-pressure systems often bring cool, wet weather. Decompression - Wind.
Visibility is a measure of the distance at which an object or light can be clearly discerned. The transparency of air. Smoke.
Amazing Mirror & Air Experiment! (youtube) - This is a demonstration of the Schlieren effect. This setup allows you to see changes in air density. The point light source is aimed at the concave mirror. The concave mirror reflects to a focal point. There you use a sharp edged object to partially block the light which helps create a shadow effect that allows you to see air movement. Flying (action physics).
Ultraviolet Index or UV Index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of sunburn-producing ultraviolet radiation at a particular place and time. The calculation starts with measurements of current total ozone amounts over the entire globe, obtained via two satellites operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. These data are used to produce a forecast of stratospheric ozone levels for the next day at many points across the country. A computer model uses the ozone forecast and the incident angle of sunlight at each point to calculate the strength of UV radiation at ground level. Sunlight angle is determined by latitude, day of year, and time of day (solar noon). The strength of UV radiation is calculated for several wavelengths between 280 and 400 nm, the full spectrum of UVB (280-314 nm) and UVA (315-400 nm) radiation. Factors that determine the UV Index: The thickness of the ozone layer over your city (detected using satellites) - UV Index (weather.com). The cloud cover over your city (clouds block UV radiation to varying degrees). Air pollution: Similar to the way clouds shield the Earth's surface from the suns UV, urban smog can reduce the amount of UV energy reaching the Earth by reflecting UV back towards space or absorbing UV. The time of year (in winter, UV radiation is lower than in the summer because of the sun's angle). Time of day: On any day the greatest amount of UV reaches the Earth around midday when the sun is at its highest point. Up to 50% of daily UV radiation levels is received between 11am and 2pm. The elevation of your city (higher elevations get more UV radiation). Latitude: Since the sun's UV energy impacts the Earth's surface at the most direct angle over the equator it is the most intense at this latitude.
Sun Burn - Degrees of Burns - Ozone - Warming
Solar Irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units. Average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is roughly 1361 W/m2. The Sun's rays are attenuated as they pass through the atmosphere, leaving maximum normal surface irradiance at approximately 1000 W/m2 at sea level on a clear day. Solar radiation can be categorized into four classes: levels less than 2.6 kWh/m2 are classified as low solar radiation while solar irradiance between 2.6-3 kWh/m2 is moderate solar radiation; irradiance of between 3-4 kWh/m2 is high solar radiation and irradiance higher than 4 kWh/m2 is very high radiation.
Testing UV Absorption Eyewear and Sunscreen with a Deuterium Light Source (youtube)
CIE Erythema Action Spectrum and Standard Erythema Dose - International Commission on Illumination.
Erythema is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology include nervous blushes.
Absorbance is the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, and spectral absorbance or spectral decadic absorbance is the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. Absorbance is dimensionless, and in particular is not a length, though it is a monotonically increasing function of path length, and approaches zero as the path length approaches zero. The use of the term "optical density" for absorbance is discouraged. In physics, a closely related quantity called "optical depth" is used instead of absorbance: the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material. The optical depth equals the absorbance times ln(10). The term absorption refers to the physical process of Absorbing Light, while absorbance does not always measure absorption: it measures attenuation (of transmitted radiant power). Attenuation can be caused by absorption, but also reflection, scattering, and other physical processes.
Ozone Layer is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains high concentrations of ozone or O3 in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in relation to other gases in the stratosphere. The ozone layer contains less than 10 parts per million of ozone, while the average ozone concentration in Earth's atmosphere as a whole is about 0.3 parts per million. The ozone layer is mainly found in the lower portion of the stratosphere, from approximately 20 to 30 kilometres (12 to 19 mi) above Earth, although its thickness varies seasonally and geographically. The ozone layer continues to thin. The ozone layer protects life on earth from high-energy radiation. Ozone is formed in the stratosphere, mainly at altitudes above 30 km in the tropics. From there it is distributed around the globe by atmospheric circulation. When excessive quantities of ozone-depleting chlorinated and brominated hydrocarbons (e.g. CFCs) were released into the atmosphere, the ozone layer in the stratosphere - i.e. at altitudes of 15 to 50 km thinned out globally. The Montreal Protocol introduced a ban on these long-lasting substances in 1989. Despite the ban on CFCs, the concentra-tion of ozone in the lower part of the stratosphere (15 to 24 km) - where the ozone layer is at its den-sest - has continued to decline at latitudes between 60° S and 60° N. The scientists were able to de-monstrate this using satellite measurements spanning the last three decades together with advanced statistical methods. very short-lived substances (VSLSs) containing chlorine and bromine are on the rise, and could increasingly enter the lower stratosphere.
Indoor Air Monitoring - Weather Effects on the Body and Mind
Surface Weather Observation are the fundamental data used for safety as well as climatological reasons to forecast weather and issue warnings worldwide. They can be taken manually, by a weather observer, by computer through the use of automated weather stations, or in a hybrid scheme using weather observers to augment the otherwise automated weather station.
Weather Instruments List (wiki) - Eyes in the Sky (drones) - Satellites - Earthquakes - Volcanoes - Fires.
Wind
 Wind is the
flow of gases on a large scale. On
the surface of the Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of
Air.
High pressure always moves towards an area of low
pressure.
Wind is the
flow of gases on a large scale. On
the surface of the Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of
Air.
High pressure always moves towards an area of low
pressure.Thermals - Columns of Rising Air - Aerodynamics - Solar Winds - Upward Drafts (hot air) - Ocean Currents
Santa Ana Winds are caused by high pressure over the desert of the southwestern U.S., that pushes through the mountain passages in Southern California toward an area of lower pressure off the Pacific coast. As the air mass drops in altitude, it compresses and heats up — by about 10 degrees Celsius per kilometer (18 degrees Fahrenheit per 0.6 of a mile). It's a "very effective way of warming up the air. As the air warms up, it also decreases its humidity. Funneling through narrow mountain passes, it also speeds up in much the same way that air moving through a tunnel or the wind between buildings is stronger. Normally, that makes for warm, dry Santa Anas that can be reach 40–60 mph, with gusts exceeding 70 mph.
Wind Direction is reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a northerly wind blows from the north to the south. Wind direction is usually reported in cardinal directions or in azimuth degrees. Wind direction is measured in degrees clockwise from due north and so a wind coming from the south has a wind direction of 180 degrees; one from the east is 90 degrees. Winds are described after the direction from which they come, followed by '-erly'. For example, winds from the north are called ‘northerly winds’(north +-erly).
Weather Vane is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word vane comes from the Old English word fana, meaning 'flag'.
Windsock is a conical textile tube that resembles a giant sock. Windsocks can be used as a basic guide to wind direction and speed, or as decoration.
Microburst or air bombs, is a small downdraft that moves in a way opposite to a tornado. Microbursts are found in strong thunderstorms.
Wind Shear is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with change in lateral position for a given altitude.
Turbulence is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers. Clear-Air Turbulence is the turbulent movement of air masses in the absence of any visual clues, such as clouds, and is caused when bodies of air moving at widely different speeds meet. Mountain Waves are associated with severe turbulence, strong vertical currents, and icing. These waves are generated when strong winds flowing toward mountains in a generally perpendicular fashion are raised up over the mountains. As the winds rise, they may encounter a strong inversion or stable air barrier over the mountains that causes the winds to be redirected toward the surface.
Convection is the heat transfer due to bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids, including molten rock (rheid). Convection takes place through advection, diffusion or both. Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air, and is a means by which thermal energy is distributed on the surface of the Earth, together with the much slower (lagged) ocean circulation system. The large-scale structure of the atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the basic climatological structure remains fairly constant. Latitudinal circulation occurs because incident solar radiation per unit area is highest at the heat equator, and decreases as the latitude increases, reaching minima at the poles. It consists of two primary convection cells, the Hadley cell and the polar vortex, with the Hadley cell experiencing stronger convection due to the release of latent heat energy by condensation of water vapor at higher altitudes during cloud formation. Longitudinal circulation, on the other hand, comes about because the ocean has a higher specific heat capacity than land (and also thermal conductivity, allowing the heat to penetrate further beneath the surface) and thereby absorbs and releases more heat, but the temperature changes less than land. This brings the sea breeze, air cooled by the water, ashore in the day, and carries the land breeze, air cooled by contact with the ground, out to sea during the night. Longitudinal circulation consists of two cells, the Walker circulation and El Niño / Southern Oscillation.
Less dense air rises above air that is more dense, or water that is more dense then air. Hot air rises because when you heat air it expands. When the air expands, it becomes less dense than the air around it. The less dense hot air then floats above the denser cold air much like wood floats on water because wood is less dense than water. Gravity pulls cooler, denser air toward the Earth's surface. As the denser air reaches the Earth's surface, it spreads out and undercuts the less dense air, which in turn forces the less dense air up and into motion, causing it to rise. Air has molecules that are constantly moving. Because air has mass, Earth's gravity attracts it and gives it weight. Because it has weight, and the air molecules are constantly bumping into things, it exerts pressure. Air at higher altitudes thins out as the gas particles expand and lose energy, creating low air pressure. Air expands as it rises, and the fewer gas molecules—including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide—have fewer chances to bump into each other. The air in contact with the ground is warmer than air just above. As you get further and further from the warm ground, the air is colder and colder. This explains why air temperature decreases with increasing altitude in the troposphere.
Hadley Cell is a tropical atmospheric circulation that features air rising near the equator, flowing poleward at 10–15 kilometers above the surface, descending in the subtropics, and then flowing equatorward near the surface. This circulation creates the trade winds, tropical rain-belts and hurricanes, subtropical deserts and the jet streams.
 Atmospheric River is a narrow corridor or filament of concentrated
moisture in the atmosphere. Atmospheric rivers consist of narrow bands of
enhanced water vapor transport, typically along the boundaries between
large areas of divergent surface air flow, including some frontal zones in
association with extratropical cyclones that form over the oceans.
Pineapple Express storms are the most commonly represented and
recognized type of atmospheric rivers; they are given the name due to the
warm water vapor plumes originating over the Hawaiian tropics that follow
a path towards California. Ocean Currents.
Atmospheric River is a narrow corridor or filament of concentrated
moisture in the atmosphere. Atmospheric rivers consist of narrow bands of
enhanced water vapor transport, typically along the boundaries between
large areas of divergent surface air flow, including some frontal zones in
association with extratropical cyclones that form over the oceans.
Pineapple Express storms are the most commonly represented and
recognized type of atmospheric rivers; they are given the name due to the
warm water vapor plumes originating over the Hawaiian tropics that follow
a path towards California. Ocean Currents.Jet Stream are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east). Their paths typically have a meandering shape. Jet streams may start, stop, split into two or more parts, combine into one stream, or flow in various directions including opposite to the direction of the remainder of the jet. The strongest jet streams are the Polar Jets, at 9–12 km (30,000–39,000 ft) above sea level, and the higher altitude and somewhat weaker subtropical jets at 10–16 km (33,000–52,000 ft). The Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere each have a polar jet and a subtropical jet. The northern hemisphere polar jet flows over the middle to northern latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia and their intervening oceans, while the southern hemisphere polar jet mostly circles Antarctica all year round. Jet streams are the product of two factors: the atmospheric heating by solar radiation that produces the large scale Polar, Ferrel, and Hadley circulation cells, and the action of the Coriolis force acting on those
 moving masses. The Coriolis Force is caused by the planet's rotation on
its axis. On other planets, internal heat rather than solar heating drives
their jet streams. The Polar jet stream forms near the interface of the
Polar and Ferrel circulation cells; the subtropical jet forms near the
boundary of the Ferrel and Hadley circulation cells. Other jet streams
also exist. During the Northern Hemisphere summer, easterly jets can form
in tropical regions, typically where dry air encounters more humid air at
high altitudes. Low-level jets also are typical of various regions such as
the central United States. There are also jetstreams in the thermosphere.
Meteorologists use the location of some of the jet streams as an aid in
weather forecasting. The main commercial relevance of the jet streams is
in air travel, as flight time can be dramatically affected by either
flying with the flow or against, which results in significant fuel and
time cost savings for airlines. Often, the airlines work to fly 'with' the
jet stream for this reason. Dynamic North Atlantic Tracks are one example
of how airlines and air traffic control work together to accommodate the
jet stream and winds aloft that results in the maximum benefit for
airlines and other users. Clear-air turbulence, a potential hazard to
aircraft passenger safety, is often found in a jet stream's vicinity, but
it does not create a substantial alteration on flight times. These are a
narrow belt.
Large atmospheric waves in the jet stream present risk to global food
production. Researchers have discovered jet stream patterns that could
affect up to a quarter of global food production.
moving masses. The Coriolis Force is caused by the planet's rotation on
its axis. On other planets, internal heat rather than solar heating drives
their jet streams. The Polar jet stream forms near the interface of the
Polar and Ferrel circulation cells; the subtropical jet forms near the
boundary of the Ferrel and Hadley circulation cells. Other jet streams
also exist. During the Northern Hemisphere summer, easterly jets can form
in tropical regions, typically where dry air encounters more humid air at
high altitudes. Low-level jets also are typical of various regions such as
the central United States. There are also jetstreams in the thermosphere.
Meteorologists use the location of some of the jet streams as an aid in
weather forecasting. The main commercial relevance of the jet streams is
in air travel, as flight time can be dramatically affected by either
flying with the flow or against, which results in significant fuel and
time cost savings for airlines. Often, the airlines work to fly 'with' the
jet stream for this reason. Dynamic North Atlantic Tracks are one example
of how airlines and air traffic control work together to accommodate the
jet stream and winds aloft that results in the maximum benefit for
airlines and other users. Clear-air turbulence, a potential hazard to
aircraft passenger safety, is often found in a jet stream's vicinity, but
it does not create a substantial alteration on flight times. These are a
narrow belt.
Large atmospheric waves in the jet stream present risk to global food
production. Researchers have discovered jet stream patterns that could
affect up to a quarter of global food production. Outflow Boundary is a boundary separating thunderstorm-cooled air (outflow) from the surrounding air; similar in effect to a cold front, with passage marked by a wind shift and usually a drop in temperature and a related pressure jump.
Mesoscale Meteorology horizontal dimensions generally range from around 5 kilometers to several hundred kilometers. Vertical velocity often equals or exceeds horizontal velocities in mesoscale meteorological systems due to nonhydrostatic processes such as buoyant acceleration of a rising thermal or acceleration through a narrow mountain pass.
North Atlantic Oscillation is a weather phenomenon in the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level (SLP) between the Icelandic low and the Azores high. Through fluctuations in the strength of the Icelandic low and the Azores high, it controls the strength and direction of westerly winds and location of storm tracks across the North Atlantic. It is part of the Arctic oscillation, and varies over time with no particular periodicity.
Entrainment in meteorology is a phenomenon of the atmosphere which occurs when a turbulent flow captures a non-turbulent flow. It is typically used to refer to the capture of a wind flow of high moisture content, or in the case of tropical cyclones, the capture of drier air. Detrainment is the opposite effect when the air from a convective cloud, usually at its top, is injected in the environment.
Wind Chill is the perceived decrease in air temperature felt by the body on exposed skin due to the flow of air. The temperature of the Air does not change, the wind helps remove the warm air immediately next to the skin and this causes a feeling of it being colder. The wind chill was developed because of the feeling that it gets colder when the wind is stronger due to a more rapid heat loss from the body. Wind chill numbers are always lower than the air temperature for values where the formula is valid. When the apparent temperature is higher than the air temperature, the heat index is used instead.
Air Vortex Cannon is a piece of weaponry that releases doughnut-shaped air vortices — similar to smoke rings but larger, stronger and invisible. The vortices are able to ruffle hair, disturb papers or blow out candles after travelling several metres. The design consists of a short and broad barrel with a slight taper, closed by a flexible diaphragm at the larger end. The diaphragm is internally attached to the barrel by elastic strips. The cannon is "armed" by pulling the diaphragm out, distending the elastic bands, and is "fired" by releasing the diaphragm. The diaphragm quickly pushes a quantity of air out of the open end, creating a vortex ring. An air vortex cannon can be made easily at home, from just a cardboard box. A toy commercial version, with a barrel 12 inches (30 cm) wide and useful range of 20 feet (6.1 m) is sold under the name Air bazooka or Airzooka.
Wind Speeds in Atmospheric Layers. Loon stratospheric balloons confirm wind data from Aeolus. Researchers recommend more vertical measurements for follow-up mission. ESA's novel Aeolus satellite reliably measures wind speed also in higher air layers and thus in a region of the atmosphere where other direct global wind measurements are relatively sparse. This is the result of a study for which data from the satellite were compared with wind observations from stratospheric balloons. Stratospheric balloons would provide highly accurate data on the horizontal wind speed and are therefore also suitable for the validation of future satellite missions. This novel satellite has a powerful laser on board, the Atmospheric Laser Doppler Instrument. ALADIN is the first Doppler wind lidar in space to provide profiles of horizontal wind speed from the Earth's surface or from the top of thick clouds up to a height of about 30 km on a global scale. To do this, the satellite emits short ultraviolet laser pulses as it orbits the Earth. A small part of these light pulses is scattered back to the satellite by air molecules, aerosols and clouds and collected and processed in the detector there. For one circumnavigation of the globe Aeolus takes 90 minutes, within a week the satellite collects wind data around the entire globe. This data is assimilated by weather forecasting centres around the world to improve their forecasts. Since there have been no comparable satellite missions so far, the data are checked particularly critically and compared with other wind measurements. Loon was a commercial project that had provided remote regions with internet access via helium balloons in the stratosphere. The balloons, which were about 12 metres in diameter, acted as floating mobile phone stations at altitudes of 16 to 20 kilometres above the ground. For maintaining the network, the balloons had to automatically correct the wind direction by changing the altitude. This created an extensive data set on wind speeds in these atmospheric layers, which partially fills the gap in wind data at this altitude in the global observation system. The Loon project was discontinued in 2021 for economic reasons, but a highly interesting data set remains for atmospheric research.
Clouds
 Clouds
is an aerosol comprising a visible mass of minute liquid droplets,
frozen
crystals, or particles suspended in the atmosphere
above the surface of a planetary body. The droplets and
crystals may be
made of water or various chemicals. On Earth, clouds are
formed as a
result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its
dew point, or
when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor)
from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature.
They are seen in the Earth's Homosphere, which includes the troposphere,
stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds which is
undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology.
Rain falls when tiny water droplets come together to form bigger water
droplets until the weight of gravity forces the
rain drops to fall.
Storms.
Clouds
is an aerosol comprising a visible mass of minute liquid droplets,
frozen
crystals, or particles suspended in the atmosphere
above the surface of a planetary body. The droplets and
crystals may be
made of water or various chemicals. On Earth, clouds are
formed as a
result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its
dew point, or
when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor)
from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature.
They are seen in the Earth's Homosphere, which includes the troposphere,
stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds which is
undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology.
Rain falls when tiny water droplets come together to form bigger water
droplets until the weight of gravity forces the
rain drops to fall.
Storms.Coalescence is the process by which two or more droplets, bubbles or particles merge during contact to form a single daughter droplet, bubble or particle. It can take place in many processes, ranging from meteorology to astrophysics, which is the branch of astronomy that employs the principles of physics and chemistry.
Droplet is a tiny liquid drop with a shape that is spherical and small.
All About Clouds for Kids: Types and Names of Clouds - FreeSchool (youtube)
The Three Main Clouds - Cirrus, Stratus, Cumulus (youtube)
Cloud Types List (wiki) - Cumulus (white fluffy) and Stratus (blanket) are low clouds below 6,500 feet. Cirrus Clouds are above 20,000 feet. Arcus Cloud - Roll cloud - Mustache Cloud. Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability is the difference in air densities in the clouds.
Noctilucent Cloud or Electric Blue Polar Cloud, are tenuous cloud-like phenomena that are the "ragged edge" of a much brighter and pervasive polar cloud layer called polar mesospheric clouds in the upper atmosphere, visible in a deep twilight. They are made of ice crystals and are only visible in a deep twilight. These clouds can be observed only when the Sun is below the horizon for the observer, but while the clouds are still in sunlight. Noctilucent roughly means night shining in Latin. They are most commonly observed in the summer months at latitudes between 50° and 70° north and south of the equator. These clouds can be observed only during local summer months and when the Sun is below the horizon for the observer, but while the clouds are still in sunlight.
ScienceCasts: Electric-Blue Clouds Appear Over Antarctica (youtube)
Polar Mesospheric Clouds are a phenomenon known as noctilucent clouds. From satellites, PMCs are most frequently observed above 70°-75° in latitude and have a season of 60 to 80 days duration centered about a peak which occurs about 20 days after the summer solstice. This holds true for both hemispheres. Great variability in scattering is observed from day-to-day and year-to- year, but averaging over large time and space scales reveals a basic underlying symmetry and pattern. The long- term behaviour of polar mesospheric cloud frequency has been found to vary inversely with solar activity.
Polar Stratospheric Cloud also known as nacreous clouds, are clouds in the winter polar stratosphere at altitudes of 15,000–25,000 meters (49,000–82,000 ft). They are best observed during civil twilight when the sun is between 1 and 6 degrees below the horizon as well as in winter and in more northerly latitudes. They are implicated in the formation of ozone holes. The effects on ozone depletion arise because they support chemical reactions that produce active chlorine which catalyzes ozone destruction, and also because they remove gaseous nitric acid, perturbing nitrogen and chlorine cycles in a way which increases ozone destruction. (from nacre, or mother of pearl, due to its iridescence).
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud, usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog has affected many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.
Dust are fine particles of solid matter. It generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil, dust lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes, offices, and other human environments contains small amounts of plant pollen, human and animal hairs, textile fibers, paper fibers, minerals from outdoor soil, human skin cells, burnt meteorite particles, and many other materials which may be found in the local environment.
Mineral Dust is atmospheric aerosols originated from the suspension of minerals constituting the soil. It is composed of various oxides and carbonates. Human activities lead to 30% of the dust load in the atmosphere. The Sahara Desert is the major source of mineral dust, which subsequently spreads across the Mediterranean (where it is the origin of rain dust) and Caribbean seas into northern South America, Central America, North America, and Europe. Additionally, it plays a significant role in the nutrient inflow to the Amazon rainforest. The Gobi Desert is another source of dust in the atmosphere, which affects eastern Asia and western North America. Smoke.
Rain
Rain is liquid water in the form of droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then precipitated—that is, become heavy enough to fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems, as well as water for hydroelectric power plants and crop irrigation.
Erosion - Rain Water Management - Snow
Drizzle is a light liquid precipitation consisting of liquid water drops smaller than those of rain – generally smaller than 0.5 mm (0.02 in) in diameter.
Even knowing that the earth has 100 lightning strikes every second, and has earthquakes every minute, and has 1,000's of fires burning everyday, with 1,000 Meteorites hitting the earth every day, I have had a mostly a calm life in Danbury Ct. from 1960 till 2015. Being born in 1960 was extremely lucky, Turning 40 in 2000.
Evaporation (water knowledge) - Droughts - Oceans
Flood is an overflow of water that submerges land which is usually dry. Flooding may occur as an overflow of water from water bodies, such as a river, lake, or ocean, in which the water overtops or breaks levees, resulting in some of that water escaping its usual boundaries, or it may occur due to an accumulation of rainwater on saturated ground in an areal flood. While the size of a lake or other body of water will vary with seasonal changes in precipitation and snow melt, these changes in size are unlikely to be considered significant unless they flood property or drown domestic animals.
Torrent is a heavy rain of an overwhelming number or amount. A violently fast stream of water. Torrential is something pouring in abundance.
Explosive Cyclogenesis (Weather Bomb)
The Who - Love Reign Over Me (youtube) - Only Love Can make it Rain. - Singing In The Rain (Gene Kelly) (youtube)
Lightning
 Earth has 8.6 Million
Lightning Strikes a day. 3.6 trillion lightning strikes each
year. Lightning hits the earth an
estimated
100 times per second on average. When
Moisture
Condenses the movement of air produces
Wireless
Electricity. Global Atmospheric Electrical Circuit is the continuous movement of
electric current between the ionosphere and the earth's surface. This flow
is powered by thunderstorms, which cause a build-up of positive charge in
the ionosphere. In fair weather this positive charge slowly flows back
to the surface.
Earth has 8.6 Million
Lightning Strikes a day. 3.6 trillion lightning strikes each
year. Lightning hits the earth an
estimated
100 times per second on average. When
Moisture
Condenses the movement of air produces
Wireless
Electricity. Global Atmospheric Electrical Circuit is the continuous movement of
electric current between the ionosphere and the earth's surface. This flow
is powered by thunderstorms, which cause a build-up of positive charge in
the ionosphere. In fair weather this positive charge slowly flows back
to the surface. The Brain - Electricity in Nature - Electric Universe
Lightning is a abrupt electric discharge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to earth accompanied by the emission of light. The flash of light that accompanies an electric discharge in the atmosphere (or something resembling such a flash); can scintillate for a second or more. Scintillate is to emit or reflect light in a flickering manner.
Lightning Rod is a metal rod mounted on a structure and intended to protect the structure from a lightning strike. If lightning hits the structure, it will preferentially strike the rod and be conducted to ground through a wire, instead of passing through the structure, where it could start a fire or cause electrocution. Lightning rods are also called finials, air terminals, or strike termination devices. In a lightning protection system, a lightning rod is a single component of the system. The lightning rod requires a connection to earth to perform its protective function. Lightning rods come in many different forms, including hollow, solid, pointed, rounded, flat strips, or even bristle brush-like. The main attribute common to all lightning rods is that they are all made of conductive materials, such as copper and aluminum. Copper and its alloys are the most common materials used in lightning protection.
Spark is a momentary flash of light. Electrical conduction through a gas in an applied electric field. A small fragment of a burning substance thrown out by burning material or by friction.
Flash is to appear briefly and make known or cause to appear with great speed. A sudden intense burst of radiant energy. A momentary brightness. UFO.
Twinkle is a rapid change in brightness or a brief spark or flash. To gleam or glow intermittently. Emit or reflect light in a flickering manner.
Flicker is a momentary flash of light that moves back and forth very rapidly or flashes intermittently.
Lightning Strike is an electric discharge between the atmosphere and an earth-bound object. They mostly originate in a cumulonimbus cloud and terminate on the ground, called cloud to ground (CG) lightning. A less common type of strike, called ground to cloud (GC), is upward propagating lightning initiated from a tall grounded object and reaches into the clouds. About 25% of all lightning events worldwide are strikes between the atmosphere and earth-bound objects. The bulk of lightning events are intra-cloud (IC) or cloud to cloud (CC), where discharges only occur high in the atmosphere. A single lightning event is a "flash", which is a complex, multi-stage process, some parts of which are not fully understood. Most cloud to ground flashes only "strike" one physical location, referred to as a "termination". The primary conducting channel, the bright coursing light that may be seen and is called a "strike", is only about one inch in diameter, but because of its extreme brilliance, it often looks much larger to the human eye and in photographs. Lightning Discharges are typically miles long, but certain types of horizontal discharges can be upwards of tens of miles in length. The entire flash lasts only a fraction of a second. Most of the early formative and propagation stages are much dimmer and not visible to the human eye.
Step Potential is the Step Voltage between the feet of a person standing near an energized grounded object. It is equal to the difference in voltage, given by the voltage distribution curve, between two points at different distances from the electrode. Earth Potential Rise occurs when a large current flows to earth through an earth grid impedance. The potential relative to a distant point on the Earth is highest at the point where current enters the ground, and declines with distance from the source. Ground potential rise is a concern in the design of electrical substations because the high potential may be a hazard to people or equipment. The change of voltage over distance (potential gradient) may be so high that a person could be injured due to the voltage developed between two feet, or between the ground on which the person is standing and a metal object. Any conducting object connected to the substation earth ground, such as telephone wires, rails, fences, or metallic piping, may also be energized at the ground potential in the substation. This transferred potential is a hazard to people and equipment outside the substation.
Positive Lightning strikes tend to be much more intense than their negative counterparts. An average bolt of negative lightning carries an electric current of 30,000 amperes (30 kA), and transfers 15 coulombs of electric charge and 500 megajoules of energy. Large bolts of negative lightning can carry up to 120 kA and 350 coulombs. The average positive ground flash has roughly double the peak current of a typical negative flash, and can produce peak currents up to 400,000 amperes (400 kA) and charges of several hundreds coulombs. Furthermore, positive ground flashes with high peak currents are commonly followed by long continuing currents, a correlation not seen in negative ground flashes.
Sprite Lightning are large-scale electrical discharges that occur high above thunderstorm clouds, or cumulonimbus, giving rise to a quite varied range of visual shapes flickering in the night sky. They are triggered by the discharges of positive lightning between an underlying thundercloud and the ground. Sprites appear as luminous reddish-orange flashes. They often occur in clusters above the troposphere at an altitude range of 50–90 km (31–56 mi). Sporadic visual reports of sprites go back at least to 1886, but they were first photographed on July 6, 1989 by scientists from the University of Minnesota and have subsequently been captured in video recordings many thousands of times. Sprites are sometimes inaccurately called upper-atmospheric lightning. However, sprites are cold plasma phenomena that lack the hot channel temperatures of tropospheric lightning, so they are more akin to fluorescent tube discharges than to lightning discharges. Northern Lights.
Upper-Atmospheric Lightning are short-lived electrical-breakdown phenomena that occur well above the altitudes of normal lightning and storm clouds. Upper-atmospheric lightning is believed to be electrically induced forms of luminous plasma. The preferred usage is transient luminous event (TLE), because the various types of electrical-discharge phenomena in the upper atmosphere lack several characteristics of the more familiar tropospheric lightning.
Ball Lightning is an unexplained atmospheric electrical phenomenon. The term refers to reports of luminous, spherical objects that vary from pea-sized to several meters in diameter. Though usually associated with thunderstorms, the phenomenon lasts considerably longer than the split-second flash of a lightning bolt. Many early reports claim that the ball eventually explodes, sometimes with fatal consequences, leaving behind the odor of sulfur.
Superbolt is an unusually powerful lightning bolt that unleash a thousand times more low-frequency energy than regular lightning bolts -- occur in dramatically different patterns than regular lightning.
Volcanic Lightning is an electrical discharge caused by a volcanic eruption, rather than from an ordinary thunderstorm. Volcanic lightning arises from colliding, fragmenting particles of volcanic ash (and sometimes ice), which generate static electricity within the volcanic plume, leading to the name dirty thunderstorm. Moist convection and ice formation also drive the eruption plume dynamics and can trigger volcanic lightning. But unlike ordinary thunderstorms, volcanic lightning can also occur before any ice crystals have formed in the ash cloud.
Atmospheric Electricity is the study of electrical charges in the Earth's atmosphere. The movement of charge between the Earth's surface, the atmosphere, and the ionosphere is known as the global atmospheric electrical circuit. Atmospheric electricity is an interdisciplinary topic with a long history, involving concepts from electrostatics, atmospheric physics, meteorology and Earth science. Thunderstorms act as a giant battery in the atmosphere, charging up the ionosphere to about 400,000 volts with respect to the surface. This sets up an electric field throughout the atmosphere, which decreases with increase in altitude. Atmospheric ions created by cosmic rays and natural radioactivity move in the electric field, so a very small current flows through the atmosphere, even away from thunderstorms. Near the surface of the earth, the magnitude of the field is on average around 100 V/m. Atmospheric electricity involves both thunderstorms, which create lightning bolts to rapidly discharge huge amounts of atmospheric charge stored in storm clouds, and the continual electrification of the air due to ionization from cosmic rays and natural radioactivity, which ensure that the atmosphere is never quite neutral.
515-mile lightning flash caught from space. Researchers used space-based instruments to measure a record-setting megaflash horizontal lightning.
Most tropical lightning storms are radioactive. Researchers have known for several decades that thunderstorms can act as miniature particle accelerators that produce antimatter, gamma rays and other nuclear phenomena. But they did not know how common the phenomenon was. In observations taken by a retrofitted U2 spy plane, they've discovered essentially all large thunderstorms produce gamma rays in many dynamic, unexpected and unknown ways.
Earth is charged negatively and carries about 5x10^5 C due to the Ionosphere - Earth capacitance which is about 1 F. The positive charge of Ionosphere is formed by the predominantly positively charged cosmic rays with intensity is about 10^4 nuclei per square meter per second with energy > 1 GeV. Planets are charged and all bodies in space have a voltage that depends on their immediate environment to the degree that they interact with it through the interplanetary medium, which transfers charge to an extent. Earth has a minor negative charge that causes lightening. However, overall the planet is very close to neutral when combined with the atmosphere. Since moons, planets and stars are the things that make up the universe, it is only logical to deduce that the universe therefore has a total electric charge of zero.
Sun is made of positively charged ions. and negatively charged electrons, in a state of matter called plasma. The properties of the gas are controlled by electromagnetic forces among constituent ions and electrons, which results in a different type of behavior.The Sun is positive with a magnitude that is estimated as 77 Coulombs, or about 1 electron per million tons of matter. Equilibrium of these forces establishes the allowed net charge.
Scientists discover phenomenon impacting Earth's radiation belts. Two scientists discovered a new type of 'whistler,' an electromagnetic wave that carries a substantial amount of lightning energy to the Earth's magnetosphere. Lightning energy entering the ionosphere at higher latitudes reaches the magnetosphere as a different type of whistler called a magnetospherically reflected whistler, which undergoes one or more reflections within the magnetosphere. Earth's magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding the planet and created by Earth's magnetic field. It provides a protective barrier that prevents most of the solar wind's particles from reaching the atmosphere and harming life and technology. The ionosphere is a layer of Earth's upper atmosphere characterized by a high concentration of ions and free electrons. It is ionized by solar radiation and cosmic rays, making it conductive and crucial for radio communication because it reflects and modifies radio waves.
Charge Conservation is the principle that the total electric charge in an isolated system never changes. The net quantity of electric charge, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge in the universe, is always conserved. Charge conservation, considered as a physical conservation law, implies that the change in the amount of electric charge in any volume of space is exactly equal to the amount of charge flowing into the volume minus the amount of charge flowing out of the volume. This does not mean that individual positive and negative charges cannot be created or destroyed. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles such as electrons and protons. Charged particles can be created and destroyed in elementary particle reactions. In particle physics, charge conservation means that in reactions that create charged particles, equal numbers of positive and negative particles are always created, keeping the net amount of charge unchanged. Similarly, when particles are destroyed, equal numbers of positive and negative charges are destroyed. This property is supported without exception by all empirical observations so far. Although conservation of charge requires that the total quantity of charge in the universe is constant, it leaves open the question of what that quantity is. Most evidence indicates that the net charge in the universe is zero; that is, there are equal quantities of positive and negative charge.
Storms - Strong Winds
Storms is any disturbed state of an environment or astronomical body's atmosphere especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), heavy precipitation (snowstorm, rainstorm), heavy freezing rain (ice storm), strong winds (tropical cyclone, windstorm), or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere as in a dust storm, blizzard, sandstorm, etc. Storms have the potential to harm lives and property via storm surge, heavy rain or snow causing flooding or road impassibility, lightning, wildfires, and vertical wind shear; however, systems with significant rainfall and duration help alleviate drought in places they move through. Heavy snowfall can allow special recreational activities to take place which would not be possible otherwise, such as skiing and snowmobiling.
Cyclones is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including Hurricane, typhoon, tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, and simply cyclone. A hurricane is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean and northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean; while in the south Pacific or Indian Ocean, comparable storms are referred to simply as “tropical cyclones” or “severe cyclonic storms”.
Flooding - Earth Magnetics - Earthquake Tsunamis
Hurricanes originating in the northern hemisphere rotate counterclockwise. And those developing in the southern hemisphere spin in a clockwise direction. Hurricanes don't cross the equator because at the equator the Coriolis effect is nearly zero, which means there's not enough twist to fuel a hurricane. The effect of Earth's rotation causes moving air to twist in a circular motion.
Dropwindsondes are deployed from the aircraft and drift down on a parachute measuring vertical profiles of pressure, temperature, humidity and wind as they fall.
Explosive Cyclogenesis or weather bomb, meteorological bomb, explosive development, or bombogenesis, refers in a strict sense to a rapidly deepening extratropical cyclonic low-pressure area. To enter this category, the central pressure of a depression at 60° latitude is required to decrease by 24 mb (hPa) or more in 24 hours. This is a predominantly maritime, winter event, but also occurs in continental settings. This process is the extratropical equivalent of the tropical rapid deepening.
Tornados is a rapidly rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as twisters, whirlwinds or cyclones, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often visible in the form of a condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than 110 miles per hour (180 km/h), are about 250 feet (80 m) across, and travel a few miles (several kilometers) before dissipating. The most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of more than 300 miles per hour (480 km/h), are more than two miles (3 km) in diameter, and stay on the ground for dozens of miles (more than 100 km).
Waterspout is an intense columnar vortex usually appearing as a funnel-shaped cloud that occurs over a body of water. Some are connected to a cumulus congestus cloud, some to a cumuliform cloud and some to a cumulonimbus cloud.
Steam Devil is a small, weak whirlwind over water or sometimes wet land that has drawn fog into the vortex, thus rendering it visible.
Landspout is a term for a kind of tornado not associated with a mesocyclone
Dust Devil is a strong, well-formed, and relatively short-lived whirlwind. Its size ranges from small (half a metre wide and a few metres tall) to large (more than 10 m wide and more than 1 km tall). The primary vertical motion is upward. Dust devils are usually harmless, but can on rare occasions grow large enough to pose a threat to both people and property. Dust Devils form when hot air at the surface begins to rise rapidly with much cooler air above it and higher up into the atmosphere. The hot air then stretches and causes a spinning motion much like a tornado.
Whirlwind is a weather phenomenon in which a vortex of wind or a vertically oriented rotating column of air, forms due to instabilities and turbulence created by heating and flow or current gradients. Whirlwinds occur all over the world and in any season.
Mesocyclone is a meso-gamma mesoscale (or storm scale) region of rotation (vortex), typically around 2 to 6 mi (3.2 to 9.7 km) in diameter, most often noticed on radar within thunderstorms. Mesocyclones are medium-scale vortices of rising and converging air that circulate around a vertical axis. They are most often associated with a local region of low-pressure. Their rotation is (usually) in the same direction as low pressure systems in a given hemisphere: counter-clockwise in the northern, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, with the only occasional exceptions being the smallest-scale mesocyclones. Meso Anticyclones that rotate in an opposite direction may accompany mesocyclones within a supercell but these tend to be weaker and often more transient than mesocyclones, which can be sustained for tens of minutes or hours, and also cyclically form in succession within a supercell.
Mesoscale Meteorology is the study of weather systems smaller than synoptic-scale systems but larger than microscale and storm-scale cumulus systems. Horizontal dimensions generally range from around 5 kilometres (3 mi) to several hundred kilometers. Examples of mesoscale weather systems are sea breezes, squall lines, and mesoscale convective complexes. Mesoscale Meteorology is divided into these subclasses: Meso-alpha 200–2000 km scale of phenomena like fronts, squall lines, mesoscale convective systems (MCS), tropical cyclones at the edge of synoptic scale. Meso-beta 20–200 km scale of phenomena like sea breezes, lake effect snow storms. Meso-gamma 2–20 km scale of phenomena like thunderstorm convection, complex terrain flows (at the edge to microscale, also known as storm-scale).
Weather Prediction Services
Rain (floods) - Volcanoes - Fires
Scientific Modeling Atmosphere Composition Diagram (image)
"Red Sky at Night, Sailors' Delight. Red Sky at Morning, Sailors take Warning" is a rhyme that was used as an unreliable type of weather forecasting during the past two millennia. It's based on the reddish glow of the morning or evening sky, caused by haze or clouds related to storms in the region. If the morning skies are red, it is because clear skies over the horizon to the east permit the sun to light the undersides of moisture-bearing clouds. The saying assumes that more such clouds are coming in from the west. Conversely, in order to see red clouds in the evening, sunlight must have a clear path from the west, so therefore the prevailing westerly wind must be bringing clear skies. There are occasions where a storm system might rain itself out before reaching the observer (who had seen the morning red sky). For ships at sea however, the wind and rough seas from an approaching storm system could still be a problem, even without rainfall. Because of different prevailing wind patterns around the globe, the traditional rhyme is generally not correct at lower latitudes of both hemispheres, where prevailing winds are from east to west. The rhyme is generally correct at mid-latitudes where, due to the rotation of the Earth, prevailing winds travel west to east.
Earth also has other natural occurring events that sometimes causes major problems, and death. Causes of Death - Extinctions - Plant Diseases - Invasive Species.
There are also other events that threaten us that can be avoided. Pollution - Climate Change - Viruses - Disease - War - Crimes.
Earth Quakes
Earthquake is the shaking of the surface of the Earth, resulting from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in size from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt to those violent enough to toss people around and destroy whole cities. The seismicity or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.
Meteoroids - Volcanoes - Geoology
Shaking is the act of causing something to move up and down or back and forth or sideways with quick movements. Vibrate rapidly and intensively. Excite the feelings or emotions of or to disturb the peace.
Tremor is a small earthquake with shaking or trembling. Rumble is a loud low dull continuous noise or sound.
Seismometer or seismograph is an instrument that measures motion of the ground, caused by, for example, an earthquake, a volcanic eruption, or the use of explosives. Records of Seismic Waves allow seismologists to map the interior of the Earth and to locate and measure the size of events like these.
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. Seismic Tomography.
Zhang Heng Zhang's Seismoscope was made around 91 BC that in 780 BC. Sand-Tracing Pendulum is a pointed weight at the end of a long wire suspended over a tray of sand. The vibrations of the quake produced an intricate, rose-like shape in the sand.
Measuring the tempo of Utah's red rock towers. Geologists know well how rock towers and arches shimmy, twist and sway in response to far-off earthquakes, wind and even ocean waves. Their latest research compiles a first-of-its-kind dataset to show that the dynamic properties, i.e. the frequencies at which the rocks vibrate and the ways they deform during that vibration, can be largely predicted using the same mathematics that describe how beams in built structures resonate.
Earthquake Resistant Building Techniques.
Earth may be the only planet in our solar system with plate tectonics, which move 2 CM's a year.
Plate Tectonics is a scientific theory describing the large-scale motion of seven large plates and the movements of a larger number of smaller plates of the Earth's lithosphere, since tectonic processes began on Earth between 3 and 3.5 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted plate-tectonic theory after seafloor spreading was validated in the late 1950s and early 1960s. List of 15 Tectonic Plates (wiki).
Subduction is a geological process that takes place at convergent boundaries of tectonic plates where one plate moves under another and is forced or sinks due to gravity into the mantle. Regions where this process occurs are known as subduction zones. Rates of subduction are typically in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Sinking Land.
Fault in geology is a crack in the earth's crust resulting from the displacement of one side with respect to the other. A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake - or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers. Most faults produce repeated displacements over geologic time. Earthquakes occur on faults - strike-slip earthquakes occur on strike-slip faults, normal earthquakes occur on normal faults, and thrust earthquakes occur on reverse or thrust faults. When an earthquake occurs on one of these faults, the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other. The fault surface can be vertical, horizontal, or at some angle to the surface of the earth. A Quaternary fault is one that has been recognized at the surface and that has moved in the past 1,600,000 years (1.6 million years). That places fault movement within the Quaternary Period, which covers the last 2.6 million years. Fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A fault plane is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A fault trace or fault line is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A fault zone is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the distinction, as the rock between the faults is converted to fault-bound lenses of rock and then progressively crushed.
Find the nearest fault to a property or specific location.
Rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. Failed rifts are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to the point of seafloor spreading, while the third ultimately fails, becoming an aulacogen.
Divergent Boundary is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys. Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges. Divergent boundaries also form volcanic islands, which occur when the plates move apart to produce gaps that molten lava rises to fill. Current research indicates that complex convection within the Earth's mantle allows material to rise to the base of the lithosphere beneath each divergent plate boundary. This supplies the area with vast amounts of heat and a reduction in pressure that melts rock from the asthenosphere (or upper mantle) beneath the rift area, forming large flood basalt or lava flows. Each eruption occurs in only a part of the plate boundary at any one time, but when it does occur, it fills in the opening gap as the two opposing plates move away from each other. Over millions of years, tectonic plates may move many hundreds of kilometers away from both sides of a divergent plate boundary. Because of this, rocks closest to a boundary are younger than rocks further away on the same plate.
Lithospheric Foundering is a process where a portion of the lithosphere sinks into the mantle. It's a mechanism that contributes to the formation of continental plateaus, mountain belts, and basins.
Lithosphere is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite.
Foundered Strata describes rock strata which have collapsed due, for example, to the dissolution of underlying strata. Foundered strata may retain original bedding more or less intact or they may assume a chaotic structure in the process of collapse or some intermediate state of disruption.
Delamination refers to the loss and sinking or foundering of the portion of the lowermost lithosphere from the tectonic plate to which it was attached.
Seafloor Spreading is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
Mid-Ocean Ridge is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of ~ 2,600 meters (8,500 ft) and rises about two kilometers above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean ridges. Mid-ocean ridges around the globe are linked by plate tectonic boundaries and the trace of the ridges across the ocean floor appears similar to the seam of a baseball. The mid-ocean ridge system thus is the longest mountain range on Earth, reaching about 65,000 km (40,000 mi). An oceanic spreading ridge is the fracture zone along the ocean bottom where molten mantle material comes to the surface, thus creating new crust. This fracture can be seen beneath the ocean as a line of ridges that form as molten rock reaches the ocean bottom and solidifies.
There are several million Earthquakes occurring in the world each year, mostly low in magnitude. There are 14,000 earthquakes of magnitude 4 or greater every year, approximately 40 per day. The total Number of Earthquakes per year with 8 or Higher Magnitude is only 1. Between 7-7.9 is 18, 6-6.9 is 120, 5-5.9 is 800, 4-4.9 6 is 200, 3-3.9 is 49,000. The Largest Recorded Earthquake in the World is 9.5 on the Richter Scale.
P-wave are a type of elastic wave, and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology, that travel through a continuum and are the first waves from an earthquake to arrive at a seismograph. The continuum is made up of gases (as sound waves), liquids, or solids, including the Earth. P-waves can be produced by earthquakes and recorded by seismographs. The name P-wave can stand for either pressure wave as it is formed from alternating compressions and rarefactions or primary wave, as it has the highest velocity and is therefore the first wave to be recorded. Waves - S-wave (wiki).
G Plates interactive plate-tectonic reconstructions.
Earth Byte geodata synthesis through space and time, assimilating the wealth of disparate geological and geophysical data into a four-dimensional Earth model including tectonics, geodynamics and surface processes.
Episodic Tremor and Slip is a seismological phenomenon observed in some subduction zones that is characterized by non-earthquake seismic rumbling, or tremor, and slow slip along the plate interface. Slow slip events are distinguished from earthquakes by their propagation speed and focus. In slow slip events, there is an apparent reversal of crustal motion, although the fault motion remains consistent with the direction of subduction. ETS events themselves are imperceptible to human beings and do not cause damage.
Slow Earthquake is a discontinuous, earthquake-like event that releases energy over a period of hours to months, rather than the seconds to minutes characteristic of a typical earthquake. First detected using long term strain measurements, most slow earthquakes now appear to be accompanied by fluid flow and related tremor, which can be detected and approximately located using seismometer data filtered appropriately (typically in the 1–5 Hz band). That is, they are quiet compared to a regular earthquake, but not "silent" as described in the past. Slow earthquakes should not be confused with tsunami earthquakes, in which relatively slow rupture velocity produces tsunami out of proportion to the triggering earthquake. In a tsunami earthquake, the rupture propagates along the fault more slowly than usual, but the energy release occurs on a similar timescale to other earthquakes.
Tsunami Earthquake triggers a tsunami of a magnitude that is very much larger than the magnitude of the earthquake as measured by shorter-period seismic waves. The term was introduced by Hiroo Kanamori in 1972. Such events are a result of relatively slow rupture velocities. They are particularly dangerous as a large tsunami may arrive at a coastline with little or no warning. A tsunami is a sea wave of local or distant origin that results from large-scale seafloor displacements associated with large earthquakes, major submarine slides, or exploding volcanic islands. Floods.
Disaster Monitoring - Emergencies - Where to Live? (the right location)
Tide Gauges Capture Tremor Episodes in Cascadian Subduction Zone. Cascadia Subduction Zone is a convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States.
Volcanoes
 Volcano is a rupture in the crust of a
planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows
hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below
the surface. Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17
major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a
hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on
Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging
or converging, and most are found underwater. Earth's volcanoes occur
because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that
float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. 70 to 90% of all
Volcanic Activity occurs under the ocean.
About 70% of the Volcanism on Earth occurs Underwater. (mid
ocean ridge, mantel plum, subduction zone).
Why China's
Largest Volcano Is So Unusual (youtube).
Volcano is a rupture in the crust of a
planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows
hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below
the surface. Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17
major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a
hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on
Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging
or converging, and most are found underwater. Earth's volcanoes occur
because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that
float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. 70 to 90% of all
Volcanic Activity occurs under the ocean.
About 70% of the Volcanism on Earth occurs Underwater. (mid
ocean ridge, mantel plum, subduction zone).
Why China's
Largest Volcano Is So Unusual (youtube).Shield Volcano is a type of volcano usually composed almost entirely of fluid lava flows. It is named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid (low viscosity) lava erupted, which travels farther than lava erupted from a stratovolcano, and results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes are distinguished from the three other major volcanic archetypes—stratovolcanoes, lava domes, and cinder cones—by their structural form, a consequence of their unique magmatic composition. Largest and hottest shield volcano on Earth.
There are around 20 known Super-Volcanoes on Earth, with major eruptions occurring on average once every 100,000 years. One of the greatest threats an eruption may pose is thought to be starvation, with a prolonged volcanic winter potentially prohibiting civilisation from having enough food for the current population. In 2012, the United Nations estimated that food reserves worldwide would last 74 days. But if more of the heat could be extracted, then the supervolcano would never erupt. Nasa estimates that if a 35% increase in heat transfer could be achieved from its magma chamber, Yellowstone would no longer pose a threat. Geothermal Energy - Volcanic Lightning.
Mount Tambora 1815 Eruption on the Indonesian island of Sumbawa was one of the most powerful eruptions in recorded history, with a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 7. Causing the Year Without a Summer, which is a volcanic winter event caused by the massive 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora leaving 100,000 dead. Little Ice Age are cold intervals: one beginning about 1650, another about 1770, and the last in 1850. Medieval Warm Period 950 to c.1250. Krakatoa (wiki) - Mount Vesuvius (wiki) - Mount Pelée (wiki).
Largest Volcanic Eruptions. In a volcanic eruption, lava, volcanic bombs and ash, and various gases are expelled from a volcanic vent and fissure. While many eruptions only pose dangers to the immediately surrounding area, Earth's largest eruptions can have a major regional or even global impact, with some affecting the climate and contributing to mass extinctions. Volcanic eruptions can generally be characterized as either explosive eruptions, sudden ejections of rock and ash, or effusive eruptions, relatively gentle outpourings of lava. A separate list is given below for each type. Volcanic Eruptions by Death Toll (wiki).
Volcanic Winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by volcanic ash and droplets of sulfuric acid and water obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, particularly explosive volcanic eruption. Long-term cooling effects are primarily dependent upon injection of sulfur gasses into the stratosphere where they undergo a series of reactions to create sulfuric acid which can nucleate and form aerosols. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols cool the surface by reflecting solar radiation and warm the stratosphere by absorbing terrestrial radiation. The variations in atmospheric warming and cooling result in changes in tropospheric and stratospheric circulation.
Lava is molten or partially molten rock or magma that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from 800 to 1,200 °C (1,470 to 2,190 °F). The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called lava.
Molten State describes an object that's reduced to liquid form by heating. When an element or compound is melted, to achieve a liquid state, it is called molten.
Seafloor Volcano Pulses may Alter Climate.
Ring of Fire has 90% of all Earthquakes, and the ring is dotted with 75% of all active Volcanoes on Earth. The Ring of Fire isn’t quite a circular ring. It is shaped more like a 40,000-kilometer (25,000-mile) horseshoe. A string of 452 volcanoes stretches from the southern tip of South America, up along the coast of North America, across the Bering Strait, down through Japan, and into New Zealand. Several active and dormant volcanoes in Antarctica, however, “close” the ring. A convergent plate boundary is formed by tectonic plates crashing into each other. Convergent boundaries are often subduction zones, where the heavier plate slips under the lighter plate, creating a deep trench. This subduction changes the dense mantle material into buoyant magma, which rises through the crust to the Earth’s surface. Over millions of years, the rising Magma creates a series of active volcanoes known as a volcanic arc. The Aleutian Trench reaches a maximum depth of 7,679 meters (25,194 feet). The Aleutian Islands have 27 of the United States’ 65 historically active volcanoes. A divergent boundary is formed by tectonic plates pulling apart from each other. Divergent boundaries are the site of seafloor spreading and rift valleys. Seafloor spreading is the process of Magma welling up in the rift as the old crust pulls itself in opposite directions. Cold seawater cools the magma, creating new crust. The upward movement and eventual cooling of this magma has created high ridges on the ocean floor over millions of years. The San Andreas Fault, stretching along the central west coast of North America, is one of the most active faults on the Ring of Fire. Seismic Tomography.
Moving 'hotspot' created world's longest straight underwater mountain belt. New research has revealed that the Ninetyeast Ridge -- the Earth's longest straight underwater mountain chain -- formed through a different process than previously believed. Stretching 5000 km along the Indian Ocean's 90-degree east longitude and nearly matching the length of North America's Rocky Mountains, the ridge offers crucial new insights into the movement of the Earth's tectonic plates.
Alaska contains over 130 volcanoes and volcanic fields which have been active within the last two million years.
Flood Basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reaching the surface of the earth via a mantle plume. Flood basalt provinces such as the Deccan Traps of India are often called traps, after the Swedish word trappa (meaning "stairs"), due to the characteristic stairstep geomorphology of many associated landscapes. Extinctions.
Volcanic Rock is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano.
Mantle Plume is a proposed mechanism of convection of abnormally hot rock within the Earth's mantle. Because the plume head partly melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii or Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan and Siberian traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries.
Siberian Traps is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest known volcanic events in the last 500 million years. The eruptions continued for roughly two million years and spanned the Permian–Triassic boundary, or P–T boundary, which occurred between 251 to 250 million years ago. Large volumes of basaltic lava covered a large expanse of Siberia in a flood basalt event. Today, the area is covered by about 7 million km2 (3 million sq mi) of basaltic rock, with a volume of around 4 million km3 (1 million cu mi).
Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). They are one of the largest volcanic features on Earth. They consist of multiple layers of solidified flood basalt that together are more than 2,000 m (6,600 ft) thick, cover an area of c. 500,000 km2 (200,000 sq mi), and have a volume of c. 1,000,000 km3 (200,000 cu mi). Originally, the Deccan Traps may have covered c. 1,500,000 km2 (600,000 sq mi), with a correspondingly larger original volume.
Efficient removal of recalcitrant deep-ocean dissolved organic matter during hydrothermal circulation.
New Lava Flows at Axial Seamount are Confirmed Axial Seamount eruption of April 2015 confirmed.
Submarine Volcanoes could Power a Continent. Volcanic eruptions deep in our oceans are capable of extremely powerful releases of energy, at a rate high enough to power the whole of the United States, according to new research.
Deep learning artificial intelligence keeps an eye on volcano movements. Radar satellites can collect massive amounts of remote sensing data that can detect ground movements -- surface deformations -- at volcanoes in near real time. These ground movements could signal impending volcanic activity and unrest; however, clouds and other atmospheric and instrumental disturbances can introduce significant errors in those ground movement measurements. Now, researchers have used artificial intelligence (AI) to clear up that noise, drastically facilitating and improving near real-time observation of volcanic movements and the detection of volcanic activity and unrest.
Oceans
Ocean is a body of water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), and Arctic Oceans. The phrases "the ocean" or "the sea" used without specification refer to the interconnected body of salt water covering the majority of the Earth's surface. As a general term, "the ocean" is mostly interchangeable with "the sea" in American English, but not in British English. Strictly speaking, a sea is a body of water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land. Saline seawater covers approximately 361,000,000 km2 (139,000,000 sq mi) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface and 90% of the Earth's biosphere. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water, and oceanographers have stated that less than 20% of the World Ocean has been mapped. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft). As the world ocean is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, it is integral to life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. The World Ocean is the habitat of 230,000 known species, but because much of it is unexplored, the number of species that exist in the ocean is much larger, possibly over two million. The origin of Earth's oceans is unknown; oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean eon and may have been the cause for the emergence of life. Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for the existence of oceans elsewhere in the Solar System. Early in their geologic histories, Mars and Venus are theorized to have had large water oceans. The Mars ocean hypothesis suggests that nearly a third of the surface of Mars was once covered by water, and a runaway greenhouse effect may have boiled away the global ocean of Venus. Compounds such as salts and ammonia dissolved in water lower its freezing point so that water might exist in large quantities in extraterrestrial environments as brine or convecting ice. Unconfirmed oceans are speculated beneath the surface of many dwarf planets and natural satellites; notably, the ocean of the moon Europa is estimated to have over twice the water volume of Earth. The Solar System's giant planets are also thought to have liquid atmospheric layers of yet to be confirmed compositions. Oceans may also exist on exoplanets and exomoons, including surface oceans of liquid water within a circumstellar habitable zone. Ocean planets are a hypothetical type of planet with a surface completely covered with liquid.
Ocean Protection - Aquariums - Marine Ecosystems - Cargo Ships
Earths Deepest Part of the Ocean is the Mariana Trench. 7 Miles Deep in the western Pacific Ocean, to the east of the Mariana Islands. The trench is about 2,550 kilometres (1,580 mi) long with an average width of 69 kilometres (43 mi). It reaches a maximum-known depth of 10,994 metres (36,070 ft) (± 40 metres [130 ft]) at a small slot-shaped valley in its floor known as the Challenger Deep, at its southern end, although some unrepeated measurements place the deepest portion at 11,034 metres (36,201 ft). It is a subduction zone where one tectonic plate moves under another and is forced or sinks due to gravity into the mantle. Producing mostly mud volcano's that produce no lava with very little earth quakes.
Sea Level is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change.
Intertidal Zone is the area where the ocean meets the land between high tide and the low tide. The foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide, or the part of a shore between the high-water marks and the low-water marks, or between the water and the cultivated or developed land. Also known as the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. The Littoral Zone is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore, or the shallow down-sloping shelf of a lake or pond that is commonly referred to as the lake's littoral zone.
Pressure in the ocean increases by about 1 atmosphere for every 10 meters of depth. At the average ocean depth of 3,800 meters, pressure on the sea floor is a whopping 380 times greater than it is at the surface, and in the deepest trenches, it's 1,100 times greater. All that pressure causes serious problems for people and other air-breathing animals. Deep sea fish don't have air sacs in their bodies, which means they don't get crushed from pressure. Fish living closer to the surface of the ocean may have a swim bladder – that's a large organ with air in it, which helps them float up or sink down in the water.
Lakes and Oceans Depth Chart (image) - Earths Highest Lowest Points (image)
What Is Sea Level, Anyway? (youtube)
The Oceans contain 99% of the living space on the planet with an estimated 50-80% of all Life on Earth being found under the ocean surface with 2/3's not even identified, and scientists estimate that 91 percent of ocean species have not yet been classified, and 95 percent of the ocean still remains unexplored, and 85% of the area and 90% of the volume constitute the dark, cold environment we call the deep sea. The global scientific community continues to amass as much knowledge as possible about ocean life. Our Planet.
Hydrothermal Vent is a fissure on the seafloor from which geothermally heated water issues. Hydrothermal vents are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at spreading centers, ocean basins, and hotspots. Hydrothermal deposits are rocks and mineral ore deposits formed by the action of hydrothermal vents. Hydrothermal vents exist because the earth is both geologically active and has large amounts of water on its surface and within its crust. Under the sea, hydrothermal vents may form features called black smokers or white smokers. Relative to the majority of the deep sea, the areas around submarine hydrothermal vents are biologically more productive, often hosting complex communities fueled by the chemicals dissolved in the vent fluids. Chemosynthetic bacteria and archaea form the base of the food chain, supporting diverse organisms, including giant tube worms, clams, limpets and shrimp. Active hydrothermal vents are believed to exist on Jupiter's moon Europa, and Saturn's moon Enceladus, and it is speculated that ancient hydrothermal vents once existed on Mars. Extremophiles.
Fissure Vent is a linear volcanic vent through which lava erupts, usually without any explosive activity. The vent is often a few metres wide and may be many kilometres long. Fissure vents can cause large flood basalts which run first in lava channels and later in lava tubes. After some time the eruption builds up spatter cones and may concentrate on one or some of them.
Artificial Intelligence can identify Microscopic Marine Organisms. Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) program that can automatically provide species-level identification of Microscopic Marine Organisms. The next step is to incorporate the AI into a robotic system that will help advance our understanding of the world's oceans, both now and in our prehistoric past. Marine Habitats (wiki).
Chemotroph are organisms that obtain energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments.
Subterranean Biosphere exploring microbial life that populates the lower boundary of the deep sedimentary biosphere.
Ocean Biodiversity work needs improvement. An international collaboration says the world's largest marine protected areas aren't collectively delivering the biodiversity benefits they could be because of slow implementation of management strategies and a failure to restrict the most impactful human activities.
Deep Ocean - Organisms - Discovering the Deep
Scientists uncover ocean's intricate web of microbial interactions across depths. This research marks a significant advance in our understanding of how microbial interactions in the ocean's vast ecosystems operate across different depths and regions, and understanding the key role of marine microscopic microorganisms in the cycling of various nutrients and carbon fixation, as well as in the functioning of marine food webs in general.
Ocean Current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. Ocean currents flow for great distances, and together, create the global conveyor belt which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of the Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate than any other region at the same latitude. Another example is Lima, Peru, where the climate is cooler, being sub-tropical, than the tropical latitudes in which the area is located, due to the effect of the Humboldt Current. Internal Waves.
Eddy is a circular current of water. The ocean is a huge body of water that is constantly in motion. General patterns of ocean flow are called currents. Sometimes theses currents can pinch off sections and create circular currents of water called an eddy. Significant eddies are assigned names similar to hurricanes. In the U.S., an oceanographic company called Horizon Marine assigns names to each eddy as they occur. The names follow chronologically along with the alphabet and are decided upon by staff at Horizon Marine. The staff try to think of creative ways to assign names. The swirling motion of eddies in the ocean cause nutrients that are normally found in colder, deeper waters to come to the surface. Here, phytoplankton (tiny ocean plants) feeding on these nutrients color the water beautiful shades of blue and green. You may have seen an eddy if you've ever gone canoeing and you see a small whirlpool of water while you paddle through the water.
El Ninos is a warm ocean current that flows along the equator from the date line and south off the coast of Ecuador at Christmas time. The warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (between approximately the International Date Line and 120°W), including the area off the Pacific coast of South America. The ENSO is the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean. El Niño is accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific. El Niño phases are known to occur close to four years, however, records demonstrate that the cycles have lasted between two and seven years. During the development of El Niño, rainfall develops between September–November. The cool phase of ENSO is La Niña, with SSTs in the eastern Pacific below average, and air pressure high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific. The ENSO cycle, including both El Niño and La Niña, causes global changes in temperature and rainfall.
La Ninas is the positive and cold phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, and is associated with cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. A coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of El Niño, as part of the broader El Niño–Southern Oscillation climate pattern. During a period of La Niña, the sea surface temperature across the equatorial Eastern Central Pacific Ocean will be lower than normal by 3 to 5°C (5.4 to 9°F). An appearance of La Niña persists for at least five months. It has extensive effects on the weather across the globe, particularly in North America, even affecting the Atlantic and Pacific hurricane seasons.
Ocean Surface Current is when water at the ocean surface is moved primarily by winds that blow in certain patterns because of the Earth's spin and the Coriolis Effect. Winds are able to move the top 400 meters of the ocean creating surface ocean currents. Surface ocean currents form large circular patterns called gyres.
Deep Ocean Currents are driven by density and temperature gradients. Thermohaline circulation is also known as the ocean's conveyor belt (which refers to deep ocean density-driven ocean basin currents). These currents, called submarine rivers, flow under the surface of the ocean and are hidden from immediate detection.
Antarctic Circumpolar Current is the most powerful ocean current on the planet. The Circumpolar Current works as a regulator of the planet's climate. Its origins were thought to have caused the formation of the permanent ice in Antarctica about 34 million years ago. Now, a study has cast doubt on this theory, and has changed the understanding of how the ice sheet in Antarctic developed in the past, and what this could mean in the future as the planet's climate changes. AMOC is the main current system in the South and North Atlantic Oceans. It is a component of Earth's oceanic circulation system and plays an important role in the climate system. The AMOC includes currents at the surface as well as at great depths in the Atlantic Ocean. These currents are driven by changes in the atmospheric weather as well as by changes in temperature and salinity. They collectively make up one half of the global thermohaline circulation that encompasses the flow of major ocean currents. The other half is the Southern Ocean overturning circulation.
Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century. Important ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist. This is the conclusion based on new calculations that contradict the latest report from the IPCC. Using advanced statistical tools and ocean temperature data from the last 150 years, the researchers calculated that the ocean current, known as the Thermohaline Circulation or the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), will collapse -- with 95 percent certainty -- between 2025 and 2095. This will most likely occur in 34 years, in 2057, and could result in major challenges, particularly warming in the tropics and increased storminess in the North Atlantic region.
Coriolis Force is an inertial or fictitious force that seems to act on objects that are in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise (or counterclockwise) rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect.
Ocean Gyre is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity along with horizontal and vertical friction, determine the circulation patterns from the wind stress curl (torque). The term gyre can be used to refer to any type of vortex in the air or the sea, even one that is man-made, but it is most commonly used in oceanography to refer to the major ocean systems.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is the zonally-integrated component of surface and deep currents in the Atlantic Ocean. It is characterized by a northward flow of warm, salty water in the upper layers of the Atlantic, and a southward flow of colder, deep waters that are part of the thermohaline circulation. These "limbs" are linked by regions of overturning in the Nordic and Labrador Seas and the Southern Ocean. The AMOC is an important component of the Earth's climate system, and is a result of both atmospheric and thermohaline drivers. It moves around 6 mph and can be as far as 3,000 feet deep in some areas.
Shutdown of Thermohaline Circulation is a hypothesized effect of global warming on a major ocean circulation. A 2015 study suggested that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) has weakened by 15-20% in 200 years.
Thermohaline Circulation is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective thermohaline derives from thermo- referring to temperature and -haline referring to salt content, factors which together determine the density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling en route, and eventually sinking at high latitudes (forming North Atlantic Deep Water). This dense water then flows into the ocean basins. While the bulk of it upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of around 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific. Extensive mixing therefore takes place between the ocean basins, reducing differences between them and making the Earth's oceans a global system. On their journey, the water masses transport both energy (in the form of heat) and mass of substances (solids, dissolved substances and gases) around the globe. As such, the state of the circulation has a large impact on the climate of the Earth. The thermohaline circulation is sometimes called the Ocean Conveyor Belt, the great ocean conveyor, or the global conveyor belt. On occasion, it is used to refer to the meridional overturning circulation (often abbreviated as MOC). The term MOC is more accurate and well defined, as it is difficult to separate the part of the circulation which is driven by temperature and salinity alone as opposed to other factors such as the wind and tidal forces. Moreover, temperature and salinity gradients can also lead to circulation effects that are not included in the MOC itself.
New study maps how ocean currents connect the world's fisheries. The ocean is made up of highly interconnected networks where most countries depend on their neighbors to properly manage their own fisheries. Understanding the nature of this network is an important step toward more effective fishery management, and is essential for countries whose economies and food security are reliant on fish born elsewhere. The vast majority of the world's wild-caught marine fish, an estimated 90%, are caught within 200 miles of shore, within national jurisdictions.
Biological Pump is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments. It is the part of the oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). The biological pump is not so much the result of a single process, but rather the sum of a number of processes each of which can influence biological pumping.
Slowing ocean current could ease Arctic warming -- a little. Weaker AMOC could transport less heat to higher latitudes. The Arctic is warming at three to four times the global average. However, new research suggests the slowing of a key ocean current could reduce projected Arctic warming by up to 2 degrees Celsius by the end of the century.
Mesopelagic Zone or Twilight Zone is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1000 meters (~660 to 3,300 feet) below the ocean surface. It hosts a diverse biological community that includes bristlemouths, blobfish, bioluminescent jellyfish, giant squid, and a myriad of other unique organisms adapted to live in a low-light environment. It has long captivated the imagination of scientists, artists and writers; deep sea creatures are prominent in popular culture, particularly as horror movie villains.
West Coast Ocean Acidification and Hypoxia Science Panel.
Oregon Coordinating Council on Ocean Acidification and Hypoxia.
Ocean color satellites reveal glacier algae, insights for climate models.
Environmental concerns propel research into marine biofuels.
Pole of Inaccessibility is a location in the pacific ocean that is the most challenging to reach. Often it refers to the most distant point from the coastline. Pole of inaccessibility can be defined as the center of the largest circle that can be drawn within an area of interest without encountering a coast. Where a coast is imprecisely defined, the pole will be similarly imprecise.
First direct observation of the trapped waves that shook the world in 2023. A new study has finally confirmed the theory that the cause of extraordinary global tremors in September -- October 2023 was indeed two mega tsunamis in Greenland that became trapped standing waves. Using a brand-new type of satellite altimetry, the researchers provide the first observations to confirm the existence of these waves whose behavior is entirely unprecedented. Seiches are a type of trapped wave that can occur in fjords, bays, or other enclosed bodies of water. They are formed when the water surface oscillates back and forth due to the trapped waves, as observed in the Dickson Fjord in East Greenland.
Fire
 The photo on right is the number of
fires burning on earth, as seen at night.
Earth Observatory.
The photo on right is the number of
fires burning on earth, as seen at night.
Earth Observatory.Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. Fire is hot because the conversion of the weak double bond in molecular oxygen, O2, to the stronger bonds in the combustion products carbon dioxide and water releases energy (418 kJ per 32 g of O2); the bond energies of the fuel play only a minor role here. At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are produced. The flame is the visible portion of the fire. Flames consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce plasma. Depending on the substances alight, and any impurities outside, the color of the flame and the fire's intensity will be different. Fire in its most common form can result in conflagration, which has the potential to cause physical damage through burning. Fire is an important process that affects ecological systems around the globe. The positive effects of fire include stimulating growth and maintaining various ecological systems. Its negative effects include hazard to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water contamination. If fire removes protective vegetation, heavy rainfall may lead to an increase in soil erosion by water. Also, when vegetation is burned, the nitrogen it contains is released into the atmosphere, unlike elements such as potassium and phosphorus which remain in the ash and are quickly recycled into the soil. This loss of nitrogen caused by a fire produces a long-term reduction in the fertility of the soil, but this fecundity can potentially be recovered as molecular nitrogen in the atmosphere is "fixed" and converted to ammonia by natural phenomena such as lightning and by leguminous plants that are "nitrogen-fixing" such as clover, peas, and green beans. Fire has been used by humans in rituals, in agriculture for clearing land, for cooking, generating heat and light, for signaling, propulsion purposes, smelting, forging, incineration of waste, cremation, and as a weapon or mode of destruction. What Is Fire? (youtube) - Catalyst - 'Earth on Fire' 2014 (youtube) - Plasma - Aether
The Sun isn't made of fire. It's made mostly of hydrogen and helium. Its heat and light come from nuclear fusion, a very different process that doesn't require oxygen.
Fire Ecology is a scientific discipline concerned with natural processes involving fire in an ecosystem and the ecological effects, the interactions between fire and the abiotic and biotic components of an ecosystem, and the role of fire as an ecosystem process.
Fire Protection is the study and practice of mitigating the unwanted effects of potentially destructive fires. It involves the study of the behaviour, compartmentalisation, suppression and investigation of fire and its related emergencies, as well as the research and development, production, testing and application of mitigating systems. In structures, be they land-based, offshore or even ships, the owners and operators are responsible to maintain their facilities in accordance with a design-basis that is rooted in laws, including the local building code and fire code, which are enforced by the Authority Having Jurisdiction.
Fire Fighting - Red Flag Warning - Fire Investigations - Forests - Climate Change - Wood Stoves
Forest Fire is a fire in an area of combustible vegetation that occurs in the countryside or rural area. Depending on the type of vegetation where it occurs, a wildfire can also be classified more specifically as a brush fire, bush fire, desert fire, forest fire, grass fire, hill fire, peat fire, vegetation fire, or veld fire. Wind - Amazon Rain Forest.
Firestorm is a conflagration which attains such intensity that it creates and sustains its own wind system. It is most commonly a natural phenomenon, created during some of the largest bushfires and wildfires. Although the term has been used to describe certain large fires, the phenomenon's determining characteristic is a fire with its own storm-force winds from every point of the compass. The Black Saturday bushfires and the Great Peshtigo Fire are possible examples of forest fires with some portion of combustion due to a firestorm, as is the Great Hinckley Fire. Firestorms have also occurred in cities, usually as a deliberate effect of targeted explosives, such as occurred as a result of the aerial firebombings of Hamburg, Dresden, firebombing of Tokyo and the atomic bombing of Hiroshima.
Methane from megafires. Using a new detection method, scientists found a massive amount of methane, a super-potent greenhouse gas, coming from wildfires -- a source not currently being accounted for by California state air quality managers. Methane warms the planet 86 times more powerfully than carbon dioxide over the course of 20 years, and it will be difficult for the state to reach its required cleaner air and climate goals without accounting for this source, the researchers said.
Conflagration is a large and destructive fire that threatens human life, animal life, health, and/or property. It may also be described as a blaze or simply a (large) fire. A conflagration can begin accidentally, be naturally caused (wildfire), or intentionally created (arson). Arson can be for fraud, murder, sabotage or diversion, or due to a person's pyromania. A very large fire can produce a firestorm, in which the central column of rising heated air induces strong inward winds, which supply oxygen to the fire. Conflagrations can cause casualties including deaths or injuries from burns, trauma due to collapse of structures and attempts to escape, and smoke inhalation. Firefighting is the practice of attempting to extinguish a conflagration, protect life and property, and minimize damage and injury. One of the goals of fire prevention is to avoid conflagrations. When a conflagration is extinguished, there is often a fire investigation to determine the cause of the fire.
Wildfire is a fire in an area of combustible vegetation that occurs in the countryside or rural area. Depending on the type of vegetation where it occurs, a wildfire can also be classified more specifically as a brush fire, bush fire, desert fire, forest fire, grass fire, hill fire, peat fire, vegetation fire, or veld fire. Fossil charcoal indicates that wildfires began soon after the appearance of terrestrial plants 420 million years ago. Wildfire’s occurrence throughout the history of terrestrial life invites conjecture that fire must have had pronounced evolutionary effects on most ecosystems' flora and fauna. Earth is an intrinsically flammable planet owing to its cover of carbon-rich vegetation, seasonally dry climates, atmospheric oxygen, and widespread lightning and volcano ignition.
Fuel Reduction Program - California Wild Fires Map (google)
Salvaging Fire-Killed Trees - Reclaiming Timber after the Flames.
Fire Burned Trees - Letting Nature Heal itself doesn't always happen.
Earliest evidence of humans changing ecosystems with fire. A new study provides the earliest evidence to date of ancient humans significantly altering entire ecosystems with flames. The study combines archaeological evidence -- dense clusters of stone artifacts dating as far back as 92,000 years ago -- with paleoenvironmental data on the northern shores of Lake Malawi in eastern Africa to document that early humans were ecosystem engineers.
Burned area Emergency Response is an emergency risk management reaction to post wildfire conditions that pose risks to human life and property or could further destabilize or degrade the burned lands. Even though wildfires are natural events, the presence of people and man-made structures in and adjacent to the burned area frequently requires continued emergency risk management actions. High severity wildfires pose a continuing flood, debris flow and mudflow risk to people living within and downstream from a burned watershed as well as a potential loss of desirable watershed values.
Skyline System to Harvest Timber eliminates the need for kid trails because the logs are moved to the lending by an aerial cable (skyline). Consider the potential for erosion and possible alternative yarding systems before planning tractor skidding on steep or unstable slopes.
Skyline Logging harvested logs are transported on a suspended steel cable, a cableway or "highline", from various locations where the trees are felled to a central location, typically next to a road for logistical reasons.
American Forests - Emerald Ash Borer (tree deaths)
Forest Preservation (land trusts)
Dendrochronology Tree Ring Analysis - Laboratory of Tree-Ring Research at the University of Arizona
Spontaneous Human Combustion is a term encompassing reported cases of the combustion of a living (or very recently deceased) human body without an apparent external source of ignition. In addition to reported cases, examples of SHC appear in literature, and both types have been observed to share common characteristics regarding circumstances and remains of the victim. Forensic investigations have attempted to analyze reported instances of SHC and have resulted in hypotheses regarding potential causes and mechanisms, including victim behavior and habits, alcohol consumption and proximity to potential sources of ignition, as well as the behavior of fires that consume melted fats. Natural explanations, as well as unverified natural phenomena, have been proposed to explain reports of SHC. Current scientific consensus is that most, and conjectures perhaps all, cases of SHC involve overlooked external sources of ignition.
Wick Effect is the name given to the partial destruction of a human body by fire, when the clothing of the victim soaks up melted human fat and acts like the wick of a candle. The wick effect is a phenomenon that is found to occur under certain conditions, and has been thoroughly observed.
Pure Nature Features Deserts: Living in Extremes (2015 - 1 hr. 26 min.)
Amazing Experiment Actually Makes Black Fire! The Shadow Fire Experiment (youtube) - low pressure sodium vapor lamp - monochromatic light source.
Smoke
Smoke Inhalation is the primary cause of death for victims of fires. The inhalation or exposure to hot gaseous products of combustion can cause serious respiratory complications. Some 50–80% of fire deaths are the result of smoke inhalation injuries, including burns to the respiratory system. The hot smoke injures or kills by a combination of thermal damage, poisoning and pulmonary irritation and swelling, caused by carbon monoxide, cyanide and other combustion products.
Tobacco - Pollution - Smoke Levels Alert Map
Smoke is a collection of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires (including stoves, candles, oil lamps, and fireplaces), but may also be used for pest control (fumigation), communication (smoke signals), defensive and offensive capabilities in the military (smoke screen), cooking, or smoking (tobacco, cannabis, etc.). It is used in rituals where incense, sage, or resin is burned to produce a smell for spiritual purposes. Smoke is sometimes used as a flavoring agent, and preservative for various foodstuffs. Smoke is also a component of internal combustion engine exhaust gas, particularly diesel exhaust. Smoke inhalation is the primary cause of death in victims of indoor fires. The smoke kills by a combination of thermal damage, poisoning and pulmonary irritation caused by carbon monoxide, hydrogen cyanide and other combustion products. Smoke is an aerosol (or mist) of solid particles and liquid droplets that are close to the ideal range of sizes for Mie scattering of visible light. This effect has been likened to three-dimensional textured privacy glass — a smoke cloud does not obstruct an image, but thoroughly scrambles it.
Smoke from 2015 Indonesian Fires may have Caused 100,000 Premature Deaths.
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon in which dust, smoke, and other dry particulates obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic ash, dust, sand, and snow. Sources for haze particles include farming (ploughing in dry weather), traffic, industry, and wildfires. Seen from afar (e.g. an approaching airplane) and depending on the direction of view with respect to the Sun, haze may appear brownish or bluish, while mist tends to be bluish grey. Whereas haze often is thought of as a phenomenon of dry air, mist formation is a phenomenon of humid air. However, haze particles may act as condensation nuclei for the subsequent formation of mist droplets; such forms of haze are known as "wet haze." Haze also occurs when there is too much pollution in the air while there is also dust. In meteorological literature, the word haze is generally used to denote visibility-reducing aerosols of the wet type. Such aerosols commonly arise from complex chemical reactions that occur as sulfur dioxide gases emitted during combustion are converted into small droplets of sulfuric acid. The reactions are enhanced in the presence of sunlight, high relative humidity, and stagnant air flow. A small component of wet-haze aerosols appear to be derived from compounds released by trees, such as terpenes. For all these reasons, wet haze tends to be primarily a warm-season phenomenon. Large areas of haze covering many thousands of kilometers may be produced under favorable conditions each summer.
Aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets, in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog, dust, forest exudates and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols are haze, particulate air pollutants and smoke.
Magnetosphere - Earths Magnetic Field
 Earth's Magnetic Field extends 370,000 miles (600,000
kilometers) above the planet's surface. The Earth's
magnetic field
originates in the earths core. Earth has a giant ball of iron at
its core surrounded by an outer layer of molten metal. The
motion of the liquid in the outer core is driven by heat flow
from the inner core, which creates a
rotating magnetic field or
dynamo.
Earth's Magnetic Field extends 370,000 miles (600,000
kilometers) above the planet's surface. The Earth's
magnetic field
originates in the earths core. Earth has a giant ball of iron at
its core surrounded by an outer layer of molten metal. The
motion of the liquid in the outer core is driven by heat flow
from the inner core, which creates a
rotating magnetic field or
dynamo. Earth's magnetic field protects earth from solar radiation, solar storms and cosmic rays.
Ring Current is a population of medium-energy particles that drift around the Earth, with protons drifting in one direction and electrons drifting in the opposite direction. A coronal mass ejection or CME occurs when magnetic forces overcome pressure and gravity in the solar corona. This lifts a huge mass of solar plasma from the corona and creates a shock wave that accelerates some of the solar wind's particles to extremely high energies and speeds. This in turn generates radiation in the form of energetic particles.
North Pole - Dipole - Geographic Pole - Human Body Magnetic Field - Galaxy Magnetic Field - Suns Magnetic Field
Dip Pole is any point on the Earth’s surface where the dip of the Earth’s magnetic field is 90 degrees or perpendicular to the surface. There are two main dip poles, one on the Antarctic coast and one in Canada’s Arctic near Bathurst Island. Dip poles may occur locally over strongly magnetic mineral deposits. (magnetic inclination; i.e., the angle between the Earth’s surface and the total magnetic field vector).
Magnetic Dip is the angle made with the horizontal by the Earth's magnetic field lines. This angle varies at different points on the Earth's surface. Positive values of inclination indicate that the magnetic field of the Earth is pointing downward, into the Earth, at the point of measurement, and negative values indicate that it is pointing upward. The dip angle is in principle the angle made by the needle of a vertically held compass, though in practice ordinary compass needles may be weighted against dip or may be unable to move freely in the correct plane. The value can be measured more reliably with a special instrument typically known as a dip circle.
Plasmasphere is composed of low-energy particles that drift up from the ionosphere, forming a sphere-like reservoir of very cold, fairly dense plasma that co-rotates with the Earth. Magnetosphere.
Van Allen Radiation Belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind that is captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetic field. The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The Van Allen Belts consist of high-energy particles that are trapped in two regions. These particles move along the field lines toward the poles until they are reflected back, creating a bouncing movement. Particles with a high enough velocity along the magnetic field will follow the field lines to the poles and enter the upper atmosphere.
Probes found that Mars and Venus do not have a significant magnetic field. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune all have magnetic fields much stronger than that of the Earth. Jupiter is the champion- having the largest magnetic field.
So why doesn't the Moon get pulled into the earth by its gravitational Pull? Because the Earth is moving, so the Moon is chasing the Earth, just like the Earth gets pulled by gravity from the Sun. And also Earths gravity gets weaker as you go further out. The moon does not fall to Earth because it is in an Orbit, which is the gravitationally curved path of an object about a point in space. Laws of Motion (action physics).
Impenetrable Barrier in Space (nasa)
Geomagnetic Reversal happens once every few hundred thousand years. The magnetic poles flip so that a compass would point south instead of north. The flip takes around a hundred to a few thousand years to complete. During past polarity flips there were no mass extinctions or evidence of radiation damage. Most reversals are estimated to take between 1,000 and 10,000 years. The latest one, the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, occurred 780,000 years ago, and may have happened very quickly, within a human lifetime. Local Geomagnetic Fields - Magnetic Reversal.
Laschamp Event was a geomagnetic excursion or a short reversal of the Earth's magnetic field. It occurred 41,400 years ago, during the end of the Last Glacial Period. It is known from geomagnetic anomalies discovered in the 1960s in the Laschamps lava flows in Clermont-Ferrand, France. Earth's magnetic field dropped to below 6% of the current level, carbon 14 production increased, ozone levels decreased, and atmospheric circulation changed. This loss of the geomagnetic shield was also claimed to cause extinction of Australian megafauna, extinction of Neanderthals, and appearance of cave art. The weakening of the Earth's magnetic field would have briefly transformed the world by altering its climate and allowing far more ultraviolet light to pour in. The Australian Research Council is funding research to analyze a kauri tree uncovered in New Zealand in 2019. According to its carbon-dating, the tree was alive during the event 41,000–42,500 years ago.
Paleomagnetism is the study of the record of the Earth's magnetic field in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Certain minerals in rocks lock-in a record of the direction and intensity of the magnetic field when they form.
Earth's Magnetic North Pole has been moving away from the Canadian Arctic towards Siberia at a rate of 55 km per Year or 34 miles per year The World Magnetic Model.
Earth's Magnetic Field Is Weakening 10 Times Faster Now. Solar Storm Vulnerability - Collapse.
Earth's Magnetic Field Almost Collapsed 565 Million Years Ago. Young inner core inferred from Ediacaran ultra-low geomagnetic field intensity. Our planet’s molten core probably began to solidify during the late Ediacaran period, according to the new paper. This recharged Earth’s magnetic field right when it was at its weakest point. Now, a half-billion years later, Earth’s magnetic field is ten times stronger than it was in was during this early era. Suns Magnetic Field is Flipping.
Magnetic Anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field resulting from variations in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. South Atlantic Anomaly "I don't think you fully understand the gravity of this situation".
Ancient Jars Found in Judea Reveal Earth's Magnetic Field is Fluctuating, Not Diminishing.
How does Earth sustain its magnetic field? Life as we know it could not exist without Earth's magnetic field and its ability to deflect dangerous ionizing particles. It is continuously generated by the motion of liquid iron in Earth's outer core, a phenomenon called the geodynamo.
New Data helps explain recent Fluctuations in Earth’s Magnetic Field.
A small but evolving dent in Earth's magnetic field can cause big headaches for satellites. Researchers track slowly splitting 'dent' in Earth's magnetic field. Earth's magnetic field acts like a protective shield around the planet, repelling and trapping charged particles from the Sun. But over South America and the southern Atlantic Ocean, an unusually weak spot in the field -- called the South Atlantic Anomaly, or SAA -- allows these particles to dip closer to the surface than normal. The South Atlantic Anomaly arises from two features of Earth's core: The tilt of its magnetic axis, and the flow of molten metals within its outer core. Earth is a bit like a bar magnet, with north and south poles that represent opposing magnetic polarities and invisible magnetic field lines encircling the planet between them. But unlike a bar magnet, the core magnetic field is not perfectly aligned through the globe, nor is it perfectly stable. That's because the field originates from Earth's outer core: molten, iron-rich and in vigorous motion 1800 miles below the surface. These churning metals act like a massive generator, called the geodynamo, creating electric currents that produce the magnetic field.
UNH Scientists Capture Space Energy Explosion. Magnetic reconnection is the process by which sparse particles and energy around Earth collide producing a quick but mighty explosion -- in the Earth's magnetotail, the magnetic environment that trails behind the planet.
Earth's Magnetic Field measured using artificial stars at 90 kilometers altitude. In 2011, researchers proposed that artificial guide stars could be used to measure the Earth's magnetic field in the mesosphere. An international group of scientists has recently managed to do this with a high degree of precision. The technique may also help to identify magnetic structures in the solid Earth's lithosphere, to monitor space weather, and to measure electrical currents in the part of the atmosphere called ionosphere. Human Body Magnetic Field (EMF)
First evidence that water can be created on the lunar surface by Earth's magnetosphere. The prevailing theory is that positively charged hydrogen ions propelled by the solar wind bombard the lunar surface and spontaneously react to make water (as hydroxyl (OH-) and molecular (H2O)). However, a new multinational study published in Astrophysical Journal Letters proposes that solar wind may not be the only source of water-forming ions. The researchers show that particles from Earth can seed the moon with water, as well, implying that other planets could also contribute water to their satellites. Water is far more prevalent in space than astronomers first thought, from the surface of Mars to Jupiter's moons and Saturn's rings, comets, asteroids and Pluto; it has even been detected in clouds far beyond our solar system.
 Birkeland Current is a set of currents that flow along geomagnetic
field lines connecting the Earth’s magnetosphere to the Earth's high
latitude ionosphere. In the Earth’s magnetosphere, the currents are driven
by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of
plasma through the magnetosphere (convection indirectly driven by the
interplanetary environment). The strength of the Birkeland currents
changes with activity in the magnetosphere (e.g. during substorms). Small
scale variations in the upward current sheets (downward flowing electrons)
accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper
atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis. In the high
latitude ionosphere (or auroral zones), the Birkeland currents close
through the region of the auroral electrojet, which flows perpendicular to
the local magnetic field in the ionosphere. The Birkeland currents occur
in two pairs of field-aligned current sheets. One pair extends from noon
through the dusk sector to the midnight sector. The other pair extends
from noon through the dawn sector to the midnight sector. The sheet on the
high latitude side of the auroral zone is referred to as the Region 1
current sheet and the sheet on the low latitude side is referred to as the
Region 2 current sheet.
Kristian Birkeland was a Norwegian scientist(December 13, 1867 – June
15, 1917).
Lightning.
Birkeland Current is a set of currents that flow along geomagnetic
field lines connecting the Earth’s magnetosphere to the Earth's high
latitude ionosphere. In the Earth’s magnetosphere, the currents are driven
by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of
plasma through the magnetosphere (convection indirectly driven by the
interplanetary environment). The strength of the Birkeland currents
changes with activity in the magnetosphere (e.g. during substorms). Small
scale variations in the upward current sheets (downward flowing electrons)
accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper
atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis. In the high
latitude ionosphere (or auroral zones), the Birkeland currents close
through the region of the auroral electrojet, which flows perpendicular to
the local magnetic field in the ionosphere. The Birkeland currents occur
in two pairs of field-aligned current sheets. One pair extends from noon
through the dusk sector to the midnight sector. The other pair extends
from noon through the dawn sector to the midnight sector. The sheet on the
high latitude side of the auroral zone is referred to as the Region 1
current sheet and the sheet on the low latitude side is referred to as the
Region 2 current sheet.
Kristian Birkeland was a Norwegian scientist(December 13, 1867 – June
15, 1917).
Lightning.Global Atmospheric Electrical Circuit is the course of continuous movement of atmospheric electricity between the ionosphere and the Earth. Through solar radiation, thunderstorms, and the fair-weather condition, the atmosphere is subject to a continual and substantial electrical current. Principally, thunderstorms throughout the world carry negative charges to the earth, which is then discharged gradually through the air in fair weather. This atmospheric circuit is central to the study of atmospheric physics and meteorology. It is used in the prediction of thunderstorms, and was central to the understanding of electricity. In the past it has been suggested as a source of available energy, or communications platform. The global electrical circuit is also applied to the study human health and air pollution, due of the interaction of negative ions and aerosols. The effect of global warming, and temperature-sensitivity of the Earth's electrical circuit is unknown.
Wave-Particle Interactions allow collision-free Energy Transfer in space plasma. The Earth's magnetosphere contains plasma, an ionized gas composed of positive ions and negative electrons. The motion of these charged plasma particles is controlled by electromagnetic fields. The energy transfer processes that occur in this collisionless space plasma are believed to be based on wave-particle interactions such as particle acceleration by plasma waves and spontaneous wave generation, which enable energy and momentum transfer.
Measuring Tools (electromagnetic) - North Pole
Aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude Arctic and Antarctic regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. New type of aurora nicknamed the dunes was discovered by citizen scientists in Finland. The dunes appear as thin ribbons of green light in the sky. Researchers suspect the dunes are visible manifestations of air undulations called atmospheric waves. Atmospheric wave is a periodic disturbance in the fields of atmospheric variables (like surface pressure or geopotential height, temperature, or wind velocity) which may either propagate (traveling wave) or not (standing wave). Atmospheric waves range in spatial and temporal scale from large-scale planetary waves (Rossby waves) to minute sound waves. Atmospheric waves with periods which are harmonics of 1 solar day (e.g. 24 hours, 12 hours, 8 hours... etc.) are known as atmospheric tides.
Halos - Vapor Tracers - Rainbows - Cosmic Rays - Lightning
Aurora Borealis is most often seen in a striking green color, but it also occasionally shows off its many colors ranging from red to pink, blue to purple, dark to light. The reason that the aurora is seen in so many colors is that our atmosphere is made up of many different compounds like Oxygen and Nitrogen. When the charged particles that come from the sun hit the atoms and molecules of the Earth's atmosphere, they excite those atoms, giving off light. Different atoms give off different colors of the spectrum when they are excited. A familiar example is the Neon lights that we see on many business signs in our modern world. The Neon lights contain the gas Neon. These lights have electricity run through them to excite the Neon gas. When the Neon is excited, it gives off a brilliant red-orange color. The Neon lights are the same idea as the aurora, only on a lot smaller scale. Different gases give off different colors when they are excited. Oxygen at about 60 miles up gives off the familiar yellow-green color, Oxygen at higher altitudes (about 200 miles above us) gives the all red auroras. Ionic nitrogen produces the blue light and neutral Nitrogen gives off the red-purple and the rippled edges. Imagine if the atmosphere were made of Neon gas and Sodium gas. We would see red-orange and yellow auroras. Auroral electrons are accelerated before colliding with the iono-sphere and producing auroral light. Powerful Alfvén waves are often found traveling. Earthward above auroras with sufficient energy to generate auroras, the natural light show starts when disturbances on the sun pull on Earth's magnetic field. That creates cosmic undulations known as Alfvén waves that launch electrons at high speeds into Earth's atmosphere where they create the aurora.
Alfvén Wave is a type of magnetohydrodynamic wave in which ions oscillate in response to a restoring force provided by an effective tension on the magnetic field lines. Sometimes electrons hitch a ride on these superfast Alfvén waves, reaching speeds as high as 45 million miles per hour as they hurtle downward.
Stunning Aurora Borealis from Space in Ultra-High Definition (4K) (youtube) - Aurora in Fairbanks Alaska (reddit video)
Aurora Colors - Northern Lights Centre
Red Aurora Australis Southern Lights (video)
Thin ribbons of purple and white light called STEVE is produced by a different atmospheric process than the Aurora.
Strong winds power electric fields in the upper atmosphere. Using observations from NASA's ICON mission, scientists presented the first direct measurements of Earth's long-theorized dynamo on the edge of space: a wind-driven electrical generator that spans the globe 60-plus miles above our heads. The dynamo churns in the ionosphere, the electrically charged boundary between Earth and space. It's powered by tidal winds in the upper atmosphere that are faster than most hurricanes and rise from the lower atmosphere, creating an electrical environment that can affect satellites and technology on Earth.
Geomagnetic field protects Earth from electron showers. The ionosphere is a wide region between roughly 60 and more than 600 kilometers above the Earth's surface. It contains electrically charged particles that are a mixture of ions and free electrons generated by the interaction of the atmosphere with radiation from the sun. Polar regions of the ionosphere are subjected to a particularly steady and energetic stream of incoming electrons in a process called electron precipitation.
Globe is a three-dimensional, spherical, scale model of Earth (terrestrial globe or geographical globe) or other celestial body such as a planet or moon.
Lunar and Planetary Institute - Navigation
Constellation Program was a human spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a "return to the Moon no later than 2020" with a crewed flight to the planet Mars as the ultimate goal.
 Overview Effect is a
cognitive shift and an
emotional shift in a person's
awareness and identity when
they see the Earth from space or from the lunar surface,
or while viewing the earth from orbit as reported
by some astronauts and cosmonauts during spaceflight. This emotional or
mental reaction is strong enough to disrupt a person's previous
assumptions about humanity and the Earth and the cosmos. The experience of seeing firsthand
the reality of the Earth
in space is immediately understood to be a
tiny and fragile ball of life that is hanging in the void that is shielded and nourished
by a paper-thin atmosphere. From space, national boundaries vanish
and the
conflicts that divide people become less important, and the need to create
a planetary society with the united will
to protect this
pale blue dot
becomes both obvious and imperative.
Third-hand observers of these
individuals may also report a noticeable difference in attitude.
Of course you don't need to travel into space in
order to realize how precious life is. There is a difference
between intellectual knowledge and
experiential knowledge,
but that all depends on what knowledge you read and understand, and how
you interpret a particular experience to be.
Overview Effect is a
cognitive shift and an
emotional shift in a person's
awareness and identity when
they see the Earth from space or from the lunar surface,
or while viewing the earth from orbit as reported
by some astronauts and cosmonauts during spaceflight. This emotional or
mental reaction is strong enough to disrupt a person's previous
assumptions about humanity and the Earth and the cosmos. The experience of seeing firsthand
the reality of the Earth
in space is immediately understood to be a
tiny and fragile ball of life that is hanging in the void that is shielded and nourished
by a paper-thin atmosphere. From space, national boundaries vanish
and the
conflicts that divide people become less important, and the need to create
a planetary society with the united will
to protect this
pale blue dot
becomes both obvious and imperative.
Third-hand observers of these
individuals may also report a noticeable difference in attitude.
Of course you don't need to travel into space in
order to realize how precious life is. There is a difference
between intellectual knowledge and
experiential knowledge,
but that all depends on what knowledge you read and understand, and how
you interpret a particular experience to be.Overview Effect (youtube) - Astronauts - Shuttle - Savikalpa is meditation with support of an object. - Gaia in Mythology - Mother Earth - Awareness - Emergence - Out of Body Experience
The farther you travel from earth, the smaller the earth becomes. When you see something from a different perspective, it can change your understanding of it, and change how you feel about it. Its like seeing your house and home from a distance. You know how special your home is and how valuable it is. Earth is your shelter, your home, and the reason why you live. When you have empathy, you have the ability to see things from a different perspective. When having empathy, you don't have to physically move, because the mind moves for you.
Solar Eclipse
 Solar Eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun,
thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth,
totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six
months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's
orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. In a total
eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial
and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar
eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a
solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the
world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth
every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once
every 360 to 410 years.
Solar Eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun,
thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth,
totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six
months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's
orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. In a total
eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial
and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar
eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a
solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the
world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth
every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once
every 360 to 410 years. Why does a Solar Eclipse move Eastward even though the Earth Rotates from West to East? The Earth Rotates counter clockwise or west to east. The moon travels in the same direction. The Moon takes 27.3 days to travel once around the earth, that is why the moon travels east to west in the sky during earths 24 hour to spin cycle. So the earth is spinning faster then the moon even though the moon is moving faster at 3,400 km/hour (2,112 mph) when compared to earths spinning speed of 1,670 km/hr (1,037 mph) at the equator. To keep up with the shadow of the eclipse you would have to be traveling at Mach 1.5 or 1,150.9 mph. (eclipse paths image).
Solar Eclipse Photos (images) - Lunar Eclipse (wiki) - Path of Totality (2024)
Saros is a period of exactly 223 synodic months or approximately 6585.3211 days, or 18 years, 11 days, 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the Sun and Moon. Antikythera Mechanism.
Annular Solar Eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, but when it is at or near its farthest point from Earth. Because the Moon is farther away from Earth, it appears smaller than the Sun and does not completely cover the Sun.
Baily's Beads or diamond ring effect, is a feature of total and annular solar eclipses. As the Moon covers the Sun during a solar eclipse, the rugged topography of the lunar limb allows beads of sunlight to shine through in some places while not in others. Ring of Fire.
Circumference of Earths Spin on its Axis vs. One complete Orbit of the Moon. Earth spins at around 1,000 mph on the equator and takes close to 24 hours to travel 24,901 miles or 40,075 kilometers. The Moon travels 2,288 mph making of full orbit distance of 1,423,000 miles or 2,290,000 kilometers. (27.3 days x 24 hours = 655.2 hours x 2,288 mph = 1,499,097 miles)? Surface.
Why the Sun and the Moon look like they're the Same Size? The Sun is 403 times as wide as the Moon but the Sun is also roughly 400 times farther away from Earth. These two qualities almost cancel each other out. The ratio of the sun’s distance from earth (149.6 million km or 92,957,130.3587 miles) to the moon’s distance from earth (384,400 km or 238.85509 miles) is 389, rather close to the diameter ratio of 403. This means that there is a difference of only 3 percent in the apparent sizes of the sun and moon and so they appear to be about the same size. More significantly the moon covers all but a tiny bit of the sun during an eclipse. The diameter of the sun is 1.4 million kilometers. The diameter of the moon is 3,474 kilometers. The sun is often recognized as a symbol of rebirth, strength and power. The moon is associated with the female in many cultures often in the form of a goddess. Sun and Moon Dualism is the moral or spiritual belief that two fundamental concepts exist, which often oppose each other, which means that you should know the difference between good and bad and right and wrong, and that life is filled with symbiotic relationships that must be balanced.
The moon's shadow cast on earth's surface during an eclipse is around 274 kilometers or 170 miles across, and covers roughly 37,015 square kilometers or 23,000 square miles at any one time, though the size of the shadow differs when measuring the umbra, which is when the Sun is completely blocked, or the penumbra or penumbral diameter, where the Sun is partially obscured. The shadow from the moon during a full solar eclipse is only 0.01% of the total surface area of Earth.
A solar eclipse on the opposite side of the earth around midnight is perfect for seeing more stars and planets. When the sun and the moon are behind the earth, it's better for seeing the stars and planets.
Antipode of any spot on Earth is the point on Earth's surface diametrically opposite to it. A pair of points antipodal to each other are situated such that a straight line connecting the two would pass through Earth's center. Antipodal points are as far away from each other as possible. The North and South Poles are antipodes of each other. Antipodean is situated at opposite sides of the earth. Antipode is the direct opposite of something.
Satellites - Orbiting Mechanical Machines
Satellite is an artificial object which has been intentionally placed into orbit. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as Earth's Moon. Satellites are used to make star maps and maps of planetary surfaces, and also take pictures of planets they are launched into. Common types include military and civilian Earth observation satellites, communications satellites, navigation satellites, weather satellites, and space telescopes. Space stations and human spacecraft in orbit are also satellites. Satellite orbits vary greatly, depending on the purpose of the satellite, and are classified in a number of ways. Well-known (overlapping) classes include low Earth orbit, polar orbit, and geostationary orbit.
GPS - Global Positioning System - Navigation - Timeline of Artificial Satellites and Space Probes wiki) - Voyager Probe.
Sputnik 1 was the first artificial Earth satellite. The Soviet Union launched it into an elliptical low Earth orbit on 4 October 1957.
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States on January 31, 1958.
Apollo 11 was the spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 UTC. Over 400,000 people contributed to the project. When We Were Apollo (Feature Documentary) | Spark (youtube - 56 mins.)
Orbital Mechanics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It is a core discipline within space mission design and control. Celestial mechanics treats more broadly the orbital dynamics of systems under the influence of gravity, including both spacecraft and natural astronomical bodies such as star systems, planets, moons and comets. Orbital mechanics focuses on spacecraft trajectories, including orbital maneuvers, orbit plane changes, and interplanetary transfers, and is used by mission planners to predict the results of propulsive maneuvers. General relativity is a more exact theory than Newton's laws for calculating orbits, and is sometimes necessary for greater accuracy or in high-gravity situations (such as orbits close to the Sun).
Specific Mechanical Energy, rather than simply energy, is often used in astrodynamics, because gravity changes the kinetic and potential specific energies of a vehicle in ways that are independent of the mass of the vehicle, consistent with the conservation of energy in a Newtonian gravitational system. The specific energy of an object such as a meteoroid falling on the earth from outside the earth's gravitational well is at least one half the square of the escape velocity of 11.2 km/s. This comes to 63 MJ/kg (15 kcal/g, or 15 tonnes TNT equivalent per tonne). Comets have even more energy, typically moving with respect to the sun, when in our vicinity, at about the square root of two times the speed of the earth. This comes to 42 km/s, or a specific energy of 882 MJ/kg. The speed relative to the earth may be more or less, depending on direction. Since the speed of the earth around the sun is about 30 km/s, a comet's speed relative to the earth can range from 12 to 72 km/s, the latter corresponding to 2592 MJ/kg. If a comet with this speed fell to the earth it would gain another 63 MJ/kg, yielding a total of 2655 MJ/kg with a speed of 72.9 km/s. Since the equator is moving at about 0.5 km/s, the impact speed has an upper limit of 73.4 km/s, giving an upper limit for the specific energy of a comet hitting the earth of about 2690 MJ/kg. If the Hale-Bopp comet (50 km in diameter) had hit the earth, it would have vaporized the oceans and sterilized the surface of the earth.
Union of Concerned Scientists says there are 1,419 active satellites currently orbiting Earth. There are estimates of roughly 2,600 satellites that no longer work floating in space. Some of the biggest telecommunications satellites can weigh several tons, be the size of a bus, and orbit from a fixed point about 22,000 miles (35,000 km) above Earth. On November 15 2016, SpaceX filed a lengthy application with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to launch 4,425 new satellites. Each satellite in SpaceX's planned constellation will weigh about 850 lbs (386 kg) and be roughly the size of a MINI Cooper car. They will orbit at altitudes ranging from 715 miles (1,150 km) to 790 miles (1,275 km). Each satellite could cover an ellipse about 1,300 miles (2,120 km) wide. That's about the distance from Maine to the Florida panhandle. With deployment of the first 800 satellites, SpaceX will be able to provide widespread U.S. and international coverage for broadband services," A speed of 1 Gbps. The global average for internet speed in late 2015, according Akamai's "State of the Internet" report, was 5.1 Mbps per user — about 200 times slower than SpaceX's target — with most of the higher speeds tied up in cable and fiberoptic connections. Downlink capacity to users ranging from 17 to 23 Gbps.
Ultrathin solar cells promise improved satellite performance. Radiation damage to photovoltaics in orbit can be reduced by making the cells thinner. As low Earth orbit becomes more cluttered, it becomes increasingly necessary to use middle Earth orbits, and radiation-tolerant cell designs will be needed. Making photovoltaics thinner should increase their longevity because the charge carriers have less far to go during their shortened lifetimes. Scientists propose a radiation-tolerant photovoltaic cell design that features an ultrathin layer of light-absorbing material. Compared to thicker cells, nearly 3.5 times less cover glass is needed for the ultra-thin cells to deliver the same amount of power after 20 years of operation.
Orbit Zones of Satellites
High Earth Orbit is a geocentric orbit with an altitude entirely above that of a geosynchronous orbit (35,786 kilometres (22,236 mi). List of Orbits (wiki).
Geostationary Orbit is a satellite orbiting at the same speed as the Earth rotates, so it stays over one place. The circular orbit is around 35,786 kilometres or 22,236 mi above the Earth's equator and following the direction of the Earth's rotation. Satellites need to be very far away from earth and above the equator to rotate in this kind of orbit. A geosynchronous orbit or GSO is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that, for an observer on Earth's surface, an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period of one sidereal day. Over the course of a day, the object's position in the sky may remain still or trace out a path, typically in a figure-8 form, whose precise characteristics depend on the orbit's inclination and eccentricity. A circular geosynchronous orbit has a constant altitude of 35,786 km or 22,236 mi. A special case of geosynchronous orbit is the geostationary orbit, which is a circular geosynchronous orbit in Earth's equatorial plane with both inclination and eccentricity equal to 0. A satellite in a geostationary orbit remains in the same position in the sky to observers on the surface. Communications satellites are often given geostationary or close to geostationary orbits so that the satellite antennas that communicate with them do not have to move, but can be pointed permanently at the fixed location in the sky where the satellite appears. Geosynchronous Orbit is an orbit around the Earth that matches Earth's rotation on its axis with an orbital period of one sidereal day. (23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds).
Medium Earth Orbit is the region of space around the Earth above low Earth orbit (altitude of 2,000 kilometres (1,243 mi)) and below geostationary orbit.
Low Earth Orbiting Satellite is an orbit around Earth with an altitude between 160 kilometers (99 mi) (orbital period of about 88 minutes), and 2,000 kilometers (1,200 mi) (about 127 minutes). Objects below approximately 160 kilometers (99 mi) will experience very rapid orbital decay and altitude loss. The orbital velocity needed to maintain a stable low Earth orbit is about 7.8 km/s, but reduces with increased orbital altitude. Orbital Decay.
Synchronous Orbit is an orbit in which an orbiting body (usually a satellite) has a period equal to the average rotational period of the body being orbited (usually a planet), and in the same direction of rotation as that body.
Atmospheric Entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: uncontrolled entry, such as the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides; and controlled entry (or reentry) of a spacecraft capable of being navigated or following a predetermined course. Technologies and procedures allowing the controlled atmospheric entry, descent, and landing of spacecraft are collectively termed as EDL.
Miniature Satellites - Internet
Small Satellite is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under 500 kg (1,100 lb). While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites can be built small to reduce the large economic cost of launch vehicles and the costs associated with construction. Miniature satellites, especially in large numbers, may be more useful than fewer, larger ones for some purposes – for example, gathering of scientific data and radio relay. Technical challenges in the construction of small satellites may include the lack of sufficient power storage or of room for a propulsion system.
Satellite Building Kits - New Nanosatellite System captures better Imagery at Lower Cost.
Communications Satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunications signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications.
Satellite Internet Constellation is a constellation of artificial satellites providing satellite internet service. In particular, the term has come to refer to a new generation of very large constellations (sometimes referred to as a megaconstellations) orbiting in low-Earth orbit (LEO) to provide low-latency, high bandwidth (broadband) internet service.
Satellite Internet Access is Internet access provided through communication satellites. Modern consumer grade satellite Internet service is typically provided to individual users through geostationary satellites that can offer relatively high data speeds, with newer satellites using Ku band to achieve downstream data speeds up to 506 Mbit/s. In addition, new satellite internet constellations are being developed in low-earth orbit to enable low-latency internet access from space.
OneWeb commenced launches of the OneWeb satellite constellation, a network of more than 650 low Earth orbit satellites, on February 27, 2019. Satellites have 5-7 year lifespan.
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation being constructed by SpaceX providing satellite Internet access. The constellation will consist of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), working in combination with ground transceivers. SpaceX plans to sell some of the satellites for military, scientific, or exploratory purposes. As of 25 November 2020, SpaceX has launched 955 Starlink satellites. They plan to launch up to 60 more per Falcon 9 flight, with launches as often as every two weeks in 2020. In total, nearly 12,000 satellites are planned to be deployed, with a possible later extension to 42,000. The initial 12,000 satellites are planned to orbit in three orbital shells: First: 1,440 in a 550 km (340 mi) altitude shell. Second: 2,825 Ku-band and Ka-band spectrum satellites at 1,110 km (690 mi). Third: 7,500 V-band satellites at 340 km (210 mi).In June 2020, SpaceX applied in the United States for use of the E-band in the Gen2 constellation. The generation 2 Starlink constellation is expected to include up to 30,000 satellites and provide complete global coverage. The deployment of the first 1,440 satellites will be into 72 orbital planes of 20 satellites each.
Kuiper Systems is a subsidiary of Amazon that was setup in 2019 to deploy a large broadband satellite internet constellation to provide broadband internet connectivity.
Satellite Images - Telescopes - Environmental Monitoring
Smart Satellites to Repair and Refuel stranded Satellites in Space.
Gaia spacecraft is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA) designed for astrometry: measuring the positions and distances of stars with unprecedented precision. The mission aims to construct the largest and most precise 3D space catalog ever made, totaling approximately 1 billion astronomical objects, mainly stars, but also planets, comets, asteroids and quasars among others. Gaia satellite has mapped 1.7 billion stars in the milky way galaxy.
Over a span of 12 years, the CORONA satellites captured more than 800,000 images. That's 2.1 million feet of film.
Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993.
ISRO Launches 104 Satellites in a Single Rocket Launch - a world record as of 15/02/2017 (youtube)
Space Junk - Orbital Debris - Avoidance Maneuvers
There are approximately 1,300 nonfunctional satellites in the graveyard orbit 22,000 mile above earth.
Space Debris: 1957 - 2015 (youtube) - Almost 20,000 pieces of space debris are currently orbiting the Earth.
Summer Science Exhibition 2016: Cleaning up space junk (youtube)
Trashopolis S02 E07: Moscow (youtube)
Kessler Syndrome is a collisional cascading scenario with satellites in which the density of objects in low Earth orbit is high enough that collisions between objects could cause a cascade in which each collision generates space debris that increases the likelihood of further collisions. One implication is that the distribution of debris in orbit could render space activities and the use of satellites in specific orbital ranges difficult for many generations.
Active Debris Removal (ADR) capture and deorbit two space debris DebriSATs.
Darpa Satellite Scavenging Phoenix Project.
Laser measurements to track space debris and observe water masses. More accurate orbit predictions for satellites and space debris as well as a better understanding of the water masses present on Earth: Researchers at achieved both using satellite laser ranging.
Spacecraft works by attempting to attach itself to dead satellites and pushing them toward Earth to burn up in the atmosphere. A multi-target end-of-life space debris removal catch and release process repeatedly over the course of six months. The spacecraft is not designed to capture dead satellites already in orbit, but rather future satellites that would be launched with compatible docking plates on them. According to a recent report by NASA, at least 26,000 of the millions of pieces of space junk are the size of a softball. Orbiting along at 17,500 mph, they could "destroy a satellite on impact." More than 500,000 pieces are a "mission-ending threat" because of their ability to impact protective systems, fuel tanks and spacecraft cabins.And the most common debris, more than 100 million pieces, is the size of a grain of salt and could puncture a spacesuit, amplifying the risk of catastrophic collisions to spacecraft and crew.
Satellite captures space junk for the first time. An experimental cleanup device called RemoveDebris has successfully cast a net around a dummy satellite, simulating a technique that could one day capture spaceborne garbage.
Space Junk Tether - Soft Capture - Space Debris Clean-up
Let's clean up the space junk orbiting Earth: Natalie Panek (video and interactive text)
Graveyard Orbit is an orbit that lies away from common operational orbits. One significant graveyard orbit is a supersynchronous orbit well above geosynchronous orbit. Satellites are typically moved into such orbits at the end of their operational life to reduce the probability of colliding with operational spacecraft and generating space debris.
Shielding the International Space Station from Micro-Meteoroid Orbital Debris - PDF.
Collision course: Amateur astronomers play a part in efforts to keep space safe. With over 22,000 artificial satellites in orbit it is essential to keep track of their positions in order to avoid unexpected collisions. Amateur astronomers have been helping the Ministry of Defense explore what is possible using high-end consumer equipment to track objects in space.
Avoidance Maneuver or collision avoidance is the process of preventing a spacecraft from colliding with any other vehicle or object.
Collision Avoidance is the implementation and study of processes minimizing the chance of orbiting spacecraft inadvertently colliding with other orbiting objects. The most common subject of spacecraft collision avoidance research and development is for human-made satellites in geocentric orbits. The subject includes procedures designed to prevent the accumulation of space debris in orbit, analytical methods for predicting likely collisions, and avoidance procedures to maneuver offending spacecraft away from danger. Orbital velocities around large bodies (like the Earth) are fast, resulting in significant kinetic energy being involved in on-orbit collisions. For example, at the mean Low Earth orbital velocity of ~7.8 km/s, two perpendicularly colliding spacecraft would have a combined relative impact velocity of ~12.2 km/s. Almost no known structurally solid materials are capable of withstanding such an energetic impact, most of which would be instantly vaporized by the collision and broken up into myriad pieces ejected at force in all directions. Because of this, it's exceedingly likely that any spacecraft colliding with another object in orbit would be critically damaged or completely destroyed by the impact.
The German Experimental Space Surveillance and Tracking Radar (GESTRA)
Tracking undetectable space junk. Satellite and spacecraft operators may finally be able to detect small pieces of debris orbiting Earth using a new approach. Colliding pieces of space debris emit electric signals that could help track small debris littering Earth's orbit, potentially saving satellites and spacecraft.
Space Situational Awareness - Space Track
Whipple Shield is a type of hypervelocity impact shield used to protect crewed and uncrewed spacecraft from collisions with micrometeoroids and orbital debris whose velocities generally range between 3 and 18 kilometres per second (1.9 and 11.2 mi/s). Bumper wall and Rear Wall Design.
Escape Pod is a capsule or craft used to escape a vessel in an emergency, usually only big enough for one person. An escape ship is a larger, more complete craft also used for the same purpose. Escape pods are ubiquitous in science fiction, but infrequently used in real vehicles such as supersonic aircraft.
Meteorite - Meteor - Meteoroid
Meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body travelling through outer space. Meteoroids are significantly smaller than asteroids, and range in size from small grains to one-meter-wide objects. International Meteor - American Meteor Society.
Micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid or a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through the Earth's atmosphere and reaches the Earth's surface.
Meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheric gases cause it to heat up and radiate energy. It then becomes a meteor and forms a fireball, also known as a shooting star; astronomers call the brightest examples "bolides". Once it settles on the larger body's surface, the meteor becomes a meteorite. Meteorites vary greatly in size. For geologists, a bolide is a meteorite large enough to create an impact crater. Meteorites that are recovered after being observed as they transit the atmosphere and impact the Earth are called meteorite falls. All others are known as meteorite finds. Meteorites have traditionally been divided into three broad categories: stony meteorites that are rocks, mainly composed of silicate minerals; iron meteorites that are largely composed of ferronickel; and stony-iron meteorites that contain large amounts of both metallic and rocky material. Modern classification schemes divide meteorites into groups according to their structure, chemical and isotopic composition and mineralogy. Meteorites smaller than 2 mm are classified as micrometeorites. Extraterrestrial meteorites have been found on the Moon and on Mars. Meteorite is a stony or metallic object that is the remains of a meteoroid that has reached the earth's surface.
Shooting Star is a common name for the visible path of a meteoroid as it enters the atmosphere, becoming a meteor, which is any of the small solid extraterrestrial bodies that hits the earth's atmosphere. A streak of light in the sky at night that results when a meteoroid hits the earth's atmosphere and air friction causes the meteoroid to melt, vaporize or explode.
Many meteors come from one direction. As the Earth swings around the sun, it encounters meteors as it sweeps through space at 30 km/sec, or 67,000 miles per hour. These meteors can hit the Earth at all angles and from all directions, and only occasionally appear to be moving parallel to the ground. Most meteors occur in the region of the atmosphere called the thermosphere. This “meteoric region” lies between about 80 km and 120 km (50 to 75 miles) in altitude. This is a general guideline only, since very fast meteors may first become visible above this height, and slow, bright meteors may penetrate below this band. Meteors enter the atmosphere at speeds ranging from 11 km/sec (25,000 mph), to 72 km/sec (160,000 mph) On the evening side, or trailing edge of the Earth, meteoroids must catch up to the earth’s atmosphere to cause a meteor, and tend to be slow. On the morning side, or leading edge of the earth, meteoroids can collide head-on with the atmosphere and tend to be fast.
Did you know that 100 tons of meteorites and dust enter our atmosphere everyday? Even space rocks up to 25 metres across (80 feet) will likely explode and disintegrate in the upper layers of our atmosphere, causing little or no damage, according to NASA. The Moon is bombarded by so much space rock that its surface gets a complete facelift every 81,000 years. Varieties of space dust, barely the width of a human hair. These photomicrographs were made with a special camera setup that magnifies the dust grains nearly 3,000 times. (Credit Jan Braly Kihle/Jon Larsen).
Geminids are a prolific meteor shower caused by the object 3200 Phaethon, which is thought to be a Palladian asteroid with a "rock comet" orbit. This would make the Geminids, together with the Quadrantids, the only major meteor showers not originating from a comet. The meteors from this shower are slow moving, can be seen in December and usually peak around December 4–16, with the date of highest intensity being the morning of December 14. The shower is thought to be intensifying every year and recent showers have seen 120–160 meteors per hour under optimal conditions, generally around 02:00 to 03:00 local time. Geminids were first observed in 1862, much more recently than other showers such as the Perseids (36 AD) and Leonids (902 AD).
Micrometeorite is an extraterrestrial particle, ranging in size from 50 µm to 2 mm, collected on the Earth's surface. Micrometeorites are micrometeoroids which have survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. They differ from meteorites in being smaller, more plentiful and different in composition and are a subset of cosmic dust, which also includes the smaller interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). Micrometeorites enter the Earth's atmosphere with high velocities (at least 11 km/s) and undergo heating through atmospheric friction and compression. Individual micrometeorites weigh between 10-9 and 10-4 g and collectively contribute most of the extraterrestrial material that has come to the present day Earth. Fred Lawrence Whipple first coined the term "micro-meteorite" to describe dust-sized objects that fall to the Earth. Sometimes meteoroids and micrometeoroids entering the Earth's atmosphere are visible as meteors or "shooting stars", whether or not they reach the ground and survive as meteorites and micrometorites.
An urban collection of modern-day large micrometeorites: Evidence for variations in the extraterrestrial dust flux through the Quaternary.
Space Dust Photo (image) - Image 2 (photo)
More than 5,000 tons of extraterrestrial dust fall to Earth each year. Every year, our planet encounters dust from comets and asteroids. These interplanetary dust particles pass through our atmosphere and give rise to shooting stars. Some of them reach the ground in the form of micrometeorites. An international program conducted for nearly 20 has determined that 5,200 tons per year of these micrometeorites reach the ground.
Kuiper Belt is a circumstellar disc in the solar system beyond the known planets, extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia and water. The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets: Pluto, Haumea and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, are thought to have originated in the region. Heliosphere - Oort Cloud.
Circumstellar Disc is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accumulation of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reservoirs of material out of which planets may form. Around mature stars, they indicate that planetesimal formation has taken place and around white dwarfs, they indicate that planetary material survived the whole of stellar evolution. Such a disc can manifest itself in various ways.
Space Weather - Space Weather - Telescopes
Figure 3: Oxygen and chromium isotopic composition of Meteorites.
New method to determine the origin of stardust in meteorites. Meteorites are critical to understanding the beginning of our solar system and how it has evolved over time. However, some meteorites contain grains of stardust that predate the formation of our solar system and are now providing important information about how the elements in the universe formed.
Astronomers find the smallest asteroids ever detected in the main belt. Astronomers have found a way to spot the smallest, 'decameter,' asteroids within the main asteroid belt. They used their approach to detect more than 100 new asteroids, ranging from the size of a bus to several stadiums wide, which are the smallest asteroids within the main belt detected to date.
Meteor Shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extremely high speeds on parallel trajectories. Most meteors are smaller than a grain of sand, so almost all of them disintegrate and never hit the Earth's surface. Very intense or unusual meteor showers are known as meteor outbursts and meteor storms, which produce at least 1,000 meteors an hour, most notably from the Leonids. The Meteor Data Centre lists over 900 suspected meteor showers of which about 100 are well established. Several organizations point to viewing opportunities on the Internet. NASA maintains a daily map of active meteor showers.
Perseids are prolific meteor showers associated with the comet Swift–Tuttle. The Perseids are so called because the point from which they appear to hail (called the radiant) lies in the constellation Perseus. Orionids (wiki)
April Lyrids are a meteor shower lasting from April 16 to April 25 each year. The radiant of the meteor shower is located in the constellation Lyra, near its brightest star, Vega. The peak of the shower is typically around April 22 each year. The shower usually peaks around April 22 and the morning of April 23. Counts typically range from 5 to 20 meteors per hour, averaging around 10. The source of the meteor shower are particles of dust shed by the long-period Comet C/1861 G1 Thatcher. The April Lyrids are the strongest annual shower of meteors from debris of a long-period comet, mainly because as far as other intermediate long-period comets go (200–10,000 years), this one has a relatively short orbital period of about 415 years. The Lyrids have been observed and reported since 687 BC; no other modern shower has been recorded as far back in time. Occasionally, the shower intensifies when the planets steer the one-revolution dust trail of the comet into Earth's path, an event that happens about once every 60 years.
Are meteor showers a danger to satellites? Space is big, and satellites are small, and a meteor shower is incredibly sparse. When a meteor hits a satellite at high speed, the tiny rock vaporizes into hot, electrically charged gas—or plasma—that can short out circuits and damage onboard electronics, causing the satellite to spin out of control. A meteor is moving fast enough to cause damage, but it won't destroy a satellite, it'll put a small crater in whatever it hits.
Leonids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Tempel–Tuttle, which are also known for their spectacular meteor storms that occur about every 33 years. The Leonids get their name from the location of their radiant in the constellation Leo, where the meteors appear to radiate from that point in the sky. The Leonids also produce meteor storms or very large outbursts about every 33 years, during which activity exceeds 1,000 meteors per hour, with some events exceeding 100,000 meteors per hour, in contrast to the sporadic background (5 to 8 meteors per hour) and the shower background (several meteors per hour). November 12, 1833, there was a meteor shower so intense that it was possible to see up to 100,000 meteors crossing the sky every hour. (2023 November 17).
Taurids are an annual meteor shower, associated with the comet Encke. The Taurids are actually two separate showers, with a Southern and a Northern component. The Southern Taurids originated from Comet Encke, while the Northern Taurids originated from the asteroid 2004 TG10. They are named after their radiant point in the constellation Taurus, where they are seen to come from in the sky. Because of their occurrence in late October and early November, they are also called Halloween fireballs. Encke and the Taurids are believed to be remnants of a much larger comet, which has disintegrated over the past 20,000 to 30,000 years, breaking into several pieces and releasing material by normal cometary activity or perhaps occasionally by close encounters with the tidal force of Earth or other planets (Whipple, 1940; Klacka, 1999). In total, this stream of matter is the largest in the inner Solar System. Since the meteor stream is rather spread out in space, Earth takes several weeks to pass through it, causing an extended period of meteor activity, compared with the much smaller periods of activity in other showers. The Taurids are also made up of weightier material, pebbles instead of dust grains.
Asteroids
Asteroid are minor planets, especially those of the inner Solar System. Any of numerous small celestial bodies composed of rock and metal that move around the sun ranging in size from nearly 600 miles (1,000 km) across (Ceres) to dust particles, are found (as the asteroid belt ) especially between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, though some have more eccentric orbits, and a few pass close to the earth or enter the atmosphere as meteors.
Near-Earth Object is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth.
Asteroid Impact Avoidance comprises a number of methods by which near-Earth objects or NEO could be diverted, preventing destructive impact events. A sufficiently large impact by an asteroid or other NEOs would cause, depending on its impact location, massive tsunamis, multiple firestorms and an impact winter caused by the sunlight-blocking effect of placing large quantities of pulverized rock dust, and other debris, into the stratosphere.
Asteroid Watch
How many near-Earth asteroids have been discovered so far? At the start of 2019, the number of discovered near-Earth asteroids totaled more than 19,000. An average of 30 new discoveries are added each week. No known asteroid poses a significant risk of impact with Earth over the next 100 years.
How to Deflect a Killer Asteroid - Double Asteroid Redirection Test or DART is a planned space probe that will visit the double asteroid Didymos and demonstrate the kinetic effects of crashing an impactor spacecraft into an asteroid moon for planetary defense purposes. The mission is intended to test whether a spacecraft impact could successfully deflect an asteroid on a collision course with Earth.
Planetary Defense Coordination Office provides early detection of potentially hazardous objects or PHOs – the subset of NEOs whose orbits predict they will come within 5 million miles of Earth’s orbit; and of a size large enough (30 to 50 meters) to cause significant damage on Earth; Tracks and characterizes PHOs and issues warnings of the possible effects of potential impacts; Studies strategies and technologies for mitigating PHO impacts; and Plays a lead role in coordinating U.S. government planning for response to an actual impact threat.
How to Deflect an Asteroid. Use the force of a nuclear bomb detonation that would blast the asteroid away, though the planet would then have to contend with any nuclear fallout. Or use a kinetic impactor or a spacecraft, rocket, or other projectile that, if aimed at just the right direction, with adequate speed, should collide with the asteroid, and transfer some fraction of its momentum, and veer it off course and prevent a keyhole passage.
Impact Event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.
Supercharged Light Pulverizes Asteroids. The majority of stars in the universe will become luminous enough to blast surrounding asteroids into successively smaller fragments using their light alone, according to an astronomer.
Asteroid Belt is the circumstellar disc in the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. It is occupied by numerous irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids or minor planets.
Asteroids Videos (youtube) - Day of the Asteroid (youtube)
If You Could See All The Asteroids, What Would The Sky Look Like? (youtube)
Asteroid Hunter Named Lucy. A NASA spacecraft named Lucy rocketed into the sky with diamonds Saturday morning on a 12-year quest to explore eight asteroids. NASA Launches a Robotic Explorer Named Lucy. “Tar clear.” NASA on Saturday launched a probe toward clusters of asteroids along Jupiter's orbital path. They're known as the Trojan swarms, and they represent the final unexplored regions of asteroids in the solar system.
The number of asteroid impacts on the Moon and Earth increased by two to three times starting around 290 million years ago. The relative rarity of large craters on Earth older than 290 million years and younger than 650 million years is not because we lost the craters, but because the impact rate during that time was lower than it is now.
Geological Time - Space Law
Astronomical Object is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms object and body are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial object is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures. Examples of astronomical objects include planetary systems, star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies, while asteroids, moons, planets, and stars are astronomical bodies. A comet may be identified as both body and object: It is a body when referring to the frozen nucleus of ice and dust, and an object when describing the entire comet with its diffuse coma and tail.
Asteroid Mining is the exploitation of raw materials from asteroids and other minor planets, including near-Earth objects. Hard rock minerals could theoretically be mined from an asteroid or a spent comet. Precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum group metals could be transported back to Earth, while iron group metals and other common ones could be used for construction in space. Difficulties include the high cost of spaceflight, unreliable identification of asteroids which are suitable for mining, and ore extraction challenges. Thus, terrestrial mining remains the only means of raw mineral acquisition used today. If space program funding, either public or private, dramatically increases, this situation may change as resources on Earth become increasingly scarce compared to demand and the full potentials of asteroid mining—and space exploration in general—are researched in greater detail.
Comets
Comet is an icy small solar system body that, when passing close to the Sun, heats up and begins to outgas, displaying a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. Periodic comets or short-period comets are generally defined as those having orbital periods of less than 200 years. Long-period comets have highly eccentric orbits and periods ranging from 200 years to thousands of years.
Heliosphere - Oort Cloud - Our Solar System - Planets
Hypatia is a small stone, thought to be the first known specimen of a comet nucleus.
Episode 3 Symbols of an Alien Sky: The Electric Comet (Full Documentary on youtube)
The Comet Is Coming - Super Zodiac, Summon The Fire, Blood Of The Past. (tiny desk concert)
Comet 2I/Borisov is a mysterious visitor from another star and is only the second interstellar object known to have passed through the solar system on its way back to interstellar space. The Sun's gravity is slightly deflecting its trajectory, but can't capture it because of the shape of its orbit and high velocity of about 100,000 miles per hour. (Comet 2I/Borisov is 3,200 feet across length of nine football fields.) Clovis Comet.
Minor Planets
Dwarf Planet is a planetary-mass object that does not dominate its region of space (as a true or classical planet does) and is not a satellite. That is, it is in direct orbit of the Sun and is massive enough to be plastic – for its gravity to maintain it in a hydrostatically equilibrious shape (usually a spheroid) – but has not cleared the neighborhood of its orbit of similar objects. The prototype dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to planetary geologists is that, being possibly differentiated and geologically active bodies, they may display planetary geology, an expectation borne out by the 2015 New Horizons ission to Pluto.
 Dwarf Planet 2014 QZ22
on the right is about 330 miles across and some 8.5 billion
miles from the sun. It takes 1,100 years to complete one orbit. Sedna,
Eris and Makemake have all been discovered in the past decade or so. Add to that Pluto.
Dwarf Planet 2014 QZ22
on the right is about 330 miles across and some 8.5 billion
miles from the sun. It takes 1,100 years to complete one orbit. Sedna,
Eris and Makemake have all been discovered in the past decade or so. Add to that Pluto.Minor Planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun (or more broadly, any star with a planetary system) that is neither a planet nor exclusively classified as a comet. Before 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially used the term minor planet, but during that year's meeting it reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs). Minor planets can be dwarf planets, asteroids, trojans, centaurs, Kuiper belt objects, and other trans-Neptunian objects. As of 2019, the orbits of 794,832 minor planets were archived at the Minor Planet Center, 541,128 of which had received permanent numbers.
Minor Planet Center takes positional measurements of minor planets, comets and outer irregular natural satellites of the major planets. The MPC is responsible for the identification, designation and orbit computation for all of these objects. This involves maintaining the master files of observations and orbits, keeping track of the discoverer of each object, and announcing discoveries to the rest of the world via electronic circulars and an extensive website. The MPC operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, under the auspices of Division F of the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
Earth-Crossing Minor Planets is a near-Earth asteroid whose orbit crosses that of Earth as observed from the ecliptic pole of Earth's orbit. Theia (wiki)
Cross orbits of smaller moons that collided and merge, slowly building the bigger moon.
Centaur is a small Solar System body with either a perihelion or a semi-major axis between those of the outer planets. Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one centaur, 514107 Ka?epaoka?awela, which may be in a stable (though retrograde) orbit. Centaurs typically behave with characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000.
Trojan is a small celestial body (mostly asteroids) that shares the orbit of a larger one, remaining in a stable orbit approximately 60° ahead or behind the main body near one of its Lagrangian points L4 and L5. Trojans can share the orbits of planets or of large moons.
Moon
 The Moon
is
Earths natural satellite
that orbits the Earth every 27.3 days.
The Moon keeps nearly the same face turned towards the Earth at all times
because of
gravitational locking.
The moon is 238,857 miles from the Earth and has a diameter of
2,160 miles. The Moon is currently moving away from the Earth at
about 3.8 centimeters per year. The moon is an astronomical body that
orbits planet Earth, being Earth's only permanent natural satellite.
It is the fifth-largest natural satellite in the
Solar System, and the largest among planetary satellites relative to
the size of the planet that it orbits (its primary). Following Jupiter's
satellite Io, the Moon is second-densest satellite among those whose
densities are known. The average distance of the Moon from the Earth is
384,400 km, or
1.28 light-seconds. The Moon is thought to have formed about 4.51 billion
years ago, not long after Earth. There are several hypotheses for its
origin; the most widely accepted explanation is that the Moon formed from
the debris left over after a giant impact between Earth and a Mars-sized
body called Theia. There are more than 200 moons
in our solar system. Most of the major planets – all except Mercury and
Venus – have moons. Pluto and some other dwarf planets, as well as many
asteroids, also have small moons. Eclipse.
The Moon
is
Earths natural satellite
that orbits the Earth every 27.3 days.
The Moon keeps nearly the same face turned towards the Earth at all times
because of
gravitational locking.
The moon is 238,857 miles from the Earth and has a diameter of
2,160 miles. The Moon is currently moving away from the Earth at
about 3.8 centimeters per year. The moon is an astronomical body that
orbits planet Earth, being Earth's only permanent natural satellite.
It is the fifth-largest natural satellite in the
Solar System, and the largest among planetary satellites relative to
the size of the planet that it orbits (its primary). Following Jupiter's
satellite Io, the Moon is second-densest satellite among those whose
densities are known. The average distance of the Moon from the Earth is
384,400 km, or
1.28 light-seconds. The Moon is thought to have formed about 4.51 billion
years ago, not long after Earth. There are several hypotheses for its
origin; the most widely accepted explanation is that the Moon formed from
the debris left over after a giant impact between Earth and a Mars-sized
body called Theia. There are more than 200 moons
in our solar system. Most of the major planets – all except Mercury and
Venus – have moons. Pluto and some other dwarf planets, as well as many
asteroids, also have small moons. Eclipse.Quasi Moon or quasi-satellite is an object in a specific type of co-orbital configuration (1:1 orbital resonance) with a planet (or dwarf planet) where the object stays close to that planet over many orbital periods. A quasi-satellite's orbit around the Sun takes the same time as the planet's, but has a different eccentricity (usually greater). When viewed from the perspective of the planet by an observer facing the Sun, the quasi-satellite will appear to travel in an oblong retrograde loop around the planet
Other types of orbit in a 1:1 resonance with the planet include horseshoe orbits and tadpole orbits around the Lagrangian points, but objects in these orbits do not stay near the planet's longitude over many revolutions about the star. Objects in horseshoe orbits are known to sometimes periodically transfer to a relatively short-lived quasi-satellite orbit, and are sometimes confused with them. Earth currently has eight known quasi-satellites or quasi-moons, a type of asteroid that orbits the Sun but appears to be orbiting Earth from a certain vantage point, following a path that moves in and out of the planet's vicinity. These include objects like 2025 PN7, Kamoʻoalewa (469219), and 2023 FW1.
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter captured the sharpest images ever of the Moon taken from space that you can see where Apollo missions landed.
Lunar Mare are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient volcanic eruptions. They were dubbed maria, Latin for 'seas', by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich composition, and hence appear dark to the naked eye. The maria cover about 16% of the lunar surface, mostly on the side visible from Earth. The few maria on the far side are much smaller, residing mostly in very large craters. The traditional nomenclature for the Moon also includes one oceanus (ocean), as well as features with the names lacus ('lake'), palus ('marsh'), and sinus ('bay'). The last three are smaller than maria, but have the same nature and characteristics.
The face that the Moon shows to Earth looks far different from the one it hides on its far side. Researchers have a new explanation for the two-faced Moon. The nearside is home to a compositional anomaly known as the Procellarum KREEP terrane (PKT) -- a concentration of potassium (K), rare earth elements (REE), phosphorus (P), along with heat-producing elements like thorium. KREEP seems to be concentrated in and around Oceanus Procellarum, the largest of the nearside volcanic plains, but is sparse elsewhere on the Moon. Far Side of the Moon is the hemisphere of the Moon that always faces away from Earth. The far side's terrain is rugged, with a multitude of impact craters and relatively few flat lunar maria. It has one of the largest craters in the Solar System, the South Pole–Aitken basin. Although both sides of the moon experience two weeks of sunlight followed by two weeks of night, the far side is sometimes incorrectly referred to as the Dark Side of the Moon, but all parts of the Moon see around 14.77 days of sunlight, followed by 14.77 days of night.
 The Moon Orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one
revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the stars in about
27.32
days (a tropical month and sidereal month) and one revolution relative
to the Sun in about 29.53 days (a synodic month). Earth and the Moon
orbit about their barycentre (common center of
mass), which lies about 4,600 km (2,900 mi) from Earth's center (about
72% of its radius). On average, the distance to the Moon is about
385,000 km (239,000 mi) from Earth's center, which corresponds to about
60 Earth radii or 1.282 light-seconds. With a mean
orbital velocity of 1.022 km/s (0.635 miles/s), the Moon covers a
distance approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the
celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most
satellites of other planets in that its orbit
is close to the ecliptic plane instead of to its primary's (in this
case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital
plane is inclined by about 5.1° with respect to the ecliptic plane,
whereas the Moon's equatorial plane is tilted by only 1.5°. Moon does
not orbit around the Earth directly above our equator. The Moon's orbit
is tilted by 6.7 degrees to the Earth's equator. So sometimes we can see
more of the Moon's south pole, and at other times, more of its north
pole. High tide and
low tide is the
bulge of water that earth rotates into and out of.
The Moon Orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one
revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the stars in about
27.32
days (a tropical month and sidereal month) and one revolution relative
to the Sun in about 29.53 days (a synodic month). Earth and the Moon
orbit about their barycentre (common center of
mass), which lies about 4,600 km (2,900 mi) from Earth's center (about
72% of its radius). On average, the distance to the Moon is about
385,000 km (239,000 mi) from Earth's center, which corresponds to about
60 Earth radii or 1.282 light-seconds. With a mean
orbital velocity of 1.022 km/s (0.635 miles/s), the Moon covers a
distance approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the
celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most
satellites of other planets in that its orbit
is close to the ecliptic plane instead of to its primary's (in this
case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital
plane is inclined by about 5.1° with respect to the ecliptic plane,
whereas the Moon's equatorial plane is tilted by only 1.5°. Moon does
not orbit around the Earth directly above our equator. The Moon's orbit
is tilted by 6.7 degrees to the Earth's equator. So sometimes we can see
more of the Moon's south pole, and at other times, more of its north
pole. High tide and
low tide is the
bulge of water that earth rotates into and out of.Horseshoe Orbit is a type of co-orbital motion of a small orbiting body relative to a larger orbiting body (such as Earth). The orbital period of the smaller body is very nearly the same as for the larger body, and its path appears to have a horseshoe shape as viewed from the larger object in a rotating reference frame.
 Lunar Phase
is the shape of the illuminated or sunlit portion of the Moon as seen by an
observer on Earth. The lunar phases change cyclically as the Moon orbits
the Earth, according to the changing positions of the Moon and Sun
relative to the Earth.
Each moon phase has a name. New Moon, waxing crescent, first
quarter, waxing gibbous, full Moon, waning gibbous, third quarter and
waning crescent. The Moon's rotation is tidally locked by the
Earth's gravity, therefore the same lunar surface always faces Earth. This
face is variously sunlit depending on the position of the Moon in its
orbit. Therefore, the portion of this hemisphere that is visible to an
observer on Earth can vary from about 100% (full moon) to 0% (new moon).
The lunar terminator is the boundary between the illuminated and darkened
hemispheres. Each of the four "intermediate" lunar phases is
roughly seven days (~7.4 days) but this varies slightly due to the
elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit. Aside from some craters near the
lunar poles such as Shoemaker, all parts of the Moon see around 14.77 days
of sunlight, followed by 14.77 days of "night". (The side of the Moon
facing away from the Earth is sometimes called the "dark side", which is a
misnomer). Lunar Phase or Moon phase is the
shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from Earth. The
lunar phases gradually change over a synodic month (about
29.53 days) as the Moon's orbital
positions around Earth and Earth around the Sun shift. The visible side
of the moon is variously sunlit, depending on the position of the Moon
in its orbit. Thus, this face's sunlit portion can vary from 0% (at new
moon) to 100% (at full moon). Each of the four "intermediate" lunar
phases is approximately 7.4 days, with slight variation due to the
Moon's orbit's elliptical shape.
Lunar Phase
is the shape of the illuminated or sunlit portion of the Moon as seen by an
observer on Earth. The lunar phases change cyclically as the Moon orbits
the Earth, according to the changing positions of the Moon and Sun
relative to the Earth.
Each moon phase has a name. New Moon, waxing crescent, first
quarter, waxing gibbous, full Moon, waning gibbous, third quarter and
waning crescent. The Moon's rotation is tidally locked by the
Earth's gravity, therefore the same lunar surface always faces Earth. This
face is variously sunlit depending on the position of the Moon in its
orbit. Therefore, the portion of this hemisphere that is visible to an
observer on Earth can vary from about 100% (full moon) to 0% (new moon).
The lunar terminator is the boundary between the illuminated and darkened
hemispheres. Each of the four "intermediate" lunar phases is
roughly seven days (~7.4 days) but this varies slightly due to the
elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit. Aside from some craters near the
lunar poles such as Shoemaker, all parts of the Moon see around 14.77 days
of sunlight, followed by 14.77 days of "night". (The side of the Moon
facing away from the Earth is sometimes called the "dark side", which is a
misnomer). Lunar Phase or Moon phase is the
shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from Earth. The
lunar phases gradually change over a synodic month (about
29.53 days) as the Moon's orbital
positions around Earth and Earth around the Sun shift. The visible side
of the moon is variously sunlit, depending on the position of the Moon
in its orbit. Thus, this face's sunlit portion can vary from 0% (at new
moon) to 100% (at full moon). Each of the four "intermediate" lunar
phases is approximately 7.4 days, with slight variation due to the
Moon's orbit's elliptical shape.Moon Phases - Calendars (time measuring) - Solar Eclipse - Moon Rise Times
New Moon is the first phase of the Moon, when it orbits not seen from the Earth, the moment when the Moon and the Sun have the same ecliptical longitude. The Moon is not visible at this time except when it is seen in silhouette during a solar eclipse when it is illuminated by earthshine. A new moon is when the moon is in between the earth and the sun, which causes more gravitational pull on the earth. There is also more gravitational pull on the earth from the moon when the moon is the closet to the earth during it's elliptical orbit. During these moments when the gravitational pull is at it's peak, the earth has higher ocean tides and sometimes experiences earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Apsis is an extreme point in an object's orbit. During the new moon, the moon is between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon that is lit by the sun is facing away from our planet. This means that the moon is still up there, but we can’t see it in the daytime, because all of the sun’s light is getting reflected away from us. As the moon continues in its orbit around the Earth, away from the sun, increasingly more of its sunlit surface is visible. This is why the moon sometimes appears as a crescent or half-moon. When it’s farther from the sun and visible above the horizon, it’s easier to spot during the day. Usually, the moon travels at an angle that still allows sunlight to reach it when it’s behind the Earth. But a few times in the year, it passes behind the Earth at a precise angle where no light can reach it. This is what’s called a lunar eclipse. With some variations, the Waxing Crescent Moon rises in the daytime before noon and becomes visible in the day sky. It gets more visible around sunset but typically sets before midnight. The moon rises in the east and sets in the west just like everything else in the night sky. That's because Earth is rotating from west to east.
Supermoons are when a full moon coincides with the Moon's closest approach to Earth in its elliptical orbit, a point known as perigee. During every 27-day orbit around Earth, the Moon reaches both its perigee, about 226,000 miles (363,300 km) from Earth, and its farthest point, or apogee, about 251,000 miles (405,500 km) from Earth. A perigean full moon, better known as a supermoon, happens when the moon is full during the closest point in its orbit around Earth. This gives its appearance an extra pop, making it look up to 8% bigger and 16% brighter than a typical full moon, the moon's typical orbit ranges between 226,000 and 251,000 miles from Earth. The end-of-August supermoon will be the biggest and brightest of 2023 because the moon will be "exceptionally close" to Earth at 222,043 miles. A blue moon has to do with frequency, referring to when there's a second full moon in a single calendar month. Blue moon is also used to describe the third of four full moons in an astrological season. The moon takes 27.3 days to orbit the Earth, but because of how the sun's light hits the satellite, it takes 29.5 days to complete its lunar cycle from one new moon to the next. This year's blue supermoon will peak at 9:36 p.m. ET on Aug. 30, the last blue supermoon was in December 2009, and the next one won't be until August 2032.
Moon illusion is an optical illusion which causes the Moon to appear larger near the horizon than it does higher up in the sky.
Waning Gibbous moon phase is between a half moon and full moon. Waning means it is getting smaller. It's at this point that the moon is more than one half illuminated but not fully and is constantly decreasing. The Moon displays these eight phases one after the other as it moves through its cycle each month. Moon phases are believed to have effects on humans and not just the planet. Waning Gibbous is a sign of gratitude. This is a time to look inwards and reflect on the intentions and goals you set for yourself at the beginning of the lunar cycle. The best crystal to work with at this time is opalite as it will help you rebalance yourself. Spiritually, it is time to get rid of some of those bad habits, stresses, and any negative thinking that you have been experiencing. Waning moon represents a time of reflection, purging and decluttering. Time to let go of people and things that no longer serve you. Individuals born on a Waning Gibbous are highly self-aware, giving them a unique potential for growth. They make great communicators, but sometimes need to remind themselves when it's time to listen.
 Earthlight is the diffuse
reflection of
sunlight reflected from
Earth's surface and clouds. Earthshine is
an example of planetshine, also known as the
Moon's Ashen Glow or the Da Vinci Glow,
which is the dim illumination of the otherwise unilluminated portion of the Moon by this
indirect sunlight. Earthlight on the Moon during the waxing crescent is
called "the old Moon in the new Moon's arms", while that during the waning
crescent is called "the new Moon in the old Moon's arms". Earthshine is a dull glow which
lights up the unlit part of the Moon because the
Sun's light reflects off the Earth's surface and back onto the Moon.
When you look at a
crescent moon shortly after sunset or before sunrise, you can
sometimes see not only the bright crescent of the moon, but also the
rest of the moon as a dark disk. That pale glow on the unlit part of a
crescent moon is light reflected from Earth.
It's called earthshine.
Earthlight is the diffuse
reflection of
sunlight reflected from
Earth's surface and clouds. Earthshine is
an example of planetshine, also known as the
Moon's Ashen Glow or the Da Vinci Glow,
which is the dim illumination of the otherwise unilluminated portion of the Moon by this
indirect sunlight. Earthlight on the Moon during the waxing crescent is
called "the old Moon in the new Moon's arms", while that during the waning
crescent is called "the new Moon in the old Moon's arms". Earthshine is a dull glow which
lights up the unlit part of the Moon because the
Sun's light reflects off the Earth's surface and back onto the Moon.
When you look at a
crescent moon shortly after sunset or before sunrise, you can
sometimes see not only the bright crescent of the moon, but also the
rest of the moon as a dark disk. That pale glow on the unlit part of a
crescent moon is light reflected from Earth.
It's called earthshine.Planetshine is the dim illumination, by sunlight reflected from a planet, of all or part of the otherwise dark side of any moon orbiting the body. Planetlight is the diffuse reflection of sunlight from a planet, whose albedo can be measured. Albedo
is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation.
Lunar Theory attempts to account for the motions of the Moon.
 Lunar
Eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly behind Earth and into its
shadow. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and the Moon are aligned
(in syzygy) exactly or very closely so, with the planet in between. Hence,
a lunar eclipse can occur only on the night of a full moon. The type and
length of an eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to either node of its
orbit. (a totally eclipsed Moon is sometimes called a
blood moon.)
Selenelion or selenehelion, also called a
horizontal eclipse, occurs where and when both the Sun and an
eclipsed Moon can be observed at the same time. The event can only be
observed just before sunset or just after sunrise, when both bodies will
appear just above opposite horizons at nearly opposite points in the
sky, or when the sun and moon are 180 degrees apart in the sky at the
same time.
Lunar
Eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly behind Earth and into its
shadow. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and the Moon are aligned
(in syzygy) exactly or very closely so, with the planet in between. Hence,
a lunar eclipse can occur only on the night of a full moon. The type and
length of an eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to either node of its
orbit. (a totally eclipsed Moon is sometimes called a
blood moon.)
Selenelion or selenehelion, also called a
horizontal eclipse, occurs where and when both the Sun and an
eclipsed Moon can be observed at the same time. The event can only be
observed just before sunset or just after sunrise, when both bodies will
appear just above opposite horizons at nearly opposite points in the
sky, or when the sun and moon are 180 degrees apart in the sky at the
same time.Natural Satellite or moon is an astronomical body that orbits a planet or minor planet, or sometimes another small Solar System body. In the Solar System there are six planetary satellite systems containing 185 known natural satellites. Four IAU-listed dwarf planets are also known to have natural satellites: Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris. As of September 2018, there are 334 other minor planets known to have moons. The Earth–Moon system is unique in that the ratio of the mass of the Moon to the mass of Earth is much greater than that of any other natural-satellite–planet ratio in the Solar System (although there are minor-planet systems with even greater ratios, notably the Pluto–Charon system). At 3,474 km (2,158 miles) across, the Moon is 0.27 times the diameter of Earth.
Subsatellite is a natural satellite or an artificial satellite that orbits a natural satellite, i.e. a "moon of a moon", also known as a moonmoon, submoon, or grandmoon. It is inferred from the empirical study of natural satellites in the Solar System that subsatellites may be elements of planetary systems. In the Solar System, the giant planets have large collections of natural satellites. The majority of detected exoplanets are giant planets; at least one, Kepler-1625b, may have a very large exomoon, named Kepler-1625b I. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that subsatellites may exist in the Solar System, and in planetary systems beyond the Solar System. Nonetheless, no "moon of a moon" or subsatellite is known as of 2018 in the Solar System or beyond the Solar System. In most cases, the tidal effects of the planet would make such a system unstable.
Moons may yield clues to what makes planets habitable. Because the moon is so important to life on Earth, scientists conjecture that a moon may be a potentially beneficial feature in harboring life on other planets. Most planets have moons, but Earth's moon is distinct in that it is large compared to the size of Earth; the moon's radius is larger than a quarter of Earth's radius, a much larger ratio than most moons to their planets. New research finds that distinction significant.
How the moon turned itself inside out. Scientists combined computer simulations and spacecraft data to solve a long-standing mystery surrounding the moon's 'lopsided' geology. Linking analyses of the moon's gravity field with models of its earliest evolution, scientists tell a story of the moon turning itself inside out after it solidified from a primordial magma ocean. The process left behind a vestige of dense, titanium-rich material beneath its Earth-facing side that makes its presence known by gravity anomalies. About 4.5 billion years ago, a small planet smashed into the young Earth, flinging molten rock into space. Slowly, the debris coalesced, cooled and solidified, forming our moon. This scenario of how the Earth's moon came to be is the one largely agreed upon by most scientists.
Supermoon Lunar Eclipse | NASA (youtube) - Lunar Eclipse Viewing Path - 2018 (image)
First to the Moon: The Journey of Apollo 8 (youtube) - In 1968 the battle for civil rights was turning and the world was in turmoil. This is the story of the first people to leave the Earth and travel to the Moon, this is Apollo 8. Three men went faster and farther than anyone thought possible. They launched on December 21, 1968. Apollo 8 was the first crewed spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit, reach the Moon, orbit it, and return safely to Earth. Frank Borman was Commander, Bill Anders was Lunar Module Pilot, and Jim Lovell was the Command Module Pilot. Earthrise is a photograph of Earth and some of the Moon's surface that was taken from lunar orbit by astronaut William Anders on December 24, 1968, during the Apollo 8 mission. EARTHRISE: The First Lunar Voyage Apollo 8 Mission (youtube)
Apollo Program (wiki) - Neil Armstrong. Space Shuttle - Apollo is the Greek god of light. Artemis is the goddess of the moon and twin sister of Apollo. Artemis Program (wiki) - Exploration of the Moon (wiki).
Apollo 11 was the first Human on the Moon on July 20,1969. "One small step for man, one giant leap for mankind" Video.
Biggest Space Milestones: Project Gemini, Venus Express, NASA's EMU | Trajectory | Free Documentary (youtube)
Space Travel - Living in Space - Solar System
Other Moons of Earth (wiki) - 3753 Cruithne (wiki) - Near-Earth Asteroid 3753 Cruithne (youtube)
 You Can Fit Every Planet In The
Solar System Between Earth And The Moon.
Planet Average Diameter.
You Can Fit Every Planet In The
Solar System Between Earth And The Moon.
Planet Average Diameter.Mercury 4,879 km
Venus 12,104 km
Mars 6,771 km
Jupiter 139,822 km
Saturn 116,464 km
Uranus 50,724 km
Neptune 49,244 km
Total = 380,008 km
The average distance from the Earth to the Moon is 384,400 km. And check it out, that leaves us with 4,392 km to spare. So even Pluto could fit. 2,302 km.
1 AU = 150 million kilometers (93 million miles).
Moon Base: The moon doesn’t have an atmosphere or a magnetic field to protect us from the Sun, meteors or cosmic rays, so we can’t live on its surface. But a team of Japanese scientists looking at some deep lunar pits think they’ve found more than just a hole—they think they’ve found tunnels that cut through our satellite’s volcanic rock for miles. They might be our first home beyond Earth.

 I'm kind of like the Moon. I'm totally necessary but I'm not
the main attraction. And my skin looks like I have been hit by millions of
asteroids, but I still look interesting when I'm far away, and people are
still interested in visiting me. Some of us are
born to be planets and some of us are born to shine like the sun, and some
of us are just satellites waiting to be a part
of something bigger than ourselves. We all have a place in this life and
we all have a job to do. Our time in this universe is just beginning.
And we are more together that we are apart.
I'm kind of like the Moon. I'm totally necessary but I'm not
the main attraction. And my skin looks like I have been hit by millions of
asteroids, but I still look interesting when I'm far away, and people are
still interested in visiting me. Some of us are
born to be planets and some of us are born to shine like the sun, and some
of us are just satellites waiting to be a part
of something bigger than ourselves. We all have a place in this life and
we all have a job to do. Our time in this universe is just beginning.
And we are more together that we are apart.Moonstruck is being dazed or distracted with romantic sentiment from being in love, sometimes a person is unable to think or act normally because of the over whelming effects of love, love that can sometimes make you a little loony. Moonstruck is also a 1987 American romantic comedy drama film.
Fly Me To The Moon - Frank Sinatra (youtube) - Fly me to the moon, Let me play among the stars, Let me see what spring is like on, A-Jupiter and Mars.
Elton John - Rocket Man (youtube) - Space Travel
Ground Control to Major Tom by David Bowie (youtube) - I wouldn't say that planet earth is blue and there's nothing I can do, I would say there is always something to do, especially on planet earth, but if you had to express a particular feeling based on a particular time period in human history, then the lyrics are perfect.
“Shoot for the moon. Even if you miss, you'll land among the stars.” ― Norman Vincent Peale. (the phrase meant to inspire people to pursue ambitious goals, reasoning that even if they fail to achieve them, they may still accomplish other great things while trying.) - "Do or do not. There is no try." Yoda.
"What can we gain by sailing to the moon if we are not able to cross the abyss that separates us from ourselves?"
Voyager 1 and 2 Space Probes
 Voyager
2 was launched first, on August 20, 1977; has been operating for 40
years and 17 days as of September 6, 2017. It remains in contact through
the
Deep Space Network.
NASA’s Voyager 2
Enters Interstellar Space Forty-one years after it launched into space (youtube).
More than 11 billion miles from the sun. ET Phone Home.
Voyager
2 was launched first, on August 20, 1977; has been operating for 40
years and 17 days as of September 6, 2017. It remains in contact through
the
Deep Space Network.
NASA’s Voyager 2
Enters Interstellar Space Forty-one years after it launched into space (youtube).
More than 11 billion miles from the sun. ET Phone Home. Voyager 1 was launched on a faster, shorter trajectory on September 5, 1977. Both spacecraft were delivered to space aboard Titan-Centaur expendable rockets. Voyager is traveling around 40,000 mph or a million miles a day. Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator will run out of energy around 2026. V'ger (youtube) - Voyager
Voyager 1 and 2 Flight Paths (image)
Voyager 1 Gold Record Messages are already out of date, oh well. It's like the difference between what you would say when you are 5 years old compared to what you would say when you are 50 years old. I just hope that intelligent life has a good sense of humor, otherwise they will be in for a big surprise. (kidding). Voyager 1 was a Symbol of Life. This was our attempt to explain what we thought life was in 1977. Knowledge Preservation.
Viking Program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, Viking 1 and Viking 2 both launched in 1975, and landed on Mars in 1976. Each spacecraft was composed of two main parts: an orbiter spacecraft which photographed the surface of Mars from orbit, and a lander which studied the planet from the surface. The orbiters also served as communication relays for the landers once they touched down.
Space Probe is a robotic spacecraft that does not orbit the Earth, but, instead, explores further into outer space. A space probe may approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land on other planetary bodies; or enter interstellar space. Space Probes for Data Storage.
Deep Space 1 was launched on 24 October 1998 and carried out a flyby of asteroid 9969 Braille, which is a small Mars-crossing asteroid that orbits the Sun once every 3.58 years. Space Travel - Pulsar Navigation - Telescopes.
The Strangest Sights Cassini Saw: Postcards From Saturn | NPR's SKUNK BEAR (youtube)
Cassini Burns into Saturn After Grand Finale | Out There (youtube)
NASA at Saturn: Cassini's Grand Finale (youtube)
Space Shuttle
 Space Shuttle was a partially reusable low Earth
orbital spacecraft system. The first of four orbital test flights occurred
in 1981, leading to operational flights beginning in 1982. Five complete
Shuttle systems were built and used on a total of 135 missions from 1981
to 2011, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida.
Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary
probes,
and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST); conducted science experiments in
orbit; and participated in construction and servicing of the International
Space Station. The Shuttle fleet's total mission time was 1322 days, 19
hours, 21 minutes and 23 seconds. The Space Shuttle was retired from
service upon the conclusion of Atlantis's final flight on July 21, 2011.
Space Shuttle was a partially reusable low Earth
orbital spacecraft system. The first of four orbital test flights occurred
in 1981, leading to operational flights beginning in 1982. Five complete
Shuttle systems were built and used on a total of 135 missions from 1981
to 2011, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida.
Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary
probes,
and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST); conducted science experiments in
orbit; and participated in construction and servicing of the International
Space Station. The Shuttle fleet's total mission time was 1322 days, 19
hours, 21 minutes and 23 seconds. The Space Shuttle was retired from
service upon the conclusion of Atlantis's final flight on July 21, 2011.Space Shuttle Program - Shuttle Missions - Apollo
Space Shuttle Launch (youtube) - Space Shuttle (video)
Space Shuttle Thermal Protection System is the barrier that protected the Space Shuttle Orbiter during the searing 1,650 °C (3,000 °F) heat of atmospheric reentry. A secondary goal was to protect from the heat and cold of space while in orbit.
12 Miles High is the limit for a human without a Space Suit, you can actually survive in space for 2 minutes without a Space Suit, so what would you do in those last 2 minutes?
Suit Up - 50 Years of Spacewalks (youtube)
Smoke and fire RS 25 Rocket Engine Test (youtube) - NASA conducted a developmental test firing of the RS-25 rocket engine, on August 13 at the agency’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. The 535 second test was the sixth in the current series of seven-tests of the former space shuttle main engine. Four RS-25 engines will power the core stage of the new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket , which will carry humans deeper into space than ever before, including to an asteroid and Mars.
XS-1 Spacecraft is a planned experimental spaceplane/booster designed to deliver small satellites into orbit for the U.S. Military. It is intended to be reusable as frequently as 10 times in 10 days. The XS-1 is to directly replace the "first stage" of a multistage rocket that will be capable of flying at hypersonic speed at suborbital altitude, enabling one or more expendable upper stages to separate and deploy a payload into low Earth orbit. The XS-1 would then return to Earth, where it could be serviced fast enough to repeat the process at least once every 24 hours.
Aerojet Rocketdyne is an American rocket and missile propulsion manufacturer. Headquartered in Sacramento, California, the company is owned by Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings. Aerojet Rocketdyne was formed in 2013 when Aerojet (then owned by GenCorp) and Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne were merged, following the latter's acquisition by GenCorp from Pratt & Whitney. On April 27, 2015, the name of the holding company, GenCorp, was changed from GenCorp, Inc. to Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc.
Space Adventures (zero gravity flights) - Space Travel - The Moon - Action Physics - Light Speed.
Boeing X-37, also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle or OTV, is a reusable robotic spacecraft. It is boosted into space by a launch vehicle, then re-enters Earth's atmosphere and lands as a spaceplane. The X-37 is operated by the United States Space Force for orbital spaceflight missions intended to demonstrate reusable space technologies. It is a 120-percent-scaled derivative of the earlier Boeing X-40. The X-37 began as a NASA project in 1999, before being transferred to the United States Department of Defense in 2004. Until 2019, the program was managed by Air Force Space Command. An X-37 first flew during a drop test in 2006; its first orbital mission was launched in April 2010 on an Atlas V rocket, and returned to Earth in December 2010. Subsequent flights gradually extended the mission duration, reaching 780 days in orbit for the fifth mission, the first to launch on a Falcon 9 rocket. The latest mission, the sixth, launched on an Atlas V on 17 May 2020 and concluded on 12 November 2022, reaching a total of 908 days in orbit.
Robotic Spacecraft is an uncrewed spacecraft, usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather than crewed operation, due to lower cost and lower risk factors. In addition, some planetary destinations such as Venus or the vicinity of Jupiter are too hostile for human survival, given current technology. Outer planets such as Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are too distant to reach with current crewed spacecraft technology, so telerobotic probes are the only way to explore them. Nearly all satellites, landers and rovers are robotic spacecraft.
Unmanned Spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be remote controlled, remote guided or even autonomous, meaning they have a pre-programmed list of operations, which they will execute unless otherwise instructed.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle or a Drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system or UAS, which includes adding a ground-based controller and a system of communications with the UAV. The flight of UAVs may operate under remote control by a human operator, as remotely-piloted aircraft or RPA, or with various degrees of autonomy, such as autopilot assistance, up to fully autonomous aircraft that have no provision for human intervention.
NASA's Europa Clipper sails toward ocean moon of Jupiter. The massive spacecraft heads for Europa to search for signs of whether the ocean thought to exist beneath the moon's icy shell could support life. Europa Clipper also carries the largest solar arrays NASA has ever used for an interplanetary mission. With arrays extended, the spacecraft spans 100 feet (30.5 meters) from end to end. With propellant loaded, it weighs about 13,000 pounds (5,900 kilograms). In all, more than 4,000 people have contributed to Europa Clipper mission since it was formally approved in 2015. In 2031, the spacecraft will begin conducting its science-dedicated flybys of Europa. Coming as close as 16 miles or 25 kilometers to the surface. Eyes in the Sky.
Telerobotics is the area of robotics concerned with the control of semi-autonomous robots from a distance, chiefly using television, wireless networks (like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and the Deep Space Network) or tethered connections. It is a combination of two major subfields, which are teleoperation and telepresence.
Space Station
 International Space Station is a habitable artificial
satellite, in low Earth orbit. Its first component launched into orbit in
1998, and the ISS is now the largest artificial body in orbit and can
often be seen with the naked eye from Earth. The ISS consists of
pressurised modules, external trusses, solar arrays, and other components.
ISS components have been launched by Russian Proton and Soyuz rockets, and
American Space Shuttles. The ISS serves as a microgravity and space
environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments
in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and other
fields. The station is suited for the testing of spacecraft systems and
equipment required for missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS maintains an
orbit with an altitude of between 330 and 435 km (205 and 270 mi) by means
of reboost manoeuvres using the engines of the Zvezda module or visiting
spacecraft. It completes 15.54 orbits per day.
International Space Station is a habitable artificial
satellite, in low Earth orbit. Its first component launched into orbit in
1998, and the ISS is now the largest artificial body in orbit and can
often be seen with the naked eye from Earth. The ISS consists of
pressurised modules, external trusses, solar arrays, and other components.
ISS components have been launched by Russian Proton and Soyuz rockets, and
American Space Shuttles. The ISS serves as a microgravity and space
environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments
in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and other
fields. The station is suited for the testing of spacecraft systems and
equipment required for missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS maintains an
orbit with an altitude of between 330 and 435 km (205 and 270 mi) by means
of reboost manoeuvres using the engines of the Zvezda module or visiting
spacecraft. It completes 15.54 orbits per day. Gaia - Overview Effect - Shuttle - Moon
International Space Station (nasa) - Self Healing Material
Space Station also known as an orbital station or an orbital space station, is a Space craft capable of supporting crewmembers, which is designed to remain in space (most commonly as an artificial satellite in low Earth orbit) for an extended period of time and for other spacecraft to dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by lack of major propulsion or landing systems. Instead, other vehicles transport people and cargo to and from the station. As of 2018, two space stations are in Earth orbit: the International Space Station (operational and permanently inhabited) and China's Tiangong-2 spacelab (operational but not permanently inhabited). Various other components of future space stations, such as Japan's space elevator and U.S. inflatable modules, are also being tested in orbit. Previous stations include the Almaz and Salyut series, Skylab, Mir, and Tiangong-1. China, Russia, the U.S., as well as a few private companies are all planning other stations for the coming decades. Today's space stations are research platforms, used to study the effects of long-term space flight on the human body as well as to provide platforms for greater number and length of scientific studies than available on other space vehicles. Each crew member stays aboard the station for weeks or months, but rarely more than a year. Since the ill-fated flight of Soyuz 11 to Salyut 1, all human spaceflight duration records have been set aboard space stations. The duration record for a single spaceflight is 437.7 days, set by Valeriy Polyakov aboard Mir from 1994 to 1995. As of 2016, four cosmonauts have completed single missions of over a year, all aboard Mir. Space stations have also been used for both military and civilian purposes. The last military-use space station was Salyut 5, which was used by the Almaz program of the Soviet Union in 1976 and 1977. (150 billion Dollars). Electrical System of the ISS uses solar cells to directly convert sunlight to electricity. The ISS power system uses radiators to dissipate the heat away from the spacecraft. The radiators are shaded from sunlight and aligned toward the cold void of deep space.
Experiments in Space - Human Tissue Experiments on the ISS Could Advance 3D Printed Organs (youtube).
Departing Space Station Commander Provides Tour of Orbital Laboratory (youtube) Best Space Station Tour Ever. The ISS takes about 90 minutes to complete one orbit. Astronauts living on-board experience 16 sunrises and sunsets in a 24-hour period. ISS is 250 miles high and traveling at 17,000 miles per hour, More than 220 astronauts and cosmonauts from 18 different countries have been on the ISS since its "first element launch" in 1998. As of May 16, 2016, at 06:10 at GMT, 18 years after its initial launch, the ISS will begin its 100,000th orbit — 2.6 billion miles — around planet Earth as it crosses the equator. Effect of gravity and microgravity on intracranial pressure. Microgravity raises pressure in the head and reshapes the eyeballs, which could be problematic for long-term space travel.
Space Travel
 Interstellar Travel is a hypothetical
piloted or
unpiloted travel between stars or planetary systems. Interstellar travel
will be much more difficult than
interplanetary spaceflight; the distances
between the planets in the solar system are less than 30
astronomical
units (AU)—whereas the distances between stars are typically
hundreds of
thousands of AU, and usually expressed in light-years. Because of the
vastness of those distances, interstellar travel would require a high
percentage of the speed of light, huge travel time, lasting from decades
to millennia or longer, or a combination of both. There has to be a
way to travel faster than the speed of light, or, travel
without the
constraints of space and time like with a wormhole
portal or time travel. Matter and
mass has it limits, so maybe the key to traveling to other galaxies is
to be something else besides matter.
Interstellar Travel is a hypothetical
piloted or
unpiloted travel between stars or planetary systems. Interstellar travel
will be much more difficult than
interplanetary spaceflight; the distances
between the planets in the solar system are less than 30
astronomical
units (AU)—whereas the distances between stars are typically
hundreds of
thousands of AU, and usually expressed in light-years. Because of the
vastness of those distances, interstellar travel would require a high
percentage of the speed of light, huge travel time, lasting from decades
to millennia or longer, or a combination of both. There has to be a
way to travel faster than the speed of light, or, travel
without the
constraints of space and time like with a wormhole
portal or time travel. Matter and
mass has it limits, so maybe the key to traveling to other galaxies is
to be something else besides matter. Pulsar Navigation - Rockets - Dimensions - Communications - ET - Hospitable Planets - Astronaut Training - Human Body Vulnerabilities
Space Exploration is the ongoing discovery and exploration of celestial structures in outer space by means of continuously evolving and growing space technology. While the study of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, the physical exploration of space is conducted both by unmanned robotic space probes and human spaceflight.
"You don't have to travel faster than the speed of light, you just have to travel faster than time and space."
'Tube Map' around planets and moons made possible by knot theory. Scientists have developed a new method using knot theory to find the optimal routes for future space missions without the need to waste fuel.
Deep Field: The Impossible Magnitude of our Universe (youtube).
Per aspera ad astra is a popular Latin phrase meaning "through hardships to the stars". The phrase is one of the many Latin sayings that use the expression ad astra, meaning "to the stars".
Laika was a Soviet space dog who became one of the first animals in space, and the first animal to orbit the Earth. Laika, a stray dog from the streets of Moscow, was selected to be the occupant of the Soviet spacecraft Sputnik 2 that was launched into outer space on 3 November 1957. From the Earth to the Moon is an 1865 novel by Jules Verne.
NASA Space Flight - Space X
Astronaut is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the terms are sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists and tourists, who are low level armatures with just enough training to understand the challenges of space travel. A high level professional astronaut has extensive training. The candidate must complete a master's degree in a STEM field, including engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science or mathematics. The candidate must have at least two years of related professional experience obtained after degree completion or at least 1,000 hours pilot-in-command time on jet aircraft. The candidate must be able to pass the NASA long-duration flight astronaut physical. The candidate must also have skills in leadership, teamwork and communications. The master's degree requirement can also be met by: Two years of work toward a doctoral program in a related science, technology, engineering or math field. A completed Doctor of Medicine or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine degree. Completion of a nationally recognized test pilot school program. Astronaut Candidate is the rank of those training to be NASA astronauts. Upon graduation, candidates are promoted to Astronaut and receive their Astronaut Pin. The pin is issued in two grades, silver and gold, with the silver pin awarded to candidates who have successfully completed astronaut training and the gold pin to astronauts who have flown in space. Why are astronauts such good people and some of the nicest people? Is it the training? is it the love of life? Is it the need to explore? Is it the need to learn and to know? Is it the overview effect? I believe that most astronauts are good people to begin with. They obviously need patience, they need the abilities to adapt, the abilities to solve problems, and the abilities to communicate effectively and work together as a team. The training seems to help finely tune and strengthen these abilities. So What actually is the right stuff? Ten people beat 8,000 others to become NASA astronaut candidates.
Starfleet requires its officers to have a broad range of skills and knowledge, encompassing both practical abilities and personal attributes. These include technical proficiency, scientific understanding, tactical acumen, diplomatic skills, and strong leadership qualities. While specific requirements vary depending on the role, all Starfleet personnel must demonstrate a commitment to the Federation's ideals and undergo rigorous training at Starfleet Academy. Key Skills and Areas of Expertise: Technical Proficiency: Officers need expertise in various technologies, including starship operation, weapons systems, engineering, and computer systems. Scientific Understanding: A strong foundation in science, particularly physics, astrophysics, and other relevant fields, is crucial for understanding the universe and its phenomena. Tactical Acumen: Officers must be skilled in tactical planning, combat strategy, and the use of weaponry, whether on starships or in away missions. Diplomatic Skills: Starfleet officers often engage in diplomacy and negotiations with other civilizations, requiring strong communication, cross-cultural understanding, and conflict resolution skills. Leadership Qualities: Starfleet values strong leadership, including the ability to inspire, motivate, and make difficult decisions under pressure. Medical Knowledge: While specific medical roles require advanced training, basic knowledge of emergency medicine and first aid is essential for all officers. Personal Attributes: Beyond technical skills, Starfleet seeks individuals with traits like courage, integrity, compassion, and a strong sense of duty. Training and Education: Starfleet Academy: All Starfleet officers attend Starfleet Academy, a rigorous training program that can last for several years. Curriculum: The Academy curriculum includes a wide range of subjects, from theoretical physics to practical skills training. Specializations: Cadets can choose to specialize in various fields, such as command, science, engineering, or medicine. Ongoing Training: Starfleet officers continue to receive training and education throughout their careers, both on starships and at specialized training facilities. Example Skills by Role (from a fan perspective): Helmsman: Requires precise control of the starship, navigation skills, and knowledge of spatial orientation. Security Officer: Requires hand-to-hand combat skills, knowledge of weapons, and training in emergency situations. Bridge Officer: Requires a combination of technical, scientific, and tactical skills, as well as strong leadership abilities. Star Trek.
Air Traffic Controller Requirements
Parastronaut is an astronaut with physical disabilities.
Astronaut Ranks and Positions hold a variety of ranks and positions. Each of these roles carries responsibilities that are essential to the operation of a spacecraft. A spacecraft's cockpit, filled with sophisticated equipment, requires skills differing from those used to manage the scientific equipment on board, and so on. Pilot serves as systems engineer, copilot, and would perform any other mission objectives. Commander is responsible for the overall mission success, safety of crew and spacecraft, pilot in command of spacecraft during launch, trans-lunar coast, and Earth return coast. Command Module Pilot is responsible for knowing the CSM and their systems fully. Serve as flight engineer during launch phase while commander would be in full control of the vehicle. Perform navigation and mid-course correction procedures during trans-lunar and trans-Earth phases of flight, command pilot of CSM during lunar orbit phase. The CM pilot would also have other objectives during lunar orbit phase such as lunar photography, research and study for future landing sites for subsequent Apollo missions, deploy lunar satellite in some cases, as well as being responsible for relaying messages from mission control if radio contact with the LM was lost or weak, and also responsible for performing an orbital rescue with the LM if it were to malfunction and not be able to perform as needed to rendezvous with CSM as planned for in normal cases, but this never was needed. However, the CM pilot was responsible for docking the two ships together when the LM returned to orbit after being on the surface. Lunar Module Pilot is a flight engineer responsible for its systems during all phases of flight between Earth and Moon. The LMP would callout key information to the commander during the most critical descent and landing phases when all of the commander's attention would be focused out the window and on visually flying the LM to a suitable landing spot on the surface. He would also control the navigation computer and other subsystems of the craft while the commander had hands on the controls to fly the ship down manually the last portion of the descent when manual control was taken over from the computer.
Flight Engineer is the member of an aircraft's flight crew who monitors and operates its complex aircraft systems. In the early era of aviation, the position was sometimes referred to as the "air mechanic".
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of air flight capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University.
Aerospace Engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering. Orbital Mechanics.
Spacecraft is a vehicle, or machine designed to Fly in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. Light Year.
Space Shuttle - Voyager - Space Station - Space Adventures - Moon Travel
Self-Healing Nano-Spacecraft could reach Alpha Centauri in 20 years. With our current technology, it would take a conventional spacecraft over 18,000 years to reach the nearest star, Alpha Centauri.
‘Terminator’-style material heals itself (youtube) - Nano Technology - Wound Healing
Metals can heal themselves. Microscopic cracks vanish in experiments, revealing possibility of self-healing machines.
Engineers create Miniature Self-Sealing Wound.
Self-Healing Metal Oxides could protect against Corrosion.
Self-Healing Plastic becomes biodegradable.
Light-Controlled Polymers can switch between sturdy and soft - Bio-Mimicry.
3D printing in microgravity. To advance space colonization, new research explores 3D printing in microgravity. Research into how 3D printing works in a weightless environment aims to support long-term exploration and habitation on spaceships, the moon or Mars. The team's recent experiments focused on how a weightless microgravity environment affects 3D printing using titania foam, a material with potential applications ranging from UV blocking to water purification.
Scientists develop 'mini-brains' to help robots recognize pain and to self-repair. The new NTU approach embeds AI into the network of sensor nodes, connected to multiple small, less-powerful, processing units, that act like 'mini-brains' distributed on the robotic skin. This means learning happens locally and the wiring requirements and response time for the robot are reduced five to ten times compared to conventional robots.
Soft robot detects damage, heals itself. Engineers have created a soft robot capable of detecting when and where it was damaged -- and then healing itself on the spot. o do this, researchers have pioneered a technique using fiber-optic sensors coupled with LED lights capable of detecting minute changes on the surface of the robot. These sensors are combined with a polyurethane urea elastomer that incorporates hydrogen bonds, for rapid healing, and disulfide exchanges, for strength. The resulting SHeaLDS -- self-healing light guides for dynamic sensing -- provides a damage-resistant soft robot that can self-heal from cuts at room temperature without any external intervention.
Ultra-lightweight multifunctional space skin created to withstand extreme conditions in space. A new nano-barrier coating could help protect ultra-lightweight carbon composite materials from extreme conditions in space, according to a new study.
How will the Human Body Adapt to Space Travel?
Effect of Spaceflight on the Human Body. Venturing into the environment of space can have negative effects on the human body. Significant adverse effects of long-term weightlessness include muscle atrophy and deterioration of the skeleton (spaceflight osteopenia). Other significant effects include a slowing of cardiovascular system functions, decreased production of red blood cells (space anemia), balance disorders, eyesight disorders and changes in the immune system. Additional symptoms include fluid redistribution (causing the "moon-face" appearance typical in pictures of astronauts experiencing weightlessness), loss of body mass, nasal congestion, sleep disturbance, and excess flatulence. Overall, NASA refers to the various deleterious effects of spaceflight on the human body by the acronym RIDGE (i.e., "space radiation, isolation and confinement, distance from Earth, gravity fields, and hostile and closed environments"). The effects of space exposure can result in ebullism, hypoxia, hypocapnia, and decompression sickness. In addition to these, there is also cellular mutation and destruction from high energy photons and sub-atomic particles that are present in the surroundings.
Humans have Genes that will help them to Evolve during Interstellar Space Travel.
Will Humans Keep Evolving on Ultra-Long Space Voyages?
How Humans could evolve to survive in space: Lisa Nip (video and text).
Space Travel reduces the expression of 100 genes related to the immune system. This could be why some people get rashes in space, due to the reduced activity of one hundred immune-related genes, which help give opportunistic infections a toehold. Spaceflight leads to the deconditioning of multiple body systems including the immune system. When an astronaut enters microgravity, their blood shifts from their legs to their torsos and heads. It's uncomfortable and throws things out of whack. Their body resolves the problem by reducing the fluid by up to 15%. But that now means that there are too many immune cells crammed into this smaller amount of blood. The drop in gene activity helps eliminate those extra cells. And this in turn affects the way the immune system responds to pathogens.
Adaptation - CRISPR - Hibernation - NASA's landmark Twins Study reveals resilience of human body in space - Micro-Evolution - Living in Space - Overview Effect
Predicting changes inside astronauts' bodies during space travel through blood sample analysis. The human body undergoes various transformations in space. However, a direct examination of organs and tissues is challenging. This study successfully identified these changes inside the body by analyzing tiny quantities of DNA and RNA molecules released from various tissues into the bloodstream while the astronauts were on the International Space Station or ISS.
Sedentary - Sitting Too Long - Physiological Effects in Space (wiki) - Sensory Deprivation
How Conan the Bacterium withstands extreme radiation. New discovery finds simple metabolites combine to form a powerful antioxidant. Thanks for a powerful antioxidant, Deinococcus radiodurans can withstand radiation doses 28,000 times greater than what would kill a human. In a new study, scientists discovered how the antioxidant works. Finding could drive the development of designer antioxidants to shield astronauts from cosmic radiation.
South Atlantic Anomaly is a region in space where Earth's magnetic field is significantly weaker than usual, allowing increased levels of radiation to reach lower altitudes, including near Earth's surface. This anomaly is located primarily over the South Atlantic Ocean and parts of South America. It is a region where the Van Allen radiation belts dip closer to the Earth than anywhere else, exposing satellites and spacecraft in low Earth orbit to higher radiation levels. The SAA is thought to be linked to the Earth's core and the movement of molten iron within it, which affects the magnetic field. The anomaly is not static; it drifts westward and its shape and intensity can change over time. The increased radiation can cause malfunctions in spacecraft electronics and pose risks to astronauts.
Why meals taste bad in space? Food aroma study may help explain. A new study on common food aromas may help explain why astronauts report that meals taste bland in space and struggle to eat their normal nutritional intake. This research has broader implications for improving the diets of isolated people, including nursing home residents, by personalizing aromas to enhance the flavor of their food. The team found a particular sweet chemical in the aromas of vanilla and almond, called benzaldehyde, could explain the change in perceptions, in addition to an individual's sensitivity to the particular smell. Food in Space (vertical farming).
Study explores effects of extended spaceflight on brain. The researchers found that while all of the astronauts and cosmonauts they studied had a similar level of cerebrospinal fluid buildup in the brain, along with reduced space between the brain and the surrounding membrane at the top of the head, there was a noteworthy difference when it came to the Americans. They had more enlargement in the perivascular spaces in the brain, passages that serve as a cleaning system during sleep. That's something the researchers say warrants further investigation. An important implication of our findings is that the volume of fluid-filled channels in the brain of astronauts is linked to the development of the spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome, a syndrome characterized by vision changes and whose mechanisms are still not completely clear.
Space travel influences the way the brain works. Scientists have found how the human brain changes and adapts to weightlessness, after being in space for 6 months. Some of the changes turned out to be lasting -- even after 8 months back on Earth. A child who learns not to drop a glass on the floor, or a tennis player predicting the course of an incoming ball to hit it accurately are examples of how the brain incorporates the physical laws of gravity to optimally function on Earth. Astronauts who go to space reside in a weightless environment, where the brain's rules about gravity are no longer applicable. A new study on brain function in cosmonauts has revealed how the brain's organization is changed after a six-month mission to the International Space Station (ISS), demonstrating the adaptation that is required to live in weightlessness. We found that connectivity was altered after spaceflight in regions which support the integration of different types of information, rather than dealing with only one type each time, such as visual, auditory, or movement information.
Brain cells remain healthy after a month on the International Space Station, but mature faster than brain cells on Earth. Microgravity is known to alter the muscles, bones, the immune system and cognition, but little is known about its specific impact on the brain. To discover how brain cells respond to microgravity, scientists sent tiny clumps of stem-cell derived brain cells called 'organoids' to the International Space Station.
First infection of human cells during spaceflight. Scientists have described the infection of human cells by the intestinal pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium during spaceflight. They show how the microgravity environment of spaceflight changes the molecular profile of human intestinal cells and how these expression patterns are further changed in response to infection. The researchers were also able to detect molecular changes in the bacterial pathogen while inside the infected host cells. Wearable Sensors.
The International Space Station is overly sterile, and making it dirtier could improve astronaut health. Astronauts often experience immune dysfunction, skin rashes, and other inflammatory conditions while traveling in space. A new study suggests that these issues could be due to the excessively sterile nature of spacecraft. The study showed that the International Space Station has a much lower diversity of microbes compared to human-built environments on Earth, and the microbes that are present are mostly species carried by humans onto the ISS, suggesting that the presence of more microbes from nature could help improve human health in the space station.
Simulated microgravity affects sleep and physiological rhythms. Simulated effects of microgravity significantly affect rhythmicity and sleep in humans, a new study finds. Such disturbances could negatively affect the physiology and performance of astronauts in space. Microgravity results in headward fluid shifts, ventricular expansion, an upward shift of the brain within the skull, and remodeling of grey and white matter. The fluid changes are correlated with changes to perivascular space and spaceflight associated neuro-ocular syndrome. NASA astronauts have experienced altered vision and increased intracranial pressure during flight aboard the International Space Station. The VIIP syndrome is thought to result from the redistribution of body fluid toward the head during long-term microgravity exposure; however, the exact cause is unknown.
Sensory overload or sensory confusion? Many astronauts suddenly feel as if they are upside-down or may even have difficulty sensing the location of their own arms and legs. This disorientation is described as Space Adaptation Syndrome and is widely recognized as the main cause of Space Motion Sickness. Space Adaptation Syndrome or space sickness is a kind of motion sickness that can occur when one's surroundings visually appear to be in motion, but without a corresponding sense of bodily motion. This incongruous condition can occur during space travel when changes in g-forces and pressure changes compromise one's spatial orientation. Just as space sickness has the opposite cause compared to terrestrial motion sickness, the two conditions have opposite non-medicinal remedies. The idea of sensory conflict implies that the most direct remedy for motion sickness in general is to resolve the conflict by re-synchronizing what one sees and what one feels. For most (but not all) kinds of terrestrial motion sickness, that can be achieved by viewing one's surroundings from a window or (in the case of seasickness) going up on deck to observe the seas. For space sickness, relief is available via the opposite move of restricting one's vision to a small area such as a book or a small screen, disregarding the overall surroundings until the adaptation process is complete, or simply to close one's eyes until the nauseated feeling is reduced in intensity during the adjustment period. Some research indicates that blindness itself does not provide relief; "Motion sickness can occur during exposure to physical motion, visual motion, and virtual motion, and only those without a functioning vestibular system are fully immune. Sensory Deprivation.
Astronauts receive 10x the amount of radiation exposure as we do on Earth. Such high exposure can damage the immune system, causing astronauts to be susceptible to infection while in space. Long-term exposure can damage cells and DNA, leading to cataracts and cancers.
Project Space Health is a program focuses on the protection, long-duration preservation, and predictive adaptation of life beyond the earthbound, integrated throughout the Space Exploration Initiative’s portfolio.
Chemical contamination on International Space Station is out of this world. Concentrations of potentially harmful chemical compounds in dust collected from air filtration systems on the International Space Station (ISS) exceed those found in floor dust from many American homes, a new study reveals. Contaminants found in the 'space dust' included polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD), 'novel' brominated flame retardants (BFRs), organophosphate esters (OPEs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Indoor Air Pollution - Toxins.
Somatic Mutations and Clonal Hematopoiesis in Astronauts.
Spaceflight wreaks havoc on liver metabolism. Researchers have demonstrated that microgravity and other environmental factors in space play different roles in inducing oxidative stress, which, in turn, alters the metabolism of sulfur-containing compounds in the liver of mice. The study highlighted steps that can be taken, such as boosting antioxidant capacity with dietary supplements, to safeguard astronaut health. During spaceflight, the human body is exposed to a harmful environment, characterized by null or microgravity and high radiation levels. The liver is affected by spaceflight more than any other organ -- its crucial role in neutralizing harmful substances in the body means that spaceflight places incredible demands on the organ. Mice that traveled to space and back had a lower antioxidant capacity because they had lower levels of the sulfur-containing compounds (e.g., ergothioneine, cysteine, and glutathione) that play a role in protecting cells by reducing reactive oxygen compounds, which limits free-radical damage.
Bone aging in fast forward. Researcher investigates the effects of zero gravity on the skeleton. Long periods in space damage bone structure irreparably in some cases and can make parts of the human skeleton age prematurely by up to 10 years, according to new research. Adapted training programs in conjunction with medication could provide better protection for astronauts on future space missions. The research findings also have implications for treating rheumatic conditions in clinical practice.
How does the immune system react to altered gravity? It has long been known that continuous exposure to microgravity conditions human physiology and causes effects that compromise muscular, sensory, endocrine and cardiovascular functions. But is it also risky to be exposed to altered gravity for short periods of time?
Space-trekking muscle tests drugs for microgravity-induced muscle impairment. Space is a really unique environment that accelerates qualities associated with aging and also impairs many healthy processes.
Health effects of long-duration Space Flight. Research found that chronic oxidative stress during spaceflight contributed to the telomere elongation they observed. They also found that astronauts had shorter telomeres after spaceflight than they did before.
Space Anemia is an effect of space travel that can lower red blood cell counts. Red blood cells deliver oxygen to all the cells of the body and a lack of sufficient red blood cells results in anemia, which can affect physical and mental functions necessary on a space mission.
 Making Oxygen and breathable air.
New reaction for Generating Oxygen that could help humans explore the
universe and perhaps even fight climate change at home. Comet inspires
chemistry for making breathable oxygen on Mars. Reaction
turns carbon dioxide
into molecular oxygen.
Electrolysis.
Making Oxygen and breathable air.
New reaction for Generating Oxygen that could help humans explore the
universe and perhaps even fight climate change at home. Comet inspires
chemistry for making breathable oxygen on Mars. Reaction
turns carbon dioxide
into molecular oxygen.
Electrolysis.Moxie Reverse Fuel Cell Pumps out Oxygen.
A Mission to Mars could make its own Oxygen, thanks to plasma technology. Mars, with its 96 per cent carbon dioxide atmosphere, has nearly ideal conditions for creating oxygen from CO2 through a process known as decomposition, which is the process by which organic substances are broken down into simpler organic matter.
Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment is an exploration technology experiment that will produce a small amount of pure oxygen from Martian atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) in a process called solid oxide electrolysis. MOXIE is a 1% scale model aboard the planned Perseverance rover, as part of the Mars 2020 mission. The Principal Investigator of the MOXIE instrument is Michael Hecht from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen is collaborating with MIT to develop this prototype. If successful, the technology can be scaled up as a means of producing oxygen for propellant oxidant in a Mars Ascent Vehicle (MAV) for a sample return.
Lunar soil has the potential to generate oxygen and fuel. Soil on the moon contains active compounds that can convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and fuels, scientists report. They are now exploring whether lunar resources can be used to facilitate human exploration on the moon or beyond.
Aircraft Emergency Oxygen Systems or air masks, are emergency equipment fitted to pressurized commercial aircraft, intended for use when the cabin pressurisation system has failed and the cabin altitude has climbed above a safe level. It consists of a number of individual yellow oxygen masks stored in compartments near passenger seats and near areas like lavatories and galleys, and an oxygen source, like a centralized gaseous cylinder or decentralized chemical oxygen generator.
Chemical Oxygen Generator is a device that releases oxygen via a chemical reaction. The oxygen source is usually an inorganic superoxide, chlorate, or perchlorate; ozonides are a promising group of oxygen sources. The generators are usually ignited by a firing pin, and the chemical reaction is usually exothermic, making the generator a potential fire hazard. Potassium superoxide was used as an oxygen source on early manned missions of the Soviet space program, for firefighters, and for mine rescue.
Lunar soil has the potential to generate oxygen and fuel. Soil on the moon contains active compounds that can convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and fuels, scientists report. They are now exploring whether lunar resources can be used to facilitate human exploration on the moon or beyond.
Artificial Habitats - Plants Make Oxygen and Remove CO2 - Information Backup - Sending Robots with Human DNA.
Turning human waste into plastic, nutrients could aid long-distance space travel. Imagine you're on your way to Mars, and you lose a crucial tool during a spacewalk. Not to worry, you'll simply re-enter your spacecraft and use some microorganisms to convert your urine and exhaled carbon dioxide into chemicals to make a new one.
Sabatier Reaction process produces methane and water from a reaction of hydrogen with carbon dioxide at elevated temperatures (optimally 300–400 °C) and pressures (perhaps 30 bar ) in the presence of a nickel catalyst. The Sabatier reaction has been proposed as a key step in reducing the cost of human mission to Mars (Mars Direct, SpaceX Starship) through in-situ resource utilization. Hydrogen is combined with CO2 from the atmosphere, with methane then stored as fuel and the water side product electrolyzed yielding oxygen to be liquefied and stored as oxidizer and hydrogen to be recycled back into the reactor. The original hydrogen could be transported from Earth or separated from Martian sources of water.
In Situ Resource Utilization is the practice of collection, processing, storing and use of materials found or manufactured on other astronomical objects (the Moon, Mars, asteroids, etc.) that replace materials that would otherwise be brought from Earth. ISRU could provide materials for life support, propellants, construction materials, and energy to a spacecraft payloads or space exploration crews. It is now very common for spacecraft and robotic planetary surface mission to harness the solar radiation found in situ in the form of solar panels. The use of ISRU for material production has not yet been implemented in a space mission, though several field tests in the late 2000s demonstrated various lunar ISRU techniques in a relevant environment. ISRU has long been considered as a possible avenue for reducing the mass and cost of space exploration architectures, in that it may be a way to drastically reduce the amount of payload that must be launched from Earth in order to explore a given planetary body. According to NASA, "in-situ resource utilization will enable the affordable establishment of extraterrestrial exploration and operations by minimizing the materials carried from Earth."
Space Travel Songs
Rocket Man - Elton John (Rocket man, burning out his fuse up here alone).
Space Oddity - David Bowie (Though I'm past one hundred thousand miles, I'm feeling very still, And I think my spaceship knows which way to go).
Rocket - Def Leppard (Jack Flash, rocket man, Sergeant Pepper and the band, Ziggy, Benny and the Jets, Take a rocket, we just gotta fly).
Ride Captain Ride upon your Mystery Ship - Blues Image (youtube)
Space Cowboy - Steve Miller Band (youtube)
Propulsion - Thrust - Rockets
Rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle that obtains thrust from a rocket engine. Rocket engine exhaust is formed entirely from propellant carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction and push rockets forward simply by expelling their exhaust in the opposite direction at high speed, and can therefore work in the vacuum of space. In fact, rockets work more efficiently in space than in an atmosphere. To obtain Escape Velocity a rocket needs to travel 11 kilometers (7 miles) per second, or over 40,000 kilometers per hour (25,000 miles per hour), to enter Low Earth Orbit. (Thrust - Efficiency - Weight).
Advanced Propulsion Rockets
Multistage Rockets are capable of attaining Escape Velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, and/or gravity. Multistage Rocket is a rocket that uses two or more stages, each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A tandem or serial stage is mounted on top of another stage; a parallel stage is attached alongside another stage. The result is effectively two or more rockets stacked on top of or attached next to each other. Taken together these are sometimes called a launch vehicle. Two-stage rockets are quite common, but rockets with as many as five separate stages have been successfully launched. By jettisoning stages when they run out of propellant, the mass of the remaining rocket is decreased. This staging allows the thrust of the remaining stages to more easily accelerate the rocket to its final speed and height. In serial or tandem staging schemes, the first stage is at the bottom and is usually the largest, the second stage and subsequent upper stages are above it, usually decreasing in size. In parallel staging schemes solid or liquid rocket boosters are used to assist with lift-off. These are sometimes referred to as "stage 0". In the typical case, the first-stage and booster engines fire to propel the entire rocket upwards. When the boosters run out of fuel, they are detached from the rest of the rocket (usually with some kind of small explosive charge) and fall away. The first stage then burns to completion and falls off. This leaves a smaller rocket, with the second stage on the bottom, which then fires. Known in rocketry circles as staging, this process is repeated until the final stage's motor burns to completion. In some cases with serial staging, the upper stage ignites before the separation- the interstage ring is designed with this in mind, and the thrust is used to help positively separate the two vehicles. Why SpaceX Built A Stainless Steel Starship (youtube).
Water Rocket is a type of model rocket using water as its reaction mass. The water is forced out by a pressurized gas, typically compressed air. Like all rocket engines, it operates on the principle of Newton's third law of motion. Water rocket hobbyists typically use one or more plastic soft drink bottle as the rocket's pressure vessel. A variety of designs are possible including multi-stage rockets. Water rockets are also custom-built from composite materials to achieve world record altitudes.
Spacecraft Propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. There are many different methods. Each method has drawbacks and advantages, and spacecraft propulsion is an active area of research. However, most spacecraft today are propelled by forcing a gas from the back/rear of the vehicle at very high speed through a supersonic de Laval nozzle. This sort of engine is called a rocket engine.
Thruster is a propulsive device used by spacecraft and watercraft for station keeping, attitude control, in the reaction control system, or long-duration, low-thrust acceleration.
Rocket Propellant is a material used either directly by a rocket as the reaction mass (propulsive mass), or indirectly to produce the reaction mass in a chemical reaction. The reaction mass is that which is ejected, typically with very high speed, from a rocket engine to produce thrust. Propelling is to cause something to move forward with force.
Hypergolic Propellant combination used in a rocket engine is one whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other. The two propellant components usually consist of a fuel and an oxidizer. The main advantages of hypergolic propellants are that they can be stored as liquids at room temperature and that engines which are powered by them are easy to ignite reliably and repeatedly. Although commonly used, hypergolic propellants are difficult to handle due to their extreme toxicity and/or corrosiveness. In contemporary usage, the terms "hypergol" or "hypergolic propellant" usually mean the most common such propellant combination, dinitrogen tetroxide plus hydrazine and/or its relatives monomethylhydrazine and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine.
Rocket Engine uses stored rocket propellant mass for forming its high-speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines, obtaining thrust in accordance with Newton's third law. Most rocket engines use combustion, although non-combusting forms (such as cold gas thrusters) also exist. Vehicles propelled by rocket engines are commonly called rockets. Since they need no external material to form their jet, rocket engines can perform in a vacuum and thus can be used to propel spacecraft and ballistic missiles. Thermal Rockets.
Rocket Engine Nozzle is a propelling nozzle (usually of the de Laval type) used in a rocket engine to expand and accelerate the combustion gases produced by burning propellants so that the exhaust gases exit the nozzle at hypersonic velocities. Simply: the rocket (pumps and a combustion chamber) generates high pressure, a few hundred atmospheres (Bar). The nozzle turns the static high pressure high temperature gas into rapidly moving gas at near-ambient pressure.
Aerospike Engine is a type of rocket engine that maintains its aerodynamic efficiency across a wide range of altitudes. It belongs to the class of altitude compensating nozzle engines. A vehicle with an aerospike engine uses 25–30% less fuel at low altitudes, where most missions have the greatest need for thrust. Aerospike engines have been studied for a number of years and are the baseline engines for many single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) designs and were also a strong contender for the Space Shuttle Main Engine. However, no such engine is in commercial production, although some large-scale aerospikes are in testing phases. Aerospike Engines Instead of Bell-Shaped Rocket Engines (youtube).
Scramjet is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully before combustion (hence ramjet), but whereas a ramjet decelerates the air to subsonic velocities before combustion, the airflow in a scramjet is supersonic throughout the entire engine. That allows the scramjet to operate efficiently at extremely high speeds. (supersonic combustion ramjet).
Launch Pad is an above-ground facility from which a rocket-powered missile or space vehicle is vertically launched. The term launch pad can be used to describe just the central launch platform (mobile launcher platform), or the entire complex (launch complex). The entire complex will include a launch mount or launch platform to physically support the vehicle, a service structure with umbilicals, and the infrastructure required to provide propellants, cryogenic fluids, electrical power, communications, telemetry, rocket assembly, payload processing, storage facilities for propellants and gases, equipment, access roads, and drainage. Most launch pads include fixed service structures to provide one or more access platforms to assemble, inspect, and maintain the vehicle and to allow access to the spacecraft, including the loading of crew. The pad may contain a flame deflection structure to prevent the intense heat of the rocket exhaust from damaging the vehicle or pad structures, and a sound suppression system spraying large quantities of water may be employed. The pad may also be protected by lightning arresters. A spaceport typically includes multiple launch complexes and other supporting infrastructure.
Fully 3D-printed electrospray engine. Ideal for propelling tiny satellites, the lightweight devices could be produced on board a spacecraft and cost much less than traditional thrusters. Researchers demonstrated the first fully 3D-printed, droplet-emitting electrospray engine. The low-cost device can be fabricated more quickly than traditional thrusters, potentially from on board a spacecraft, and could enable CubeSats to perform precise, in-orbit maneuvers, aiding space research projects. An electrospray engine applies an electric field to a conductive liquid, generating a high-speed jet of tiny droplets that can propel a spacecraft. These miniature engines are ideal for small satellites called CubeSats that are often used in academic research.
Service Structure is a steel framework or tower that is built on a rocket launch pad to facilitate assembly and servicing. An umbilical tower also usually includes an elevator which allows maintenance and crew access. Immediately before ignition of the rocket's motors, all connections between the tower and the craft are severed, and the bridges over which these connections pass often quickly swing away to prevent damage to the structure or vehicle.
Mobile Launcher Platform is a structure used to support a large multistage space vehicle which is assembled (stacked) vertically in an integration facility (e.g. the Vehicle Assembly Building) and then transported by a crawler-transporter (CT) to a launch pad. This becomes the support structure for launch. Alternatives to this method include horizontal assembly and transport to the pad, as used by Russia; and assembling the vehicle vertically on the launch pad, as the United States used for smaller launch vehicles. The use of mobile launcher platform is a part of the Integrate-Transfer-Launch (ITL) system, which involves vertical assembly, transport, and launch of rockets. The concept was first implemented in the 1960s for the United States Air Force's Titan III rocket, and it was later used by NASA for their Saturn V rocket vehicle.
Space Jellyfish is a rocket launch-related phenomenon caused by sunlight reflecting off the high altitude rocket plume gases emitted by a launching rocket during morning or evening twilight. The observer is in darkness, while the exhaust plumes at high altitudes are still in direct sunlight. This luminous apparition is reminiscent of a jellyfish. Sightings of the phenomenon have led to panic, fear of nuclear missile strike, and reports of unidentified flying objects. It is also called a jellyfish UFO or a rocket jellyfish.
Advanced Propulsion Engines
Pulse Detonation Engine is a type of propulsion system that uses detonation waves to combust the fuel and oxidizer mixture. The engine is pulsed because the mixture must be renewed in the combustion chamber between each detonation wave and the next. Theoretically, a PDE can operate from subsonic up to a hypersonic flight speed of roughly Mach 5. An ideal PDE design can have a thermodynamic efficiency higher than other designs like turbojets and turbofans because a detonation wave rapidly compresses the mixture and adds heat at constant volume. Consequently, moving parts like compressor spools are not necessarily required in the engine, which could significantly reduce overall weight and cost. PDEs have been considered for propulsion since 1940. Key issues for further development include fast and efficient mixing of the fuel and oxidizer, the prevention of autoignition, and integration with an inlet and nozzle. To date, no practical PDE has been put into production, but several testbed engines have been built and one was successfully integrated into a low-speed demonstration aircraft that flew in sustained PDE powered flight in 2008. In June 2008, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) unveiled Blackswift, which was intended to use this technology to reach speeds of up to Mach 6. However the project was reported cancelled soon afterward, in October 2008.
Magnetodynamics - Antigravity - Space Travel
Rotating Detonation Engine is a proposed engine using a form of pressure gain combustion, where one or more detonations continuously travel around an annular channel. Although none are in production, computational simulations and experimental results have shown that the RDE has potential, and a there is wide interest and research into the concept. Theoretically, detonative combustion, (i.e. that which happens at speeds above the speeds of sound), is more efficient than the conventional deflagrative combustion. If this theoretical gain in efficiency can be realized, there would be a major fuel savings benefit. Because the combustion is supersonic, it can also more efficiently provide thrust at speeds above the speed of sound. The disadvantages of the RDE include stability and noise.
Simple, fuel-efficient rocket engine could enable cheaper, lighter spacecraft. A rotating detonation engine promises to make rockets not only more fuel-efficient but also more lightweight and less complicated to construct. A conventional rocket engine works by burning propellant and then pushing it out of the back of the engine to create thrust. Rotating detonation engine is made of concentric cylinders. Propellant flows in the gap between the cylinders, and, after ignition, the rapid heat release forms a shock wave, a strong pulse of gas with significantly higher pressure and temperature that is moving faster than the speed of sound.
Plasma Propulsion Engine is a type of electric propulsion that generates thrust from a quasi-neutral plasma. This is in contrast to ion thruster engines, which generates thrust through extracting an ion current from plasma source, which is then accelerated to high velocities using grids/anodes.
Plasma Reforming of CO2. Plasma technology could hold the key to creating a sustainable oxygen supply on Mars. Creating oxygen from CO2 through a process known as decomposition.
Anti-Gravity Field Propulsion
Electrically Powered Spacecraft Propulsion system uses electrical energy to change the velocity of a spacecraft. Most of these kinds of spacecraft propulsion systems work by electrically expelling propellant (reaction mass) at high speed, but electrodynamic tethers work by interacting with a planet's magnetic field.
Electron Rocket is a two-stage orbital launch vehicle (with an optional third stage) developed by the New Zealand aerospace company Rocket Lab to cover the commercial small satellite launch segment (CubeSats). Its Rutherford engines are the first electric pump-fed engine to power an orbital rocket. In December 2016, Electron completed flight qualification. The first rocket was launched on 25 May 2017, reaching space but not achieving orbit. During its second flight on 21 January 2018, Electron reached orbit and deployed three CubeSats.
EmDrive is a controversial proposed type of electromagnetic thruster in which sustaining a resonant anisotropic electromagnetic field inside the microwave cavity purportedly produces a consistent thrust.
Ion Thruster is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. It creates thrust by accelerating ions with electricity. The term refers strictly to gridded electrostatic ion thrusters, but may more loosely be applied to all electric propulsion systems that accelerate plasma, since plasma consists of ions. Tesla / Slayer Ionic Propulsion (youtube).
Ion wind is the airflow of charged particles induced by electrostatic forces linked to corona discharge arising at the tips of some sharp conductors (such as points or blades) subjected to high voltage relative to ground. Ion wind is an electrohydrodynamic phenomenon. Ion wind generators can also be considered electrohydrodynamic thrusters. The term "ionic wind" is considered a misnomer due to misconceptions that only positive and negative ions were primarily involved in the phenomenon. A 2018 study found that electrons play a larger role than negative ions during the negative voltage period. As a result, the term "electric wind" has been suggested as a more accurate terminology. Ion wind is also known as ionic wind, corona wind or electric wind. Ions.
Virtual Particles - Quantum Flux
Lightsails could reach distant star systems. A team of scientists has made the first experimental measurements of laser-induced motions of miniature lightsails in the lab.
Helical Engine is a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive that, like other reactionless drives, would violate the laws of physics. The Helical engine accelerates ions that are confined in a locked loop. Once they are accelerated, the system changes the velocity of the ions in order to change their momentum. Afterward, Burns hypothesized that the engine, by moving the ions along its axis, could produce thrust. The proposed engine is mainly intended to be used to maintain the orbit of satellite stations during long periods of time without the need of refueling.
Anti-Matter Rocket is a proposed class of rockets that use antimatter as their power source. There are several designs that attempt to accomplish this goal. The advantage to this class of rocket is that a large fraction of the rest mass of a matter/antimatter mixture may be converted to energy, allowing antimatter rockets to have a far higher energy density and specific impulse than any other proposed class of rocket.
Thermal Rocket is a rocket engine that uses a propellant that is externally heated before being passed through a nozzle to produce thrust, as opposed to being internally heated by a redox (combustion) reaction as in a Chemical Rocket.
Nuclear Thermal Rocket is a proposed spacecraft propulsion technology that was ground tested in the 1960s. The NTR is a type of thermal rocket where the heat from a nuclear reaction replaces the chemical energy of the propellants in a chemical rocket. In an NTR, a working fluid, usually liquid hydrogen, is heated to a high temperature in a nuclear reactor and then expands through a rocket nozzle to create thrust. The external nuclear heat source theoretically allows a higher effective exhaust velocity and is expected to double or triple payload capacity compared to chemical propellants that store energy internally. To date, no nuclear thermal rocket has flown, although TOPAZ series and the SNAP-10A fission-powered electrical generators and Radioisotope thermoelectric generators have been launched to space.
Reactionless Drive is a device producing motion without the exhaust of a propellant. A propellantless drive is not necessarily reactionless when it constitutes an open system interacting with external fields; but a reactionless drive is a particular case of a propellantless drive as it is a closed system presumably in contradiction with the law of conservation of momentum and often considered similar to a perpetual motion machine. The name comes from Newton's third law, which is usually expressed as, "for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction." A large number of infeasible devices, such as the Dean drive, are a staple of science fiction particularly for space propulsion. To date, no reactionless device has ever been validated under properly controlled conditions. Boing.
Direct Fusion Drive is a conceptual low radioactivity, nuclear-fusion engine designed to produce both thrust and electric power for interplanetary spacecraft. The concept is based on the Princeton field-reversed configuration reactor invented in 2002 by Samuel A. Cohen, and is being modeled and experimentally tested at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, a US Department of Energy facility, and modeled and evaluated by Princeton Satellite Systems. As of 2018, the concept has moved on to Phase II to further advance the design.
Photonic Laser Thruster is a photonic propulsion system where lasers can propel spacecraft with giant sails using a giant Earth-based lasers. Electromagnetic acceleration is only limited by the speed of light while chemical systems are limited to the energy of chemical processes.
Warp Speed
Trapping Atoms, not space ships, with Tractor Beams. A powerful Tractor Beam, or light-driven energy trap, for atoms. Action Physics.
Flight Dynamics
Space Launch is the earliest part of a flight that reaches space. Space launch involves liftoff, when a rocket or other space launch vehicle leaves the ground, floating ship or midair aircraft at the start of a flight. Liftoff is of two main types: rocket launch (the current conventional method), and non-rocket spacelaunch (where other forms of propulsion are employed, including airbreathing jet engines or other kinds).
Launch Window is the time period on a given day during which a particular rocket or vehicle must be launched in order to reach its intended target. If the rocket is not launched within a given window, it has to wait for the window on the next day of the period. Launch periods and launch windows are very dependent on both the rocket's capability and the orbit to which it is going.
Falcon 1 - Falcon 9 - Falcon-Heavy
Space Shuttle weighs more than 2.04 million kilograms (4.5 million pounds) and it takes eight seconds for the engines and boosters to accelerate the ship to 161 kilometers per hour (100 mph.) But by the time the first minute has passed, the shuttle is traveling more than 1,609 kilometers per hour (1,000 mph) and it has already consumed more than one and a half million pounds of fuel. After about two minutes, when the shuttle is about 45 kilometers (28 miles) high and traveling more than 4,828 kilometers per hour (3,000 mph), the propellant in the two boosters is exhausted and the booster casings are jettisoned. They parachute into the Atlantic Ocean, splashing down about 225 kilometers (140 miles) off the Florida coast.
Orbital Refueling is when a spacecraft to be fueled in space. Propellant Depot is a cache of propellant that is placed in orbit around Earth or another body to allow spacecraft or the transfer stage of the spacecraft to be fueled in space. It is one of the types of space resource depot that have been proposed for enabling infrastructure-based space exploration. Many different depot concepts exist depending on the type of fuel to be supplied, location, or type of depot which may also include a propellant tanker that delivers a single load to a spacecraft at a specified orbital location and then departs. In-space fuel depots are not necessarily located near or at a space station. United Launch Alliance is a US launch service provider that manufactures and operates a number of rocket vehicles capable of orbiting spacecraft. It was formed as a joint venture between Lockheed Martin Space Systems and Boeing Defense, Space & Security in December 2006. United States government launch customers include the DoD and NASA, as well as other organizations. ULA provides launch services using two expendable launch systems – Delta IV and Atlas V. The Atlas and Delta launch system families have launched a variety of payloads including weather, telecommunications, and national security satellites and scientific probes and orbiters. ULA provides launch services to commercial satellites. ULA is currently in the process of developing Vulcan Centaur, a successor to the Atlas V that also incorporates some Delta IV technology. The Advanced Cryogenic Evolved Stage (ACES) is planned to replace Centaur V on Vulcan no earlier than 2023.
Avangard Hypersonic Glide Vehicle is a hypersonic glider, developed by Russia. The glider reached a speed of 11,200 kilometres per hour (7,000 mph; 3,100 m/s).
Boost-Glide are a class of spacecraft guidance and reentry trajectories that extend the range of suborbital spaceplanes and reentry vehicles by employing aerodynamic lift in the high upper atmosphere. In most examples, boost-glide roughly doubles the range over the purely ballistic trajectory. In others, a series of skips allows range to be further extended, and leads to the alternate terms skip-glide and skip reentry.
Hypersonic Speed is one that greatly exceeds the speed of sound, particularly Mach 5 and above.
Subsonic <0.8 (Mach number) <614 (mph) <988 (km/h) <274 (m/s). Ultrasound.
Supersonic 1.2–5.0 (Mach number) 921–3,836 (mph) 1,482–6,174 (km/h) 412–1,715 (m/s).
Hypersonic 5.0–10.0 (Mach number) 3,836–7,673 (mph) 6,174–12,348 (km/h) 1,715–3,430 (m/s).
High-Hypersonic 10.0–25.0 (Mach number) 7,673–19,182 (mph) 12,348–30,870 (km/h) 3,430–8,575 (m/s).
Hypersonic Aircraft would be great for emergency services, rescue missions and emergency aid, especially when time is so extremely important. Ambulances in the Sky.
Shock Wave is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. (300 meters per second). Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distance. When a shock wave passes through matter, energy is preserved but entropy increases. This change in the matter's properties manifests itself as a decrease in the energy which can be extracted as work, and as a drag force on supersonic objects; shock waves are strongly irreversible processes. Cavitation - Torus.
Scientists find upper limit for the speed of sound. Waves, such as sound or light waves, are disturbances that move energy from one place to another. Sound waves can travel through different mediums, such as air or water, and move at different speeds depending on what they're travelling through. For example, they move through solids much faster than they would through liquids or gases, which is why you're able to hear an approaching train much faster if you listen to the sound propagating in the rail track rather than through the air. Einstein's theory of special relativity sets the absolute speed limit at which a wave can travel which is the speed of light, and is equal to about 300,000 km per second. However until now it was not known whether sound waves also have an upper speed limit when travelling through solids or liquids.
Delta-v is symbolized as ∆v and pronounced delta-vee, as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse that is needed to perform a maneuver such as launch from, or landing on a planet or moon, or in-space orbital maneuver. It is a scalar that has the units of speed. As used in this context, it is not the same as the physical change in velocity of the vehicle. As a simple example, take a conventional rocket which achieves thrust by burning fuel. Delta-v is the change in velocity that can be achieved by burning that rocket's entire fuel load. Delta-v is produced by reaction engines, such as rocket engines, and is proportional to the thrust per unit mass and the burn time. It is used to determine the mass of propellant required for the given maneuver through the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation. For multiple maneuvers, delta-v sums linearly. For interplanetary missions delta-v is often plotted on a porkchop plot, which displays the required mission delta-v as a function of launch date.
Flight Dynamics is the science of space vehicle performance, stability, and control. It requires analysis of the six degrees of freedom of the vehicle's flight, which are similar to those of Aircraft: translation in three dimensional axes; and its orientation about the vehicle's center of mass in these axes, known as pitch, roll and yaw, with respect to a defined frame of reference. Dynamics is the modeling of the changing position and orientation of a vehicle, in response to external forces acting on the body. For a spacecraft, these forces are of three types: propulsive force (usually provided by the vehicle's engine thrust); gravitational force exerted by the Earth or other celestial bodies; and aerodynamic lift and drag (when flying in the atmosphere of the Earth or other body, such as Mars or Venus). The vehicle's attitude must be taken into account because of its effect on the aerodynamic and propulsive forces. There are other reasons, unrelated to flight dynamics, for controlling the vehicle's attitude in non-powered flight (e.g., thermal control, solar power generation, communications, or astronomical observation). The principles of flight dynamics are normally used to control a spacecraft by means of an inertial navigation system in conjunction with an attitude control system. Together, they create a subsystem of the spacecraft bus often called ADCS.
Max Q is the point at which aerodynamic stress on a vehicle in atmospheric flight is maximized. It is an important factor in the structural and mission design of rockets, missiles, and other aerospace vehicles which travel through an atmosphere; the flight envelope may be limited to reduce the total structural load on a vehicle near max Q. Gravity.
Transonic refers to the condition of flight in which a range of velocities of airflow exist surrounding and flowing past an air vehicle or an airfoil that are concurrently below, at, and above the speed of sound in the range of Mach 0.8 to 1.0, i.e. 965–1,236 km/h (600–768 mph) at sea level. This condition depends not only on the travel speed of the craft, but also on the temperature of the airflow in the vehicle's local environment. It is formally defined as the range of speeds between the critical Mach number, when some parts of the airflow over an air vehicle or airfoil are supersonic, and a higher speed, typically near Mach 1.2, when most of the airflow is supersonic. Between these speeds some of the airflow is supersonic, but a significant fraction is not. Most modern jet powered aircraft are engineered to operate at transonic air speeds. Transonic airspeeds see a rapid increase in drag from about Mach 0.8, and it is the fuel costs of the drag that typically limits the airspeed. Attempts to reduce wave drag can be seen on all high-speed aircraft. Most notable is the use of swept wings, but another common form is a wasp-waist fuselage as a side effect of the Whitcomb area rule. Severe instability can occur at transonic speeds. Shock waves move through the air at the speed of sound. When an object such as an aircraft also moves at the speed of sound, these shock waves build up in front of it to form a single, very large shock wave. During transonic flight, the plane must pass through this large shock wave, as well as contend with the instability caused by air moving faster than sound over parts of the wing and slower in other parts. Transonic speeds can also occur at the tips of rotor blades of helicopters and aircraft. This puts severe, unequal stresses on the rotor blade and may lead to accidents if it occurs. It is one of the limiting factors of the size of rotors and the forward speeds of helicopters (as this speed is added to the forward-sweeping [leading] side of the rotor, possibly causing localized transonics).
Gravity Assistance
Spin Launch Suborbital Accelerator is an alternative method for putting 200 kilogram class satellites into low earth orbit. Unlike traditional fuel-based rockets, SpinLaunch uses a ground-based, electric powered kinetic launch system that delivers a substantially less expensive and environmentally sustainable approach to space access.
Slingshot Effect or Gravity Assist is the use of the relative movement and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense (e.g. orbit around the Sun). Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon, and it was used by interplanetary probes from Mariner 10 onwards, including the two Voyager Probes' notable flybys of Jupiter and Saturn.
Hohmann Transfer Orbit is an elliptical orbit used to transfer between two circular orbits of different radii in the same plane.
Low-Energy Transfer or low-energy trajectory, is a route in space that allows spacecraft to change orbits using very little fuel. These routes work in the Earth–Moon system and also in other systems, such as between the moons of Jupiter. The drawback of such trajectories is that they take longer to complete than higher-energy (more-fuel) transfers, such as Hohmann transfer orbits.
Non-ballistic atmospheric entry is a class of atmospheric entry trajectories that follow a non-ballistic trajectory by employing aerodynamic lift in the high upper atmosphere. It includes trajectories such as skip and glide. Skip is a flight trajectory where the spacecraft goes in and out the atmosphere. Glide is a flight trajectory where the spacecraft stays in the atmosphere for a sustained flight period of time. In most examples, a skip reentry roughly doubles the range of suborbital spaceplanes and reentry vehicles over the purely ballistic trajectory. In others, a series of skips allows the range to be further extended.
Communications Blackout is a total lack of radio communications capability, caused by ionospheric anomalies, e.g., during strong auroral activity or during re-entry of a spacecraft into the Earth's atmosphere.
Hohmann Transfer Orbit is an elliptical orbit used to transfer between two circular orbits of different radii in the same plane. In general a Hohmann transfer orbit uses the lowest possible amount of energy in traveling between two objects orbiting at these radii, and so is used to send the maximum amount of mission payload with the fixed amount of energy that can be imparted by a particular rocket. Non-Hohmann transfer paths may have other advantages for a particular mission such as shorter transfer times, but will necessarily require a reduction in payload mass and/or use of a more powerful rocket.
Wormholes
 Wormhole or
"Einstein-Rosen bridge" is a hypothetical topological feature that would
fundamentally be a shortcut linking two separate points in
spacetime. A
wormhole may connect extremely long distances such as a billion light
years or more; short distances such as a few meters; different universes;
and/or different points in time. A wormhole is much like a tunnel with two
ends, each at separate points in
spacetime.
Wormhole or
"Einstein-Rosen bridge" is a hypothetical topological feature that would
fundamentally be a shortcut linking two separate points in
spacetime. A
wormhole may connect extremely long distances such as a billion light
years or more; short distances such as a few meters; different universes;
and/or different points in time. A wormhole is much like a tunnel with two
ends, each at separate points in
spacetime.Stargate is a 1994 American science fiction adventure film where the plot centers on the premise of a "Stargate", an ancient ring-shaped device that creates a wormhole enabling travel to a similar device elsewhere in the universe.
Physicists observe wormhole dynamics using a quantum computer. Wormholes are bridges between two remote regions in spacetime. We performed a kind of quantum teleportation equivalent to a traversable wormhole in the gravity picture. To do this, we had to simplify the quantum system to the smallest example that preserves gravitational characteristics so we could implement it on the Sycamore quantum processor at Google.
Teleportation is the hypothetical transfer of matter or energy from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. Teleportation is often paired with time travel, being that the travelling between the two points takes an unknown period of time, sometimes being immediate, or maybe traveling through another dimension? Quantum Teleportation is a technique for transferring quantum information from a sender at one location to a receiver some distance away. While teleportation is commonly portrayed in science fiction as a means to transfer physical objects from one location to the next, quantum teleportation only transfers quantum information. An important note is that the sender knows neither the location of the recipient nor the quantum state that will be transferred. Sixth Sense.
Space Portal is a hypothetical opening in space or time that connects travelers to distant realms. A good portal is a shortcut, a guide, a door into the unknown. Portal is a grand and imposing entrance, or something that provides access or the right or opportunity to enter into another area.
No one would build a universe this big without having the ability to travel through it and be anywhere without the constraints of space and time. You don't have to travel faster than the speed of light, you just need to remove the space in between and and adjust your clock. Maybe the universe was designed in a way that stops life forms from physically infecting other planets, just like oceans that kept civilizations apart. But when civilizations made boats, they could invade other areas. But with so much space between solar systems, no spaceship could travel that distance. So there has to be another way to travel, but we have not matured enough as a species to figure this out just yet, which is most likely by design. The Universes doesn't want ignorant life infecting other planets until they are mature enough. So this forces civilizations to mature and advance enough to be worthy of such a journey.
ER=EPR | Leonard Susskind (youtube)
Magnetic Reconnection s a physical process in highly conducting plasmas in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection occurs on timescales intermediate between slow resistive diffusion of the magnetic field and fast Alfvénic timescales.
Boom Tube is a slang expression for a fictional extra-dimensional point-to-point Einstein-Rosen bridge (a form of teleportation) opened by a Mother Box used primarily by residents of New Genesis and Apokolips in DC Comics.
Flux Transfer Event occurs when a magnetic portal opens in the Earth's magnetosphere through which high-energy particles flow from the Sun. This connection, while previously thought to be permanent, has been found to be brief and very dynamic.
Flux Tube is a generally tube-like (cylindrical) region of space containing a magnetic field, B, such that the field is perpendicular to the normal vector, n ^ {\displaystyle {\hat {n}}} {\hat {n}}. Both the cross-sectional area of the tube and the field contained may vary along the length of the tube, but the magnetic flux is always constant.
Warp Speed is equal to breaking the light barrier, while the actual velocity corresponding to higher factors is determined using an ambiguous formula.
Breaking the warp barrier for faster-than-light travel. New theoretical hyper-fast soliton solutions.
Alcubierre Drive a spacecraft could achieve apparent faster-than-light travel if a configurable energy-density field lower than that of vacuum (that is, negative mass) could be created. Rather than exceeding the speed of light within a local reference frame, a spacecraft would traverse distances by contracting space in front of it and expanding space behind it, resulting in effective faster-than-light travel. Objects cannot accelerate to the speed of light within normal spacetime; instead, the Alcubierre drive shifts space around an object so that the object would arrive at its destination more quickly than light would in normal space without breaking any physical laws. Although the metric proposed by Alcubierre is consistent with the Einstein field equations, construction of such a drive is not necessarily possible. The proposed mechanism of the Alcubierre drive implies a negative energy density and therefore requires exotic matter. If exotic matter with the correct properties cannot exist, then the drive cannot be constructed. At the close of his original article, however, Alcubierre argued (following an argument developed by physicists analyzing traversable wormholes) that the Casimir vacuum between parallel plates could fulfill the negative-energy requirement for the Alcubierre drive. Another possible issue is that, although the Alcubierre metric is consistent with Einstein's equations, general relativity does not incorporate quantum mechanics. Some physicists have presented arguments to suggest that a theory of quantum gravity (which would incorporate both theories) would eliminate those solutions in general relativity that allow for backwards time travel (see the chronology protection conjecture) and thus make the Alcubierre drive invalid. Alcubierre Drive: Warp Speed - Star Trek fantasy or plausible? (youtube). Eagleworks Laboratories: Advanced Propulsion Physics Research.
Ralph Ring - Blue Star Enterprise
Suppressed Anti-Gravity Tech (youtube)
Wanderers - a short film by Erik Wernquist (video)
Diffusion Current is a current in a semiconductor caused by the diffusion of charge carriers (holes and/or electrons). This is the current which is due to the transport of charges occurring because of nonuniform concentration of charged particles in a semiconductor. The drift current, by contrast, is due to the motion of charge carriers due to the force exerted on them by an electric field. Diffusion current can be in the same or opposite direction of a drift current. The diffusion current and drift current together are described by the drift–diffusion equation.
Alpha Centauri is 4.3 light-years away, or 25 trillion miles. How long would that take? Apollo 10 traveled at 24,791 mph. So lets say we can travel 50,000 mph. In 20 hours we would travel 1 million miles. So almost 1 day to travel a million miles.
It would take a million days, or 2,739 years, to travel a trillion miles? So 68, 475 years for someone to reach Alpha Centauri.
The microscopic Tardigrade—also known as the water bear—is the only animal that can survive the cold, irradiated vacuum of outer space.
"Funny how movies about space travel make us realize that we are all on a spaceship called Earth, and everything we learn about surviving in space will help us survive on planet earth."
Twin Paradox is a thought experiment in special relativity involving identical twins, one of whom makes a journey into space in a high-speed rocket and returns home to find that the twin who remained on Earth has aged more. This result appears to be puzzling because each twin sees the other twin as moving, and so, according to an incorrect naive application of time dilation and the principle of relativity, each should paradoxically find the other to have aged more slowly. However, this scenario can be resolved within the standard framework of special relativity: the travelling twin's trajectory involves two different inertial frames, one for the outbound journey and one for the inbound journey, and so there is no symmetry between the spacetime paths of the two twins. Therefore, the twin paradox is not a paradox in the sense of a logical contradiction.
Dream Big, But always have a Backup Plan
The thing about people wanting to go to mars, or to mine asteroids, or to colonize space. I believe that these things will eventually happen in the future, but we should focus more on humanities future first, because you can dream all you want about future endeavors, but if there is no future, then what's the point? Secure humanities future first, then you will have a future where you will be able to explore space. These dreams of space travel will bring us full circle anyway. The technologies and the knowledge that we learn from trying to live in space, will actually be used on earth to secure our own planets future and ours. After all, we have the greatest spaceship in the universe, it's called Earth. Lets take care of this one before we start thinking about building another one. Besides, the longer we wait, the more advanced will be in the future, and then we can set out and explore the universe in full fashion.
6 Space Technologies we can use to Improve Life on Earth: Danielle Wood (video and text)
Technology Spinoffs that came from Space Exploration highlights NASA technologies that are benefiting life on Earth in the form of commercial products. We've profiled nearly 2,000 spinoffs since the publication began in 1976 — there's more space in your life than you think! NASA Spinoff Technologies are commercial products and services which have been developed with the help of NASA, through research and development contracts, such as Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) or STTR awards, licensing of NASA patents, use of NASA facilities, technical assistance from NASA personnel, or data from NASA research. Information on new NASA technology that may be useful to industry is available in periodical and website form in "NASA Tech Briefs", while successful examples of commercialization are reported annually in the NASA publication "Spinoffs". Repurpose.
Laws in Space
Space Law encompasses national and international law governing activities in outer space. International lawyers have been unable to agree on a uniform definition of the term "outer space", although most lawyers agree that outer space generally begins at the lowest altitude above sea level at which objects can orbit the Earth, approximately 100 km (62 mi) (the Kármán line).
Space Policy is the political decision-making process for, and application of, public policy of a state (or association of states) regarding spaceflight and uses of outer space, both for civilian (scientific and commercial) and military purposes. International treaties, such as the 1967 Outer Space Treaty, attempt to maximize the peaceful uses of space and restrict the militarization of space. Space policy intersects with science policy, since national space programs often perform or fund research in space science, and also with defense policy, for applications such as spy satellites and anti-satellite weapons. It also encompasses government regulation of third-party activities such as commercial communications satellites and private spaceflight. Space policy also encompasses the creation and application of space law, and space advocacy organizations exist to support the cause of space exploration.
National Aeronautics and Space Act in 1958 charged a new Agency with conducting the aeronautical and space activities of the United States "so as to contribute materially to one or more of the following objectives:" The expansion of human knowledge of phenomena in the atmosphere and space; The improvement of the usefulness, performance, speed, safety, and efficiency of aeronautical and space vehicles; The development and operation of vehicles capable of carrying instruments, equipment, supplies and living organisms through space; The establishment of long-range studies of the potential benefits to be gained from, the opportunities for, and the problems involved in the utilization of aeronautical and space activities for peaceful and scientific purposes. The preservation of the role of the United States as a leader in aeronautical and space science and technology and in the application thereof to the conduct of peaceful activities within and outside the atmosphere. The making available to agencies directly concerned with national defenses of discoveries that have military value or significance, and the furnishing by such agencies, to the civilian agency established to direct and control nonmilitary aeronautical and space activities, of information as to discoveries which have value or significance to that agency; Cooperation by the United States with other nations and groups of nations in work done pursuant to this Act and in the peaceful application of the results, thereof; and The most effective utilization of the scientific and engineering resources of the United States, with close cooperation among all interested agencies of the United States in order to avoid unnecessary duplication of effort, facilities, and equipment.
Office of Planetary Protection promotes the responsible exploration of the solar system by implementing and developing efforts that protect the science, explored environments, and Earth. The objectives of planetary protection are several-fold and include: Preserving our ability to study other worlds as they exist in their natural states; Avoiding the biological contamination of explored environments that may obscure our ability to find life elsewhere – if it exists; and To ensure that we take prudent precautions to protect Earth’s biosphere in case life does exist elsewhere.
Outer Space Treaty is a treaty that forms the basis of international space law that represents the basic legal framework of international space law. Among its principles, it bars states party to the treaty from placing weapons of mass destruction in orbit of Earth, installing them on the Moon or any other celestial body, or otherwise stationing them in outer space. It exclusively limits the use of the Moon and other celestial bodies to peaceful purposes and expressly prohibits their use for testing weapons of any kind, conducting military maneuvers, or establishing military bases, installations, and fortifications (Article IV). However, the Treaty does not prohibit the placement of conventional weapons in orbit and thus some highly destructive attack strategies such as kinetic bombardment are still potentially allowable. The treaty also states that the exploration of outer space shall be done to benefit all countries and that space shall be free for exploration and use by all the States. The treaty explicitly forbids any government from claiming a celestial resource such as the Moon or a planet. Article II of the Treaty states that "outer space, including the Moon and other celestial bodies, is not subject to national appropriation by claim of sovereignty, by means of use or occupation, or by any other means". However, the State that launches a space object retains jurisdiction and control over that object. The State is also liable for damages caused by their space object.
NASA needed 14 new astronauts. A record-breaking 18,300 folks applied.
"The journey inward is as important as the journey outward, sometimes looking in is looking out." ET (intelligent life).
In order for humans to travel to another habitable planet like earth, we first have to learn how to keep our planet habitable long enough so that humans can live long enough in order to learn how to travel to another habitable planet, and save quadrillions of human lives at the same time.
Extraterrestrial Life - ET - Space Aliens
 Extraterrestrial Life
is life that does not originate from Earth. Other life forms may range
from simple single-celled organisms to beings with civilizations far
more
advanced than humanity. Extraterrestrial
are objects not originating from earth or
occurring outside Earth or
outside its atmosphere. Celestial.
Extraterrestrial Life
is life that does not originate from Earth. Other life forms may range
from simple single-celled organisms to beings with civilizations far
more
advanced than humanity. Extraterrestrial
are objects not originating from earth or
occurring outside Earth or
outside its atmosphere. Celestial. Don't assume that incredible space crafts are Extraterrestrial. It's not so unusual to believe that there is advanced aircraft technology that the public does not know about. Military secrets are nothing new. Besides that, all those people who have seen advanced aircraft can't be wrong. We have eye witness accounts from pilots, astronauts, military personal, and also civilians who were in several different locations at the same time seeing the same thing. And on top of that, advancements in technology in the last 50 years has shown us that almost anything is possible. Gravity Control Propulsion Research in the 1950's was setup to discover and develop technologies and theories for the manipulation of gravity or gravity-like fields for propulsion. Alien Reproduction Vehicle.
Singularity - Technological Advancement
Unidentified Flying Object or UFO is an object observed in the sky that is not readily identified. Most UFOs are later identified as conventional objects or phenomena. The term is widely used for claimed observations of extraterrestrial spacecraft. Your eyes can sometimes play tricks on you and illusions are common. There's a good reason why astronomers don't see UFO's, because they know about illusions and low information zones, so they don't make assumptions.
Ufology is the investigation of unidentified flying objects or UFOs by people who believe that they may be of extraordinary origins (most frequently of extraterrestrial alien visitors). When it comes to UFO sightings, the people in power don't want people asking questions, because when people start asking questions, they will eventually learn some things that will make them realize that they have been lied to in all kinds of ways.
Interdimensional Hypothesis states unidentified flying objects or UFOs and related events involve visitations from other "realities" or "dimensions" that coexist separately alongside our own. Don't ever assume that you know what intelligent life forms look like.
 Michael Herrera
- Witness Testimony in 2009 - Unidentified Aerial Phenomena or UAP. (youtube)
Michael Herrera
- Witness Testimony in 2009 - Unidentified Aerial Phenomena or UAP. (youtube)
David Grusch - UFO whistleblower claims. The U.S. federal government maintains a secretive UFO or UAP retrieval program and is in possession of "non-human" spacecraft and "dead pilots".
I believe in the possibility of life outside our solar system, but I don't fantasize about what that belief means, or do I fantasize about the millions of other possible scenarios that surround that possibility. I have to live in reality and use my common sense as much as possible. Fantasizing about a belief is to live in a fantasy world where your mind is imprisoned by your belief. Though it's good to believe, it's not logical to allow a belief to stop you from learning the truth, or stop you from exploring other possibilities. You're alive because people did more than just believe in something, they did something, like learn.
First Contact will be when humans finally discover who we really are. The answer will always come from within. Understanding ourselves helps us to understand the world around us.
What if there is extraterrestrial life? How will it change human life? How will it impact our world? So where are the space aliens? Did the aliens visit earth and then leave earth for some reason? Or did the aliens all die off for some strange reason? Or, are the aliens still here but are not letting humans know about their presence for some strange reason? Maybe the aliens are intentionally avoiding communication because they're following the prime directive or the zoo hypothesis, or maybe they're just avoiding interplanetary contamination? Maybe aliens are doing something positive, and we just don't know it. Or maybe the end is near, and the aliens don't want to tell us because it will ruin the experiment, or just bum us out. Maybe a big advancement is coming soon, so the aliens are thinking that there is no need to intervene. What ever the answer is, we may never know. But you still have to wonder, will these so called intelligent life forms from another planet or galaxy, intervene, especially when they can clearly see that we are killing ourselves, and see that we're also destroying the environment that we all need to survive and live in. So what kind of intelligent life would just sit back and watch a species self destruct? Can't they see that we're hurting ourselves and hurting each other. What ever the answer is, this life on earth is not a fair test of human capabilities, and this is not some form of virtual reality where nothing is real. Humans are much better than this, and so is ET. So, the only thing that makes sense, is to do what is right and do what is good, for everyone and for every life form in our galaxy. If a higher power can not intervene, then that means we have to solve our own problems because no one is coming to our rescue. So heaven will have to wait. This is the here and now, this is our chance. Let's prove to our makers that we are worthy of this planet, and worthy of any other planet. A peaceful coexistence would be the goal no matter where humans may live. But first, we have to prove that to be true on our own planet, and at the moment, we are doing a horrible job, which means that the human race will most likely die here on earth, a tragedy that would reverberate through the entire universe.
What if we do find a planet close enough? Are we going to go there and say "Hey, can we stay with you guys, we fucked our planet and can't live there no more." New TV show "Assholes from Space."
The search for intelligent life starts within, and not looking outward in outer space, especially when something is light years away that you will never reach. The information we're looking for is on planet earth.
"In a very real sense, we are all aliens on a strange planet. We spend most of our lives trying to reach out and communicate. If during our lifetime we could reach out and really communicate with just two people, we are indeed very fortunate." Gene Roddenberry - Star Trek.
Could our world be the result of biogenesis? Are humans the result of intelligent design or creationism? Or maybe other life forms from other planets just sent their DNA with the instructions? Or maybe our existance was a collaboration of several intelligent beings that were from different planets and from different galaxies, with each intelligent life contributing to our design.
Searching for Life on other Planets. The search for extraterrestrial life is not just about looking outward, it's also about looking inward.
The Great Filter is the idea that in the development of life from the earliest stages of abiogenesis to reaching the highest levels of development on the Kardashev scale, there is a barrier to development that makes detectable extraterrestrial life exceedingly rare. Republicans and religious fanatics are barriers to human development and advancement, which is why life is going through another mass extinction and why our earth is dying. In regards to the Fermi paradox, humans are the living evidence of extraterrestrial life.
The Great Silence could be the result of civilizations being so far advanced that we don’t recognize them, or, that we don't have the ability or the technology to detect them, or that people in power on earth are hiding evidence of extraterrestrial life because these psychopaths in power fear that they will lose their power and control over people when people finally realize that advanced civilizations have a better alternative to living, and that advanced civilizations have no need to be manipulated or controlled by corrupt and ignorant people in power, who are mainly scumbag republicans and the gullible religious people who vote for them. So why doesn't anyone call us? Or why hasn't anyone tried to reach out to us? Maybe because extraterrestrial life thinks that humans are too stupid to talk to because republicans and conservatives are busy killing humans. So extraterrestrial life doesn't think that humans are worth talking to, or worth saving.
Russian Cosmism is the philosophical theory that the cosmos is a self-existent whole and was not created by a god, though an intelligent being who is capable of intelligent design would be seen as a god, and thus be a God to us. Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in 1903, published the first serious scientific work on space travel. His work was essentially unknown outside the Russian Empire, but inside the country it inspired further research, experimentation and the formation of the Society for Studies of Interplanetary Spaceflight. Astronautics is the theory and practice of travel beyond Earth's atmosphere into outer space. Spaceflight is one of its main applications and space science its overarching field.
Even if we did find another exo-planet like ours, how could we even assume that life as we know it exists there? Bias Errors - Celestial.
The drake equation only assumes the possibility of life, it does not explain how life exists elsewhere. Do you think that finding Extraterrestrial Life will somehow improve our world like some magic potion? Technology can only do so much, unless of course, Extraterrestrial Life can show us how to improve our dysfunctional inadequate education system. Then I believe we will see improvements. Till then, I have more important things to think about, like how to improve education without having to depend on Extraterrestrial Life to do it for us.
Habitable Zone - Stars Like Ours.
Fermi Paradox is the apparent contradiction between the lack of evidence and high probability estimates, e.g., those given by the Drake equation, for the existence of extraterrestrial civilizations. The basic points of the argument, made by physicists Enrico Fermi (1901–1954) and Michael H. Hart (born 1932), are: There are billions of stars in the galaxy that are similar to the Sun, many of which are billions of years older than Earth. With high probability, some of these stars will have Earth-like planets, and if the Earth is typical, some might develop intelligent life. Some of these civilizations might develop interstellar travel, a step the Earth is investigating now. Even at the slow pace of currently envisioned interstellar travel, the Milky Way galaxy could be completely traversed in a few million years. According to this line of reasoning, the Earth should have already been visited by extraterrestrial aliens. In an informal conversation, Fermi noted no convincing evidence of this, leading him to ask, "Where is everybody?" There have been many attempts to explain the Fermi paradox, primarily either suggesting that intelligent extraterrestrial life is extremely rare or proposing reasons that such civilizations have not contacted or visited Earth.
Physical Paradox is an apparent contradiction in physical descriptions of the universe.
Holography - VR - Awareness - Reality
Phased-Array Optics is the technology of controlling the phase of light waves transmitting or reflecting from a two-dimensional surface by means of adjustable surface elements. It is the optical analogue of phased array radar. By dynamically controlling the optical properties of a surface on a microscopic scale, it is possible to steer the direction of light beams, or the view direction of sensors, without any moving parts. Hardware associated with beam steering applications is commonly called an optical phased array (OPA). Phased array beam steering is used for optical switching and multiplexing in optoelectronic devices, and for aiming laser beams on a macroscopic scale.
Crop Circles is a pattern created by flattening high grass in a large field or in a cereal crop that is located on farmland.
Impermanence - Snow Art - Landscaping - Weaving - Symmetry
Waterhole Frequency refers to a specific range on the electromagnetic spectrum used in radio astronomy, typically between 1420 and 1720 Megahertz or MHz. It is considered a relatively quiet band ideal for searching for potential extraterrestrial signals due to the natural emission of hydrogen atoms at 1420 MHz. The signal's frequency of 1420 MHz is also part of a protected spectrum, which is a frequency range reserved for astronomical research in which terrestrial transmissions are forbidden.
Wow Signal was a strong narrowband radio signal detected on August 15, 1977, by Ohio State University's Big Ear radio telescope in the United States, then used to support the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. The signal appeared to come from the direction of the constellation Sagittarius and bore expected hallmarks of extraterrestrial origin.
 Arecibo Message is a 1974 interstellar
radio message
carrying basic information about humanity and Earth sent to globular
star cluster M13 in the hope that extraterrestrial intelligence might
receive and decipher it. The message was broadcast into space a single
time via frequency modulated radio waves at a ceremony to mark the
remodeling of the
Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico on 16 November
1974. The message was aimed at the current location of M13 some 25,000
light years away because M13 was a large and close collection of stars
that was available in the sky at the time and place of the ceremony. The
message consisted of 1,679 binary digits, approximately 210 bytes,
transmitted at a frequency of 2,380 MHz and modulated by shifting the
frequency by 10 Hz, with a power of 1,000 kW. The
"ones" and "zeros" were
transmitted by frequency shifting at the rate of 10 bits per second. The
total broadcast was less than three minutes. The cardinality of 1,679 was
chosen because it is a semiprime (the product of two prime numbers), to be
arranged rectangularly as 73 rows by 23 columns. The alternative
arrangement, 23 rows by 73 columns, produces jumbled nonsense (as do all
other X/Y formats). The message forms the image shown on the right, or its
inverse, when translated into graphics, characters and spaces. Dr. Frank
Drake, then at Cornell University and creator of the Drake equation, wrote
the message with help from Carl Sagan, among others.
The message
consists of seven parts that encode the following (from the top down): The numbers one (1) to ten (10)
(white). The atomic numbers of the elements hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen,
oxygen, and phosphorus, which make up deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
(purple). The formulas for the sugars and bases in the nucleotides of
DNA (green). The number of nucleotides in DNA, and a graphic of the
double helix structure of DNA (white & blue). A
graphic figure of a
human, the dimension (physical height) of an average man, and the human population of Earth (red, blue/white, & white respectively).A
graphic of the Solar System indicating which of the planets the message is
coming from (yellow). A graphic of the Arecibo radio telescope and the
dimension (the physical diameter) of the transmitting antenna dish
(purple, white, & blue). Since it will take nearly 25,000 years for the
message to reach its intended destination (and an additional 25,000
years for any reply), the
Arecibo message is viewed as a demonstration of
human technological achievement, versus a real attempt to enter into a
conversation with extraterrestrials. In fact, the core of M13, to
which the message was aimed, will no longer be in that location when the
message arrives. However, as the proper motion of M13 is small, the
message will still arrive near the center of the cluster. According to
the Cornell News press release of November 12, 1999, the real purpose of
the message was not to make contact but to demonstrate the
capabilities of newly installed equipment.
Arecibo Message is a 1974 interstellar
radio message
carrying basic information about humanity and Earth sent to globular
star cluster M13 in the hope that extraterrestrial intelligence might
receive and decipher it. The message was broadcast into space a single
time via frequency modulated radio waves at a ceremony to mark the
remodeling of the
Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico on 16 November
1974. The message was aimed at the current location of M13 some 25,000
light years away because M13 was a large and close collection of stars
that was available in the sky at the time and place of the ceremony. The
message consisted of 1,679 binary digits, approximately 210 bytes,
transmitted at a frequency of 2,380 MHz and modulated by shifting the
frequency by 10 Hz, with a power of 1,000 kW. The
"ones" and "zeros" were
transmitted by frequency shifting at the rate of 10 bits per second. The
total broadcast was less than three minutes. The cardinality of 1,679 was
chosen because it is a semiprime (the product of two prime numbers), to be
arranged rectangularly as 73 rows by 23 columns. The alternative
arrangement, 23 rows by 73 columns, produces jumbled nonsense (as do all
other X/Y formats). The message forms the image shown on the right, or its
inverse, when translated into graphics, characters and spaces. Dr. Frank
Drake, then at Cornell University and creator of the Drake equation, wrote
the message with help from Carl Sagan, among others.
The message
consists of seven parts that encode the following (from the top down): The numbers one (1) to ten (10)
(white). The atomic numbers of the elements hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen,
oxygen, and phosphorus, which make up deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
(purple). The formulas for the sugars and bases in the nucleotides of
DNA (green). The number of nucleotides in DNA, and a graphic of the
double helix structure of DNA (white & blue). A
graphic figure of a
human, the dimension (physical height) of an average man, and the human population of Earth (red, blue/white, & white respectively).A
graphic of the Solar System indicating which of the planets the message is
coming from (yellow). A graphic of the Arecibo radio telescope and the
dimension (the physical diameter) of the transmitting antenna dish
(purple, white, & blue). Since it will take nearly 25,000 years for the
message to reach its intended destination (and an additional 25,000
years for any reply), the
Arecibo message is viewed as a demonstration of
human technological achievement, versus a real attempt to enter into a
conversation with extraterrestrials. In fact, the core of M13, to
which the message was aimed, will no longer be in that location when the
message arrives. However, as the proper motion of M13 is small, the
message will still arrive near the center of the cluster. According to
the Cornell News press release of November 12, 1999, the real purpose of
the message was not to make contact but to demonstrate the
capabilities of newly installed equipment. Voyager Messages - Symbols - Robot Ethics
E.T. Phone Home from the 1982 movie E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial.
(A) Beware the bearers of FALSE gifts and their BROKEN PROMISES.
(B) Much PAIN but still time. BELIEVE.
(C) There is GOOD out there. We Oppose DECEPTION.
Conduit CLOSING (Ding!)
 Close Encounters of the Third Kind
(wiki)
Close Encounters of the Third Kind
(wiki)Movie Clip with the 5 Tones (youtube) - B flat, C, A flat, (octave lower) A flat, E flat.
Language Interpretation Problems and Procedures
Eighth Note is a musical note played for half the value of a quarter note (crotchet) and twice that of the sixteenth note (semiquaver), which amounts to one quarter the duration of a half note (minim), one eighth the duration of whole note (semibreve), one sixteenth the duration of a double whole note (breve), and one thirty-second the duration of a longa, hence the name. It is the equivalent of the fusa in mensural notation (Morehen and Rastell 2001). G, A, F, (octave lower) F, C.
Kodaly Method is an approach to Music Education developed in Hungary during the mid-twentieth century by Zoltán Kodály.
Lee Cronin: Making Matter come Alive (youtube)
TROM - 2.23 UFOs and Extraterrestrial Life (youtube)
Foo Fighter was used by Allied aircraft pilots during World War II to describe various UFOs or mysterious aerial phenomena seen in the skies over both the European and Pacific theaters of operations.
Even if we did come in contact with other life form, there is no way of knowing what it would do to our lives? There is no way of calculating this probability, you can only guess. And we all know what a guess is? So how can a guess prepare you?
Archaeoastronomy is the study of how people in the past "have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures. Knowledge Preservation.
Astro-Engineering is engineering at astronomical scale, i.e. at planetary, stellar, stellar system, galactic or even larger scale. It is a form of megascale engineering. An example is the hypothetical Dyson Sphere, which is a hypothetical megastructure that completely encompasses a star and captures most or all of its power output.
Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
Dimitar Sasselov: How we found hundreds of Earth-like planets (youtube)
There's a big difference between a Technologically Advanced Civilization and an Intelligent Civilization. Humans are advanced but we are not so intelligent as a whole. We are like Klingons, except that we would not be that stupid as to send Neanderthals out into space. But Hollywood has this strange idea that Humans will still be stupid in the future, which is idiotic in itself. I laughed when I saw the movie Prometheus. When the crew woke up from their deep sleep they realized that one of the crew members was an a**hole. Who the hell sends an a**hole into space? Really..What idiot choose those crew members? You see it doesn't make sense. And that is just one of many examples there are in Movies and TV shows about space travel. Pigs in Space (youtube). They're Made Out of Meat (youtube) - Based on the short story by Terry Bisson.
"The only Intelligent Life Form man will ever meet is himself, as soon as he wakes up, that is when and if? Not to say that there are not other life forms in our universe, it's just that we have not yet defined what ' intelligent ' is. Just because someone is advanced does not mean that they are intelligent. A perfect example is 21st century humans."
Aliens will not come to earth to kill all the humans. Aliens will only roundup all the scumbags in power who are doing all the environmental destruction. Intelligent life is not born to kill, only ignorant people kill.
"I only believe in the possibility that there could be life on other planets. To take a belief any farther than that is not really necessary. The same goes for multiverses. Elaborating more on a belief does not make it any more real. You have to have proof. I'm not saying that you must see a space alien in order to prove that space aliens exist. Example, we didn't have to see atoms to know that atoms existed. We did a lot of testing and experiments, we did a lot of research, and we built a lot of complex machines that ultimately proved that atoms were there. We can see farther into space and see smaller into molecules then any other time in human history, But the one thing that we learned is that our universe is far in all directions. We can't see what's inside protons, and we can't see the edge of our universe. So I'm guessing that space aliens are also going to be hard to see, after all they have almost a 9 Billion year head start. But everything leaves a trail, and everything has some form of evidence that proves that it exists. We would have to make amazing complex machines that would be able to measure things, things that we don't even know exist. So we will always have work to do because there is no end to science, there will never be an end to what we could know, there is no end to knowledge, and there's is no end to information. I wouldn't say that it goes on forever, I'm just saying that no one can define what 'END' is, so we don't know what 'END' means, so you see, There is No End.....well at least not for now there isn't, but maybe some day?... I wonder if or when we do find an end, that it will be like telling someone the ending of a movie before they see it, hey don't ruin it for me! I want it to be a surprise. So you see, there's not even an end to this conversation, it keeps going and going..."
 The photo on right are creatures found
deep in our ocean. They have a scientific name but to me they
look like Intelligent life. Is there a limit to how small a
human like brain can be? We haven't fully explored what
intelligence really means. The
second to the last final frontier. The photo reminds me of the 1989 movie
THE ABYSS
(youtube) - Neuron
Evolution.
The photo on right are creatures found
deep in our ocean. They have a scientific name but to me they
look like Intelligent life. Is there a limit to how small a
human like brain can be? We haven't fully explored what
intelligence really means. The
second to the last final frontier. The photo reminds me of the 1989 movie
THE ABYSS
(youtube) - Neuron
Evolution.Sea Angel are a large group of extremely small, swimming sea slugs, not to be confused with Cnidarians (Jellies and other similar creatures), classified into six different families. They are pelagic opisthobranchs in the clade Gymnosomata within the larger mollusc clade Heterobranchia. Sea angels were previously referred to as a type of pteropod. Clionidae (wiki).
Encephalization is defined as the amount of brain mass related to an animal's total body mass. Quantifying an animal's encephalization has been argued to be directly related to that animal's level of intelligence? Of course that is just a guess from a pea brain.
Brittle stars can learn just fine -- even without a brain. Headless animals called brittle stars have no brains at all and still manage to learn through experience, new research reveals. This type of learning involves associating different stimuli via a process called classical conditioning.
Don't assume that incredible space crafts could only be operated by aliens from another planet, because the fact is that 99% of the people on the planet are not aware of all the technological advances that are known to humans. And don't ever assume that alien life needs to look a particular way, because the fact is that 99% of people on the planet don't know all the different ways that life can exist, or how intelligent a life form should be or can be. It's best to keep an open mind and not jump to any conclusions. In order to be properly prepared and less vulnerable, you should believe nothing and expect anything. Meaning, don't limit yourself to only a few possible scenarios, because that may not prepare you for something new or something totally unexplainable. Remember, learning has got us this far, so we can't stop learning now. Think before you jump, it could very well save your life. Singularity.
The point is that intelligent life from another planet may already be here. We just can't see them because we don't know all the different ways that life could exist just yet, and we also haven't fully explored our own planet just yet. To say that ET life does exist or does not exist, you would first have to say what exactly is ET life? And that's like trying to say that you know what God looks like.
People who are looking for intelligent life are looking in the wrong direction. Don't just look out into outer space, look within your own body, intelligent life is in our DNA.
Could there be Another Planet like Earth
Exoplanet is a planet outside our solar system. About 1 in 5 sun-like stars have an "Earth-sized" planet in the habitable zone.
Circumstellar Habitable Zone is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure. A Goldilock Zone refers to the habitable zone around a star that is not to far from the Sun or not too close to the Sun, which depends on the Star Size and Star Type. In order to have water a planet must be the right distance from its star. To close water boils away, to far water freezes. Then it is just a matter of reaching a planet at the right time in its life when it is stable enough to support animal life. Does a galaxy have a habitable zone too?
Bio-Signatures - Knowledge Preservation
Planetary Habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and maintain environments hospitable to life.
A Star like Ours - Solar System like Ours
Scientists spot planet that may be hospitable to human life, but human life is not that hospitable and not always kind.
Exobiology is the branch of science that deals with the possibility and likely nature of life on other planets or in space.
Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary scientific field that studies the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. Astrobiology is the multidisciplinary field that investigates the deterministic conditions and contingent events with which life arises, distributes, and evolves in the universe. Astrobiology makes use of molecular biology, biophysics, biochemistry, chemistry, astronomy, physical cosmology, exoplanetology, geology, paleontology, and ichnology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from that on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data, and although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.
Finding another planet just like Earth is unlikely, at least not the same kind of planet, or even at the right time in the planets development that would allow the planet to safely sustain human life. So finding another planet like Earth is mostly just fantasy for now. We should be more focused on survival and sustainability. And just maybe in a few thousand years, we just might be able to find another home some where in the Universe, but we have to be able to live that long first. First things first.
There is not one planet like earth that is close enough to us that we could reach in one lifetime. But the fact is, no human alive is just one lifetime. Everyone alive today is a combination of millions of lifetimes that were passed on to us from our past generations. So our future is also made up of millions of lifetimes, if not trillions of lifetimes. So could we ever reach another planet like earth? Yes. We just have to understand that "we" is not "us" who are alive today. We means the humans that will live millions of years from now. And if you want to be on that spaceship, you have to pass on knowledge that future humans will consider worth taking to another world. We have come full-circle, except this time around we will know a lot more than we ever did before, but will we not know as much as future generations will, we hope.
 Drake Equation is a probabilistic argument used to estimate the number
of active, communicative extraterrestrial civilizations
in the Milky Way galaxy. The equation was written in 1961 by Frank Drake,
not for purposes of quantifying the number of civilizations, but as a way
to stimulate scientific dialogue at the first scientific meeting on the
search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). The equation summarizes
the main concepts which scientists must contemplate when considering the
question of other radio-communicative life. It is more properly thought of
as a Fermi problem rather than as a serious attempt to nail down a precise
number. Criticism related to the Drake equation focuses not on the
equation itself, but on the fact that the estimated values for several of
its factors are highly conjectural, the combined effect being that the
uncertainty associated with any derived value is so large that the
equation cannot be used to draw firm conclusions. N = the number of
civilizations in our galaxy with which communication might be possible
(i.e. which are on our current past light cone); and R = the average
rate of star formation in our galaxy. fp
= the fraction of those stars that have planets. ne = the average number
of planets that can potentially support life per star that has planets.
fl = the fraction of planets that could support life that actually develop
life at some point. fi = the fraction of planets with life that actually
go on to develop intelligent life (civilizations). fc = the fraction of
civilizations that develop a technology that releases detectable signs of
their existence into space. L = the length of time for which such
civilizations release detectable signals into space. 80 billion possible
planets just in our galaxy?
The Search
for Life: The Drake Equation (video).
Drake Equation is a probabilistic argument used to estimate the number
of active, communicative extraterrestrial civilizations
in the Milky Way galaxy. The equation was written in 1961 by Frank Drake,
not for purposes of quantifying the number of civilizations, but as a way
to stimulate scientific dialogue at the first scientific meeting on the
search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). The equation summarizes
the main concepts which scientists must contemplate when considering the
question of other radio-communicative life. It is more properly thought of
as a Fermi problem rather than as a serious attempt to nail down a precise
number. Criticism related to the Drake equation focuses not on the
equation itself, but on the fact that the estimated values for several of
its factors are highly conjectural, the combined effect being that the
uncertainty associated with any derived value is so large that the
equation cannot be used to draw firm conclusions. N = the number of
civilizations in our galaxy with which communication might be possible
(i.e. which are on our current past light cone); and R = the average
rate of star formation in our galaxy. fp
= the fraction of those stars that have planets. ne = the average number
of planets that can potentially support life per star that has planets.
fl = the fraction of planets that could support life that actually develop
life at some point. fi = the fraction of planets with life that actually
go on to develop intelligent life (civilizations). fc = the fraction of
civilizations that develop a technology that releases detectable signs of
their existence into space. L = the length of time for which such
civilizations release detectable signals into space. 80 billion possible
planets just in our galaxy?
The Search
for Life: The Drake Equation (video).Biosignature is any substance such as an element, isotope, molecule, or phenomenon, that provides scientific evidence of past or present life. (If there are pollutants in the atmosphere, then we could say, "we just found life on another planet, and they're stupid just like us, lets say hello.")
When looking for another planet to move to, you should want the new planet to have a few qualities. The planet should be around 3 billion years old and orbit a stars sweet spot, and the star should be around 4 billion years old. This should give you around 1 billion years or so of a somewhat stable environment, which you will need in order to survive and live a sustainable existence. And if other life forms are already on the planet, then you will need to work out some kind of an agreement, one that proves that you are a symbiotic life form, which means that you will have to avoid telling your new friends about the history of humans. Good luck.
Just looking at earth, we can see that a planet like earth is extremely rare and extremely lucky. No other planet in our solar system has life. Many things have to happen in order for an earth like planet to have life. Even then, a planet goes through extreme changes, with some changes killing almost every living thing, like during extinction events. Even if you find another planet, you will not know what state it's in. It could be frozen in ice like our planet was for over a million years, it could be hit by asteroids like our planet was, it could be going through a mass extinction like our planet has several times, the planets atmosphere could be changing as our planet did, microbes and viruses could kill us just like here on earth, and this is just name a few of the dangers. Looking at the history of our earth, you can say that it takes over 4 billion years for a planet to stabilize enough to support life, animal life that is, the type of life most important to us. So the first half of the lifespan of a planet is used for stabilization, around 4.5 billion years, and the other half of the lifespan of a planet is used to support life, around 4.5 billion years. So if we find another planet like ours, we will have to determine how old it is, is it still a reckless teenage planet, or a stable adult planet. That could make all the difference on choosing the right one. But of course there is no guarantee, after all, we have only one experience with planets like ours, which is very little experience. Even when we find a planet in the goldilock zone or habitable zone. there are still has many deadly dangers. Our planet is not stable even now. And most of the stability in life comes from humans learning about their environment and adapting to those changes. But if we don't increase public awareness to the dangers humans face now, the human race will not live long enough to find a new home. So first we need to stay alive long enough in order to have the time to solve this problem of finding a new home. Our earth will reach its end someday, so we need to face the facts. And the only way to face the facts is making sure that every human alive knows the facts. The only way for people to be aware of reality is when they have the knowledge that's needed in order to understand the reality that everyone lives in. Your life may differ from other peoples lives, but every person alive is a human living on planet earth. Humans coexist with life. Without coexistence their is no life. Working together and feeling connected is what humans do, but this only comes from learning, and we have a lot of learning to do.
"The memory of planet Earth will be remembered forever. Even though Earth was not the planet of human birth, Earth was still the most monumental turning point in Human evolution."
Planet Hunters - Kepler Planet Seeking - Backyard-Worlds - Telescopes
Interplanetary Contamination refers to biological contamination of a planetary body by a space probe or spacecraft, either deliberate or unintentional. There are two types of interplanetary contamination: Forward contamination is the transfer of life and other forms of contamination from Earth to another celestial body. Back contamination is the introduction of extraterrestrial organisms and other forms of contamination into Earth's biosphere. It also covers infection of humans and human habitats in space and on other celestial bodies by extraterrestrial organisms, if such habitats exist. The main focus is on microbial life and on potentially invasive species. Non-biological forms of contamination have also been considered, including contamination of sensitive deposits (such as lunar polar ice deposits) of scientific interest. In the case of back contamination, multicellular life is thought unlikely but has not been ruled out. In the case of forward contamination, contamination by multicellular life (e.g. lichens) is unlikely to occur for robotic missions, but it becomes a consideration in crewed missions to Mars. Current space missions are governed by the Outer Space Treaty and the COSPAR guidelines for planetary protection. Forward contamination is prevented primarily by sterilizing the spacecraft. In the case of sample-return missions, the aim of the mission is to return extraterrestrial samples to Earth, and sterilization of the samples would make them of much less interest. So, back contamination would be prevented mainly by containment, and breaking the chain of contact between the planet of origin and Earth. It would also require quarantine procedures for the materials and for anyone who comes into contact with them.
Planetary Protection is a guiding principle in the design of an interplanetary mission, aiming to prevent biological contamination of both the target celestial body and the Earth in the case of sample-return missions. Planetary protection reflects both the unknown nature of the space environment and the desire of the scientific community to preserve the pristine nature of celestial bodies until they can be studied in detail.
Ethics of Terraforming has constituted a philosophical debate within biology, ecology, and environmental ethics as to whether terraforming other worlds is an ethical endeavor.
Directed Panspermia is the deliberate transport of microorganisms into space to be used as introduced species on lifeless but habitable astronomical objects. It's been hypothesized that life on the Earth may have been seeded deliberately by other civilizations.
Genetic Engineering - Intelligent Design
W. M. Keck Observatory is a two-telescope astronomical observatory at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes feature 10 m (33 ft) primary mirrors, currently among the largest astronomical telescopes in use. Keck Interferometer was a ground-based instrument that combined the light from the twin Keck telescopes to create an instrument equal in power to an 85-meter telescope that could detect and study stars and planets beyond our solar system. Interferometer is an instrument in which the interference of two beams of light is employed to make precise measurements. Michelson Interferometer (wiki).
"Maybe the reason why solar systems are far apart is to avoid having other planets infected or invaded by beings from other planets, who for some reason, are not intelligent enough to avoid ignorantly killing things they don't yet understand, kind of like what humans are on planet earth right now."
Exoplanet List. There are 3,903 known exoplanets, or planets outside our solar system that orbit a star, as of December 1, 2018; only a small fraction of these are located in the vicinity of the Solar System. Within 10 parsecs (32.6 light-years), there are 56 exoplanets listed as confirmed by the NASA Exoplanet Archive. Among the over 400 known stars within 10 parsecs, 29 have been confirmed to have planetary systems; 51 stars in this range are visible to the naked eye, nine of which have planetary systems. Light Speed.
The closest exoplanet found is Proxima Centauri b, which was confirmed in 2016 to orbit Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our Solar System (4.25 ly). Voyager.
James Webb Space Telescope is a space telescope that will be the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope with a planned Launch date on March 30, 2021. The JWST will provide greatly improved resolution and sensitivity over the Hubble, and will enable a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology. One of its major goals is observing some of the most distant events and objects in the universe, such as the formation of the first galaxies. These types of targets are beyond the reach of current ground- and space-based instruments. Other goals include understanding the formation of stars and planets, and direct imaging of exoplanets and novas.
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer is a NASA infrared-wavelength astronomical space telescope launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation in February 2011 when its transmitter turned off. It was re-activated in 2013. WISE discovered thousands of minor planets and numerous star clusters. Its observations also supported the discovery of the first Y Dwarf and Earth trojan asteroid. Telescopes.
Kepler has already identified more than 1,000 Exoplanets since the beginning of its journey. We are not alone, or unique.
Allen Telescope Array is a radio telescope array dedicated to astronomical observations and a simultaneous search for extraterrestrial intelligence or SETI. The array is situated at the Hat Creek Radio Observatory in Shasta County, 290 miles (470 km) northeast of San Francisco, California. The project was originally developed as a joint effort between the SETI Institute and the Radio Astronomy Laboratory (RAL) at the University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley), with funds obtained from an initial US$11.5 million donation by the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation. The first phase of construction was completed and the ATA finally became operational on 11 October 2007 with 42 antennas (ATA-42), after Paul Allen (co-founder of Microsoft) had pledged an additional $13.5 million to support the construction of the first and second phases. Although overall Allen has contributed more than $30 million to the project, it has not succeeded in building the 350 6.1 m (20 ft) dishes originally conceived, and the project suffered an operational hiatus due to funding shortfalls between April and August 2011, after which observations resumed. Subsequently, UC Berkeley exited the project, completing divestment in April 2012. The facility is now managed by SRI International (formerly Stanford Research Institute), an independent, nonprofit research institute. As of 2016, the SETI Institute performs observations with the ATA between the hours of 6 pm and 6 am daily. In August 2014, the installation was threatened by a forest fire in the area and was briefly forced to shut down, but ultimately emerged largely unscathed.
Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence or SETI is a collective term for scientific searches for intelligent extraterrestrial life, for example, monitoring electromagnetic radiation for signs of transmissions from civilizations on other planets. Scientific investigation began shortly after the advent of radio in the early 1900s, and focused international efforts have been going on since the 1980s. In 2015, Stephen Hawking and Russian billionaire Yuri Milner announced a well-funded effort called Breakthrough Listen.
Fast Radio Burst is a transient radio pulse or electromagnetic radiation of a time length ranging from a fraction of a millisecond to a few milliseconds, caused by some high-energy astrophysical process not yet identified. While extremely energetic at their source, the strength of the signal reaching Earth has been described as 1,000 times less than from a mobile phone on the Moon. Although the exact origin and cause is uncertain, they are almost definitely extragalactic or originating outside the Milky Way galaxy. When the FRBs are polarized, it indicates that they are emitted from a source contained within an extremely powerful magnetic field. The origin of the FRBs has yet to be identified; proposals for their origin range from a rapidly rotating neutron star and a black hole, to extraterrestrial intelligence.
Space Travel - People from other Planets
"There are a lot of things that are Alien to us, especially things that are on our own planet, new things that we discover everyday. But there is no value in fantasizing about what kinds of alien life may exist, no matter how real you make your fantasy to be. I don't deny the possibilities of alien life, I just don't waste time fantasizing about alien life. There are a lot of things that are alien to us, like our own brain. So people should spend more time understanding their own brain and stop trying to understand a brain they never met, which is likely their own brain. Balance your priorities and responsibilities and choose your creative fantasy's well. You only have so much time to be productive, so try not to waste too much time. It's OK to Dream, just don't let you dream become an obsession or distract you from dreaming about things that are more important."
How do we know they're aliens? They might be just like us, except in a different body, which proves just how dangerous and illogical that racism is, or any kind of prejudice for that matter. To prejudge someone is like hating yourself for living, or worse, it's hating someone you don't even know, someone that could be a friend, someone who can benefit society."
"The more I learn about the Universe, the more I see an amazing design, an incredible machine. Whether this machine was created by God, or created by a life form that resembles a God, matters little to me, what matters most to me is learning about how this machine was dreamed up and created in the first place. I applaud whom ever the Creator is, for thou has created something that is truly amazing. Thank you, and, where can I get one of these universe makers?"
"Even if just some of the life here on earth were created by a highly intelligent life form from another planet, I assume they too believe in a God, and if so, then the existence of highly intelligent life form does not disprove God, it will only makes the belief in God more interesting."
"I know that we can create a Heaven right here on Earth. And the best part is that we don't have to leave our Heaven on Earth, because everyone is welcome in Heaven. So I'm staying right here with Mother Earth. And I'm not leaving until she gets consumed by the Sun and gets recycled back into the Universe. But of course someone will have to venture out into space and find us a new home in the Universe, but until then, our Mother Earth is the Greatest and the Most Beautiful Planet in the Universe, I can't even imagine another planet being more amazing then Earth. But if people from another planet would like to debate who's got the best planet in the universe, then I would have to correct my original statement to say that "Earth is one of the Two Best Planets in the Universe."
"Every time I find my self thinking about what life would be like outside the universe, like if life existed in some other way that was unknown to us, I have to immediately stop thinking about it, because it's impossible to even guess, the scenarios can go on forever like infinity, and I have only so much time to think about things, so I don't even bother, though it blows my mind just to think about it for only a few seconds, wow!"
"You're an interesting species, an interesting mix. You're capable of such beautiful dreams and such horrible nightmares. You feel so lost, so cut off, so alone, only you're not. See, in all our searching, the only thing we've found that makes the emptiness bearable is each other." Quote from the 1997 Film 'Contact'.
Sun - Star
 Our Sun is a
Yellow Dwarf
Star. It's about 92 million miles from
Earth. Earth gets to 147 million km close
to the sun and 152 million km max distance from the sun. Earths Sun is about
4.7 Billion years old and has about 5
Billion years left in its life, though we will have to leave earth way
before then. Our star is also a second or third generation star that was
formed from the remains of other stars.
Our Sun is a
Yellow Dwarf
Star. It's about 92 million miles from
Earth. Earth gets to 147 million km close
to the sun and 152 million km max distance from the sun. Earths Sun is about
4.7 Billion years old and has about 5
Billion years left in its life, though we will have to leave earth way
before then. Our star is also a second or third generation star that was
formed from the remains of other stars. New Star Formation - Elliptical Orbit - Eclipse - Telescopes - Star Types - Light - Star Death
A ray of light from our Sun takes about 8.3 minutes to reach us on earth and about 5.3 hours to reach Pluto, which depends on where pluto is in its orbit. Our sun is only 4.5 billion years old, so its light can only extend 4.5 billion light years away from us right now. But there's nothing to stop that light from expanding outwards forever, as time goes on. Photons.
Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, with internal convective motion that generates a magnetic field via a dynamo process. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. Its diameter is about 109 times that of Earth, and its mass is about 330,000 times that of Earth, accounting for about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. About three quarters of the Sun's mass consists of Hydrogen (~73%); the rest is mostly Helium (~25%), with much smaller quantities of heavier elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. Sun's core rotates four times faster than its surface. The core has a temperature of approximately 29 million degrees Fahrenheit, which is 15.7 million Kelvin. The sun's surface is "only" about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit, or 5,800 Kelvin. The Sun Emits X-Rays, UV, Light, IR and Radio Waves. In order to produce the energy we see it produce, the Sun needs to fuse 4 × 1038 protons into helium-4 every second. The result of that fusion is that 596 million tons of helium-4 are produced with each second that passes, while 4 million tons of mass are converted into pure energy via E = mc2. Over the lifetime of the entire Sun, it's lost approximately the mass of the planet Saturn due to the nuclear reactions in its core.
Solar Heat - Radiant Heat - Solar Flares - Radiation
 Star is
a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own
gravity. The nearest
star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye
from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed
luminous
points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth. A star shines
due to thermonuclear Fusion of
Hydrogen into
Helium in its core, releasing
energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer
space. Almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are
created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime, and for
some stars by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of
its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can
determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many
other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, its
luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the
main factor that determines its evolution and eventual fate. Other
characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over
its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement.
A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities
produces a plot known as a
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram).
Plotting a particular star on that diagram allows the age and evolutionary
state of that star to be determined. A star's life begins with the
gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily
of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. When
the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily
converted into helium through
nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the
process. The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the
core through a combination of radiative and convective heat transfer
processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing
further under its own gravity. A star with mass greater than 0.4 times the
Sun's will expand to become a red giant when the hydrogen fuel in its core
is exhausted. In some cases, it will fuse heavier elements at the core or
in shells around the core. As the star expands it throws a part of its
mass, enriched with those heavier elements, into the interstellar
environment, to be recycled later as new stars. Meanwhile, the core
becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or if it is
sufficiently massive, a black hole.
Star is
a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own
gravity. The nearest
star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye
from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed
luminous
points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth. A star shines
due to thermonuclear Fusion of
Hydrogen into
Helium in its core, releasing
energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer
space. Almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are
created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime, and for
some stars by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of
its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can
determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many
other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, its
luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the
main factor that determines its evolution and eventual fate. Other
characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over
its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement.
A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities
produces a plot known as a
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram).
Plotting a particular star on that diagram allows the age and evolutionary
state of that star to be determined. A star's life begins with the
gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily
of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. When
the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily
converted into helium through
nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the
process. The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the
core through a combination of radiative and convective heat transfer
processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing
further under its own gravity. A star with mass greater than 0.4 times the
Sun's will expand to become a red giant when the hydrogen fuel in its core
is exhausted. In some cases, it will fuse heavier elements at the core or
in shells around the core. As the star expands it throws a part of its
mass, enriched with those heavier elements, into the interstellar
environment, to be recycled later as new stars. Meanwhile, the core
becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or if it is
sufficiently massive, a black hole.Solar Mass is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately 2×1030 kg. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes.
Stellar is relating to a star or stars or resembling or emanating from stars. Seeing the Same Stars.
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When the direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat. When it is blocked by clouds or reflects off other objects, it is experienced as diffused light. A photon starting at the center of the Sun and changing direction every time it encounters a charged particle would take between 10,000 and 170,000 years to get to the surface. 149 xenon short-arc lamps spotlights equivalent of 10,000 times the amount of solar radiation (Synlight, Juelich).
Scientists help discover the highest-energy light coming from the sun. Although the high-energy light doesn't reach the Earth's surface, these gamma rays create telltale signatures that were detected by Nisa and her colleagues working with the High-Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory, or HAWC.
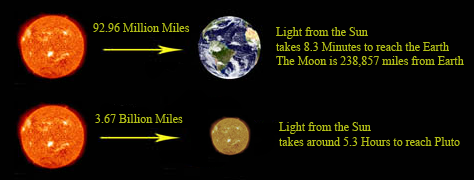 Films and Videos about Stars:
Cosmic Journeys - Solar Super Storms (youtube - 7/28/15 - 44:37)
Films and Videos about Stars:
Cosmic Journeys - Solar Super Storms (youtube - 7/28/15 - 44:37)
Time-Lapse Video of Milky Way (youtube)
Sun Video (youtube)
NASA | 5 Year Time-lapse of the Sun (youtube)
Three Years of Sun in Three Minutes (youtube)
NASA | Solar Dynamics Observatory SDO: Year 5 (youtube)
Sun Dance [ 4K ] (youtube)
A spacecraft has 'touched' the sun for the first time. On April 28, 2021, NASA's Parker Solar Probe reached the sun's extended solar atmosphere, known as the corona, and spent five hours there. The spacecraft is the first to enter the outer boundaries of our sun. NASA Solar Probe Finally "Touches The Sun", Here's What It Found. (youtube).
Solar Analog are stars that are particularly similar to the Sun. Planets like Ours.
Our Sun is small when compared to other Stars. Star Size Comparisons (youtube)
Universe's Most Massive known Star. By harnessing the capabilities of the 8.1-meter Gemini South telescope in Chile, which is part of the International Gemini Observatory operated by NSF's NOIRLab, astronomers have obtained the sharpest image ever of the star R136a1, the most massive known star in the Universe, a mass somewhere between 250 to 320 times the mass of the Sun. The new Zorro observations, however, indicate that this giant star may be only 170 to 230 times the mass of the Sun. Even with this lower estimate, R136a1 still qualifies as the most massive known star. Astronomers have yet to fully understand how the most massive stars -- those more than 100 times the mass of the Sun -- are formed. Giant stars also live fast and die young, burning through their fuel reserves in only a few million years. In comparison, our Sun is less than halfway through its 10 billion year lifespan. The combination of densely packed stars, relatively short lifetimes, and vast astronomical distances makes distinguishing individual massive stars in clusters a daunting technical challenge.
Sun consists of Hydrogen (about 74% of its Mass, or 92% of its Volume), Helium (about 24% of mass, 7% of volume), and trace quantities of other elements, including Iron, Nickel, Oxygen, Silicon, Sulfur, Magnesium, Carbon, Neon, Calcium, and Chromium.
Our Sun takes One Month to Rotate, and it rotates counterclockwise, depending how you look at it, looking up or looking down.
SDO: Year 6 Ultra-HD (youtube) - Simulation of the Sun's Magnetic Field (youtube)
Each Second, more than 4 million tonnes of matter are converted into energy within the Sun's core. The Suns surface temperature is 6,000 C or 10,832 F. Diameter 1,392,000 km just over 109 times the diameter of the Earth, that means that 1,300,000 Earths could fit in the Sun. The Sun orbits the Milky Way Galaxy at a distance of approximately 24,000–26,000 light years from the Galactic Center. The Sun is moving 486,000 miles per hour and takes 240 million years to complete one orbit around our Galaxy. The Sun rotates one complete turn every 34 days. The Sun's magnetic field reverses polarity, "flips" every 11 years. The Earth takes 24 Hours to rotate and spins 1,000 miles per hour, and the earth travels nearly 67,000 miles per hour around the sun. The sun is 99.8 percent of all the mass in the solar system. - Atoms.
Sun's coldest region stores secret to heating million-degree corona. Researchers have unveiled the discovery of intense wave energy from a relatively cool, dark and strongly magnetized plasma region on the Sun, capable of traversing the solar atmosphere and maintaining temperatures of a million degrees Kelvin inside the corona. Researchers say the finding is the latest key to unraveling a host of related mysteries pertaining to Earth's nearest star.
The world's largest turbulence simulation unmasks the flow of energy in astrophysical plasmas. Researchers uncover the long-hidden process that helps explain why the Sun's corona can be vastly hotter than the solar surface that emits it. The hidden ingredient is a process called magnetic reconnection that separates and violently reconnects magnetic fields in plasma, the soup of electrons and atomic nuclei that forms the solar atmosphere. Dong's simulation revealed how rapid reconnection of the magnetic field lines turns the large-scale turbulent energy into small-sale internal energy. As a consequence the turbulent energy is efficiently converted to thermal energy at small scales, thus superheating the corona.
Long-period oscillations control the Sun's differential rotation. The interior of the Sun does not rotate at the same rate at all latitudes. The physical origin of this differential rotation is not fully understood. It turns out, long-period solar oscillations discovered in 2021 play a crucial role in controlling the Sun's rotational pattern. The long-period oscillations are analogous to the baroclinically unstable waves in Earth's atmosphere that shape the weather. In the Sun, these oscillations carry heat from the slightly hotter poles to the slightly cooler equator.
Solar Core is considered to extend from the center to about 0.2 to 0.25 of solar radius. It is the hottest part of the Sun and of the Solar System. It has a density of 150 g/cm³ (150 times the density of liquid water) at the center, and a temperature of 15 million degrees Celsius. The core is made of hot, dense gas in the plasmic state (ions and electrons), at a pressure estimated at 265 billion bar (3.84 trillion psi or 26.5 petapascals (PPa)) at the center. Due to fusion, the composition of the solar plasma drops from 68-70% hydrogen by mass at the outer core, to 33% hydrogen at the core/Sun center. The core inside 0.20 of the solar radius, contains 34% of the Sun's mass, but only 0.8% of the Sun's volume. Inside 0.24 solar radius, the core generates 99% of the fusion power of the Sun. There are two distinct reactions in which four hydrogen nuclei may eventually result in one helium nucleus: the proton-proton chain reaction – which is responsible for most of the Sun's released energy – and the CNO cycle. Proton-proton chain reaction is one of the two (known) sets of fusion reactions by which stars convert hydrogen to helium.
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons, primarily protons and neutrons.
Big Bang - Conservation of Mass - Fusion - Super Nova's
Stellar Nucleosynthesis is the process by which the natural abundances of the chemical elements within stars change due to nuclear fusion reactions in the cores and their overlying mantles. Stars are said to evolve (age) with changes in the abundances of the elements within. Core fusion increases the atomic weight of elements and reduces the number of particles, which would lead to a pressure loss except that gravitation leads to contraction, an increase of temperature, and a balance of forces. A star loses most of its mass when it is ejected late in the star's stellar lifetimes, thereby increasing the abundance of elements heavier than helium in the interstellar medium.
Stars grow old. All stars with initial masses up to about eight times that of our Sun, will eventually become red giants in the later stages of their lives. They start to cool down and lose a large amount of their mass in a steady, dense wind that streams outwards from the star. As any star ages, part of its mass evaporates into space, while the remaining mass is squeezed tighter and tighter at the core. Eventually, as the outside envelope continues to expand and evaporate, the core of the star will cool, and the star will become a white dwarf. Massive stars become supergiant and later undergo supernova explosions. If they have a large mass during this stage, they can develop into a black hole, or if they have a smaller mass, they can develop into a neutron star. The more mass a star has, the faster it will convert its hydrogen fuel into helium. It turns out that high mass stars, even though they have more fuel, use up that fuel much more quickly than low mass stars can. Low mass stars have much longer lives than high mass stars. Short people live longer than tall people.
Synthesis of the Elements in Stars - Periodic Table - Carbon - Solar System
The science of spin: Asteroseismologists confirm older stars rotate faster than expected. All stars, like the Sun, are born spinning. As they grow older, their spin slows down due to magnetic winds in a process called 'magnetic braking'. Research published in 2016 by scientists at Carnegie Observatories delivered the first hints that stars at a similar stage of life as the Sun were spinning faster than magnetic braking theories predicted.
One of the fastest-spinning stars in the Universe. New research in our Milky Way has revealed a neutron star that rotates around its axis at an extremely high speed. It spins 716 times per second, making it one of the fastest-spinning objects ever observed. It is a small but extremely massive and fast-spinning object -- a neutron star, part of a so-called 'X-ray binary star system' named '4U 1820-30'. It's found in the Sagittarius constellation towards the centre of our galaxy.
Nearby star could help explain why our Sun didn’t have sunspots for 70 years. Astronomers identified a nearby star whose sunspot cycles appear to have stopped. Studying this star might help explain the unusual period from the mid 1600s to the early 1700s when our Sun paused its sunspot cycles.
Celestial Body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe.
Pleiades, also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance of about 444 light years, it is among the nearest star clusters to Earth. In Greek mythology it is the 7 daughters of Atlas and half-sisters of the Hyades; placed among the stars to save them from the pursuit of Orion.
Solar Path - Sunrise and Sunset Times
James Webb Telescope catches glimpse of possible first-ever 'dark stars'. Stars powered with dark matter still need proving but could reveal clues about the nature of one of the universe's great mysteries. The three candidate dark stars (JADES-GS-z13-0, JADES-GS-z12-0, and JADES-GS-z11-0) were originally identified as galaxies in December 2022 by the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES). Using spectroscopic analysis, the JADES team confirmed the objects were observed at times ranging from about 320 million to 400 million years after the Big Bang, making them some of the earliest objects ever seen
When the stars align: Astronomers find answers to mysterious action of ghost stars in our Galaxy. Scientists have found a source for the mysterious alignment of stars near the Galactic Center. Planetary nebulae are clouds of gas that are expelled by stars at the end of their lives -- the Sun will also form one about five billion years from now. The ejected clouds are 'ghosts' of their dying stars and they form beautiful structures such as an hourglass or butterfly shape.
Dyson Sphere is a hypothetical megastructure that completely encompasses a star and captures most or all of its power output.
Star Types
Our Sun is a Yellow Dwarf, or G Dwarf Star known as a G-Type Main-Sequence Star (luminosity class V) of spectral type G. Such a star has about 0.8 to 1.2 solar masses and surface temperature of between 5,300 and 6,000 K. Each second, our Sun fuses approximately 600 million tons of hydrogen to helium, converting about 4 million tons of matter to energy.
70% of Stars are Red Dwarfs which are small and relatively cool stars, of either K or M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4,000 K. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun, but because of their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs cannot be easily observed. From Earth, not one is visible to the naked eye. Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun, is a red dwarf (Type M5, apparent magnitude 11.05), as are twenty of the next thirty nearest stars. According to some estimates, red dwarfs make up three-quarters of the stars in the Milky Way. New Star Formation.
Most Stars in the Universe are M-Stars, Small Red Dwarfs. Red Dwarf Stars have masses from about 0.08 to 0.6 times that of the Sun. Objects smaller than red dwarf stars are called Brown Dwarfs and do not shine through the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen. Lighter stars are much more plentiful than heavier stars, and red dwarfs are thus the most numerous type of star, about 70%. 1 in 10 stars have planets.?
Habitability of Red Dwarf Systems - Planet transiting a nearby Low-Mass Star
Red Giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses (M☉)) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around 5,000 K [K] (4,700 °C; 8,500 °F) or lower. The appearance of the red giant is from yellow-white to reddish-orange, including the spectral types K and M, sometimes G, but also class S stars and most carbon stars.
Pulsar is a highly magnetized, rotating neutron star or white dwarf, that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (much like the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense, and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. Centrifugal Mechanism of Acceleration of astroparticles to relativistic energies might take place in rotating astrophysical objects. It is strongly believed that active galactic nuclei and pulsars have rotating magnetospheres, therefore, they potentially can drive charged particles to high and ultra-high energies. It is a proposed explanation for ultra-high-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) and extreme-energy cosmic rays (EECRs) exceeding the Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin limit. Centrifuge.
Neutron Star is the collapsed core of a large star (10–29 solar masses). Neutron stars are the smallest and densest stars known to exist. Though neutron stars typically have a radius on the order of 10 kilometres (6.2 mi), they can have masses of about twice that of the Sun. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past the white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons, which are subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons. They are supported against further collapse by neutron degeneracy pressure, a phenomenon described by the Pauli exclusion principle. If the remnant has too great a density, something which occurs in excess of an upper limit of the size of neutron stars at 2–3 solar masses, it will continue collapsing to form a black hole. Astronomers have discovered the most massive neutron star to date. A rapidly spinning pulsar approximately 4,600 light-years from Earth. This record-breaking object is teetering on the edge of existence, approaching the theoretical maximum mass possible for a neutron star. A team of astronomers using the National Science Foundation's (NSF) Green Bank Telescope (GBT) has brought us closer to finding the answers. Members of the NANOGrav Physics Frontiers Center, discovered that a rapidly rotating millisecond pulsar, called J0740+6620, is the most massive neutron star ever measured, packing 2.17 times the mass of our Sun into a sphere only 30 kilometers across. This measurement approaches the limits of how massive and compact a single object can become without crushing itself down into a black hole. Recent work involving gravitational waves observed from colliding neutron stars by LIGO suggests that 2.17 solar masses might be very near that limit. Pulsars get their name because of the twin beams of radio waves they emit from their magnetic poles. These beams sweep across space in a lighthouse-like fashion. Some rotate hundreds of times each second. Since pulsars spin with such phenomenal speed and regularity, astronomers can use them as the cosmic equivalent of atomic clocks. Such precise timekeeping helps astronomers study the nature of spacetime, measure the masses of stellar objects, and improve their understanding of general relativity.
Magnetar is a type of neutron star believed to have an extremely powerful magnetic field (~109 to 1011 T, ~1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays. Like other neutron stars, magnetars are around 20 kilometres (12 mi) in diameter and have a mass 1–2 times that of the Sun. The density of the interior of a magnetar is such that a tablespoon of its substance would have a mass of over 100 million tons. Magnetars are differentiated from other neutron stars by having even stronger magnetic fields, and by rotating comparatively more quickly. Most neutron stars rotate once every one to ten seconds, whereas magnetars rotate once in less than one second. A magnetar's magnetic field gives rise to very strong and characteristic bursts of X-rays and gamma rays. The active life of a magnetar is short. Their strong magnetic fields decay after about 10,000 years, after which activity and strong X-ray emission cease. Given the number of magnetars observable today, one estimate puts the number of inactive magnetars in the Milky Way at 30 million or more. Magnetars are the strongest magnets in the Universe. These super-dense dead stars with ultra-strong magnetic fields can be found all over our galaxy but astronomers don't know exactly how they form.
Binary Pulsar is a pulsar with a binary companion, often a white dwarf or neutron star.
Binary Star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common barycenter. Systems of two or more stars are called multiple star systems. It's estimated that approximately one third of the star systems in the Milky Way are binary or multiple, with the remaining two thirds being single stars. Sirius is a binary star and the brightest star in the night sky. Most stars born as wide binaries with weak and wildly disorganized magnetic field very near a newly emerging protostar. The Sun at a very early stage in their formation have traces of methyl isocyanate -- a chemical building block of life.
Nemesis is a hypothetical red dwarf or brown dwarf, originally postulated in 1984 to be orbiting the Sun at a distance of about 95,000 AU (1.5 light-years), somewhat beyond the Oort cloud, to explain a perceived cycle of mass extinctions in the geological record, which seem to occur more often at intervals of 26 million years. As of 2012, more than 1800 brown dwarfs have been identified. There are actually fewer brown dwarfs in our cosmic neighborhood than previously thought. Rather than one star for every brown dwarf, there may be as many as six stars for every brown dwarf. The majority of solar-type stars are single. The previous idea stated half or perhaps most stellar systems were binary, trinary, or multiple-star systems associated with clusters of stars, rather than the single-star systems that tend to be seen most often. Precession.
O-Type Star is a hot, blue-white star of spectral type O in the Yerkes classification system employed by astronomers. They have temperatures in excess of 30,000 Kelvin (K).
Brown Dwarf are substellar objects that occupy the mass range between the heaviest gas giants and the lightest stars.
Red Dwarf is the smallest and coolest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun, but because of their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs cannot be easily observed. From Earth, not one that fits the stricter definitions of a red dwarf is visible to the naked eye. Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun, is a red dwarf, as are fifty of the sixty nearest stars. According to some estimates, red dwarfs make up three-quarters of the stars in the Milky Way.
White Dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: in an Earth-sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place in a white dwarf; what light it radiates is from its residual heat. Star Death.
Black Dwarf is a theoretical stellar remnant, specifically a white dwarf that has cooled sufficiently to no longer emit significant heat or light. Because the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to significantly exceed the current age of the universe (13.79 billion years), no black dwarfs are expected to exist in the universe at the present time. The temperature of the coolest white dwarfs is one observational limit on the universe's age.
Blue Supergiant Star are hot luminous stars, referred to scientifically as OB supergiants. They are larger than the Sun but smaller than a red supergiant, with surface temperatures of 10,000–50,000 K and luminosities from about 10,000 to a million times the Sun. Blue supergiants are supergiant stars (class I) of spectral type O. They are extremely hot and bright, with surface temperatures of between 20,000 - 50,000 degrees Celsius. The best known example is Rigel, the brightest star in the constellation of Orion.
Compact Star is used to refer collectively to white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. It would grow to include exotic stars if such hypothetical dense bodies are confirmed. Most compact stars are the endpoints of stellar evolution and are thus often referred to as stellar remnants, the form of the remnant depending primarily on the mass of the star when it formed. These objects are all small in volume for their mass, giving them a very high density. The term compact star is often used when the exact nature of the star is not known, but evidence suggests that it is very massive and has a small radius, thus implying one of the above-mentioned categories. A compact star that is not a black hole may be called a degenerate star.
Exotic Star s a hypothetical compact star composed of something other than electrons, protons, neutrons, and muons; and balanced against gravitational collapse by degeneracy pressure or other quantum properties. These include quark stars (composed of quarks) and perhaps strange stars (based upon strange quark matter, a condensate of up, down and strange quarks), as well as speculative preon stars (composed of preons, a hypothetical particle and "building block" of quarks, if quarks prove to be decomposable into component sub-particles). Of the various types of exotic star proposed, the most well evidenced and understood is the quark star.
Substellar Object sometimes called a substar, is an astronomical object whose mass is smaller than the smallest mass at which hydrogen fusion can be sustained.
Stellar Classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics.
Main Sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass, but also based upon its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydrostatic equilibrium, where outward thermal pressure from the hot core is balanced by the inward pressure of gravitational collapse from the overlying layers. The strong dependence of the rate of energy generation on temperature and pressure helps to sustain this balance. Energy generated at the core makes its way to the surface and is radiated away at the photosphere. The energy is carried by either radiation or convection, with the latter occurring in regions with steeper temperature gradients, higher opacity or both. The main sequence is sometimes divided into upper and lower parts, based on the dominant process that a star uses to generate energy. Stars below about 1.5 times the mass of the Sun (1.5 M☉) primarily fuse hydrogen atoms together in a series of stages to form helium, a sequence called the proton–proton chain. Above this mass, in the upper main sequence, the nuclear fusion process mainly uses atoms of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen as intermediaries in the CNO cycle that produces helium from hydrogen atoms. Main-sequence stars with more than two solar masses undergo convection in their core regions, which acts to stir up the newly created helium and maintain the proportion of fuel needed for fusion to occur. Below this mass, stars have cores that are entirely radiative with convective zones near the surface. With decreasing stellar mass, the proportion of the star forming a convective envelope steadily increases. Main-sequence stars below 0.4 M☉ undergo convection throughout their mass. When core convection does not occur, a helium-rich core develops surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. In general, the more massive a star is, the shorter its lifespan on the main sequence. After the hydrogen fuel at the core has been consumed, the star evolves away from the main sequence on the HR diagram, into a supergiant, red giant, or directly to a white dwarf.
Scientists discover the highest energy gamma-rays ever from a pulsar. H.E.S.S. observatory records 20 tera-electronvolts photons from the Vela pulsar. Scientists have detected the highest energy gamma rays ever from a dead star called a pulsar. The energy of these gamma rays clocked in at 20 tera-electronvolts, or about ten trillion times the energy of visible light. This observation is hard to reconcile with the theory of the production of such pulsed gamma rays, as the international team reports. Pulsars are the left-over corpses of stars that spectacularly exploded in a supernova. The explosions leave behind a tiny, dead star with a diameter of just some 20 kilometres, rotating extremely fast and endowed with an enormous magnetic field. "These dead stars are almost entirely made up of neutrons and are incredibly dense: a teaspoon of their material has a mass of more than five billion tonnes. Pulsars emit rotating beams of electromagnetic radiation, somewhat like cosmic lighthouses. If their beam sweeps across our solar system, we see flashes of radiation at regular time intervals. These flashes, also called pulses of radiation, can be searched for in different energy bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Scientists think that the source of this radiation are fast electrons produced and accelerated in the pulsar's magnetosphere, while traveling towards its periphery. The magnetosphere is made up of plasma and electromagnetic fields that surround and co-rotate with the star. On their outward journey, the electrons acquire energy and release it in the form of the observed radiation beams. The Vela pulsar, located in the Southern sky in the constellation Vela (sail of the ship), is the brightest pulsar in the radio band of the electromagnetic spectrum and the brightest persistent source of cosmic gamma rays in the giga-electronvolts (GeV) range. It rotates about eleven times per second. However, above a few GeV, its radiation ends abruptly, presumably because the electrons reach the end of the pulsar's magnetosphere and escape from it.
GRB 221009A also known as Swift J1913.1+1946, was an extraordinarily bright and long-lasting gamma-ray burst jointly discovered by the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory and the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope on October 9, 2022. The gamma-ray burst was around seven minutes long, but was detectable for more than ten hours following initial detection. Despite being around two billion light-years away, it was powerful enough to affect Earth's atmosphere, having the strongest effect ever recorded by a gamma-ray burst on the planet. The peak luminosity of GRB 221009A was measured by Konus-Wind to be ~ 2.1 × 1047 J/s and by Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor to be ~ 1.0 × 1047 J/s over the 1.024s interval. A burst as energetic and as close to Earth as 221009A is thought to be a once-in-10,000-year event. It was the brightest and most energetic gamma-ray burst ever recorded, with some dubbing it the "BOAT", or Brightest Of All Time.
Brightest Gamma-Ray Burst of all time came from the collapse of a massive star. Observations show no sign of heavy elements. In 2022, astronomers discovered the brightest gamma-ray burst or GRB of all time. Now, astronomers confirm that a 'normal' supernova, the telltale sign of a stellar collapse, accompanied the GRB. The team also looked for signatures of heavy elements like gold and platinum in the supernova. They found no evidence of such elements, deepening the mystery of their origins.
PSR J1748-2446ad is the fastest-spinning pulsar known, at 716 Hz, or 716 times per second. This pulsar was discovered by Jason W. T. Hessels of McGill University on November 10, 2004 and confirmed on January 8, 2005. If the neutron star is assumed to contain less than two times the mass of the Sun, within the typical range of neutron stars, its radius is constrained to be less than 16 km. At its equator it is spinning at approximately 24% of the speed of light, or over 70,000 km per second. The pulsar is located in a globular cluster of stars called Terzan 5, located approximately 18,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Sagittarius. It is part of a binary system and undergoes regular eclipses with an eclipse magnitude of about 40%. Its orbit is highly circular with a 26-hour period. The other object is at least 0.14 solar masses, with a radius of 5–6 solar radii. Hessels et al. state that the companion may be a "bloated main-sequence star, possibly still filling its Roche Lobe". Hessels et al. go on to speculate that gravitational radiation from the pulsar might be detectable by LIGO.
When Stars Collide or Stellar Collision is the coming together of two stars caused by stellar dynamics within a star cluster, or by the orbital decay of a binary star due to stellar mass loss or gravitational radiation, or by other mechanisms not yet well understood. Astronomers predict that events of this type occur in the globular clusters of our galaxy about once every 10,000 years. On 2 September 2008 scientists first observed a stellar merger in Scorpius (named V1309 Scorpii), though it was not known to be the result of a stellar merger at the time. Any stars in the universe can collide, whether they are "alive", meaning fusion is still active in the star, or "dead", with fusion no longer taking place. White dwarf stars, neutron stars, black holes, main sequence stars, giant stars, and supergiants are very different in type, mass, temperature, and radius, and so react differently. A gravitational wave event that occurred on 25 August 2017, GW170817, was reported on 16 October 2017 to be associated with the merger of two neutron stars in a distant galaxy, the first such merger to be observed via gravitational radiation. About half of all the stars in the sky are part of binary systems, with two stars orbiting each other. Some binary stars orbit each other so closely that they share the same atmosphere, giving the system a peanut shape. While most contact binary stars are stable, a few have become unstable and have merged in the past for reasons not well understood.
Neutron Star Merger is when two neutron stars fall into mutual orbit, they gradually spiral inward due to gravitational radiation. When they finally meet, their merger leads to the formation of either a more massive neutron star, or—if the mass of the remnant exceeds the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit—a black hole. The merger can create a magnetic field that is trillions of times stronger than that of Earth in a matter of one or two milliseconds. These events are believed to create short gamma-ray bursts. Neutrons.
Cepheid Variable is a type of star that pulsates radially, varying in both diameter and temperature and producing changes in brightness with a well-defined stable period and amplitude. A strong direct relationship between a Cepheid variable's luminosity and pulsation period established Cepheids as important indicators of cosmic benchmarks for scaling galactic and extragalactic distances.
Metal-poor stars are more life-friendly. A star's chemical composition strongly influences the ultraviolet radiation it emits into space and thus the conditions for the emergence of life in its neighborhood. Stars that contain comparatively large amounts of heavy elements provide less favourable conditions for the emergence of complex life than metal-poor stars.
The light from our nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is 4 years old. Time passes slower the faster you move. If you flew to the Star Sirius at 99% of the speed of light, then flew back again, the people you left behind on Earth would have aged more than 17 years. But you would have aged less than two and a half years.
Methuselah Star HD 140283 is a metal-poor subgiant star about 190 light years away from the Earth in the constellation Libra, near the boundary with Ophiuchus in the Milky Way Galaxy. Its apparent magnitude is 7.205, so it can be seen with binoculars. estimate an age for the star of 14.46 ± 0.8 billion years. However, more recent models of its stellar evolution have suggested revision of the star's age to 13.7 billion years or 12 billion years.
Suns Magnetic Field
Heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma "blown" out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have actively explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The overall shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun, and is not perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories. The Sun protects earth from deep space radiation, but the sun can also hurt earth.
Oort Cloud - Kuiper Belt - Galaxy Magnetic Field - Human Body Magnetic Field - Earth Magnetic Field - Magnetoception
Heliospheric Current Sheet is the surface within the Solar System where the polarity of the Sun's magnetic field changes from north to south.
The Suns Magnetic Field is about to Flip. Approximately every eleven years the polarity of the Sun's magnetic field is reversed, with solar activity peaking with the same frequency. This manifests itself in an increase in sunspots -- dark patches on the Sun's surface which originate from strongly concentrated magnetic fields. Earth Magnetic Field is Flipping.
ScienceCasts: The Sun's Magnetic Field is About to Flip (youtube)
Stellar Magnetic Field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magnetic field exerts a force on the plasma, effectively increasing the pressure without a comparable gain in density. As a result, the magnetized region rises relative to the remainder of the plasma, until it reaches the star's photosphere. This creates starspots on the surface, and the related phenomenon of coronal loops. Magnetic Field of the Sun.
Dynamo Theory proposes a mechanism by which a celestial body such as Earth or a star generates a magnetic field. The dynamo theory describes the process through which a rotating, convecting, and electrically conducting fluid can maintain a magnetic field over astronomical time scales. A dynamo is thought to be the source of the Earth's magnetic field, as well as the magnetic fields of other planets. Electromagnetism.
Dresden High Magnetic Field Laboratory - Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf
NASA’s Cassini, Voyager Missions Suggest New Picture of Sun’s Interaction with Galaxy
Vortex- Torus - Sun Trek - Solar Center
Mystery of Solar Cycle illuminated. In the convection zone of the star, the plasma currents make a huge turnover that lasts about 22 years. The sun's convection zone plays a key role in the generation and evolution of the Sun's magnetic field. Analyzing data sets spanning more than 20 years, researchers have obtained the most comprehensive picture of the north-south flow of plasma in the convection zone ever. The flow goes around the convection zone in each hemisphere in about 22 years.
Analemma is a diagram showing the deviation of the Sun from its mean motion in the sky, as viewed from a fixed location on the Earth. Due to the Earth's axial tilt and orbital eccentricity, the Sun will not be in the same position in the sky at the same time every day. The north–south component of the analemma is the Sun's declination, and the east–west component is the equation of time. This diagram has the form of a slender figure-eight, and can often be found on globes of the Earth.
Solar Eruptions - Solar Flares - Nova's
Solar Wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. This plasma consists of mostly electrons, protons and alpha particles with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV; embedded in the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona and magnetic, electrical and electromagnetic phenomena within it. Birkeland Current - Aurora - Electro-Magnetic Pulse.
Space Weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Space weather is distinct from but conceptually related to the terrestrial weather of the atmosphere of Earth (troposphere and stratosphere). The term space weather was first used in the 1950s and came into common usage in the 1990s. Plasma - Solar Radiance - Solar Irradiance.
Solar Storm of 1859 (wiki) - Solar Activity - September 6, 2017 - Space Weather
Geomagnetic Storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.
Solar Maximum is a normal period of greatest solar activity in the 11 year solar cycle of the Sun. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspots appear and the sun's irradiance output grows by about 0.07%. The increased energy output of solar maxima can impact Earth's global climate and recent studies have shown some correlation with regional weather patterns.
Solar Cycle or solar magnetic activity cycle is the nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity (including changes in the levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material) and appearance (changes in the number and size of sunspots, flares, and other manifestations).
The Sun has become 30% brighter in the last four and a half billion years and will continue to increase in brightness by 1% every 100 million years.
Coronal Mass Ejection is a significant release of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the solar corona. They often follow solar flares and are normally present during a solar prominence eruption. The plasma is released into the solar wind, and can be observed in coronagraph imagery. Coronal mass ejections are often associated with other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established. CMEs most often originate from active regions on the Sun's surface, such as groupings of sunspots associated with frequent flares. Near solar maxima, the Sun produces about three CMEs every day, whereas near solar minima, there is about one CME every five days. The largest recorded geomagnetic perturbation, resulting presumably from a CME hitting the Earth's magnetosphere, was the solar storm of 1859 (the Carrington Event), which took down parts of the recently created US telegraph network, starting fires and shocking some telegraph operators.
Solar Flare Video or Coronal Mass Ejection, by the Solar Dynamics Observatory's AIA instrument. SDO collected one frame every 12 seconds, and the movie plays at 30 frames per second, so each second in this video corresponds to 6 minutes of real time. The video covers 12:30 a.m. EDT to 10:00 p.m. EDT on July 19, 2012.
Solar Flare is a sudden flash of increased brightness on the Sun, usually observed near its surface and in close proximity to a sunspot group. Powerful flares are often, but not always, accompanied by a coronal mass ejection. Even the most powerful flares are barely detectable in the total solar irradiance (the "solar constant"). Solar flares occur in a power-law spectrum of magnitudes; an energy release of typically 1020 joules of energy suffices to produce a clearly observable event, while a major event can emit up to 1025 joules. Flares are closely associated with the ejection of plasmas and particles through the Sun's corona into outer space; flares also copiously emit radio waves. If the ejection is in the direction of the Earth, particles associated with this disturbance can penetrate into the upper atmosphere (the ionosphere) and cause bright auroras, and may even disrupt long range radio communication. It usually takes days for the solar plasma ejecta to reach Earth. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term stellar flare applies. High-energy particles, which may be relativistic, can arrive almost simultaneously with the electromagnetic radiations. Superflares once per century. More often than previously thought, sun-like stars hurl huge amounts of radiation into space: The Sun, too, is capable of such outbursts. Such superflares release more energy than a trillion hydrogen bombs and make all previously recorded solar flares pale in comparison.
Heliosphere
Polarization the ability of waves to oscillate in more than one direction; in particular polarization of light, responsible for example for the glare-reducing effect of polarized sunglasses.
Corona is an aura of plasma that surrounds the sun and other stars. The Sun's corona extends millions of kilometres into space and is most easily seen during a total solar eclipse, but it is also observable with a coronagraph. The sun's corona is much hotter (by a factor from 150 to 450) than the visible surface of the Sun: the photosphere's average temperature is 5800 kelvin compared to the corona's one to three million kelvins. The corona is 10−12 times as dense as the photosphere, and so produces about one-millionth as much visible light. The corona is separated from the photosphere by the relatively shallow chromosphere. The exact mechanism by which the corona is heated is still the subject of some debate, but likely possibilities include induction by the Sun's magnetic field and magnetohydrodynamic waves from below. The outer edges of the Sun's corona are constantly being transported away due to open magnetic flux and hence generating the solar wind.
Solar Radius is a unit of distance used to express the size of stars in astronomy. The solar radius is usually defined as the radius to the layer in the Sun's photosphere where the optical depth equals 2/3:
Sunshine Recorder is a device that records the amount of sunshine at a given location. The results provide information about the weather and climate as well as the temperature of a geographical area. This information is useful in meteorology, science, agriculture, tourism, and other fields. It has also been called a heliograph.
Candela is the base unit of luminous intensity in the International System of Units (SI); that is, luminous power per unit solid angle emitted by a point light source in a particular direction. Luminous intensity is analogous to radiant intensity, but instead of simply adding up the contributions of every wavelength of light in the source's spectrum, the contribution of each wavelength is weighted by the standard luminosity function (a model of the sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths). A common wax candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela. If emission in some directions is blocked by an opaque barrier, the emission would still be approximately one candela in the directions that are not obscured.
Luminous Intensity s a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye. The SI unit of luminous intensity is the candela (cd), an SI base unit. Photometry deals with the measurement of visible light as perceived by human eyes. The human eye can only see light in the visible spectrum and has different sensitivities to light of different wavelengths within the spectrum. When adapted for bright conditions (photopic vision), the eye is most sensitive to greenish-yellow light at 555 nm. Light with the same radiant intensity at other wavelengths has a lower luminous intensity. The curve which measures the response of the human eye to light is a defined standard, known as the luminosity function. This curve, denoted V(λ) or y ( λ ) (\lambda ), is based on an average of widely differing experimental data from scientists using different measurement techniques. For instance, the measured responses of the eye to violet light varied by a factor of ten.
Luminosity is the total amount of energy emitted by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object per unit time. It is related to the brightness, which is the luminosity of an object in a given spectral region. In SI units luminosity is measured in joules per second or watts. Values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the luminosity of the Sun. Luminosity can also be given in terms of magnitude: the absolute bolometric magnitude (Mbol) of an object is a logarithmic measure of its total energy emission rate.
Pyranometer is a type of actinometer used for measuring solar irradiance on a planar surface and it is designed to measure the solar radiation flux density (W/m2) from the hemisphere above within a wavelength range 0.3 μm to 3 μm.
Pyrheliometer is an instrument for measurement of direct beam solar irradiance. Sunlight enters the instrument through a window and is directed onto a thermopile which converts heat to an electrical signal that can be recorded. The signal voltage is converted via a formula to measure watts per square metre. It is used with a solar tracking system to keep the instrument aimed at the sun. A pyrheliometer is often used in the same setup with a pyranometer.
Ultraviolet Index - Radiation - Cosmic Rays - Dark Matter - Black Holes
Dosimeter is a device that measures exposure to ionizing radiation. It has two main uses: for human radiation protection and for measurement of dose in both medical and industrial processes.
Star Death
Nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion on a white dwarf, which causes a sudden brightening of the star. Novae are not to be confused with other brightening phenomena such as supernovae or luminous red novae. Recurrent Novae are objects that have been seen to experience multiple nova eruptions. Fusion - Nucleosynthesis.
Supernova is an astronomical event that occurs during the last stellar evolutionary stages of a massive star's life, whose dramatic and catastrophic destruction is marked by one final titanic explosion. This causes the sudden appearance of a "new" bright star, before slowly fading from sight over several weeks or months. List of Supernovae (wiki) - History of Supernova observation (wiki) - Astronomy - Eyes in the Sky.
Type Ia Supernova is a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems (two stars orbiting one another) in which one of the stars is a white dwarf. The other star can be anything from a giant star to an even smaller white dwarf.
Not all stars explode. Those with lower masses, like our Sun, will expand into red giants, and then shed their outer layers, leaving behind a white dwarf. More massive stars, after going through the red giant phase, will eventually collapse and either become neutron stars or black holes, potentially going through a supernova explosion in the process. When a white dwarf star dies, it cools and fades over a very long time, eventually becoming a black dwarf, a cold, dark remnant of a star. This process involves the white dwarf radiating away its internal energy and cooling until it no longer emits heat or light. A black dwarf is an extremely dense object. And over incredibly long timescales, black dwarfs may undergo some changes due to quantum mechanical effects and interactions with the universe. If protons are unstable and decay, black dwarfs would slowly lose mass as protons decay into other particles, potentially leading to their eventual evaporation over trillions of years. If protons don't decay, then pycnonuclear fusion, a process of very slow fusion due to quantum tunneling in dense matter, may occur, potentially transforming the black dwarf into a sphere of iron. In rare cases, if proton decay is slow and pycnonuclear fusion leads to a significant buildup of iron, a black dwarf could reach a point where electron pressure can no longer support it, leading to a supernova-like event. If black dwarfs become dense enough, they might eventually collapse into black holes due to quantum tunneling, which would then evaporate via Hawking radiation, though this is an extremely slow process.
Complete Stellar Collapse: Unusual star system proves that stars can die quietly. University of Copenhagen astrophysicists help explain a mysterious phenomenon, whereby stars suddenly vanish from the night sky. Their study of an unusual binary star system has resulted in convincing evidence that massive stars can completely collapse and become black holes without a supernova explosion.
Gravitational Collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formation in the universe. Over time an initial, relatively smooth distribution of matter, after sufficient accretion, may collapse to form pockets of higher density, such as stars or black holes.
The Subaru Telescope has captured images of more than 1800 exploding stars in the Universe, some located 8 billion light years from Earth. This telescope is capable of generating shape stellar images, and the Hyper Suprime-Cam, an 870 mega-pixel digital camera attached at its top, captures a very wide area of the night sky in one shot.
Hubble watches exploding star fade into oblivion. When a star unleashes as much energy in a matter of days as our Sun does in several billion years, you know it's not going to remain visible for long. The supernova is called SN 2018gv.
A particular cloud produced by a supernova explosion 10,000 years ago contains enough dust to make 7,000 Earths.
Star Formation
 The Photo on right is a massive
star forming 4,200 light years
away. The star, W75N(B)-VLA 2, is eight times larger than our
sun and is believed to be just a few thousand years old.
Star Types.
The Photo on right is a massive
star forming 4,200 light years
away. The star, W75N(B)-VLA 2, is eight times larger than our
sun and is believed to be just a few thousand years old.
Star Types.The process of star formation takes around a million years from the time the initial gas cloud starts to collapse until the star is created and shines like the Sun. The leftover material from the star's birth is used to create planets and other objects that orbit the central star. Galaxies - Orbits - Plasma Streams
Protostar is a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. The protostellar phase is the earliest one in the process of stellar evolution. For a low mass star (i.e. that of the Sun or lower), it lasts about 500,000 years. The phase begins when a molecular cloud fragment first collapses under the force of self-gravity and an opaque, pressure supported core forms inside the collapsing fragment. It ends when the infalling gas is depleted, leaving a pre-main-sequence star, which contracts to later become a main-sequence star at the onset of hydrogen fusion. Solar System Formation.
Proto-Suns teeming with Prebiotic Molecules
Star Formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions", fuse to form stars. Star Formation.
Nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Most nebulae are of vast size, some are hundreds of light years in diameter. Other nebulae form as the result of supernova explosions; the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The materials thrown off from the supernova explosion are then ionized by the energy and the compact object that its core produces. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus.
Cosmic Dust is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles are between a few molecules to 0.1 µm in size. Cosmic dust can be further distinguished by its astronomical location: intergalactic dust, interstellar dust, interplanetary dust (such as in the zodiacal cloud) and circumplanetary dust (such as in a planetary ring).
Lagoon Nebula Zoom and Flythrough (youtube) - Located in the constellation Sagittarius in the direction of our Milky Way galaxy’s central bulge.
National Radio Astronomy Observatory
Infant stars are born in large groups – never in isolation. Star’s chemical composition bears the signature of the evolution of its predecessors. How Many Milky Way Stars are Formed?
First pictures from Euclid satellite reveal billions of orphan stars. The first scientific pictures from the Euclid satellite mission have revealed more than 1,500 billion orphan stars scattered throughout the Perseus cluster of galaxies. Orphan Star is a star that is not part of any galaxy, but exists in intergalactic space instead. The orphan stars are characterized by their bluish hue and clustered arrangement. Based on these distinctive features the astronomers involved in the study suggest that the stars were torn from the outskirts of galaxies and from the complete disruption of smaller cluster galaxies, known as dwarfs. Although stars cannot form in the voids between galaxies (since the density of matter is far too low), there are in fact large numbers of 'intergalactic stars'. It has been estimated, for example, that 10 per cent of the mass of the Virgo galaxy cluster is in the form of these stellar interlopers. Rogue Planet or free-floating planet or an isolated planetary-mass object, is an interstellar object of planetary mass which is not gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf.
 This Galaxy
stopped making Stars only a few billion years after the big bang. This
artist's concept shows what the young, dead, disk galaxy MACS2129-1,
right, would look like when compared with the Milky Way galaxy, left.
Although three times as massive as the Milky Way, it is only half the
size. MACS2129-1 is also spinning more than twice as fast as the Milky
Way. Note that regions of Milky Way are blue from bursts of star
formation, while the young, dead galaxy is yellow, signifying an older
star population and no new star birth. Why this galaxy stopped forming
stars is still unknown. It may be the result of an active galactic
nucleus, where energy is gushing from a supermassive black hole. This
energy inhibits star formation by heating the gas or expelling it from the
galaxy. Or it may be the result of the cold gas streaming onto the galaxy
being rapidly compressed and heated up, preventing it from cooling down
into star-forming clouds in the galaxy's center.
This Galaxy
stopped making Stars only a few billion years after the big bang. This
artist's concept shows what the young, dead, disk galaxy MACS2129-1,
right, would look like when compared with the Milky Way galaxy, left.
Although three times as massive as the Milky Way, it is only half the
size. MACS2129-1 is also spinning more than twice as fast as the Milky
Way. Note that regions of Milky Way are blue from bursts of star
formation, while the young, dead galaxy is yellow, signifying an older
star population and no new star birth. Why this galaxy stopped forming
stars is still unknown. It may be the result of an active galactic
nucleus, where energy is gushing from a supermassive black hole. This
energy inhibits star formation by heating the gas or expelling it from the
galaxy. Or it may be the result of the cold gas streaming onto the galaxy
being rapidly compressed and heated up, preventing it from cooling down
into star-forming clouds in the galaxy's center.How nearby galaxies form their stars. Stars are born in dense clouds of molecular hydrogen gas that permeates interstellar space of most galaxies. The star-formation activity of typical, nearby galaxies is found to scale proportionally with the amount of gas present in these galaxies. This points to the net gas supply from cosmic distances as the main driver of galactic star formation.
Looking at the Stars in the night sky is seeing the Past, the Future and the Present all at once.
If you look at galaxies that are 5 billion light years away, then you're looking at the Universe as it was 5 billion years ago.
Seeing a supernova 150,000 light years away is seeing what happened 150,000 years ago, so the star was dead long before we saw it explode into a Supernova. So stars could be gone long before we see it. Time Perception.
Magnitude in astronomy is a logarithmic measure of the brightness of an object in a defined passband, often in the visible or infrared spectrum, but sometimes across all wavelengths. An imprecise but systematic determination of the magnitude of objects was introduced in ancient times by Hipparchus.
Seeing the light from our own Sun is 8 minutes old. - List of Nearest Stars (wiki)
Are the stars in the night sky just the History of the Universe Frozen in Time? Is what we see just an image of us, what we were like millions of years ago at different times? We can travel within our own galaxy, but if we try to reach another galaxy, we would never make it, because it's already gone.
This is What We Know, so far - Back to the Top of page
"So when you look out at the stars you're not seeing now, you're seeing the past, something that may be already gone. So what is now? We have no idea what now is. Yes we have our own personal measurement of time, but that's just for humans on planet earth. We see the universe but does somebody out there see us? Maybe not because they're already gone. Or maybe we were not seen yet because we have not yet been born yet. So even if they are looking in our direction they don't even see us because our sun has not yet been born."
Light - Photons
 Light is
electromagnetic radiation
within a certain portion of the
electromagnetic spectrum that can produce a
visual
sensation. Any device serving as a source of
illumination.
Visible light is carried by photons, and so are all the other kinds of
electromagnetic radiation like X-rays,
microwaves and radio waves.
Light is
electromagnetic radiation
within a certain portion of the
electromagnetic spectrum that can produce a
visual
sensation. Any device serving as a source of
illumination.
Visible light is carried by photons, and so are all the other kinds of
electromagnetic radiation like X-rays,
microwaves and radio waves.
Is light a particle or a wave? Does light only travel through Space? - Light Bends - What Is Light? (youtube) - LED's - Luminous
Light is invisible, darkness is invisible, but when you add darkness and light together, along with matter, then we see colors and shapes. You can only see a beam of light when there is darkness, and you can only see a beam of darkness when there is light, and you can only see light when it comes in contact with matter. The Sun does not illuminate outer space, you only see light when it comes in contact with matter, like when we see the moon at night, or when light comes in contact with your eye, which is also matter.
Brightness is the quality of being luminous, bright or radiant, and emitting or reflecting light. The location of a visual perception along a continuum from black to white.
Darkness is absence of light or illumination or the degree of visibility of your environment.
Photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of all forms of electromagnetic radiation including light. It is the force carrier for electromagnetic force, even when static via virtual photons. The photon has zero rest mass and as a result, the interactions of this force with matter at long distance are observable at the microscopic and macroscopic levels. Like all elementary particles, photons are currently best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, exhibiting properties of both waves and particles. A photon is massless, has no electric charge, and is a stable particle. A photon has two possible polarization states. Light does not carry any charge itself, so it does not attract or repel charged particles like electrons. Instead light is an oscillating electric and magnetic field. All electromagnetic radiation is transmitted as photons and photons occur on all of the frequencies. Photons are just electric fields traveling through space. Photons have no charge, no resting mass, and travel at the speed of light. Photons are emitted by the action of charged particles, although they can be emitted by other methods including radioactive decay. A photon is produced when an electron releases energy by moving to a lower energy level within the atom. When the atom absorbs energy, it re-emits it in a random direction, almost instantaneously. Photons are easily created and destroyed. An electron moving in a strong magnetic field will generate photons just from its acceleration. Similarly, when a photon of the right wavelength strikes an atom, it disappears and imparts all its energy to kicking the electron into a new energy level. That interaction is called fusion, and it naturally occurs when two atoms are heated and compressed so intensely that their nuclei merge into a new element. This process often leads to the creation of a photon, the particles of light that are released from the sun. Since photons (particles of light) have no mass, they must obey E = pc and therefore get all of their energy from their momentum.
A Photon is a Photon. There's little difference between individual photons that are emitted from the sun or from an LED or incandescent light bulb. But a light bulb emits photons at different rates and has a relatively different spectra of light, and photons have variable energy depending on their frequency, which depends on the type of light bulb that you're using. Natural sources of light like our sun have a different biological effect on us, mostly because the light bulb is missing many frequencies that are found in sunlight. You can buy bulbs that produce a spectrum that is pretty much the same as sunlight, but of course you don't want the UV in your house. With our circadian photoreceptors, an incandescent lamp will not wake you up as fast as sunlight because they don't emit much blue light. And people who sleep with lights in their bedroom have a number of health related issues a person who sleeps in a totally dark room does not have. We're programmed to sleep best when it's very dark. A women went to Alaska, and in the summer there was no dark, so she had to put foil over her windows and wear a black mask because she was having all sorts of serious mental problems as well as physical problems from the lack of darkness.
Photons - Energy Transfer - Let there be Light. The high-energy photons released in fusion reactions takes an indirect path to the sun's surface. A photon takes around 100,000 years to travel from the suns core to reach the sun's surface. According to current models, random scattering from free electrons in the solar radiative zone (the zone within 75% of the solar radius, where heat transfer is by radiation) sets the photon diffusion time scale (or "photon travel time") from the core to the outer edge of the radiative zone at about 170,000 years. From there they cross into the convective zone (the remaining 25% of distance from the Sun's center), where the dominant transfer process changes to convection, and the speed at which heat moves outward becomes considerably faster. In the process of heat transfer from core to photosphere, each gamma ray in the Sun's core is converted during scattering into several million visible light photons before escaping into space. Neutrinos are also released by the fusion reactions in the core, but unlike photons they very rarely interact with matter, so almost all are able to escape the Sun immediately. For many years measurements of the number of neutrinos produced in the Sun were much lower than theories predicted, a problem which was recently resolved through a better understanding of neutrino oscillation. Gamma Rays.
Photon Energy is the energy carried by a single photon. The amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon's electromagnetic frequency and thus, equivalently, is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The higher the photon's frequency, the higher its energy. Equivalently, the longer the photon's wavelength, the lower its energy. Photon energy can be expressed using any unit of energy. Among the units commonly used to denote photon energy are the electronvolt (eV) and the joule (as well as its multiples, such as the microjoule). As one joule equals 6.24 × 1018 eV, the larger units may be more useful in denoting the energy of photons with higher frequency and higher energy, such as gamma rays, as opposed to lower energy photons, such as those in the radio frequency region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Photic Sneeze Reflex is why the Sun makes you sneeze.
Photophysics is the physics of light, especially of its interaction with matter.
Light Therapy - Photonics - Photo-Chemistry - Dark Matter - Photosynthesis
The Nature of Nuclear Forces imprinted in Photons. IFJ PAN scientists together with colleagues from the University of Milano (Italy) and other countries confirmed the need to include the three-nucleon interactions in the description of electromagnetic transitions in the 20O atomic nucleus. Vital for validating the modern theoretical calculations of the nuclear structure was the application of state-of-the-art gamma-ray detector systems and the newly developed technique for measurements of femtosecond lifetimes in exotic nuclei produced in heavy-ion deep-inelastic reactions. Atomic nuclei consist of nucleons—protons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are systems of quarks and gluons held together by strong nuclear interactions. The physics of quarks and gluons is described by quantum chromodynamics (QCD), so we could expect that the properties of nuclear forces would also result from this theory. Unfortunately, despite many attempts, determining the characteristics of strong interactions based on QCD faces enormous computational difficulties. However, relatively much is known about the properties of nuclear forces—this knowledge is based on many years of experimentation. Theoretical models were also developed that can reproduce the basic properties of forces acting between a pair of nucleons—they make use of the so-called effective nucleon-nucleon interaction potentials. Knowing the details of the interaction between two nucleons, we would expect that the description of the structure of any atomic nucleus will not be a problem. Surprisingly, it turns out that when a third nucleon is added to the two-nucleon system, the attraction between the initial two nucleons increases. What follows, the strength of the interaction between the components of each pair of nucleons in the three-body system increases—an additional force shows up that seems not to exist in the case of an isolated pair. This puzzling contribution is called the irreducible three-nucleon force.
How Light is detected affects the atom that emits it, An atom or molecule in the fluorescent tube that is in an excited state spontaneously decays to a lower energy state, releasing a particle called a photon. When the photon enters your eye, something similar happens but in reverse. The photon is absorbed by a molecule in the retina and its energy kicks that molecule into an excited state. Light is both a particle and a wave, and this duality is fundamental to the physics that rule the Lilliputian world of atoms and molecules. How we look at light can affect the atom that emits it (youtube).
Photometer is an instrument that measures light intensity or the optical properties of solutions or surfaces. Photometers detect the light with photoresistors, photodiodes or photomultipliers which are the class of vacuum phototubes that are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times (i.e., 160 dB), in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low. To analyze the light, the photometer may measure the light after it has passed through a filter or through a monochromator for determination at defined wavelengths or for analysis of the spectral distribution of the light. Monochromator is an optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. Photometers measure: Illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of how much the incident light illuminates the surface, wavelength-weighted by the luminosity function to correlate with human brightness perception. Similarly, luminous emittance is the luminous flux per unit area emitted from a surface. Luminous emittance is also known as luminous exitance. Irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux (power) received by a surface per unit area. Spectral irradiance is the irradiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The two forms have different dimensions: spectral irradiance of a frequency spectrum is measured in watts per square metre per hertz (W·m−2·Hz−1), while spectral irradiance of a wavelength spectrum is measured in watts per square metre per metre (W·m−3), or more commonly watts per square metre per nanometre (W·m−2·nm−1). Light Absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way in which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed into internal energy of the absorber, for example thermal energy. The reduction in intensity of a light wave propagating through a medium by absorption of a part of its photons is often called attenuation. Usually, the absorption of waves does not depend on their intensity (linear absorption), although in certain conditions (usually, in optics), the medium changes its transparency dependently on the intensity of waves going through, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. UV. Scattering of Light is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more paths due to localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections that undergo scattering are often called diffuse reflections and unscattered reflections are called specular (mirror-like) reflections. Scattering may also refer to particle-particle collisions between molecules, atoms, electrons, photons and other particles. Examples include: cosmic ray scattering in the Earth's upper atmosphere; particle collisions inside particle accelerators; electron scattering by gas atoms in fluorescent lamps; and neutron scattering inside nuclear reactors. Reflection of Light is either specular (mirror-like) or diffuse (retaining the energy, but losing the image) depending on the nature of the interface. In specular Reflection the phase of the reflected waves depends on the choice of the origin of coordinates, but the relative phase between s and p (TE and TM) polarizations is fixed by the properties of the media and of the interface between them. A Mirror provides the most common model for specular light reflection, and typically consists of a glass sheet with a metallic coating where the significant reflection occurs. Reflection is enhanced in metals by suppression of wave propagation beyond their skin depths. Reflection also occurs at the surface of transparent media, such as water or glass.
Fluorescence - Phosphorescence - Luminescence - Bending of Light - Lasers
Light Meter is a device used to measure the amount of light that allows a photographer to determine which shutter speed and f-number should be selected for an optimum exposure, given a certain lighting situation and film speed.
Exposure Value is a number that represents a combination of a camera's shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance). Exposure value is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale, with a difference of 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop. Frames Per Second.
Photodetector are sensors of light or other electromagnetic energy. A photo detector has a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar Cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy.
Photoreceptor Cell is a specialized type of sensory neuron found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.
Physicists 'trick' photons into behaving like electrons using a 'synthetic' magnetic field. Scientists have discovered an elegant way of manipulating light using a 'synthetic' Lorentz force -- which in nature is responsible for many fascinating phenomena including the Aurora Borealis.
Physicists Create New Form of Light. Newly observed optical state could enable quantum computing with photons. Individual photons that make up light do not interact. But what if light particles could be made to interact, attracting and repelling each other like atoms in ordinary matter? Quantum.
A new state of light. Physicists observe new phase in Bose-Einstein condensate of light particles. A single 'super photon' made up of many thousands of individual light particles. About ten years ago, researchers produced such an extreme aggregate state for the first time. Researchers report of a new, previously unknown phase transition in the optical Bose-Einstein condensate. This is a overdamped phase.
Structured Light is the process of projecting a known pattern (often grids or horizontal bars) on to a scene. The way that these deform when striking surfaces allows vision systems to calculate the depth and surface information of the objects in the scene, as used in structured light 3D scanners. Invisible (or imperceptible) structured light uses structured light without interfering with other computer vision tasks for which the projected pattern will be confusing. Example methods include the use of infrared light or of extremely high frame rates alternating between two exact opposite patterns. Structured light is used by a number of police forces for the purpose of photographing fingerprints in a 3D scene. Where previously they would use tape to extract the fingerprint and flatten it out, they can now use cameras and flatten the fingerprint digitally, which allows the process of identification to begin before the officer has even left the scene.
 Spontaneous Emission is the process by which a
quantum
system such as an atom, molecule,
nanocrystal or nucleus in
an excited state undergoes a transition to a state with a lower
energy (e.g., the ground state) and emits quanta of energy.
Spontaneous Emission is the process by which a
quantum
system such as an atom, molecule,
nanocrystal or nucleus in
an excited state undergoes a transition to a state with a lower
energy (e.g., the ground state) and emits quanta of energy.Excited State of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation is an elevation in energy level above an arbitrary baseline energy state.
Ground State of a quantum mechanical system is its lowest-energy state; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In the quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum.
Interference wave propagation is a phenomenon in which two waves superpose to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Interference usually refers to the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves or matter waves.
If you could fly nonstop to the Sun at 60 mph, it would take you 180 years to get there.
If a Space Ship could travel 35,000 mph, it would take 81,000 years to travel 4.3 light years.
One light year is about 5.9 trillion miles. A light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). (5.88 trillion miles or 9.5 trillion km).
Speed of Light is 299,792,458 metres per second. 300,000 km/s, or 983,571,056.4304 feet per second (9.836e+8), approximately 3.00×108 m/s. (186,000 miles per second). Light travels at a speed of about 671 Million MPH.
Speed of Light is Relative (video)
Capturing the Speed of Light One Trillion Frames Per Second (youtube)
Finding The Speed Of Light With Peeps (youtube)
Superluminal Motion is the apparently faster-than-light motion seen in some radio galaxies, BL Lac objects, quasars, blazars and recently also in some galactic sources called microquasars. Bursts of energy moving out along the relativistic jets emitted from these objects can have a proper motion that appears greater than the speed of light. All of these sources are thought to contain a black hole, responsible for the ejection of mass at high velocities. Light echoes can also produce apparent superluminal motion.
Slow Light is the propagation of an optical pulse or other modulation of an optical carrier at a very low group velocity. Slow light occurs when a propagating pulse is substantially slowed down by the interaction with the medium in which the propagation takes place. When light propagates through a material, it travels slower than the vacuum speed. Liquid properties of light emerge under special circumstances, when the photons that form the light wave are able to interact with each other. Lene Hau is a Danish physicist who in 1999 succeeded in slowing a beam of light to about 17 metres per second. Stop Light: Humans tame light, stop it from moving for a full minute.
Physics - Action Physics - Spatial Intelligence - Medical Imaging - Electromagnetic Spectrum - Colors - Polarized
 Prism is a
transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that
refract light. At least two of the flat surfaces must have an
angle between them.
The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The
traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a
triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use "prism"
usually refers to this type. Some types of optical prism are not in fact
in the shape of geometric prisms. Prisms can be made from any material
that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed.
Typical materials include glass, plastic and fluorite.
Optics.
Prism is a
transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that
refract light. At least two of the flat surfaces must have an
angle between them.
The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The
traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a
triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use "prism"
usually refers to this type. Some types of optical prism are not in fact
in the shape of geometric prisms. Prisms can be made from any material
that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed.
Typical materials include glass, plastic and fluorite.
Optics.
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to include any interaction with radiative energy as a function of its wavelength or frequency. Spectroscopic data is often represented by an emission spectrum, a plot of the response of interest as a function of wavelength or frequency. Spectrum.
Minimum Deviation a ray of light enters the transparent material, the ray's direction is deflected, based on both the entrance angle (typically measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface) and the material's refractive index, and according to Snell's Law. A beam passing through an object like a prism or water drop is deflected twice: once entering, and again when exiting. The sum of these two deflections is called the deviation angle. The deviation angle in a prism depends upon: Refractive index of the prism: The refractive index depends on the material and the wavelength of the light. The larger the refractive index, the larger the deviation angle. Angle of the prism: The larger the prism angle, the larger the deviation angle. Angle of incidence: The deviation angle depends on the angle that the beam enters the object, called angle of incidence. The deviation angle first decreases with increasing incidence angle, and then it increases. There is an angle of incidence at which the sum of the two deflections is a minimum. The deviation angle at this point is called the "minimum deviation" angle, or "angle of minimum deviation". At the minimum deviation angle, the incidence and exit angles of the ray are identical. One of the factors that causes a rainbow is the bunching of light rays at the minimum deviation angle that is close to the rainbow angle.
Light Cone is the path that a flash of light, emanating from a single event (localized to a single point in space and a single moment in time) and traveling in all directions, would take through spacetime. If one imagines the light confined to a two-dimensional plane, the light from the flash spreads out in a circle after the event E occurs, and if we graph the growing circle with the vertical axis of the graph representing time, the result is a cone, known as the future light cone.
Cloud Iridescence is a colorful optical phenomenon that occurs in a cloud and appears in the general proximity of the Sun or Moon. The colors resemble those seen in soap bubbles and oil on a water surface. It is a type of photometeor. This fairly common phenomenon is most often observed in altocumulus, cirrocumulus, lenticular, and cirrus clouds. They sometimes appear as bands parallel to the edge of the clouds. Iridescence is also seen in the much rarer polar stratospheric clouds, also called nacreous clouds. The colors are usually pastel, but can be very vivid or mingled together, sometimes similar to mother-of-pearl. When appearing near the Sun, the effect can be difficult to spot as it is drowned in the Sun's glare. This may be overcome by shielding the sunlight with one's hand or hiding it behind a tree or building. Other aids are dark glasses, or observing the sky reflected in a convex mirror or in a pool of water.
Relativistic Doppler Effect is the change in frequency (and wavelength) of light, caused by the relative motion of the source and the observer (as in the classical Doppler effect), when taking into account effects described by the special theory of relativity.
How much information is in the Light? - Li-Fi
"If I can see the light, does that mean that I'm connected to its source?"
Optical Communications is communication at a distance using light to carry information. It can be performed visually or by using electronic devices. The earliest basic forms of optical communication date back several millennia, while the earliest electrical device created to do so was the photophone, invented in 1880.
Optical Illusions (spatial Intelligence)
Sun Dog is an atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a bright spot to one or both sides of the Sun. Two sun dogs often flank the Sun within a 22° halo. The sun dog is a member of the family of halos, caused by the refraction of sunlight by ice crystals in the atmosphere. Sun dogs typically appear as a pair of subtly colored patches of light, around 22° to the left and right of the Sun, and at the same altitude above the horizon as the Sun. They can be seen anywhere in the world during any season, but are not always obvious or bright. Sun dogs are best seen and most conspicuous when the Sun is near the horizon.
Halo is the name for a family of optical phenomena produced by light (typically from the Sun or Moon) interacting with ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. Halos can have many forms, ranging from colored or white rings to arcs and spots in the sky. Many of these appear near the Sun or Moon, but others occur elsewhere or even in the opposite part of the sky. Among the best known halo types are the circular halo (properly called the 22° halo), light pillars, and sun dogs, but many others occur; some are fairly common while others are (extremely) rare.
Optical Phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter. See also list of optical topics and optics. A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon.
Lens Flare refers to a phenomenon wherein light is scattered or flared in a lens system, often in response to a bright light, producing a sometimes undesirable artifact within the image. This happens through light scattered by the imaging mechanism itself, for example through internal reflection and scattering from material imperfections in the lens. Lenses with large numbers of elements such as zooms tend to exhibit greater lens flare, as they contain a relatively large number of interfaces at which internal scattering may occur. These mechanisms differ from the focused image generation mechanism, which depends on rays from the refraction of light from the subject itself. Flare manifests itself in two ways: as visible artifacts, and as a haze across the image. The haze makes the image look "washed out" by reducing contrast and color saturation (adding light to dark image regions, and adding white to saturated regions, reducing their saturation). Visible artifacts, usually in the shape of the lens iris, are formed when light follows a pathway through the lens that contains one or more reflections from the lens surfaces. Flare is particularly caused by very bright light sources. Most commonly, this occurs when shooting into the sun (when the sun is in frame or the lens is pointed in the direction of the sun), and is reduced by using a lens hood or other shade. For good-quality optical systems, and for most images (which do not have a bright light shining into the lens), flare is a secondary effect that is widely distributed across the image and thus not visible, although it does reduce contrast.
Nonlinear Optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light.
Photolithography is a process used in microfabrication to pattern parts of a thin film or the bulk of a substrate. It uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light-sensitive chemical "photoresist", or simply "resist," on the substrate. A series of chemical treatments then either engraves the exposure pattern into, or enables deposition of a new material in the desired pattern upon, the material underneath the photo resist. For example, in complex integrated circuits, a modern CMOS wafer will go through the photolithographic cycle up to 50 times.
The Optical Society
Optical Tweezers are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to provide an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the refractive index mismatch to physically hold and move microscopic dielectric objects similar to tweezers. Optical tweezers have been particularly successful in studying a variety of biological systems in recent years.
Optogenetics is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure these manipulation effects in real-time.
Opticks is a book by English natural philosopher Isaac Newton that was published in English in 1704. (A scholarly Latin translation appeared in 1706.) The book analyzes the fundamental nature of light by means of the refraction of light with prisms and lenses, the diffraction of light by closely spaced sheets of glass, and the behaviour of color mixtures with spectral lights or pigment powders. It is considered one of the great works of science in history. Opticks was Newton's second major book on physical science. Newton's name did not appear on the title page of the first edition of Opticks.
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Telescopes.
Optical focusing deep inside dynamic scattering media with near-infrared time-reversed ultrasonically encoded (TRUE) light
Light Thermometer
Diffuse Interstellar Band are absorption features seen in the spectra of astronomical objects in the Milky Way and other galaxies. They are caused by the absorption of light by the interstellar medium. Circa 500 bands have now been seen, in ultraviolet, visible and infrared wavelengths.
Buckminsterfullerene is a spherical fullerene molecule with the formula C60. It has a cage-like fused-ring structure (truncated icosahedron) which resembles a soccer ball (football), made of twenty hexagons and twelve pentagons, with a carbon atom at each vertex of each polygon and a bond along each polygon edge.
Light Bends - Diffraction - Refraction
 Stellar Parallax is the apparent shift of position of any nearby star
(or other object) against the background of distant objects. Created by
the different orbital positions of Earth, the extremely small observed
shift is largest at time intervals of about six months, when Earth arrives
at opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit, giving a baseline distance of
about two astronomical units between observations. The
parallax itself
is considered to be half of this maximum, about equivalent to the
observational shift that would occur due to the different positions of
Earth and the Sun, a baseline of one astronomical unit (AU).
Stellar Parallax is the apparent shift of position of any nearby star
(or other object) against the background of distant objects. Created by
the different orbital positions of Earth, the extremely small observed
shift is largest at time intervals of about six months, when Earth arrives
at opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit, giving a baseline distance of
about two astronomical units between observations. The
parallax itself
is considered to be half of this maximum, about equivalent to the
observational shift that would occur due to the different positions of
Earth and the Sun, a baseline of one astronomical unit (AU). Telescope Lens Bends Light - Space is Curved - Motion Parallax - Skywaves - Sight Problems
Aberration of Light is an astronomical phenomenon which produces an apparent motion of celestial objects about their true positions, dependent on the velocity of the observer. Aberration causes objects to appear to be displaced towards the direction of motion of the observer compared to when the observer is stationary. The change in angle is typically very small — of the order of v/c where c is the speed of light and v the velocity of the observer. In the case of "stellar" or "annual" aberration, the apparent position of a star to an observer on Earth varies periodically over the course of a year as the Earth's velocity changes as it revolves around the Sun, by a maximum angle of approximately 20 arcseconds in right ascension or declination.
Diffraction is the bending and spreading around of an RF signal when it encounters an obstruction. The waves that encounter the object bend around the object, taking a longer and different path. The waves that do not encounter the object do not bend and maintain a shorter and original path. Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit. It is defined as the bending of light around the corners of an obstacle or aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle.
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another or from a gradual change in the medium. The change in direction of wave propagation due to a change in its transmission medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound waves and water waves also experience refraction. How much a wave is refracted is determined by the change in wave speed and the initial direction of wave propagation relative to the direction of change in speed.
Schlieren Photography - Prisms - Reflections
Refractive Index of a material is a dimensionless number that describes how fast light travels through the material. It is defined as n = c v, where c is the speed of light in vacuum and v is the phase velocity of light in the medium. For example, the refractive index of water is 1.333, meaning that light travels 1.333 times slower in water than in a vacuum. Increasing the refractive index corresponds to decreasing the speed of light in the material. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle.
Atmospheric Refraction is the deviation of light or other electromagnetic wave from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density as a function of height. This refraction is due to the velocity of light through air decreasing (the refractive index increases) with increased density. Atmospheric refraction near the ground produces mirages. Such refraction can also raise or lower, or stretch or shorten, the images of distant objects without involving mirages. Turbulent air can make distant objects appear to twinkle or shimmer. The term also applies to the refraction of sound. Atmospheric refraction is considered in measuring the position of both celestial and terrestrial objects. Astronomical or celestial refraction causes astronomical objects to appear higher above the horizon than they actually are. Terrestrial refraction usually causes terrestrial objects to appear higher than they actually are, although in the afternoon when the air near the ground is heated, the rays can curve upward making objects appear lower than they actually are. Refraction not only affects visible light rays, but all electromagnetic radiation, although in varying degrees. For example, in the visible spectrum, blue is more affected than red. This may cause astronomical objects to appear dispersed into a spectrum in high-resolution images. The atmosphere refracts the image of a waxing crescent Moon as it sets into the horizon. Whenever possible, astronomers will schedule their observations around the times of culmination, when celestial objects are highest in the sky. Likewise, sailors will not shoot a star below 20° above the horizon. If observations of objects near the horizon cannot be avoided, it is possible to equip an optical telescope with control systems to compensate for the shift caused by the refraction. If the dispersion is also a problem (in case of broadband high-resolution observations), atmospheric refraction correctors (made from pairs of rotating glass prisms) can be employed as well. Since the amount of atmospheric refraction is a function of the temperature gradient, temperature, pressure, and humidity (the amount of water vapor, which is especially important at mid-infrared wavelengths), the amount of effort needed for a successful compensation can be prohibitive. Surveyors, on the other hand, will often schedule their observations in the afternoon, when the magnitude of refraction is minimum. Atmospheric refraction becomes more severe when temperature gradients are strong, and refraction is not uniform when the atmosphere is heterogeneous, as when turbulence occurs in the air. This causes suboptimal seeing conditions, such as the twinkling of stars and various deformations of the Sun's apparent shape soon before sunset or after sunrise.
Snell's Law is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material. The law is also satisfied in metamaterials, which allow light to be bent "backward" at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index. F=MA
Orbital Angular Momentum of Light is the component of angular momentum of a light beam that is dependent on the field spatial distribution, and not on the polarization. It can be further split into an internal and an external OAM. The internal OAM is an origin-independent angular momentum of a light beam that can be associated with a helical or twisted wavefront. The external OAM is the origin-dependent angular momentum that can be obtained as cross product of the light beam position (center of the beam) and its total linear momentum. Orbital Angular Momentum is a property of the electron's rotational motion that is related to the shape of its orbital. The orbital is the region around the nucleus where the electron will be found if detection is undertaken. Orbital angular momentum is thought of as analogous to angular momentum in classical physics.
Angle of Incidence is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any wave: optical, acoustic, microwave, X-ray and so on.
Brewster's Angle is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized.
Total Internal Reflection is the optical phenomenon in which (for example) the surface of the water in a fish-tank, viewed from below the water level, reflects the underwater scene like a mirror with no loss of brightness. In general, TIR occurs when waves in one medium strike sufficiently obliquely against the boundary with a second ("external") medium, in which the waves travel faster than in the first ("internal") medium; the second medium must also be perfectly transparent to the waves. TIR occurs not only with electromagnetic waves such as light and microwaves, but also with other types of waves, including sound and water waves. In the case of a narrow train of waves, such as a laser beam, we tend to describe the reflection in terms of "rays" rather than waves; in a medium whose properties are independent of direction, such as air, water, or glass, the "rays" are perpendicular to the associated wavefronts. Refraction is generally accompanied by partial reflection. When waves are refracted from a medium of lower propagation speed to a medium of higher propagation speed (e.g., from water to air), the angle of refraction (between the refracted ray and the line perpendicular to the refracting surface) is greater than the angle of incidence (between the incident ray and the perpendicular). As the angle of incidence approaches a certain limit, called the critical angle, the angle of refraction approaches 90°, at which the refracted ray becomes parallel to the surface. As the angle of incidence increases beyond the critical angle, the conditions of refraction can no longer be satisfied; so there is no refracted ray, and the partial reflection becomes total. For visible light, the critical angle is about 49° for incidence at the water-to-air boundary, and about 42° for incidence at the common glass-to-air boundary.
Scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. Scattering theory is a framework for studying and understanding the scattering of waves and particles.
Light from outside our galaxy brighter than expected. Study led by RIT scientists uses data taken by LORRI on NASA's New Horizons mission. Scientists analyzed new measurements showing that the light emitted by stars outside our galaxy is two to three times brighter than the light from known populations of galaxies, challenging assumptions about the number and environment of stars are in the universe.
Evanescent Field is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero.
Scientists discover a strange new magnet that bends light like magic. Researchers cracked the mystery of altermagnets, materials with no net magnetization yet strange light-reflecting powers, by creating a new optical measurement method. Their findings confirmed altermagnetism in an organic crystal and opened doors to innovative magnetic devices.
Poynting Vector represents the directional energy flux (the energy transfer per unit area per unit time) of an electromagnetic field.
Straight Objects Shift when in a glass of water because the glass is so thin and because the light starts and finished in air, the refraction into and out of the glass causes little deviation in the light's original direction. As you sight at the portion of the pencil that was submerged in the water, light travels from water to air (or from water to glass to air). List of Refractive Indices (wiki).
Refractive Index of a material is a dimensionless number that describes how fast light propagates through the material.
Optical Phenomenon are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter. See also list of optical topics and optics. A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon.
Camera Obscura is the natural optical phenomenon that occurs when an image of a scene at the other side of a screen (or for instance a wall) is projected through a small hole in that screen as a reversed and inverted image (left to right and upside down) on a surface opposite to the opening. The surroundings of the projected image have to be relatively dark for the image to be clear, so many historical camera obscura experiments were performed in dark rooms.
Fata Morgana Mirage is an unusual and complex form of superior mirage that is seen in a narrow band right above the horizon.
Dark Matter
Binocular Disparity refers to the difference in image location of an object seen by the left and right eyes, resulting from the eyes’ horizontal separation (parallax). The brain uses binocular disparity to extract depth information from the two-dimensional retinal images in stereopsis. In computer vision, binocular disparity refers to the difference in coordinates of similar features within two stereo images.
Cosmic Distance Ladder is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are "close enough" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity, which is the total amount of energy emitted by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object per unit time. It is related to the brightness, which is the luminosity of an object in a given spectral region.
Signal Strength refers to the transmitter power output as received by a reference antenna at a distance from the transmitting antenna. High-powered transmissions, such as those used in broadcasting, are expressed in dB-millivolts per metre (dBmV/m). For very low-power systems, such as mobile phones, signal strength is usually expressed in dB-microvolts per metre (dBµV/m) or in decibels above a reference level of one milliwatt (dBm). In broadcasting terminology, 1 mV/m is 1000 µV/m or 60 dBµ (often written dBu).
 Measuring Receiver is a calibrated laboratory-grade
radio receiver designed to measure the characteristics of radio signals.
The parameters of such receivers (tuning frequency, receiving bandwidth,
gain) can usually be adjusted over a much wider range of values than is
the case with other radio receivers. Their circuitry is optimized for
stability and to enable calibration and reproducible results. Some
measurement receivers also have especially robust input circuits that can
survive brief impulses of more than 1000 V, as they can occur during
measurements of radio signals on power lines and other conductors.
Measuring Receiver is a calibrated laboratory-grade
radio receiver designed to measure the characteristics of radio signals.
The parameters of such receivers (tuning frequency, receiving bandwidth,
gain) can usually be adjusted over a much wider range of values than is
the case with other radio receivers. Their circuitry is optimized for
stability and to enable calibration and reproducible results. Some
measurement receivers also have especially robust input circuits that can
survive brief impulses of more than 1000 V, as they can occur during
measurements of radio signals on power lines and other conductors.Einstein Ring is the deformation of the light from a source (such as a galaxy or star) into a ring through gravitational lensing of the source's light by an object with an extremely large mass (such as another galaxy or a black hole).
Gravitational Lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels towards the observer. This effect is known as gravitational lensing, and the amount of bending is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity. Classical physics also predicts the bending of light, but only half that predicted by general relativity.
Could new technique for 'curving' light be the secret to improved wireless communication? A study that could help revolutionize wireless communication introduces a novel method to curve terahertz signals around an obstacle.
DNA Phantom Effect - Contrast Microscopy
Collimated Light is light whose rays are parallel, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. Such a beam cannot be created, due to Diffraction, which refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit. It is defined as the bending of light around the corners of an obstacle or aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described as the interference of waves according to the Huygens–Fresnel principle, which is a method of analysis applied to problems of wave propagation both in the far-field limit and in near-field diffraction.
Wave Propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel. With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves. For electromagnetic waves, propagation may occur in a vacuum as well as in a material medium. Other wave types cannot propagate through a vacuum and need a transmission medium to exist.
Rayleigh Scattering is the predominantly elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering particle (normal dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels through transparent solids and liquids, but is most prominently seen in gases. Rayleigh scattering of sunlight in Earth's atmosphere causes diffuse sky radiation, which is the reason for the blue color of the daytime and twilight sky, as well as the yellowish to reddish hue of the low Sun. Sunlight is also subject to Raman scattering, which changes the rotational state of the molecules and gives rise to polarization effects. Scattering by particles similar to, or larger than, the wavelength of light is typically treated by the Mie theory, the discrete dipole approximation and other computational techniques. Rayleigh scattering applies to particles that are small with respect to wavelengths of light, and that are optically "soft" (i.e., with a refractive index close to 1). Anomalous diffraction theory applies to optically soft but larger particles.
Quotes about Light, and Darkness
“Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.” Martin Luther King.
“We can easily forgive a child who is afraid of the dark; the real tragedy of life is when men are afraid of the light.” Plato.
“Light thinks it travels faster than anything but it is wrong. No matter how fast light travels, it finds the darkness has always got there first, and is waiting for it.” Terry Pratchett, Reaper Man.
“Look at how a single candle can both defy and define the darkness.” Anne Frank
"I'm like the light, you will always have me, but you can never keep me."
“When you light a candle, you also cast a shadow.” Ursula K. Le Guin
"For you were once darkness, but now you are light. Live as children of light."
“I will love the light for it shows me the way, yet I will endure the darkness for it shows me the stars.” Og Mandino
Seeing the Light is to finally understand something or to realize something after a prolonged thought or doubt.
"The Lord of Light, the giver of Heat and Energy. Our Star is truly a Star."
Star is an important performer with excellent skills who plays a principal role.
“Everything has its wonders, even darkness and silence, and I learn, whatever state I may be in, therein to be content” - Helen Keller.
Diwali is a festival that symbolizes the victory of light over darkness. Diwali is one of the major religious festivals in Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism. The name is derived from the Sanskrit term dipavali, meaning “row of lights.” The term is derived from the Sanskrit words dīpa, 'lamp, light, lantern, candle, that which glows, shines, illuminates or knowledge' and āvali, 'a row, range, continuous line, series'. Divali is the Hindu festival of lights with its variations also celebrated in other Indian religions. The festival also celebrates the end of the monsoon, held in October and November.
Space - Void - The Second to the Last Final Frontier
 Outer Space is the
void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is
not
completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density
of particles, predominantly a
plasma of
hydrogen and helium as well as
electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and
cosmic
rays and dark energy or
dark matter, and whatever
can be detected or theorized.
Outer Space is the
void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is
not
completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density
of particles, predominantly a
plasma of
hydrogen and helium as well as
electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and
cosmic
rays and dark energy or
dark matter, and whatever
can be detected or theorized.
Space is an empty area that is usually bounded in some way between things. An area reserved for some particular purpose. The interval between two times. Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. Voids, or empty spaces, exist within matter at all scales, from the astronomical to the microscopic.
Is Space Moving or in Motion? According to relativistic physics, space doesn't move, but bends and stretches in the presence of mass. As mass moves, it bends the space around it. Movement is also relative to one's frame of reference. Technically, neither space nor objects in space move. Instead it is the metric governing the size and geometry of spacetime itself that changes in scale. Although light and objects within spacetime cannot travel faster than the speed of light, this limitation does not restrict the metric itself. Warp Drive.
Void is an empty area or space. Vacuum.
Empty is holding nothing or containing nothing. Something not filled or occupied. A container left empty of its contents. To remove all the contents of a container. A word or a gesture that is lacking meaning or sincerity.
Zero - Set Theory - Fields - Vantablack - Virtual Particles - Anti-Matter - Uncertainty Principle - Black Holes - Expansion - Conservation of Energy
Nothing is not anything or nothing at all, or what seems to be nothing, or it's something that can not be measured or detected, so it's perceived as being nothing. Even if you have a space with nothing in it, you still have space, and space is something. Nothing can not exist, if it did, how would you know? The only way to know that there is nothing, is to be something. You could have nothing between your ears and still be something. Nothing is the absence of a something or particular thing that one might expect or desire to be present ("We found nothing", "Nothing was there") or the inactivity of a thing or things that are usually or could be active ("Nothing moved", "Nothing happened"). As a predicate or complement "nothing" is the absence of meaning, value, worth, relevance, standing, or significance. "The affair meant nothing"; "I'm nothing in their eyes"). "Nothingness" is a philosophical term for the general state of nonexistence, sometimes reified as a domain or dimension into which things pass when they cease to exist or out of which they may come to exist, e.g., God is understood to have created the universe ex nihilo, "out of nothing". Abiogenesis.
Śūnyatā is translated most often as "emptiness", "vacuity", and sometimes "voidness", or "nothingness". In Buddhist philosophy, the voidness that constitutes ultimate reality; sunyata is seen not as a negation of existence but rather as the undifferentiation out of which all apparent entities, distinctions, and dualities arise.
How the brain processes the number zero. Researchers clarify the neuronal basis of the mathematical concept of 'zero'. Researchers discovered that individual nerve cells in the medial temporal lobe recognize zero as a numerical value and not as a separate category 'nothing'.
Something is an unspecified thing, agency, amount, or anything that has not yet been defined.
Container is any object that can be used to hold things.
Subspace is a space that is contained within another space.
Interstellar Space is the physical space within a galaxy beyond the influence each star has upon the encompassed plasma.
Interstellar Medium is the diffuse matter and radiation that fills the space between stars within a galaxy, consisting primarily of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and dust. It exists in different phases, from cold molecular clouds where stars form, to hot, ionized gas. The ISM is essential for galactic evolution, as it contains the raw materials for new stars and planets and is continuously recycled through the life cycle of stars, including supernovae. Interstellar Medium is the matter and radiation that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field. Is space a growth medium for the Universe?
Interstitial is a space between structures or objects. Personal Space (give me some room).
Kármán Line is an attempt to define a boundary between Earth's atmosphere and outer space. This is important for legal and regulatory measures; aircraft and spacecraft fall under different jurisdictions and are subject to different treaties. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI; English: World Air Sports Federation), an international standard-setting and record-keeping body for aeronautics and astronautics, defines the Kármán line as the altitude of 100 kilometres (62 miles; 330,000 feet) above Earth's mean sea level. Other organizations do not use this definition. For instance, the US Air Force and NASA define the limit to be 50 miles (80 km) above sea level for purposes of awarding personnel with outer space badges. There is no international law defining the edge of space, and therefore the limit of national airspace, and the US is resisting regulatory movement on this front. The line is named after Theodore von Kármán (1881–1963), a Hungarian American engineer and physicist, who was active primarily in aeronautics and astronautics. He was the first person to calculate the altitude at which the atmosphere becomes too thin to support aeronautical flight and arrived at 83.6 km (51.9 miles) himself. The reason is that a vehicle at this altitude would have to travel faster than orbital velocity to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift to support itself. The line is approximately at the turbopause, above which atmospheric gases are not well-mixed. The mesopause atmospheric temperature minimum has been measured to vary from 85 to 100 km, which places the line at or near the bottom of the thermosphere.
Between is being in a place separated by two things or in a space that is separated by two objects or two regions. Between is a period of time that is separated by two other points in time, such as being in the present moment that is separated by the past and the future.
Void in astronomy are vast spaces between filaments (the largest-scale structures in the Universe), which contain very few or no galaxies. Voids typically have a diameter of 10 to 100 megaparsecs; particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich superclusters, are sometimes called supervoids. They have less than one-tenth of the average density of matter abundance that is considered typical for the observable Universe. Voids are believed to have been formed by baryon acoustic oscillations in the Big Bang, collapses of mass followed by implosions of the compressed baryonic matter. Starting from initially small anisotropies from quantum fluctuations in the early Universe, the anisotropies grew larger in scale over time. Regions of higher density collapsed more rapidly under gravity, eventually resulting in the large-scale, foam-like structure or “cosmic web” of voids and galaxy filaments seen today. Voids located in high-density environments are smaller than voids situated in low-density spaces of the universe. Voids appear to correlate with the observed temperature of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) because of the Sachs–Wolfe effect. Colder regions correlate with voids and hotter regions correlate with filaments because of gravitational redshifting. As the Sachs–Wolfe effect is only significant if the Universe is dominated by radiation or dark energy, the existence of voids is significant in providing physical evidence for dark energy.
Giant Void or Super Void is an extremely large region of space of underdensity of galaxies within the constellation Canes Venatici. It is the second largest confirmed void to date, with an estimated diameter of 300 to 400 Mpc (1 to 1.3 billion light years) and is approximately 1.5 billion light years away (z = 0.116). It was discovered in 1988, and was the largest void in the Northern Galactic Hemisphere, and possibly the second largest ever detected. Even the hypothesized "Eridanus Supervoid" corresponding to the location of the WMAP cold spot is dwarfed by this void, although the Giant Void does not correspond any significant cooling to the cosmic microwave background. Although a vast void, inside it are 17 galaxy clusters, concentrated in a spherical shaped region 50 Mpc in diameter. Studies of the motion of the clusters show that they have no interaction to each other, meaning the density of the clusters is very low resulting in weak gravitational interaction. The void's location in the sky is close to the Boötes void. The Boötes void is 5 times nearer but only has ¼ of the size of the Giant Void.
The Dipole Repeller is a center of effective repulsion in the large-scale flow of galaxies in the neighborhood of the Milky Way, first detected in 2017. It is thought to represent a large supervoid, the Dipole Repeller Void. The Great Attractor.
"Physical objects are not in space, but these objects are spatially extended as fields. In this way the concept 'empty space' loses its meaning." Albert Einstein.
Nassim Haramein 2015 - The Connected Universe (youtube) - space is black holes in various sizes.
Dimensions - Spatial Intelligence - Scale
Aether is the material that fills the region of the universe above the terrestrial sphere. The concept of aether was used in several theories to explain several natural phenomena, such as the traveling of light and gravity. In the late 19th century, physicists postulated that aether permeated all throughout space, providing a medium through which light could travel in a vacuum, but evidence for the presence of such a medium was not found in the Michelson–Morley experiment, and this result has been interpreted as meaning that no such luminiferous aether exists. Luminiferou Aether was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space, something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. Aether Theories in physics propose the existence of a medium, meaning "upper air" or "pure, fresh air", a space-filling substance or field, thought to be necessary as a transmission medium for the propagation of electromagnetic or gravitational forces.
Ether - Elements - Four States of Matter
Luminiferous Aether was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space, something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. Luminescence.
Akasha means space or sky or æther in traditional Indian cosmology, depending on the religion. The word in Sanskrit is derived from a root kāś meaning "to be". It appears as a masculine noun in Vedic Sanskrit with a generic meaning of "open space, vacuity".
Millennium Run or Millennium Simulation is a computer N-body simulation used to investigate how the distribution of matter in the Universe has evolved over time, in particular, how the observed population of galaxies was formed. It is used by scientists working in physical cosmology to compare observations with theoretical predictions.
Interstices is a small structural space between tissues or parts of an organ.
Space Science Outline encompasses all of the scientific disciplines that involve space exploration and study natural phenomena and physical bodies occurring in outer space, such as space medicine and astrobiology.
Scientists uncover warehouse-full of complex molecules never before seen in space. Radio observations of a cold, dense cloud of molecular gas reveal more than a dozen unexpected molecules. Scientists have discovered a vast, previously unknown reservoir of new aromatic material in a cold, dark molecular cloud by detecting individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecules in the interstellar medium for the first time, and in doing so are beginning to answer a three-decades-old scientific mystery: how and where are these molecules formed in space? The more than a dozen PAHs may hold clues as to the formation of comets, asteroids, stars, and even planets.
Quantum Foam or spacetime foam is a theoretical quantum fluctuation of spacetime on very small scales due to quantum mechanics. The theory predicts that at these small scales, particles of matter and antimatter are constantly created and destroyed. These subatomic objects are called virtual particles.
Quantum Fluctuation is the temporary random change in the amount of energy in a point in space. Quantum Fluctuation is also known as a vacuum state fluctuation or vacuum fluctuation.
Quantum Gravity - Quantum Fields - Plasma - Dark Matter - Planck Length
Spin Network is a type of diagram which can be used to represent states and interactions between particles and fields in quantum mechanics. From a mathematical perspective, the diagrams are a concise way to represent multilinear functions and functions between representations of matrix groups. The diagrammatic notation can thus greatly simplify calculations.
Quantum State is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a quantum-mechanical prediction for the system represented by the state. Knowledge of the quantum state, and the quantum mechanical rules for the system's evolution in time, exhausts all that can be known about a quantum system.
Shape of the Universe ~0-
Curved Space often refers to a spatial geometry which is not flat, where a flat space has zero curvature, as described by Euclidean geometry. Curved spaces can generally be described by Riemannian geometry though some simple cases can be described in other ways. Curved spaces play an essential role in general relativity, where gravity is often visualized as curved space. The Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker metric is a curved metric which forms the current foundation for the description of the expansion of space and shape of the universe.
Light Bends - Torus - Bubbles - Black Holes - Dimensions - Cartesian - Centripetal Force
Curved Spacetime in the Lab. Researchers simulate an entire family of universes with curvature in ultracold quantum gases
In a laboratory experiment, researchers have succeeded in realizing an effective spacetime that can be manipulated. In their research on ultracold quantum gases, they were able to simulate an entire family of curved universes to investigate different cosmological scenarios and compare them with the predictions of a quantum field theoretical model.
Shape of the Universe states that the curvature is a quantity describing how the geometry of a space differs locally from the one of the flat space. In General Relativity, Spacetime itself is curved toward the larger mass, and that spatial curvature is constrained by gravity. A multiply connected space like a 3 torus has everywhere zero curvature but is finite in extent, whereas a flat simply connected space is infinite in extent. (euclidean space).
If the amount of matter in the universe is constant and stays the same, then why does the universe need to expand the space in our universe? Why does the universe need more space?
Space in mathematics is a set with some added structure (sometimes called a universe). While modern mathematics uses many types of spaces, such as Euclidean spaces, linear spaces, topological spaces, Hilbert spaces, or probability spaces, it does not define the notion of "space" itself. A space consists of selected mathematical objects that are treated as points, and selected relationships between these points. The nature of the points can vary widely: for example, the points can be elements of a set, functions on another space, or subspaces of another space. It is the relationships that define the nature of the space. More precisely, isomorphic spaces are considered identical, where an isomorphism between two spaces is a one-to-one correspondence between their points that preserves the relationships. For example, the relationships between the points of a three-dimensional Euclidean space are uniquely determined by Euclid's axioms, and all three-dimensional Euclidean spaces are considered identical. Topological notions such as continuity have natural definitions in every Euclidean space. However, topology does not distinguish straight lines from curved lines, and the relation between Euclidean and topological spaces is thus "forgetful". Relations of this kind are treated in more detail in the Section "Types of spaces". It is not always clear whether a given mathematical object should be considered as a geometric "space", or an algebraic "structure". A general definition of "structure", proposed by Bourbaki, embraces all common types of spaces, provides a general definition of isomorphism, and justifies the transfer of properties between isomorphic structures.
"The internet is still open, my mind is still open. Space is not the final frontier, and the speed of light is not absolute. I have been to the farthest galaxy near the edge of the universe. I did not transverse time and space, I am time and space. I wonder, I wander, I will." -HP
If you were a photon, here and there would be the same moment. Everything is quantum entangled. Beam me up scotty. I can't, you're all ready here.
Vacuum
Vacuum is a space that is void of matter or has the perceived absence of matter. An empty area or space. The vacuum in space is primarily created by the low density and low pressure of the interstellar medium, a result of matter being spread out across immense distances. This low density translates to very low pressure, creating a vacuum. Space is not perfectly empty, but the matter it contains (mainly hydrogen and helium) is incredibly dispersed. Space is not a perfect vacuum. There are still traces of matter and energy, including dark matter and dark energy, that contribute to the overall density of space. Even a vacuum chamber is not completely devoid of matter. The best vacuum chambers still contain some residual gas molecules and other particles. A vacuum cleaner is a electrical home appliance that cleans by suction. Gravity causes matter to coalesce into stars, planets, and other celestial bodies, which reduces the density of matter in the surrounding space.
Vacuum Energy is an underlying background energy that exists in space throughout the entire Universe.
Cosmological Constant is the value of the energy density of the vacuum of space.
Zero Point - Negative Pressures - Expansion - Contraction - Virtual Particles - Anti-Matter - Black Holes - Information Paradox
False Vacuum is a metastable sector of space that appears to be a perturbative vacuum, but is unstable due to instanton effects that may tunnel to a lower energy state.
Vacuum State is the quantum state with the lowest possible energy. Generally, it contains no physical particles. Zero-point field is sometimes used as a synonym for the vacuum state of an individual quantized field. According to present-day understanding of what is called the vacuum state or the quantum vacuum, it is by no means a simple empty space. According to quantum mechanics, the vacuum state is not truly empty but instead contains fleeting electromagnetic waves and particles that pop into and out of existence. In quantum field theory the quantum vacuum state is also called the quantum vacuum or vacuum state.
Schwarzschild Metric is the solution to the Einstein field equations that describes the gravitational field outside a spherical mass, on the assumption that the electric charge of the mass, angular momentum of the mass, and universal cosmological constant are all zero.
Deriving the Schwarzschild solution describes spacetime in the vicinity of a non-rotating massive spherically-symmetric object.
Schwarzschild Radius is the radius of a sphere such that, if all the mass of an object were to be compressed within that sphere, the escape velocity from the surface of the sphere would equal the speed of light.
Vacuum Chamber is a rigid enclosure from which air and other gases are removed by a vacuum pump. This results in a low-pressure environment within the chamber, commonly referred to as a vacuum. A vacuum environment allows researchers to conduct physical experiments or to test mechanical devices which must operate in outer space (for example) or for processes such as vacuum drying or vacuum coating. Chambers are typically made of metals which may or may not shield applied external magnetic fields depending on wall thickness, frequency, resistivity, and permeability of the material used. Only some materials are suitable for vacuum use. Chambers often have multiple ports, covered with vacuum flanges, to allow instruments or windows to be installed in the walls of the chamber. In low to medium-vacuum applications, these are sealed with elastomer o-rings. In higher vacuum applications, the flanges have knife edges machined onto them, which cut into a copper gasket when the flange is bolted on. A type of vacuum chamber frequently used in the field of spacecraft engineering is a thermal vacuum chamber, which provides a thermal environment representing what a spacecraft would experience in space. Even the best vacuum chamber will still has some molecules still inside the chamber. Vacuum Sealers.
Brian Cox visits the world's biggest Vacuum Chamber - Human Universe: Episode 4 Preview - BBC Two (youtube)
Casimir effect is a physical force acting on the macroscopic boundaries of a confined space which arises from the quantum fluctuations of the field.
Feather & Hammer Drop on Moon and hit the ground at the same time (youtube) - Footage of the Apollo 15 astronaut that dropped a hammer & feather on the moon to prove Galileo's theory that in the absence of atmosphere, objects will fall at the same rate regardless of mass.
Physicists demonstrate how sound can be transmitted through vacuum. They say in space, no one can hear you scream, but in certain situations sound can be transmitted strongly across a vacuum region. A sound wave can jump or "tunnel" fully across a vacuum gap between two solids if the materials in question are piezoelectric. In such materials, vibrations (sound waves) produce an electrical response, as well, and since an electric field can exist in vacuum, it can transmit the sound waves across. The requirement is that the size of the gap is smaller than the wavelength of the sound wave. This effect works not only in audio range of frequencies (Hz-kHz), but also in ultrasound (MHz) and hypersound (GHz) frequencies, as long as the vacuum gap is made smaller as the frequencies increase.
Why do Drops of Liquid form Spheres?
Because a sphere has the smallest possible surface area for a given volume, intermolecular attractive interactions between water molecules cause the droplet to adopt a spherical shape. This maximizes the number of attractive interactions and minimizes the number of water molecules at the surface. Molecules are attracted to each other, so they naturally form the shape which minimizes the number of them that are not surrounded by others. Every molecule pulls on every molecule that's its immediate neighbor, until it gets close enough, and then it stops pulling. The system looses potential energy and transforms it into thermal energy. The sphere is the minimal potential energy configuration of the molecules. Potential Energy is defined by the relative position of molecules to each other, and the forces between them such as electromagnetic + gravitation. Bubbles are round or spherical because there is an attractive force called surface tension that pulls molecules of water into the tightest possible groupings. In a bubble, the inward surface-tension forces of the water film are exactly balanced by the outward-pushing pressure of the air inside. Adhesion and cohesion are water properties that affect every water molecule on Earth and also the interaction of water molecules with molecules of other substances. Cohesion: Water is attracted to water. Adhesion: Water is attracted to other substances. In a water molecule, the two hydrogen atoms align themselves along one side of the oxygen atom, with the result being that the oxygen side has a partial negative charge and the side with the hydrogen atoms has a partial positive charge. Thus when the positive side on one water molecule comes near the negative side of another water molecule, they attract each other and form a bond. This "bipolar" nature of water molecules gives water its cohesive nature, and thus, its stickiness and clumpability (maybe "dropability" is a better term? Meniscus is the curve in the upper surface of a liquid close to the surface of the container or another object, caused by surface tension. It can be either concave or convex, depending on the liquid and the surface. Laplace Pressure.
Bonds - Self-Assembly - Crystals
Spherical Harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations that commonly occur in science. The spherical harmonics are a complete set of orthogonal functions on the sphere, and thus may be used to represent functions defined on the surface of a sphere, just as circular functions (sines and cosines) are used to represent functions on a circle via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a central role in the group theoretic discussion of SO(3).
 Formal Charge is
the charge assigned to an atom in a
molecule, assuming that
electrons in all chemical bonds are
shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity.
When determining the best Lewis structure (or predominant resonance
structure) for a molecule, the
structure is chosen
such that the formal charge on each of the atoms is as close to zero as
possible.
Formal Charge is
the charge assigned to an atom in a
molecule, assuming that
electrons in all chemical bonds are
shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity.
When determining the best Lewis structure (or predominant resonance
structure) for a molecule, the
structure is chosen
such that the formal charge on each of the atoms is as close to zero as
possible. Why do hurricane lanterns look like that? (youtube)
Lewis Structure are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
RED 4K Video of Colorful Liquid in Space (youtube)
Bubble in physics is a round particle of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid. Due to the Marangoni effect, bubbles may remain intact when they reach the surface of the immersive substance.
Soap Bubble is a spherical layer of soap film encapsulating air or gas. The film consists of a thin sheet of water sandwiched between two layers of soap molecules. One end of each soap molecule is hydrophobic, or attracted to water. The other end consists of a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain that tends to avoid water. Surfactants are molecules, such as soaps and detergents, that reduce the surface tension of polar liquids like water. Capillary Action is the phenomenon in which liquids rise up into a narrow tube called a capillary. It results when cohesive forces, the intermolecular forces in the liquid, are weaker than adhesive forces, the attraction between a liquid and the surface of the capillary. The shape of the meniscus, the upper surface of a liquid in a tube, also reflects the balance between adhesive and cohesive forces. The viscosity of a liquid is its resistance to flow. Liquids that have strong intermolecular forces tend to have high viscosities. Soap Bubble is an extremely thin film of soapy water enclosing air that forms a hollow sphere with an iridescent surface. How to make Inverted Bubbles (youtube) - You can make a movable hole in soap film with a loop of thread. Bear Head.
Soap Film are thin layers of liquid (usually water-based) surrounded by air. For example, if two soap bubbles come into contact, they merge and a thin film is created in between. Thus, foams are composed of a network of films connected by Plateau borders. Soap films can be used as model systems for minimal surfaces, which are widely used in mathematics.
To blow bubbles that don't pop easy, add a little glycerin or corn syrup to the soap and water mixture. You can also add food coloring to give them colors. How to make DIY Bubbles that don't pop! Easy Science Experiments for kids! (youtube).
Giant Bubble Reflections in 4K | Shanks FX | PBS Digital Studios (youtube)
Surface Tension is the elastic tendency of a fluid surface which makes it acquire the least surface area possible. Surface tension allows insects (e.g. water striders), usually denser than water, to float and slide on a water surface. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). The net effect is an inward force at its surface that causes the liquid to behave as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. Thus, the surface comes under tension from the imbalanced forces, which is probably where the term "surface tension" came from. Because of the relatively high attraction of water molecules to each other through a web of hydrogen bonds, water has a higher surface tension (72.8 millinewtons per meter at 20 °C) than most other liquids. Surface tension is an important factor in the phenomenon of capillarity. Surface tension has the dimension of force per unit length, or of energy per unit area. The two are equivalent, but when referring to energy per unit of area, it is common to use the term surface energy, which is a more general term in the sense that it applies also to solids. In materials science, surface tension is used for either surface stress or surface energy. Surface Tension - Why are drops spherical? (youtube) - Inside a drop, each water molecule is pulled with a force by its neighboring molecules. But because of the inward force, each surface molecule contracts to form a shape that has minimum surface area which is a sphere. Surface tension is defined as the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a specific amount. Surface tension is therefore measured as energy per unit area, such as joules per square meter (J/m2) or dyne per centimeter (dyn/cm), where 1 dyn = 1 × 10−5 N. Surface tension is the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a given amount. The stronger the intermolecular interactions, the greater the surface tension.
Drop is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant drop. Drops may also be formed by the condensation of a vapor or by atomization of a larger mass of liquid.
Water Drop (image photo) - Rain Drops
Foam is an object formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid. A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the regions of gas. Soap foams are also known as suds. Solid foams can be closed-cell or open-cell. In closed-cell foam, the gas forms discrete pockets, each completely surrounded by the solid material. In open-cell foam, gas pockets connect to each other. A bath sponge is an example of an open-cell foam: water easily flows through the entire structure, displacing the air. A camping mat is an example of a closed-cell foam: gas pockets are sealed from each other so the mat cannot soak up water. Foams are examples of dispersed media. In general, gas is present, so it divides into gas bubbles of different sizes (i.e., the material is polydisperse)—separated by liquid regions that may form films, thinner and thinner when the liquid phase drains out of the system films. When the principal scale is small, i.e., for a very fine foam, this dispersed medium can be considered a type of colloid. Foam can also refer to something that is analogous to foam, such as quantum foam, polyurethane foam (foam rubber), XPS foam, polystyrene, phenolic, or many other manufactured foams.
Reticulated Foam is a very porous, low density solid foam. 'Reticulated' means like a net. Reticulated foams are extremely open foams i.e. there are few, if any, intact bubbles or cell windows. In contrast, the foam formed by soap bubbles is composed solely of intact (fully enclosed) bubbles. In a reticulated foam only the lineal boundaries where the bubbles meet (Plateau borders) remain. The solid component of a reticulated foam may be an organic polymer like polyurethane, a ceramic or a metal. These materials are used in a wide range of applications where the high porosity and large surface area are needed, including filters, catalyst supports, fuel tank inserts, and loudspeaker covers.
How do Foams Collapse? Foams play a key role in a wide range of industrial products, from foods, beverages, pharmaceuticals, cleaning products and cosmetics to material applications such as building insulation, aircraft interiors and flame-retardant barriers. They might also be an unwanted property of a product of e.g. frothing in stored chemicals during transit. From a scientific perspective, they also constitute a unique form of matter, a fine balance between the complex network of forces acting on the liquid film network that makes up its structure and the pressure of the gas trapped inside: understanding how foams behave may yield new physical insights as well as better ways to use them.
Marangoni Effect is the mass transfer along an interface between two fluids due to surface tension gradient. In the case of temperature dependence, this phenomenon may be called thermo-capillary convection (or Bénard–Marangoni convection).
What does a Snowflake look like in Zero Gravity? - Pi - Geometry - Torus - Helix
Wobbling droplets in space confirm late professor's theory. Specifically, the space station's microgravity environment illuminated the ways that water droplets oscillate and spread across solid surfaces -- knowledge that could have very earthbound applications in 3D-printing, spray cooling, and manufacturing and coating operations.
Toroidal Bubble Ring is an underwater vortex ring where an air bubble occupies the core of the vortex, forming a ring shape. The ring of air as well as the nearby water spins poloidally as it travels through the water, much like a flexible bracelet might spin when it is rolled on to a person's arm. The faster the bubble ring spins, the more stable it becomes. Bubble rings and smoke rings are both examples of vortex rings—the physics of which is still under active study in fluid dynamics. Devices have been invented which generate bubble vortex rings.
Watching water droplets merge on the International Space Station. The researchers sent four different surfaces with various roughness properties to the station, where they were mounted to a lab table. Cameras recorded the droplets as they spread and merged. The experimental results confirmed and expanded the parameter space of the Davis-Hocking model, a simple way to simulate droplets.
 The photo on right is a composite false-color image of
fire in space that looks like someone praying?
Smithsonian Mag.
The photo on right is a composite false-color image of
fire in space that looks like someone praying?
Smithsonian Mag.
Fluidized Bed is a physical phenomenon occurring when a quantity of a solid particulate substance (usually present in a holding vessel) is placed under appropriate conditions to cause a solid/fluid mixture to behave as a fluid. This is usually achieved by the introduction of pressurized fluid through the particulate medium. This results in the medium then having many properties and characteristics of normal fluids, such as the ability to free-flow under gravity, or to be pumped using fluid type technologies.
Sound in Space - Did you Hear That
Sound travels in waves like light or heat does. But in order for Humans to hear sounds, the sound needs to make molecules vibrate. In deep space, the large empty areas between stars and planets, there are no molecules to vibrate, so humans hear no sounds. But this does not mean that sounds are not present in space, or not traveling through space. Sound does exist in the form of electromagnetic vibrations that pulsate in wavelengths.
NASA Space Sounds (youtube) - Cosmic Noise
5 Most Mysterious Sounds Recorded in Space (youtube)
Shapes created by Sound - Space is not a perfect vacuum.
Fusion - Higgs Boson - Physics - Spheres of Water in Space
Acoustic Levitation is a method for suspending matter in a medium by using acoustic radiation pressure from intense sound waves in the medium.
Acoustic Radiation Pressure is the apparent pressure difference between the average pressure at a surface moving with the displacement of the wave propagation (the Lagrangian pressure) and the pressure that would have existed in the fluid of the same mean density when at rest. Numerous authors make a distinction between the phenomena of Rayleigh radiation pressure and Langevin radiation pressure.
Sonoluminescence is the emission of short bursts of light from imploding bubbles in a liquid when excited by sound.
Sounds from Around the Milky Way (youtube) - A new project using sonification turns astronomical images from NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory and other telescopes into sound. This allows users to listen to the center of the Milky Way as observed in X-ray, optical, and infrared light. As the cursor moves across the image, sounds represent the position and brightness of the sources.
Sonification is the use of non-speech audio to convey information or perceptualize data. Auditory perception has advantages in temporal, spatial, amplitude, and frequency resolution that open possibilities as an alternative or complement to visualization techniques. For example, the rate of clicking of a Geiger counter conveys the level of radiation in the immediate vicinity of the device. Though many experiments with data sonification have been explored in forums such as the International Community for Auditory Display (ICAD), sonification faces many challenges to widespread use for presenting and analyzing data. For example, studies show it is difficult, but essential, to provide adequate context for interpreting sonifications of data. Many sonification attempts are coded from scratch due to the lack of a flexible tool for sonification research and data exploration.
Black Holes
 Black Hole or Black Ball is a region of
spacetime exhibiting such strong gravitational effects that
nothing—not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as
light—can
escape from inside it.
Black Holes may be the result of collapsed stars from super
nova's or other phenomenon like the collision of neutron stars. A
black hole’s “surface,” called its event horizon, defines the boundary
where the velocity needed to escape exceeds the speed of light, which is
the speed limit of the cosmos. Matter and
radiation fall in, but they
can’t get out.
Two main classes of black holes have been extensively observed.
Stellar-mass black holes with three to
dozens of times the Sun’s mass are spread throughout our Milky Way galaxy,
while supermassive monsters weighing 100,000 to billions of solar masses
are found in the centers of most big galaxies, ours included. Astronomers
suspect there’s an in-between class called
intermediate-mass black holes, weighing 100 to more than 10,000
solar masses, but they have not been conclusively observed to date. A
stellar-mass black hole forms when a star with more than 20 solar masses
exhausts the nuclear fuel in its core and collapses under its own weight.
The collapse triggers a supernova explosion that blows off the star’s
outer layers. But if the crushed core contains more than about three times
the Sun’s mass, no known force can stop its collapse to a black hole. The
origin of supermassive black holes is poorly understood, but we know they
exist from the very earliest days of a galaxy’s lifetime. Once born, black
holes can grow by accreting matter that falls into them, including gas
stripped from neighboring stars and even other black holes.
Black Hole or Black Ball is a region of
spacetime exhibiting such strong gravitational effects that
nothing—not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as
light—can
escape from inside it.
Black Holes may be the result of collapsed stars from super
nova's or other phenomenon like the collision of neutron stars. A
black hole’s “surface,” called its event horizon, defines the boundary
where the velocity needed to escape exceeds the speed of light, which is
the speed limit of the cosmos. Matter and
radiation fall in, but they
can’t get out.
Two main classes of black holes have been extensively observed.
Stellar-mass black holes with three to
dozens of times the Sun’s mass are spread throughout our Milky Way galaxy,
while supermassive monsters weighing 100,000 to billions of solar masses
are found in the centers of most big galaxies, ours included. Astronomers
suspect there’s an in-between class called
intermediate-mass black holes, weighing 100 to more than 10,000
solar masses, but they have not been conclusively observed to date. A
stellar-mass black hole forms when a star with more than 20 solar masses
exhausts the nuclear fuel in its core and collapses under its own weight.
The collapse triggers a supernova explosion that blows off the star’s
outer layers. But if the crushed core contains more than about three times
the Sun’s mass, no known force can stop its collapse to a black hole. The
origin of supermassive black holes is poorly understood, but we know they
exist from the very earliest days of a galaxy’s lifetime. Once born, black
holes can grow by accreting matter that falls into them, including gas
stripped from neighboring stars and even other black holes.
Primary Black Holes - Dark Matter - Conservation of Energy - Entropy - Information Paradox - Uncertainty Principle - Empty Space
Primordial Black Holes are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang.
Stellar Black Hole is a black hole formed by the gravitational collapse of a star.
Supermassive Black Hole is the largest type of black hole, in the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses (M☉), and is found in the centre of almost all currently known massive galaxies. Mass is Smaller in Size but More Dense. Mass is the quantity of matter and density is mass per volume. Supermassive Black Holes could form from Dark Matter.
Exotic black holes could be a byproduct of dark matter. In the first quintillionth of a second, the universe may have sprouted microscopic black holes with enormous amounts of nuclear charge.
Not all black holes are the same. Black holes come in many different sizes. Black holes are also mostly empty space with a small solid core or singularity, a point where extremely large amounts of matter are packed and crushed into a small amount of space. The black hole is essentially a giant sphere of empty space limited by the event horizon, and in the center is a core that is spherical mass with space between the atoms and between the particles of atoms removed. Singularity.
Intermediate-Mass Black Holes. A series of studies sheds light on the origins and characteristics of intermediate-mass black holes. In the world of black holes, there are generally three size categories: stellar-mass black holes (about five to 50 times the mass of the sun), supermassive black holes (millions to billions of times the mass of the sun), and intermediate-mass black holes with masses somewhere in between.
The Milky Way's very own supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A*, is meant to be docile. It's not an active galactic nucleus and largely keeps to itself, unlike some other large black holes that rotate so fast that they bend space. Milky Way Galaxy has a Black hole about 4 million to 5 million times the mass of the sun. Sagittarius A* is a bright and very compact astronomical radio source at the center of the Milky Way, near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius. It is part of a larger astronomical feature known as Sagittarius A. Sagittarius A* is thought to be the location of a supermassive black hole. Central Molecular Zone is a region of the Milky Way Galaxy rich in an estimated 60 million solar masses (M☉) of gas within a complex of giant molecular clouds. It spans the centre of the Milky Way, and as such is in the Sagittarius constellation, between galactic longitude 1.7° and -0.7°, and latitudes -0.2° and +0.2°. Unexplained barrier blocking cosmic rays at the Milky Way's center.
Astronomers unveil strong magnetic fields spiraling at the edge of Milky Way's central black hole. A new image from the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration has uncovered strong and organized magnetic fields spiraling from the edge of the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*). Seen in polarized light for the first time, this new view of the monster lurking at the heart of the Milky Way Galaxy has revealed a magnetic field structure strikingly similar to that of the black hole at the center of the M87 galaxy, suggesting that strong magnetic fields may be common to all black holes.
Active Galactic Nucleus a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not produced by stars. Such excess non-stellar emission has been observed in the radio, microwave, infrared, optical, ultra-violet, X-ray and gamma ray wavebands. A galaxy hosting an AGN is called an "active galaxy". The non-stellar radiation from an AGN is theorized to result from the accretion of matter by a supermassive black hole at the center of its host galaxy. Active galactic nuclei are the most luminous persistent sources of electromagnetic radiation in the universe, and as such can be used as a means of discovering distant objects; their evolution as a function of cosmic time also puts constraints on models of the cosmos. The observed characteristics of an AGN depend on several properties such as the mass of the central black hole, the rate of gas accretion onto the black hole, the orientation of the accretion disk, the degree of obscuration of the nucleus by dust, and presence or absence of jets. Numerous subclasses of AGN have been defined based on their observed characteristics; the most powerful AGN are classified as quasars. A blazar is an AGN with a jet pointed toward the Earth, in which radiation from the jet is enhanced by relativistic beaming.
Center Of The Milky Way Has Thousands Of Black Holes, Study Shows. A localized increase in number—of stellar-mass black holes near a supermassive black hole is a fundamental prediction of galactic stellar dynamics.
Supermassive Black Hole Devours Star In Event Called ASASSN-14li.
Supermassive Black Hole at the Center of our Galaxy | Cosmic Journeys (youtube)
Observing Supermassive Black Holes in Virtual Reality (youtube)
Darkness Visible: Shedding New Light on Black Holes (youtube) - World Science Festival.
How to Understand the Image of a Black Hole (youtube Veritasium)
Scientists observe Supermassive Black Hole in infant Universe. Findings present a puzzle as to how such a huge object could have grown so quickly.
Which came first, Black holes or stars? Black holes not only existed at the dawn of time, they birthed new stars and supercharged galaxy formation, a new analysis of James Webb Space Telescope data suggests. black holes might have dramatically accelerated the birth of new stars during the first 50 million years of the universe, a fleeting period within its 13.8 billion -- year history.
More black holes than expected in the early universe. With the help of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, an international team of scientists has found more black holes in the early universe than has previously been reported. The new result can help scientists understand how supermassive black holes were created. Currently, scientists do not have a complete picture of how the first black holes formed not long after the big bang.
Evidence of primordial black holes may be hiding in planets, or even everyday objects here on Earth. A theoretical study suggests that small black holes born in the early universe may have left behind hollow planetoids and microscopic tunnels, and that we should start looking within rocks and old buildings for them. The research proposes thinking both big and small to confirm the existence of primordial black holes, suggesting that their signatures could range from very large -- hollow planetoids in space -- to minute -- microscopic tunnels in everyday materials found on Earth, like rocks, metal and glass. For objects without a liquid core, PBHs might simply pass through and leave behind a straight tunnel, the study proposes. For example, a PBH with a mass of 1022 grams -- that's a 10 with 22 zeros -- would leave behind a tunnel 0.1 micron thick.
Creation of black holes without singularities through pure gravity. Traditional black holes, as predicted by Albert Einstein's theory of General Relativity, contain what are known as singularities, i.e. points where the laws of physics break down. Identifying how singularities are resolved in the context of quantum gravity is one of the fundamental problems in theoretical physics. Now, a team of experts has described the creation of regular black holes from gravitational effects and without the need for the existence of exotic matter required by some previous models.
Black Hole Jets are the biggest seen yet. The jumbo jets blast hot plasma well beyond their own host galaxy. Astronomers have spotted the biggest pair of black hole jets ever seen, spanning 23 million light-years in total length. That's equivalent to lining up 140 Milky Way galaxies back to back. This massive population of gargantuan jets was found using Europe's LOFAR (LOw Frequency ARray) radio telescope.
Astrophysical Jet is an astronomical phenomenon where outflows of ionized matter are emitted as extended beams along the axis of rotation. When this greatly accelerated matter in the beam approaches the speed of light, astrophysical jets become relativistic jets as they show effects from special relativity. The formation and powering of astrophysical jets are highly complex phenomena that are associated with many types of high-energy astronomical sources. They likely arise from dynamic interactions within accretion disks, whose active processes are commonly connected with compact central objects such as black holes, neutron stars or pulsars. One explanation is that tangled magnetic fields are organized to aim two diametrically opposing beams away from the central source by angles only several degrees wide (c. > 1%). Jets may also be influenced by a general relativity effect known as frame-dragging.
Dropping a magnet through a copper tube. As the magnet falls it induces a current in the copper pipe. That current creates a magnetic field that opposes the changing field of the falling magnet, resulting in the magnet being repelled (falling more slowly). This is Lenz's law.
Scientists announce discovery of supermassive binary black holes. Two black holes orbiting one another eventually will merge. The two black holes, which orbit each other, likely weigh 100 million suns each. One of the black holes powers a massive jet that moves outward at very close to the speed of light. The system is so far away that the visible light seen today was emitted 8.8 billion years ago.
New discovery sheds light on very early supermassive black holes. Astronomers have discovered a rapidly growing black hole in one of the most extreme galaxies known in the very early Universe. The discovery of the galaxy and the black hole at its center provides new clues on the formation of the very first supermassive black holes. Using observations taken with the Atacama Large Millimeter Array, a radio observatory sited in Chile, the team have determined that the galaxy, named COS-87259, containing this new supermassive black hole is very extreme, forming stars at a rate 1000 times that of our own Milky Way and containing over a billion solar masses worth of interstellar dust. The galaxy shines bright from both this intense burst of star formation and the growing supermassive black hole at its centre.
Time duration changes from black holes.
Astronomers discover the fastest-feeding black hole in the early universe. Astronomers have discovered a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang that is consuming matter at a phenomenal rate -- over 40 times the theoretical limit. While short lived, this black hole's 'feast' could help astronomers explain how supermassive black holes grew so quickly in the early Universe.
Machine learning reveals how black holes grow. Black holes are surrounded by an invisible layer that swallows every bit of evidence about their past. Researchers are now using machine learning and supercomputers to reconstruct the growth histories of black holes.
What makes black holes grow and new stars form? It takes more than a galaxy merger to make a black hole grow and new stars form: machine learning shows cold gas is needed too to initiate rapid growth -- new research finds.
Sleeping supermassive black holes awakened briefly by shredded stars. Radio observations from Astronomers have concluded that an obscure class of galaxies known as Compact Symmetric Objects, or CSOs, are not young as previously thought but rather lead relatively short lives.
Dormant Black Hole found outside our galaxy. Dormant black holes are particularly hard to spot since they do not interact much with their surroundings. Stellar-mass black holes are formed when massive stars reach the end of their lives and collapse under their own gravity. In a binary, a system of two stars revolving around each other, this process leaves behind a black hole in orbit with a luminous companion star. The black hole is 'dormant' if it does not emit high levels of X-ray radiation, which is how such black holes are typically detected. "It is incredible that we hardly know of any dormant black holes, given how common astronomers believe them to be," explains co-author Pablo Marchant of KU Leuven. The newly found black hole is at least nine times the mass of our Sun, and orbits a hot, blue star weighing 25 times the Sun's mass. (VFTS 243).
Runaway black hole creating a trail of stars. There's an invisible monster on the loose, barreling through intergalactic space so fast that if it were in our solar system, it could travel from Earth to the Moon in 14 minutes. This supermassive black hole, weighing as much as 20 million Suns, has left behind a never-before-seen 200,000-light-year-long 'contrail' of newborn stars, twice the diameter of our Milky Way galaxy. It's likely the result of a rare, bizarre game of galactic billiards among three massive black holes. Rather than gobbling up stars ahead of it, like a cosmic Pac-Man, the speedy black hole is plowing into gas in front of it to trigger new star formation along a narrow corridor. The black hole is streaking too fast to take time for a snack. Nothing like it has ever been seen before, but it was captured accidentally by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope.
Could this copycat black hole be a new type of star? It looks like a black hole and bends light like a black hole, but it could actually be a new type of star. Though the mysterious object is a hypothetical mathematical construction, new simulations by Johns Hopkins researchers suggest there could be other celestial bodies in space hiding from even the best telescopes on Earth.
New proof for black hole spin. The supermassive black hole at the heart of galaxy M87, made famous by the first picture of a black hole shadow, has yielded another first: the jet shooting out from the black hole has been confirmed to wobble, providing direct proof that the black hole is spinning.
Quantum tornado provides gateway to understanding black holes. Scientists have created a giant quantum vortex to mimic a black hole in superfluid helium that has allowed them to see in greater detail how analogue black holes behave and interact with their surroundings.
The case of the missing black holes. New model aims to explain the lack of miniature black holes in the early universe. Researchers have applied the well-understood and highly verified quantum field theory, usually applied to the study of the very small, to a new target, the early universe. Their exploration led to the conclusion that there ought to be far fewer miniature black holes than most models suggest, though observations to confirm this should soon be possible. The specific kind of black hole in question could be a contender for dark matter.
Hawking Radiation is black body radiation that is theorized to be released outside a black hole's event horizon because of relativistic quantum effects. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who developed a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974. Hawking radiation is a purely kinematic effect that is generic to Lorentzian geometries containing event horizons or local apparent horizons. Hawking radiation reduces the mass and rotational energy of black holes and is therefore also theorized to cause black hole evaporation. Because of this, black hole's that do not gain mass through other means are expected to shrink and ultimately vanish. For all except the smallest black holes, this would happen extremely slowly. The radiation temperature is inversely proportional to the black hole's mass, so micro black holes are predicted to be larger emitters of radiation than larger black holes and should dissipate faster.
Explanation found for X-ray radiation from black holes. The radiation originates from the combined effect of the chaotic movements of magnetic fields and turbulent plasma gas. Using detailed supercomputer simulations, researchers at the University of Helsinki modeled the interactions between radiation, plasma, and magnetic fields around black holes. It was found that the chaotic movements, or turbulence, caused by the magnetic fields heat the local plasma and make it radiate.
What’s inside a Black Hole? In the study, the scientists were able to determine the mathematical description of the quantum state of the matrix model. Scientists relied on the holographic principle, which suggests that the two existing theories – particles and gravity – are equivalent to each other. The complexity of ideas lies in the fact that they are built in different dimensions. Both theories explain various dimensions, but they differ by one in the number of dimensions they describe. So, for example, gravity exists in three dimensions inside the geometry of a black hole, but particle physics lives in two dimensions on its surface—a flat disk. Consider the black hole, which, due to its massive mass, warps space-time. The black hole’s gravity, which exists in three dimensions, mathematically connects to the particles dancing above it, which exist in two dimensions. As a result, a black hole exists in three-dimensional space but is perceived as a projection of particles. Some scientists claim our entire universe is a holographic representation of particles, and this could lead to a consistent quantum explanation of gravity.
Plunging Region of a black hole is an area where matter stops circling a black hole and instead falls straight in. Plunging regions sit just outside of black holes' event horizons — points of no return where gravity becomes so strong that not even light can escape.
Quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus, in which a supermassive black hole with mass ranging from millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun is surrounded by a gaseous accretion disk. As gas in the disk falls towards the black hole, energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation, which can be observed across the electromagnetic spectrum. The power radiated by quasars is enormous: the most powerful quasars have luminosities thousands of times greater than a galaxy such as the Milky Way.
Closest-known black hole to Earth, roughly 1,000 light-years away. They found it hiding in a double-star system known as HR 6819. The black hole is not anywhere near close enough for the average observer on Earth to feel its effects, to be absolutely clear. But it is close enough that, during winter in the southern hemisphere, the two stars that are believed to compose its solar system can be seen without a telescope as a single point of light in the constellation Telescopium.
Astronomers find fastest-growing black hole known in space that devours a mass equivalent to our sun every two days.
Hubble uncovers black hole that shouldn't exist. Astronomers have found an unexpected thin disk of material furiously whirling around a supermassive black hole at the heart of the magnificent spiral galaxy NGC 3147, located 130 million light-years away.
Astronomers find wandering massive black holes in dwarf galaxies, discovery of 13 such black holes in dwarf galaxies less than a billion light-years from Earth. These dwarf galaxies, more than 100 times less massive than our own Milky Way, are among the smallest galaxies known to host massive black holes.
Binary Black Hole is a system consisting of two black holes in close orbit around each other. Like black holes themselves, binary black holes are often divided into stellar binary black holes, formed either as remnants of high-mass binary star systems or by dynamic processes and mutual capture, and binary supermassive black holes believed to be a result of galactic mergers.
White Hole is a hypothetical region of spacetime which cannot be entered from the outside, although matter and light can escape from it. In this sense, it is the reverse of a black hole, which can only be entered from the outside and from which matter and light cannot escape. White holes appear in the theory of eternal black holes. In addition to a black hole region in the future, such a solution of the Einstein field equations has a white hole region in its past. What Are White Holes? (youtube).
Accretion Disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffused material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction causes orbiting material in the disk to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational and frictional forces compress and raise the temperature of the material, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The frequency range of that radiation depends on the central object's mass. Accretion disks of young stars and protostars radiate in the infrared; those around neutron stars and black holes in the X-ray part of the spectrum. The study of oscillation modes in accretion disks is referred to as diskoseismology.
Event Horizon is a boundary in spacetime beyond which events cannot affect an outside observer.
Magnetorotational Instability is a fluid instability that causes an accretion disk orbiting a massive central object to become turbulent. It arises when the angular velocity of a conducting fluid in a magnetic field decreases as the distance from the rotation center increases.
Ergosphere is a region located outside a rotating black hole's outer event horizon. It is theoretically possible to extract energy and mass from this region. The ergosphere touches the event horizon at the poles of a rotating black hole and extends to a greater radius at the equator. With a low spin of the central mass the shape of the ergosphere can be approximated by an oblated spheroid, while with higher spins it resembles a pumpkin-shape.
Frame-Dragging is an effect on spacetime, predicted by Einstein's general theory of relativity, that is due to non-static stationary distributions of mass–energy. A stationary field is one that is in a steady state, but the masses causing that field may be non-static, rotating, for instance. More generally, the subject that deals with the effects caused by mass–energy currents is known as gravitomagnetism, which is analogous to classical electromagnetism. The first frame-dragging effect was derived in 1918, in the framework of general relativity, by the Austrian physicists Josef Lense and Hans Thirring, and is also known as the Lense–Thirring effect. They predicted that the rotation of a massive object would distort the spacetime metric, making the orbit of a nearby test particle precess. This does not happen in Newtonian mechanics for which the gravitational field of a body depends only on its mass, not on its rotation. The Lense–Thirring effect is very small—about one part in a few trillion. To detect it, it is necessary to examine a very massive object, or build an instrument that is very sensitive. In 2015, new general-relativistic extensions of Newtonian rotation laws were formulated to describe geometric dragging of frames which incorporates a newly discovered antidragging effect.
Black-Hole Thermodynamics is the area of study that seeks to reconcile the laws of thermodynamics with the existence of black-hole event horizons. As the study of the statistical mechanics of black-body radiation led to the advent of the theory of quantum mechanics, the effort to understand the statistical mechanics of black holes has had a deep impact upon the understanding of quantum gravity, leading to the formulation of the holographic principle.
Black Holes' Magnetism Surprisingly Wimpy.
Penrose Process is a process theorised by Roger Penrose wherein energy can be extracted from a rotating black hole.
Blandford-Znajek Process is a mechanism for the extraction of energy from a rotating black hole.
Kugelblitz in astrophysics is a concentration of light so intense that it forms an event horizon and becomes self-trapped: according to general relativity, if enough radiation is aimed into a region, the concentration of energy can warp spacetime enough for the region to become a black hole (although this would be a black hole whose original mass-energy had been in the form of radiant energy rather than matter). In simpler terms, a kugelblitz is a black hole formed from radiation as opposed to matter. According to Einstein's general theory of relativity, once an event horizon has formed, the type of energy that created it no longer matters. A kugelblitz is so hot it surpasses the Planck temperature, the temperature of the universe 5.4×10−44 seconds after The Big Bang.
The Big Star that couldn’t become a Supernova. Ohio State University watched a star disappear and possibly become a black hole. Instead of becoming a black hole through the expected process of a supernova, the black hole candidate formed through a "failed supernova."
Centripetal Force is a force that makes a body follow a curved path. Its direction is always orthogonal to the motion of the body and towards the fixed point of the instantaneous center of curvature of the path. Magnetism.
Are black holes a type of super-magnet made up of magnetite, with one side sucking in matter, and the other side expanding the universe?
Magnetic structures near supermassive black hole. A new view of the region closest to the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy Messier 87 or M87 has shown important details of the magnetic fields close to the black hole and hints about how powerful jets of material can originate in that region. The individual telescopes involved are: ALMA, APEX, the Institut de Radioastronomie Millimetrique (IRAM) 30-meter Telescope, the IRAM NOEMA Observatory, the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT), the Large Millimeter Telescope (LMT), the Submillimeter Array (SMA), the Submillimeter Telescope (SMT), the South Pole Telescope (SPT), the Kitt Peak Telescope, and the Greenland Telescope (GLT).
Astronomers Observe Evolution Of A Black Hole As It Wolfs Down Stellar. X-ray pulse detected near event horizon as black hole devours star. Pulse pattern suggests distant black hole must be spinning at least at 50 percent the speed of light.
It takes only a day for the black hole to shred the star in a process known as tidal disruption, and only about a year for the resulting fragments to pull themselves back together. This is in contrast to the millions of years required to create a planet like Jupiter from scratch. Once launched at 20 million miles per hour, it would take about a million years for one of these objects to reach Earth's neighborhood. The challenge will be to tell it apart from free-floating planets that are created during the more mundane process of star and planet formation. Harvard Smithsonian Center or Astrophysics.
Star devoured by a black hole is the closest such flare recorded to date at just over 215 million light-years from Earth, and has been studied in unprecedented detail.
Tidal Disruption Event is an astronomical phenomenon that occurs when a star approaches sufficiently close to a supermassive black hole and is pulled apart by the black hole's tidal force, experiencing spaghettification. A portion of the star's mass can be captured into an accretion disk around the black hole, resulting in a temporary flare of electromagnetic radiation as matter in the disk is consumed by the black hole. According to early papers, tidal disruption events should be an inevitable consequence of massive black holes' activity hidden in galaxy nuclei, whereas later theorists concluded that the resulting explosion or flare of radiation from the accretion of the stellar debris could be a unique signpost for the presence of a dormant black hole in the center of a normal galaxy.
Spaghettification is the vertical stretching and horizontal compression of objects into long thin shapes (rather like spaghetti) in a very strong non-homogeneous gravitational field; it is caused by extreme tidal forces. In the most extreme cases, near black holes, the stretching is so powerful that no object can withstand it, no matter how strong its components. Within a small region the horizontal compression balances the vertical stretching so that small objects being spaghettified experience no net change in volume.
CO-0.40-0.22 is 200 light years away from the central molecular zone, about 25,000 to 28,000 Light Years from Earth.
A black hole 12 billion times as massive as the sun has been found in a glowing quasar that existed when the universe was just a fraction of its current age using data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, the Two Micron All-Sky Survey, and the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. This black hole-quasar combo is estimated to exist 12.8 billion light years away.
PKS 1302-102 is a pair of supermassive black holes located in the Virgo Constellation, some 3.5 billion light-years away. These two supermassive black holes are in the process of merging, and are 180 billion miles (2.9×1011 km) apart. They are anticipated to merge within about a million years. I can't wait!
 Black Hole Information Paradox
suggests that physical information could permanently disappear in a
black
hole, allowing many physical states to devolve into the same state. This
is controversial because it violates a commonly assumed tenet of
science—that in principle complete information about a
physical system at
one point in time should determine its state at any other time. A
fundamental postulate of quantum mechanics is that complete information
about a system is encoded in its wave function up to when the
wave
function collapses. The evolution of the wave function is determined by a
unitary operator, and unitarity implies that information is conserved in the quantum sense.
Black Hole Information Paradox
suggests that physical information could permanently disappear in a
black
hole, allowing many physical states to devolve into the same state. This
is controversial because it violates a commonly assumed tenet of
science—that in principle complete information about a
physical system at
one point in time should determine its state at any other time. A
fundamental postulate of quantum mechanics is that complete information
about a system is encoded in its wave function up to when the
wave
function collapses. The evolution of the wave function is determined by a
unitary operator, and unitarity implies that information is conserved in the quantum sense.
Information Paradox (image) - Conservation of Energy - Uncertainty Principle
Hayden-Preskill thought experiment is a thought experiment that investigates the black hole information paradox by hypothesizing on how long it takes to decode information thrown in a black hole from its Hawking Radiation. The thought experiment concerning Alice and Bob is as follows: Alice throws a k qubit quantum state into a black hole that is entangled with Bob's quantum computer. Bob collects the Hawking radiation emitted by the Black hole and feeds it into his quantum computer where he applies the appropriate quantum gates that will decode Alice's state. Bob only needs at least k qubits from the black hole's Hawking radiation to decode Alice's quantum state. The black hole can be thought of as a quantum information mirror, because it returns scrambled information almost instantly. With a delay that can be account for by the scrambling time and the time it takes for the black hole to radiate the qubits. This decoding method, known as the Yoshida-Kitaev decoding scheme, can theoretically be applied to a small system thermalized with a large system. This opens up the possibility of testing the Hayden-Preskill thought experiment in real life.
Black holes do not destroy matter. Matter that had entered the black hole previously leaves in the form of energy via Hawking radiation. Hawking and Bekensteain showed that black holes could lose energy by radiation, following along the second law of thermodynamics. Mass-energy equivalence also remains, so any matter that had previously entered can leave in the form of matter particles moving at the speed of light. However, there is a much bigger issue at stake here, whether black holes destroy information. The no-hair theorem says that information that enters a black hole can never return to the universe and is lost forever. Only observers that passed the event horizon could observe the information, but no observer outside the event horizon could because of the no-hair theorem. Furthermore, the observer that passed the event horizon is also lost to the universe, so the observer could never be able to communicate about the information from beyond the event horizon. The only exceptions to the loss of information are mass, electric charge, and angular momentum. All black hole solutions to Einstein’s field equations and the relativistic form of Maxwell’s equations allow for mass, electric charge, and angular momentum to be measured external of the event horizon. All other information is lost.
No-Hair Theorem states that all stationary black hole solutions of the Einstein–Maxwell equations of gravitation and electromagnetism in general relativity can be completely characterized by only three independent externally observable classical parameters: mass, electric charge, and angular momentum. Other characteristics (such as geometry and magnetic moment) are uniquely determined by these three parameters, and all other information (for which "hair" is a metaphor) about the matter that formed a black hole or is falling into it "disappears" behind the black-hole event horizon and is therefore permanently inaccessible to external observers after the black hole "settles down" (by emitting gravitational and electromagnetic waves). Physicist John Archibald Wheeler expressed this idea with the phrase "black holes have no hair", which was the origin of the name.
No-Hiding Theorem states that if information is lost from a system via decoherence, then it moves to the subspace of the environment and it cannot remain in the correlation between the system and the environment. This is a fundamental consequence of the linearity and unitarity of quantum mechanics. Thus, information is never lost. This has implications in black hole information paradox and in fact any process that tends to lose information completely. The no-hiding theorem is robust to imperfection in the physical process that seemingly destroys the original information. The law of conservation of energy states that the energy of a closed system must remain constant. It can neither increase nor decrease without coming in contact with an external system. If we consider the whole universe as a closed system, the total amount of energy always remains the same. However, the form of energy keeps changing. One may wonder if there is any such law for the conservation of information. In the classical world, information can be copied and deleted perfectly. In the quantum world, however, the conservation of quantum information should mean that information cannot be created nor destroyed. This concept stems from two fundamental theorems of quantum mechanics: the no-cloning theorem and the no-deleting theorem. But the no-hiding theorem is the ultimate proof of the conservation of quantum information. The importance of the no-hiding theorem is that it proves the conservation of wave function in quantum theory. This had never been proved earlier. What was known before is that the conservation of entropy holds for a quantum system undergoing unitary time evolution and if entropy represents information in quantum theory, then it is believed then that information should somehow be conserved. For example, one can prove that pure states remain pure states and probabilistic combination of pure states (called as mixed states) remain mixed states under unitary evolution. However, it was never proved that if the probability amplitude disappears from one system, it will reappear in another system. Thus, one may say that as energy keeps changing its form, the wave function keep moving from one Hilbert space to another Hilbert space. Since the wave function contains all the relevant information about a physical system, the conservation of wave function is tantamount to conservation of quantum information.
No-Cloning Theorem states that it is impossible to create an independent and identical copy of an arbitrary unknown quantum state, a statement which has profound implications in the field of quantum computing among others.
No-Deleting Theorem of quantum information theory is a no-go theorem which states that, in general, given two copies of some arbitrary quantum state, it is impossible to delete one of the copies. It is a time-reversed dual to the no-cloning theorem, which states that arbitrary states cannot be copied. This theorem seems remarkable, because, in many senses, quantum states are fragile; the theorem asserts that, in a particular case, they are also robust.
Quantum machine learning hits a limit. A black hole permanently scrambles information that can't be recovered with any quantum machine learning algorithm, shedding new light on the classic Hayden-Preskill thought experiment. A new theorem from the field of quantum machine learning has poked a major hole in the accepted understanding about information scrambling.
Data Remanence is the residual representation of digital data that remains even after attempts have been made to remove or erase the data. This residue may result from data being left intact by a nominal file deletion operation, by reformatting of storage media that does not remove data previously written to the media, or through physical properties of the storage media that allow previously written data to be recovered. Data remanence may make inadvertent disclosure of sensitive information possible should the storage media be released into an uncontrolled environment (e.g., thrown in the trash or lost). Entropy.
Firewall in physics is a hypothetical phenomenon where an observer that falls into an old black hole encounters high-energy quanta at (or near) the event horizon.
Information Backup (knowledge preservation)
Big Bounce is a hypothetical scientific model of the formation of the known universe. It was originally suggested as a property of the cyclic model or oscillatory universe interpretation of the Big Bang where the first cosmological event was the result of the collapse of a previous universe; however, it is also a consequence of applying loop quantum gravity techniques to Big Bang cosmology and this need not be cyclic. Big Bang.
Radiation - Radioactive Decay
 Radioactive
Decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy
(in terms of mass in its rest frame) by emitting radiation, such as an
alpha particle, beta particle with neutrino
or only a neutrino in the case of electron capture, gamma ray, or electron in the case of
internal
conversion. A material containing such unstable nuclei is considered
radioactive. Certain highly excited short-lived
nuclear states can decay
through neutron emission, or more rarely, proton emission. Radioactive
decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) process at the level of single atoms,
in that, according to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a
particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the
atom has existed.
However, for a collection of atoms, the collection's expected decay rate
is characterized in terms of their measured decay constants or
half-lives.
This is the basis of radiometric dating. The half-lives of radioactive
atoms have no known upper limit, spanning a time range of over 55 orders
of magnitude, from nearly instantaneous to far longer than the age of the
universe. Radioactive decay is the spontaneous breakdown of an atomic
nucleus resulting in the release of energy and matter from the nucleus.
Remember that a radioisotope has unstable nuclei that does not have enough
binding energy to hold the nucleus together.
Matter can be
recreated and also be
diminished?
Radioactive
Decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy
(in terms of mass in its rest frame) by emitting radiation, such as an
alpha particle, beta particle with neutrino
or only a neutrino in the case of electron capture, gamma ray, or electron in the case of
internal
conversion. A material containing such unstable nuclei is considered
radioactive. Certain highly excited short-lived
nuclear states can decay
through neutron emission, or more rarely, proton emission. Radioactive
decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) process at the level of single atoms,
in that, according to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a
particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the
atom has existed.
However, for a collection of atoms, the collection's expected decay rate
is characterized in terms of their measured decay constants or
half-lives.
This is the basis of radiometric dating. The half-lives of radioactive
atoms have no known upper limit, spanning a time range of over 55 orders
of magnitude, from nearly instantaneous to far longer than the age of the
universe. Radioactive decay is the spontaneous breakdown of an atomic
nucleus resulting in the release of energy and matter from the nucleus.
Remember that a radioisotope has unstable nuclei that does not have enough
binding energy to hold the nucleus together.
Matter can be
recreated and also be
diminished?
Decomposition - Exponential Decay - Conservation - Plasma - Dosage
Particle Decay is the spontaneous process of one unstable subatomic particle transforming into multiple other particles. The particles created in this process (the final state) must each be less massive than the original, although the total invariant mass of the system must be conserved. A particle is unstable if there is at least one allowed final state that it can decay into. Unstable particles will often have multiple ways of decaying, each with its own associated probability. Decays are mediated by one or several fundamental forces. The particles in the final state may themselves be unstable and subject to further decay. The term is typically distinct from radioactive decay, in which an unstable atomic nucleus is transformed into a lighter nucleus accompanied by the emission of particles or radiation, although the two are conceptually similar and are often described using the same terminology.
Internal Conversion is a radioactive decay process wherein an excited nucleus interacts electromagnetically with one of the orbital electrons of the atom. This causes the electron to be emitted (ejected) from the atom. Thus, in an internal conversion process, a high-energy electron is emitted from the radioactive atom, but not from the nucleus. For this reason, the high-speed electrons resulting from internal conversion are not called beta particles, since the latter come from beta decay, where they are newly created in the nuclear decay process. Internal conversion is possible whenever gamma decay is possible, except in the case where the atom is fully ionized. During internal conversion, the atomic number does not change, and thus (as is the case with gamma decay) no transmutation of one element to another takes place. Since an electron is lost from the atom, a hole appears in an electron shell which is subsequently filled by other electrons that descend to that empty, lower energy level, and in the process emit characteristic X-ray(s), Auger electron(s), or both. The atom thus emits high-energy electrons and X-ray photons, none of which originate in that nucleus. The atom supplied the energy needed to eject the electron, which in turn caused the latter events and the other emissions. Since primary electrons from internal conversion carry a fixed (large) part of the characteristic decay energy, they have a discrete energy spectrum, rather than the spread (continuous) spectrum characteristic of beta particles. Whereas the energy spectrum of beta particles plots as a broad hump, the energy spectrum of internally converted electrons plots as a single sharp peak (see example below).
Radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes: electromagnetic radiation, such as heat, radio waves, visible light, x-rays, and gamma radiation (?). Particle radiation, such as alpha radiation (a), beta radiation (ß), and neutron radiation (particles of non-zero rest energy). Acoustic radiation, such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves (dependent on a physical transmission medium). Gravitational radiation, radiation that takes the form of gravitational waves, or ripples in the curvature of spacetime. Radiation is often categorized as either ionizing or non-ionizing depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 eV, which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules, and break chemical bonds. This is an important distinction due to the large difference in harmfulness to living organisms. A common source of ionizing radiation is radioactive materials that emit a, ß, or ? radiation, consisting of helium nuclei, electrons or positrons, and photons, respectively. Other sources include X-rays from medical radiography examinations and muons, mesons, positrons, neutrons and other particles that constitute the secondary cosmic rays that are produced after primary cosmic rays interact with Earth's atmosphere. Gamma rays, X-rays and the higher energy range of ultraviolet light constitute the ionizing part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The lower-energy, longer-wavelength part of the spectrum including visible light, infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves is non-ionizing; its main effect when interacting with tissue is heating. This type of radiation only damages cells if the intensity is high enough to cause excessive heating. Ultraviolet Radiation has some features of both ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. While the part of the ultraviolet spectrum that penetrates the Earth's atmosphere is non-ionizing, this radiation does far more damage to many molecules in biological systems than can be accounted for by heating effects, sunburn being a well-known example. These properties derive from ultraviolet's power to alter chemical bonds, even without having quite enough energy to ionize atoms. The word radiation arises from the phenomenon of waves radiating (i.e., traveling outward in all directions) from a source. This aspect leads to a system of measurements and physical units that are applicable to all types of radiation. Because such radiation expands as it passes through space, and as its energy is conserved (in vacuum), the intensity of all types of radiation from a point source follows an inverse-square law in relation to the distance from its source. This law does not apply close to an extended source of radiation or for focused beams. The Radioactivity of Space - Frances Staples (youtube).
Radionuclide is an atom that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are powerful enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single element the decay rate, and thus the half-life (t1/2) for that collection can be calculated from their measured decay constants. The range of the half-lives of radioactive atoms have no known limits and span a time range of over 55 orders of magnitude.
Black-Body Radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body), assumed for the sake of calculations and theory to be held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body. Infrared.
Black Body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. A white body is one with a "rough surface [that] reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions. Black Holes.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation is electromagnetic radiation left over from an early stage of the universe in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or "relic radiation". The CMB is a faint cosmic background radiation filling all space that is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination.
Cosmic Noise is random noise that originates outside the Earth's atmosphere. It can be detected and heard in radio receivers. Cosmic noise characteristics are similar to those of thermal noise. Cosmic noise is experienced at frequencies above about 15 MHz when highly directional antennas are pointed toward the sun or to certain other regions of the sky such as the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. Celestial objects like quasars, super dense objects that lie far from Earth, emit electromagnetic waves in its full spectrum including radio waves. We can also hear the fall of a meteorite in a radio receiver; the falling object burns from friction with the Earth's atmosphere, ionizing surrounding gases and producing radio waves. Cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) from outer space, discovered by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, who later won the Nobel Prize for this discovery, is also a form of cosmic noise. CMBR is thought to be a relic of the Big Bang, and pervades the space almost homogeneously over the entire celestial sphere. The bandwidth of the CMBR is wide, though the peak is in the microwave range.
Electromagnetic Radiation refers to the waves (or their quanta, photons) of the electromagnetic field, propagating (radiating) through space, carrying electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, commonly denoted c. In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. The wavefront of electromagnetic waves emitted from a point source (such as a light bulb) is a sphere. The position of an electromagnetic wave within the electromagnetic spectrum can be characterized by either its frequency of oscillation or its wavelength. Electromagnetic waves of different frequency are called by different names since they have different sources and effects on matter. In order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. Electromagnetic waves are emitted by electrically charged particles undergoing acceleration, and these waves can subsequently interact with other charged particles, exerting force on them. EM waves carry energy, momentum and angular momentum away from their source particle and can impart those quantities to matter with which they interact. Electromagnetic radiation is associated with those EM waves that are free to propagate themselves ("radiate") without the continuing influence of the moving charges that produced them, because they have achieved sufficient distance from those charges. Thus, EMR is sometimes referred to as the far field. In this language, the near field refers to EM fields near the charges and current that directly produced them, specifically electromagnetic induction and electrostatic induction phenomena. In quantum mechanics, an alternate way of viewing EMR is that it consists of photons, uncharged elementary particles with zero rest mass which are the quanta of the electromagnetic force, responsible for all electromagnetic interactions. Quantum electrodynamics is the theory of how EMR interacts with matter on an atomic level. Quantum effects provide additional sources of EMR, such as the transition of electrons to lower energy levels in an atom and black-body radiation. The energy of an individual photon is quantized and is greater for photons of higher frequency. This relationship is given by Planck's equation E = hν, where E is the energy per photon, ν is the frequency of the photon, and h is Planck's constant. A single gamma ray photon, for example, might carry ~100,000 times the energy of a single photon of visible light. The effects of EMR upon chemical compounds and biological organisms depend both upon the radiation's power and its frequency. EMR of visible or lower frequencies (i.e., visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves) is called non-ionizing radiation, because its photons do not individually have enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules or break chemical bonds. The effects of these radiations on chemical systems and living tissue are caused primarily by heating effects from the combined energy transfer of many photons. In contrast, high frequency ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays are called ionizing radiation, since individual photons of such high frequency have enough energy to ionize molecules or break chemical bonds. These radiations have the ability to cause chemical reactions and damage living cells beyond that resulting from simple heating, and can be a health hazard.
Nuclear Energy - Nuclear Bombs
Ionizing Radiation is radiation that carries enough energy to free electrons from atoms or molecules, thereby ionizing them. Ionizing radiation is made up of energetic subatomic particles, ions or atoms moving at high speeds (usually greater than 1% of the speed of light), and electromagnetic waves on the high-energy end of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Gamma Ray is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves and so imparts the highest photon energy.
Perovskite can detect gamma rays. Perovskites are materials made up of organic compounds bound to a metal. Propelled into the forefront of materials' research because of their structure and properties, perovskites are earmarked for a wide range of applications, including in solar cells, LED lights, lasers, and photodetectors. Gamma-rays are a kind of penetrating electromagnetic radiation that is produced from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei, e.g., in nuclear or even supernovae explosions. Gamma-rays are on the shortest end of the electromagnetic spectrum, which means that they have the highest frequency and the highest energy. Because of this, they can penetrate almost any material, and are used widely in homeland security, astronomy, industry, nuclear power plants, environmental monitoring, research, and even medicine, for detecting and monitoring tumors and osteoporosis.
Cosmic Rays are high-energy protons and atomic nuclei which move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the sun and from outside of the solar system, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with the Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays can produce showers of secondary particles that sometimes reach the surface. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidence that a significant fraction of primary cosmic rays originate from the supernova explosions of stars. Active galactic nuclei also appear to produce cosmic rays, based on observations of neutrinos and gamma rays from blazar TXS 0506+056 in 2018. Cosmic Rays are high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System. Upon impact with the Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays can produce showers of secondary particles that sometimes reach the surface. Composed primarily of high-energy protons and atomic nuclei, they are of mysterious origin. Data from the Fermi space telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidence that a significant fraction of primary cosmic rays originate from the supernovae explosions of stars. Active galactic nuclei probably also produce cosmic rays. Cosmic Ray are high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System. Aurora - Earth Magnetic Field - Lightning.
The Whole Universe seems to be filled Cosmic Rays. The earth is just a spec of dust in our solar system, and we're getting bombarded continually by cosmic rays. It's like we are living inside a huge practical accelerator. Apostle Islands National Lakeshore.
Cosmic-Ray Observatory is a scientific installation built to detect high-energy-particles coming from space called cosmic rays. This typically includes photons (high-energy light), electrons, protons, and some heavier nuclei, as well as antimatter particles. About 90% of cosmic rays are protons, 9% are alpha particles, and the remaining ~1% are other particles.
A new discovery about the source of the vast energy in cosmic rays. Ultra-high energy cosmic rays, which emerge in extreme astrophysical environments -- like the roiling environments near black holes and neutron stars -- have far more energy than the energetic particles that emerge from our sun. In fact, the particles that make up these streams of energy have around 10 million times the energy of particles accelerated in the most extreme particle environment on earth, the human-made Large Hadron Collider.
Pierre Auger Observatory is an international cosmic ray observatory in Argentina designed to detect ultra-high-energy cosmic rays: sub-atomic particles traveling nearly at the speed of light and each with energies beyond 1018 eV. In Earth's atmosphere such particles interact with air nuclei and produce various other particles. These effect particles (called an "air shower") can be detected and measured. But since these high energy particles have an estimated arrival rate of just 1 per km2 per century, the Auger Observatory has created a detection area of 3,000 km2 (1,200 sq mi)—the size of Rhode Island, or Luxembourg—in order to record a large number of these events. It is located in the western Mendoza Province, Argentina, near the Andes.
Cloud Chamber is a particle detector used for visualizing the passage of ionizing radiation. A cloud chamber consists of a sealed environment containing a supersaturated vapor of water or alcohol. An energetic charged particle (for example, an alpha or beta particle) interacts with the gaseous mixture by knocking electrons off gas molecules via electrostatic forces during collisions, resulting in a trail of ionized gas particles. The resulting ions act as condensation centers around which a mist-like trail of small droplets form if the gas mixture is at the point of condensation. These droplets are visible as a "cloud" track that persists for several seconds while the droplets fall through the vapor. These tracks have characteristic shapes. For example, an alpha particle track is thick and straight, while an electron track is wispy and shows more evidence of deflections by collisions.
Spark Chamber is a particle detector device used in particle physics for detecting electrically charged particles. They were most widely used as research tools from the 1930s to the 1960s and have since been superseded by other technologies such as drift chambers and silicon detectors. Today, working spark chambers are mostly found in science museums and educational organisations, where they are used to demonstrate aspects of particle physics and astrophysics. Spark chambers consist of a stack of metal plates placed in a sealed box filled with a gas such as helium, neon or a mixture of the two. When a charged particle from a cosmic ray travels through the box, it ionises the gas between the plates. Ordinarily this ionisation would remain invisible. However, if a high enough voltage can be applied between each adjacent pair of plates before that ionisation disappears, then sparks can be made to form along the trajectory taken by the ray, and the cosmic ray in effect becomes visible as a line of sparks. In order to control when this voltage is applied, a separate detector (often containing a pair of scintillators placed above and below the box) is needed. When this trigger senses that a cosmic ray has just passed, it fires a fast switch to connect the high voltage to the plates. The high voltage cannot be connected to the plates permanently, as this would lead to arc formation and continuous discharging.
Particle Detector is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle.
Seeing through the mystery of an X-ray emissions mechanism. Since the 1960s, scientists who study X-rays, lightning and similar phenomena have observed something curious: In lab experiments replicating these occurrences, electrons accelerated between two electrodes can be of a higher energy than the voltage applied. According to researchers, this defies an assumption in physics that the energy of the electrons should correspond with the voltage applied. Despite the decades-long awareness of this apparent contradiction, researchers couldn't figure out why this was happening. Recently, a team of researchers used mathematical modeling to explain the underlying mechanism at play. When the electrons interact with the material of the electrode, they emit X-rays, which are made of photons -- massless, charge-less particles that comprise light. Some of these photons propagate backward, enabling more electrons to release from the other electrode. A small group of these electrons have energy corresponding to the original energy. Then they accelerate again, and the process continues through several cycles.
Solar Irradiance is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Sunshine Recorder.
Harvesting renewable energy from Earth’s mid-infrared emissions
Force
Abraham Lorentz Force is the recoil force on an accelerating charged particle caused by the particle emitting electromagnetic radiation. It is also called the radiation reaction force or the self force.
Intense laser experiments provide first evidence that light can stop electrons.
Jerk in physics is the rate of change of acceleration; that is, the derivative of acceleration with respect to time, and as such the second derivative of velocity, or the third derivative of position. Jerk is a vector, and there is no generally used term to describe its scalar magnitude (more precisely, its norm, e.g. "speed" as the norm of the velocity vector). According to the result of dimensional analysis of jerk, [length/time3], the SI units are m/s3 (or m·s−3); jerk can also be expressed in standard gravity per second (g/s).
Magnetic Radiation Reaction Force is a force on an electromagnet when its magnetic moment changes. One can derive an electric radiation reaction force for an accelerating charged particle caused by the particle emitting electromagnetic radiation. Likewise, a magnetic radiation reaction force can be derived for an accelerating magnetic moment emitting electromagnetic radiation. Similar to the electric radiation reaction force, three conditions must be met in order to derive the following formula for the magnetic radiation reaction force. First, the motion of the magnetic moment must be periodic, an assumption used to derive the force. Second, the magnetic moment is traveling at non-relativistic velocities (that is, much slower than the speed of light). Finally, this only applies to the realm of classical physics. Since the magnetic moment is proportional to velocity, this force is proportional to the fifth derivative of the position as a function of time (sometimes somewhat facetiously referred to as the "Crackle"). Unlike the Abraham–Lorentz force, the force points in the direction opposite of the "Crackle".
Everything is moving at high speeds in space, even black holes are moving, and everything around the black hole moves together, it moves, it spins, it sucks in, and it spits out. If a Black hole sucks in, where does it Go? Another Dimension?
Torus (clifford)
Uncertainty Principle is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle, known as complementary variables, such as position x and momentum p, can be known.
Singularity studies spaces that are almost manifolds, but not quite. A string can serve as an example of a one-dimensional manifold, if one neglects its thickness. A singularity can be made by balling it up, dropping it on the floor, and flattening it. In some places the flat string will cross itself in an approximate "X" shape. The points on the floor where it does this are one kind of singularity, the double point: one bit of the floor corresponds to more than one bit of string. Perhaps the string will also touch itself without crossing, like an underlined 'U'. This is another kind of singularity. Unlike the double point, it is not stable, in the sense that a small push will lift the bottom of the 'U'away from the 'underline'.
Virtual Particle is a transient fluctuation that exhibits many of the characteristics of an ordinary particle, but that exists for a limited time.
Mass can Neither be Created nor Destroyed
Conservation of Mass states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as system mass cannot change quantity if it is not added or removed. Hence, the quantity of mass is "conserved" over time. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, though it may be rearranged in space, or the entities associated with it may be changed in form, as for example when light or physical work is transformed into particles that contribute the same mass to the system as the light or work had contributed. Thus, during any chemical reaction, nuclear reaction, or radioactive decay in an isolated system, the total mass of the reactants or starting materials must be equal to the mass of the products.
Thermodynamics - Entropy - Radioactive Decay - States of Matter - Information Paradox -Uncertainty Principle - Fusion - Big Bang - Nucleosynthesis
You can't destroy matter or create matter, you can only covert matter into another useful form of matter or into another unusable form of matter, which depends on your intelligence. If you convert the matter you have into an unusable form of matter, then you will eventually run out of useful matter and go extinct because you were living unsustainably. But if you convert the matter you have into another type of matter that can be reused or repurposed, then you can live indefinitely, or until the star that your planet depends on can no longer sustain life. Then you have to move. Symmetry.
Maybe the main reason why matter cannot be destroyed is so that life doesn't accidentally destroy itself or accidentally destroy the universe. And if humans could just create their own matter, then all hell would break lose, annihilation. These safety features are most likely by design. Humans are not mentally mature enough to handle any type of power, as we have all kinds of evidence that proves our immaturity, it's all around us today and throughout our history. Smashing atoms together like a bunch of cave men will not solve our problems. It's time to focus on much bigger problems, like our existence, and the lack of existence. Existence is the state or fact of existing.
What about Anti Matter? Physicists have created antimatter in the laboratory. But when they do, they create an equal amount of matter, how? Can Stars create matter?
Molecules can't be created or destroyed, just recycled or transformed into other particles. You can create new water molecules by burning hydrogen in an oxygen atmosphere. Likewise you can rip apart water molecules into their constituent parts by passing an electric current through a slightly acidic water mixture. So we can create atoms and break apart atoms, but we need other atoms or energy to do it. Molecules are collections of atoms, and atoms are composed of more fundamental particles such as protons, neutrons and electrons. It's believed that The number of existing atoms that make molecules in the universe is the same today as it was after the big bang or the beginning. So the sum of protons and neutrons doesn’t change and the amount of atoms in the universe stays the same, which is good. It seems that entropy may be an extremely long recycling period, which is also good. So if the universe will always have the same amount of atoms forever, then why does the universe need to expand? Expansion requires reproduction for growth. Air in an inflating balloon requires air from an outside source. We can say that space in the universe is expanding, which means that something outside the universe is causing the expansion. Or we could also say that our observations are wrong and that space is not expanding. Space is just curving away from us, which means that galaxies are also curving away past the cosmic horizon. And when galaxies go below the horizon, their light will never reach us. It seems that we are inside a torus shaped universe. But that's just another observation.
Conservation of Energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it transforms from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite. Action Physics.
Energy Transformation is the process of changing energy from one of its forms into another. In physics, energy is a quantity that provides the capacity to perform many actions—some as simple as lifting or warming an object. In addition to being convertible, energy is transferable to a different location or object, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
“Nothing is lost. . .Everything is transformed.” - Michael Ende.
Radioactive Decay - Radiation - Is Space made up of Decaying Matter
21 Grams is the measure of mass lost by a human when the soul departed the body at Death.
Quantum Teleportation is a process by which quantum information (e.g. the exact state of an atom or photon) can be transmitted (exactly, in principle) from one location to another, with the help of classical communication and previously shared quantum entanglement between the sending and receiving location. Because it depends on classical communication, which can proceed no faster than the speed of light, it cannot be used for faster-than-light transport or communication of classical bits. While it has proven possible to teleport one or more qubits of information between two (entangled) atoms, this has not yet been achieved between molecules or anything larger.
Bell's Theorem is a "no-go theorem" that draws an important distinction between quantum mechanics (QM) and the world as described by classical mechanics. No physical theory of local hidden variables can ever reproduce all of the predictions of quantum mechanics.
Physical Information refers generally to the information that is contained in a physical system. Its usage in quantum mechanics (i.e. quantum information) is important, for example in the concept of quantum entanglement to describe effectively direct or causal relationships between apparently distinct or spatially separated particles.
Human Energy
A Brief History of Time is a 1988 popular-science book by British physicist Stephen Hawking. What we Know so far.
Hawking Radiation is blackbody radiation that is predicted to be released by black holes, due to quantum effects near the event horizon.
Light Cone is the path that a flash of light, emanating from a single event (localized to a single point in space and a single moment in time) and traveling in all directions, would take through spacetime.
Wormhole or "Einstein-Rosen Bridge" is a hypothetical topological feature that would fundamentally be a shortcut connecting two separate points in spacetime. A wormhole may connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years or more, short distances such as a few feet, different universes, and different points in time. A wormhole is much like a tunnel with two ends, each at separate points in spacetime. Photo of a Wormhole (image).
Tidal disruption event ASASSN-14li - black hole shreds a star (youtube)
If Black Holes come in various sizes, then is Space just a huge Black Hole?
Dark Flow is an astrophysical term describing a possible non-random component of the peculiar velocity of galaxy clusters. The actual measured velocity is the sum of the velocity predicted by Hubble's Law plus a possible small and unexplained (or dark) velocity flowing in a common direction.
Anthropic Principle that observations of the Universe must be compatible with the conscious and sapient life that observes it. Some proponents of the anthropic principle reason that it explains why this universe has the age and the fundamental physical constants necessary to accommodate conscious life. As a result, they believe it is unremarkable that this universe has fundamental constants that happen to fall within the narrow range thought to be compatible with life
It's been estimated that it would take our solar system 10^30 years (1 nonillion) to end up at the center of our galaxy, which is way beyond the expected life span of earth and our sun, so we're cool.
Maybe Black Holes are Recyclers of Matter, and during that recycling process it compresses information. Black holes also gives our galaxy enough gravity, or magnetic field, to hold it together, just like when stars and planets form. If you don't have the glue, or the gravitational force to hold it together and take shape, then you end up with an asteroid belt. Matter loves to be circular in shape, because the circle shape is the shape that requires the least amount of energy to form. Planets and stars are round. Planets start out more molten then rock, so planets naturally become round. Stars are born from gas, so stars naturally become round. So it kind of makes sense that black holes are used in some way to form planets and stars, and not just used to hold galaxies together. You have to have some continuity. The universe can't be totally chaotic, even though it looks that way at times.
Do Black-Holes recycle the energy of space to supply energy to dark matter and dark energy?
Banach–Tarski Paradox in set-theoretic geometry, which states the following: Given a solid ball in 3‑dimensional space, there exists a decomposition of the ball into a finite number of disjoint subsets, which can then be put back together in a different way to yield two identical copies of the original ball.
Dark Matter - Dark Energy
 Dark Matter
is unidentified. Comprising approximately 27% of the
mass
and energy in the observable
Universe that is not accounted for by dark
energy, baryonic matter (ordinary matter), and neutrinos. The name refers
to the fact that it does not emit or interact with electromagnetic
radiation, such as light, and is thus invisible to the entire
electromagnetic spectrum.
Matter (mass).
Mathematical Models calculate that there must be something else in space
that causes matter to bind together, the claim is that the magnetic forces
of matter alone are not strong enough to form solar systems and
galaxies,
so there must be some other form of energy or matter.
Dark Matter
is unidentified. Comprising approximately 27% of the
mass
and energy in the observable
Universe that is not accounted for by dark
energy, baryonic matter (ordinary matter), and neutrinos. The name refers
to the fact that it does not emit or interact with electromagnetic
radiation, such as light, and is thus invisible to the entire
electromagnetic spectrum.
Matter (mass).
Mathematical Models calculate that there must be something else in space
that causes matter to bind together, the claim is that the magnetic forces
of matter alone are not strong enough to form solar systems and
galaxies,
so there must be some other form of energy or matter. Vacuum Energy - Space - Anti-Gravity - Negative Mass - Expansion - Big Bang - Nucleosynthesis - Conservation of Mass - Cosmic Rays - Black Holes
Invisible is something unable to be seen and not visible to the human eye.
Transparent is when a a material or article allows light to pass through so that objects behind can be distinctly seen.
Newly Observed Effect Makes Atoms Transparent to Certain Frequencies of Light. Researchers at Caltech have discovered a new phenomenon, “collectively induced transparency”, where light passes unimpeded through groups of atoms at certain frequencies. This finding could potentially improve quantum memory systems.
Ghost Particle is an unphysical state in a gauge theory. Ghosts are necessary to keep gauge invariance in theories where the local fields exceed a number of physical degrees of freedom.
Glassfrogs achieve transparency by packing red blood cells into mirror-coated liver.
Low-Mass Particles - Refractive Index - Behind the Curtain - Camouflage
Vantablack is a material developed by Surrey NanoSystems in the United Kingdom and is one of the darkest substances known, absorbing up to 99.6% of radiation in the visible spectrum.
Darkness is understood as a lack of illumination or an absence of visible light.
Maybe we should stop calling it Matter and stop calling it Dark, especially when we're not sure what it is.
Dark Matter 26.8% - Dark Energy 68.3% - Total Energy Matter Density 4.9%
Components of unknown origin (if it's unknown then why is it there?) Finding something that is there, but it's gone already by the time you look at it. How do you measure percentages? Observer Effect.
Transparency and Translucency is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without being scattered. On a macroscopic scale (one where the dimensions investigated are much, much larger than the wavelength of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's Law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) is a superset of transparency: it allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces where there is a change in index of refraction, or internally. In other words, a translucent medium allows the transport of light while a transparent medium not only allows the transport of light but allows for image formation. The opposite property of translucency is opacity. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. When light encounters a material, it can interact with it in several different ways. These interactions depend on the wavelength of the light and the nature of the material. Photons interact with an object by some combination of reflection, absorption and transmission. Some materials, such as plate glass and clean water, transmit much of the light that falls on them and reflect little of it; such materials are called optically transparent. Many liquids and aqueous solutions are highly transparent. Absence of structural defects (voids, cracks, etc.) and molecular structure of most liquids are mostly responsible for excellent optical transmission. Materials which do not transmit light are called opaque. Many such substances have a chemical composition which includes what are referred to as absorption centers. Many substances are selective in their absorption of white light frequencies. They absorb certain portions of the visible spectrum while reflecting others. The frequencies of the spectrum which are not absorbed are either reflected or transmitted for our physical observation. This is what gives rise to color. The attenuation of light of all frequencies and wavelengths is due to the combined mechanisms of absorption and scattering. Transparency can provide almost perfect camouflage for animals able to achieve it. This is easier in dimly-lit or turbid seawater than in good illumination. Many marine animals such as jellyfish are highly transparent.
Interstellar Magnetic Field are a major agent in the interstellar medium of spiral, barred, irregular and dwarf galaxies. They contribute significantly to the total pressure which balances the ISM against gravity. They may affect the gas flows in spiral arms, around bars and in galaxy halos. Galactic Magnetic Fields.
Dark Energy is an unknown form of energy which is hypothesized to permeate all of space, tending to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted hypothesis to explain the observations since the 1990s indicating that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate.
Dark Fluid is an alternative theory to both dark matter and dark energy and attempts to explain both phenomena in a single framework. Dark fluid proposes that dark matter and dark energy are not separate physical phenomena as previously thought, nor do they have separate origins, but that they are strongly linked together and can be considered as two facets of a single fluid. At galactic scales, the dark fluid behaves like dark matter, and at larger scales its behavior becomes similar to dark energy. Our observations within the scales of the Earth and the Solar System are currently insufficient to explain the gravitational effects observed at such larger scales.
Stars travel more slowly at Milky Way's edge. The findings suggest our galaxy's core may contain less dark matter than previously estimated.
A Unifying Theory of Dark Energy and Dark Matter: Negative Masses and Matter Creation within a Modified ΛCDM Framework. Dark energy and dark matter constitute 95% of the observable Universe. Yet the physical nature of these two phenomena remains a mystery. Einstein suggested a long-forgotten solution: gravitationally repulsive negative masses, which drive cosmic expansion and cannot coalesce into light-emitting structures. However, contemporary cosmological results are derived upon the reasonable assumption that the Universe only contains positive masses. By reconsidering this assumption, I have constructed a toy model which suggests that both dark phenomena can be unified into a single negative mass fluid. The model is a modified ΛCDM cosmology, and indicates that continuously-created negative masses can resemble the cosmological constant and can flatten the rotation curves of galaxies. The model leads to a cyclic universe with a time-variable Hubble parameter, potentially providing compatibility with the current tension that is emerging in cosmological measurements. In the first three-dimensional N-body simulations of negative mass matter in the scientific literature, this exotic material naturally forms haloes around galaxies that extend to several galactic radii. These haloes are not cuspy. The proposed cosmological model is therefore able to predict the observed distribution of dark matter in galaxies from first principles. The model makes several testable predictions and seems to have the potential to be consistent with observational evidence from distant supernovae, the cosmic microwave background, and galaxy clusters. These findings may imply that negative masses are a real and physical aspect of our Universe, or alternatively may imply the existence of a superseding theory that in some limit can be modelled by effective negative masses. Both cases lead to the surprising conclusion that the compelling puzzle of the dark Universe may have been due to a simple sign error.
A nearby supernova could end the search for dark matter. Axion dark matter should be produced and converted to gamma rays during a supernova. Will we be lucky enough to see them? Axions are the most likely candidate for enigmatic dark matter that dominates the universe. Astrophysicists are searching for evidence of high-mass axions produced during supernovae. Scientists propose that a quick way to find these axions is to look for a gamma ray burst coincident with a neutrino burst from a nearby core collapse supernova. But we need a fleet of gamma ray telescopes to insure we capture these rare events.
Metric Space is a set for which distances between all members of the set are defined. Those distances, taken together, are called a metric on the set. A metric on a space induces topological properties like open and closed sets, which lead to the study of more abstract topological spaces.
Bioastronautics is a specialty area of biological and astronautical research which encompasses numerous aspects of biological, behavioral, and medical concern governing humans and other living organisms in a space flight environment; and includes design of payloads, space habitats, and life support systems. In short, it spans the study and support of life in space.
Interstellar Medium is the matter and radiation that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field.
Our Space - Space - Un-Manifest Inertia
Magnetism & Inertia: Explaining the Field Geometry that defines the entire Universe (youtube)
Dark Energy Survey
Millennium Run is a computer N-body simulation used to investigate how the distribution of matter in the Universe has evolved over time, in particular, how the observed population of galaxies was formed. It is used by scientists working in physical cosmology to compare observations with theoretical predictions.
Zoom Into Millenium Simulation of Universe [720p] (youtube)
Chameleon Particle
Scalar Field Dark Matter is a classical, minimally coupled, scalar field postulated to account for the inferred dark matter.
Baryonic Dark Matter is dark matter composed of baryons. Only a small proportion of the dark matter in the universe is likely to be baryonic.
Baryon is a type of composite subatomic particle which contains an odd number of valence quarks (at least 3). Baryons belong to the hadron family of particles, which are the quark-based particles. They are also classified as fermions, i.e., they have half-integer spin.
Maybe the instruments should be in motion, like warp speed.
UCI Physicists confirm possible discovery of Fifth Force of Nature. Light particle could be key to understanding dark matter in universe. Physics.
XENON dark matter research project operated at the Italian Gran Sasso laboratory is a deep underground research facility featuring increasingly ambitious experiments aiming to finally detect long sought after dark matter particles. These particles in the form of Weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) are believed to be found by looking for rare interactions via nuclear recoils in a liquid xenon target chamber. The current detector consists of a dual phase Time projection chamber (TPC). Xenon Collaboration - Xenon1t.
Dama-Libra Collaboration investigated the presence of dark matter particles in the galactic halo by exploiting the model-independent annual modulation signature. As a consequence of its orbit, the Earth should be exposed to a higher flux of dark matter particles around June 2, when its orbital speed is added to the one of the solar system with respect to the galaxy and to a smaller one around December 2, when the two velocities are subtracted. The annual modulation signature is distinctive since the effect induced by dark matter particles must simultaneously satisfy many requirements.
Weakly Interacting Massive Particles is a hypothetical particle physics candidate for dark matter. The term “WIMP” is given to a dark matter particle that was produced by falling out of thermal equilibrium with the hot dense plasma of the early universe, although it is often used to refer to any dark matter candidate that interacts with standard particles via a force similar in strength to the weak nuclear force.
Atom Interferometer is an interferometer which uses the wave character of atoms. Similar to optical interferometers, atom interferometers measure the difference in phase between atomic matter waves along different paths. Atom interferometers have many uses in fundamental physics including measurements of the gravitational constant, the fine-structure constant, the universality of free fall, and have been proposed as a method to detect gravitational waves. They also have applied uses as accelerometers, rotation sensors, and gravity gradiometers.
Scalar Field associates a scalar value to every point in a space. The scalar may either be a mathematical number or a physical quantity. Scalar fields are required to be coordinate-independent, meaning that any two observers using the same units will agree on the value of the scalar field at the same absolute point in space (or spacetime) regardless of their respective points of origin. Examples used in physics include the temperature distribution throughout space, the pressure distribution in a fluid, and spin-zero quantum fields, such as the Higgs field. These fields are the subject of scalar field theory. Chameleon Particle.
Fifth Force is a postulated force accompanying the four known fundamental forces, in terms of which modern physics describes physical reality. Since physics has no accepted universal framework, occasionally physicists have postulated the existence of an additional fundamental fifth force. Most postulate a force of roughly the strength of gravity (i.e. it is much weaker than electromagnetism or the nuclear forces) and to have a range of anywhere from less than a millimeter to cosmological scales.
Are Dark Matter And Dark Energy The Same? (youtube)
Quantum Foam is the fluctuation of spacetime on very small scales due to quantum mechanics. With an incomplete theory of quantum gravity, it is impossible to be certain what spacetime would look like at small scales. However, there is no reason that spacetime needs to be fundamentally smooth. It is possible that instead, in a quantum theory of gravity, spacetime would consist of many small, ever-changing regions in which space and time are not definite, but fluctuate in a foam-like manner.
Light Bending - Space
Quantum State refers to the state of an isolated quantum system. A quantum state provides a probability distribution for the value of each observable, i.e. for the outcome of each possible measurement on the system. Knowledge of the quantum state together with the rules for the system's evolution in time exhausts all that can be predicted about the system's behavior.
Quantum Electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction. In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it "the jewel of physics" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.
New clues to why there's so little antimatter in the universe. New research shows radioactive molecules are sensitive to subtle nuclear phenomena. The molecules might help physicists probe violation of the most fundamental symmetries of nature, including why the universe contains relatively little antimatter. Imagine a dust particle in a storm cloud, and you can get an idea of a neutron's insignificance compared to the magnitude of the molecule it inhabits. But just as a dust mote might affect a cloud's track, a neutron can influence the energy of its molecule despite being less than one-millionth its size. And now physicists at MIT and elsewhere have successfully measured a neutron's tiny effect in a radioactive molecule. The team has developed a new technique to produce and study short-lived radioactive molecules with neutron numbers they can precisely control. They hand-picked several isotopes of the same molecule, each with one more neutron than the next. When they measured each molecule's energy, they were able to detect small, nearly imperceptible changes of the nuclear size, due to the effect of a single neutron. The fact that they were able to see such small nuclear effects suggests that scientists now have a chance to search such radioactive molecules for even subtler effects, caused by dark matter, for example, or by the effects of new sources of symmetry violations related to some of the current mysteries of the universe."If the laws of physics are symmetrical as we think they are, then the Big Bang should have created matter and antimatter in the same amount. The fact that most of what we see is matter, and there is only about one part per billon of antimatter, means there is a violation of the most fundamental symmetries of physics, in a way that we can't explain with all that we know," says Ronald Fernando Garcia Ruiz, assistant professor of physics at MIT. "Now we have a chance to measure these symmetry violations, using these heavy radioactive molecules, which have extreme sensitivity to nuclear phenomena that we cannot see in other molecules in nature," he says. "That could provide answers to one of the main mysteries of how the universe was created." Most atoms in nature host a symmetrical, spherical nucleus, with neutrons and protons evenly distributed throughout. But in certain radioactive elements like radium, atomic nuclei are weirdly pear-shaped, with an uneven distribution of neutrons and protons within. Physicists hypothesize that this shape distortion can enhance the violation of symmetries that gave origin to the matter in the universe. "Radioactive nuclei could allow us to easily see these symmetry-violating effects," says study lead author Silviu-Marian Udrescu, a graduate student in MIT's Department of Physics. "The disadvantage is, they're very unstable and live for a very short amount of time, so we need sensitive methods to produce and detect them, fast." Rather than attempt to pin down radioactive nuclei on their own, the team placed them in a molecule that futher amplifies the sensitivity to symmetry violations. Radioactive molecules consist of at least one radioactive atom, bound to one or more other atoms. Each atom is surrounded by a cloud of electrons that together generate an extremely high electric field in the molecule that physicists believe could amplify subtle nuclear effects, such as effects of symmetry violation. However, aside from certain astrophysical processes, such as merging neutron stars, and stellar explosions, the radioactive molecules of interest do not exist in nature and therefore must be created artificially. Garcia Ruiz and his colleagues have been refining techniques to create radioactive molecules in the lab and precisely study their properties. Last year, they reported on a method to produce molecules of radium monofluoride, or RaF, a radioactive molecule that contains one unstable radium atom and a fluoride atom. In their new study, the team used similar techniques to produce RaF isotopes, or versions of the radioactive molecule with varying numbers of neutrons. As they did in their previous experiment, the researchers utilized the Isotope mass Separator On-Line, or ISOLDE, facility at CERN, in Geneva, Switzerland, to produce small quantities of RaF isotopes. The facility houses a low-energy proton beam, which the team directed toward a target -- a half-dollar-sized disc of uranium-carbide, onto which they also injected a carbon fluoride gas. The ensuing chemical reactions produced a zoo of molecules, including RaF, which the team separated using a precise system of lasers, electromagnetic fields, and ion traps. The researchers measured each molecule's mass to estimate of the number of neutrons in a molecule's radium nucleus. They then sorted the molecules by isotopes, according to their neutron numbers. In the end, they sorted out bunches of five different isotopes of RaF, each bearing more neutrons than the next. With a separate system of lasers, the team measured the quantum levels of each molecule. "Imagine a molecule vibrating like two balls on a spring, with a certain amount of energy," explains Udrescu, who is a graduate student of MIT's Laboratory for Nuclear Science. "If you change the number of neutrons in one of these balls, the amount of energy could change. But one neutron is 10 million times smaller than a molecule, and with our current precision we didn't expect that changing one would create an energy difference, but it did. And we were able to clearly see this effect." Udrescu compares the sensitivity of the measurements to being able to see how Mount Everest, placed on the surface of the sun, could, however minutely, change the sun's radius. By comparison, seeing certain effects of symmetry violation would be like seeing how the width of a single human hair would alter the sun's radius. The results demonstrate that radioactive molecules such as RaF are ultrasensitive to nuclear effects and that their sensitivity may likely reveal more subtle, never-before-seen effects, such as tiny symmetry-violating nuclear properties, that could help to explain the universe's matter-antimmater asymmetry. "These very heavy radioactive molecules are special and have sensitivity to nuclear phenomena that we cannot see in other molecules in nature," Udrescu says. "This shows that, when we start to search for symmetry-violating effects, we have a high chance of seeing them in these molecules." This research was supported, in part, by the Office of Nuclear Physics, U.S. Department of Energy; the MISTI Global Seed Funds; the European Research Council; the Belgian FWO Vlaanderen and BriX IAP Research Program; the German Research Foundation; the UK Science and Technology Facilities Council, and the Ernest Rutherford Fellowship Grant.
Plasma Universe - Cosmic Wind
Plasma Cosmology is a non-standard cosmology whose central postulate is that the dynamics of ionized gases and plasmas play important, if not dominant, roles in the physics of the universe beyond the Solar System. In contrast, the current observations and models of cosmologists and astrophysicists explain the formation, development, and evolution of astronomical bodies and large-scale structures in the universe as influenced by gravity (including its formulation in Einstein's theory of general relativity) and baryonic physics. Plasma Cosmology.
Birkeland Current - Solar Radiance - Solar Wind - Cosmic Web - Star Formation - Fusion - Torus
Plasma Scaling. The parameters of plasmas, including their spatial and temporal extent, vary by many orders of magnitude. Nevertheless, there are significant similarities in the behaviors of apparently disparate plasmas. Understanding the scaling of plasma behavior is of more than theoretical value. It allows the results of laboratory experiments to be applied to larger natural or artificial plasmas of interest. The situation is similar to testing aircraft or studying natural turbulent flow in wind tunnels with smaller-scale models. Similarity transformations (also called similarity laws) help us work out how plasma properties change in order to retain the same characteristics. A necessary first step is to express the laws governing the system in a nondimensional form. The choice of non-dimensional parameters is never unique, and it is usually only possible to achieve by choosing to ignore certain aspects of the system. One dimensionless parameter characterizing a plasma is the ratio of ion to electron mass. Since this number is large, at least 1836, it is commonly taken to be infinite in theoretical analyses, that is, either the electrons are assumed to be massless or the ions are assumed to be infinitely massive. In numerical studies the opposite problem often appears. The computation time would be intractably large if a realistic mass ratio were used, so an artificially small but still rather large value, for example 100, is substituted. To analyze some phenomena, such as lower hybrid oscillations, it is essential to use the proper value. Time Scale.
Galaxy Filament are the largest known structures in the universe. They are massive, thread-like formations, with a typical length of 50 to 80 megaparsecs h-1 (or of the order of 200 to 500 million light-years) that form the boundaries between large voids in the universe. Filaments consist of gravitationally bound galaxies. Parts wherein many galaxies are very close to one another (in cosmic terms) are called superclusters. "According to Electric Universe theory, galactic evolution occurs as large-scale plasma discharges form coherent filaments that are influenced by electromagnetism. When plasma moves through a cloud of dust and gas, the cloud becomes ionized, initiating an electric field and the flow of electric charge". Plasma combines into a ring of 56 filaments.
Massive Filaments fuel the growth of Galaxies and Supermassive Black Holes. Based on direct observations researchers have discovered massive filaments between galaxies in a proto-cluster, extending over more than 1 million parsecs and providing the fuel for intense formation of stars and the growth of super massive black holes within the proto-cluster.
Filament is a threadlike structure or a chainlike series of cells. A thin wire that is heated white hot by the passage of an electric current. A very slender natural or synthetic fiber.
Massive thread of hot gas found linking galaxies — and it’s 10 times the mass of the Milky Way. Cosmic tunnels refer to newly discovered interstellar pathways, specifically channels of hot gas, that connect our solar system to other regions of the Milky Way galaxy. These tunnels, discovered by mapping the Local Hot Bubble using data from the eRosita X-ray instrument, appear to carve through the cooler interstellar medium. They are not wormholes, which are theoretical shortcuts through spacetime, but rather dynamic structures within our own galaxy, shaped by past supernova explosions.
Astronomers have uncovered a colossal, searing-hot filament of gas linking four galaxy clusters in the Shapley Supercluster a discovery that could finally solve the mystery of the Universe s missing matter. This giant thread, 10 times the mass of the Milky Way and stretching 23 million light-years, is one of the best confirmations yet of what cosmological simulations have long predicted: that vast, faint filaments connect the Universe s largest structures in a cosmic web.
Mycelium Mycorrhizal Networks (there's a fungus among us) - Consciousness - Quantum Fields
Cosmopsychism is the idea that the universe has psychological properties and that human minds and experience are grounded in the cosmos. It's a type of panpsychism that posits that the universe is filled with a ubiquitous field of consciousness. The UFC is a dual-aspect component of the cosmos, with a physical form and a phenomenological manifestation. Pantheism.
Satellite Galaxies can carry on forming stars when they pass close to their parent galaxies. Using sophisticated simulations of the whole of the Local Group of galaxies, including the Milky Way, the Andromeda galaxy and their respective satellite galaxies, researchers have shown that the satellites not only can retain their gas but can also experience many new episodes of star formation just after passing close to the pericenter of their parent galaxy. While in the majority of the cases the gas of the satellite is sucked out by the parent galaxy due to gravitational action and transfers itself to the larger galaxy, interrupting star formation in the satellite, in a process known as accretion; in some 25% of the sample they found that star formation was clearly enhanced by this interactive process. The results show that the peaks of star formation are correlated with the close pass of the satellite around the parent galaxy, and occasionally by the interaction of two satellites. The researchers identified two key features to the star formation: the satellite must enter the parent galaxy with a large reserve of cold gas, and a minimum distance not too small, so that stars may form due to compression of the gas. On the contrary, galaxies which pass too close to the parent galaxy, or to a parent galaxy with little gas, are stripped of their gas and thereby lose the possibility of forming new stars. "The passage of satellites also coincide with peaks in the star formation of their parent galaxies, which suggests that this mechanism causes bursts of stars equally in both parent galaxies and satellites, in agreement with recent studies of the history of star formation in our own Galaxy," explains Arianna di Cintio, the lead author on the paper.
How does radiation travel through dense plasma? First-of-its-kind experimental evidence defies conventional theories about how plasmas emit or absorb radiation. Most people are familiar with solids, liquids, and gases as three states of matter. However, a fourth state of matter, called plasmas, is the most abundant form of matter in the universe, found throughout our solar system in the sun and other planetary bodies. Because dense plasma -- a hot soup of atoms with free-moving electrons and ions -- typically only forms under extreme pressure and temperatures, scientists are still working to comprehend the fundamentals of this state of matter. Understanding how atoms react under extreme pressure conditions -- a field known as high-energy-density physics -- gives scientists valuable insights into the fields of planetary science, astrophysics, and fusion energy.
Black holes modulate star formation in neighboring galaxies.
Void Astronomy are vast spaces between filaments (the largest-scale structures in the Universe), which contain very few or no galaxies. Voids typically have a diameter of 10 to 100 megaparsecs; particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich superclusters, are sometimes called supervoids.
Olbers' Paradox is the argument that the darkness of the night sky conflicts with the assumption of an infinite and eternal static universe.
Collimated Beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. Such a beam cannot be created, due to diffraction. Light can be approximately collimated by a number of processes, for instance by means of a collimator. Perfectly collimated light is sometimes said to be focused at infinity. Thus, as the distance from a point source increases, the spherical wavefronts become flatter and closer to plane waves, which are perfectly collimated. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation can also be collimated. Collimation of X-rays is important in radiology. Reducing the size of the beam by collimation reduces the volume of the patient's tissue that is irradiated, and reduces intensity in the periphery of the beam. Peripheral x-rays can be absorbed by the patient's tissues and can generate scattered photons, which travel in many directions and cause film fog, reducing the quality of the x-ray image.
Astrophysical Jet is an astronomical phenomenon where outflows of ionised matter are emitted as an extended beam along the axis of rotation. When this greatly accelerated matter in the beam approaches the speed of light, astrophysical jets become relativistic jets as they show effects from special relativity. The formation and powering of astrophysical jets are highly complex phenomena that are associated with many types of high-energy astronomical sources. They likely arise from dynamic interactions within accretion disks, whose active processes are commonly connected with compact central objects such as black holes, neutron stars or pulsars. One explanation is that tangled magnetic fields are organized to aim two diametrically opposing beams away from the central source by angles only several degrees wide (c. > 1%). Jets may also be influenced by a general relativity effect known as frame-dragging.
Galactic Superwind is a high velocity stellar wind emanating from either newly formed massive stars, spiral density waves, or as the result of the effects of supermassive black holes. They are normally observed in starburst galaxies.
Stellar Wind is a flow of gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric.
Cosmic Wind is a powerful cosmic stream of charged particles that can push interstellar dust clouds of low density into intergalactic space.
Solar Wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV.
Stellar winds regulate growth of galaxies. Galactic winds enable the exchange of matter between galaxies and their surroundings. In this way, they limit the growth of galaxies, that is, their star formation rate. Although this had already been observed in the local universe, an international research team has just revealed the existence of the phenomenon in galaxies which are more than 7 billion years old and actively forming stars, the category to which most galaxies belong. The team's findings thus show this is a universal process.
The mechanism of cosmic magnetic fields explored in the laboratory. A novel experiment sheds new light on a possible mechanism that may seed magnetic fields for the galactic dynamo. Recent research shows that magnetic fields can spontaneously emerge in a plasma if the plasma has a temperature anisotropy. This mechanism is known as the Weibel instability. This new research is the first to unambiguously observe the Weibel instability in the laboratory. It offers a possible solution to the problem of the origin of the microgauss-level magnetic fields that permeate the galaxies.
Is space a form of radiant energy, which is energy that exists in the absence of matter?
Radiant Energy is the energy of electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. Solar Radiance.
Electricity - Space is not matter or energy as we know it.
Conductor - Are Planets semiconductors, and is space a conductor? Conductor also means Director, as controls resources and expenditures, so is space a type of controlling mechanism?
How do electrons close to Earth reach almost the speed of light? In the Van Allen radiation belts, electrons can reach almost the speed of light. Researchers have revealed conditions for such strong accelerations. They had demonstrated in 2020: during solar storm plasma waves play a crucial role. However, it remained unclear why ultra-relativistic electron energies are not achieved in all solar storms. They now show: extreme depletions of the background plasma density are crucial. New study found that electrons can reach ultra-relativistic energies for very special conditions in the magnetosphere when space is devoid of plasma.
Torus - Vortex
 Torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a
circle in three-dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a
ring shape and is called a torus of revolution.
Torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a
circle in three-dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a
ring shape and is called a torus of revolution.
The Universal Pattern Torus (youtube) - Double Torus (youtube)
Clifford Torus is a special kind of torus sitting inside the unit 3-sphere S3 in R4, the Euclidean space of four dimensions. Or equivalently, it can be seen as a torus sitting inside C2 since C2 is topologically equivalent to R4. It is specifically the torus in S3 that is geometrically the cartesian product of two circles, each of radius sqrt(1/2). The Clifford torus is an example of a square torus, because it is isometric to a square with opposite sides identified. It is further known as a Euclidean 2-torus (the "2" is its topological dimension); figures drawn on it obey Euclidean geometry as if it were flat, whereas the surface of a common "doughnut"-shaped torus is positively curved on the outer rim and negatively curved on the inner. Although having a different geometry than the standard embedding of a torus in three-dimensional Euclidean space, the square torus can also be embedded into three-dimensional space, by the Nash embedding theorem; one possible embedding modifies the standard torus by a fractal set of ripples running in two perpendicular directions along the surface.
3-Torus - Spherical 3-Manifold - Shape of the Universe
Tokamak is a device that uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus.
Vector Equilibrium - Torus Flow Process - Manifolds
Vortex is the shape of something rotating rapidly. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in phenomena such as smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of boat, or the winds surrounding a tornado or dust devil.
Spirals - Laminar Flow - Fusion - Plasma
Vortex Ring is a torus-shaped vortex in a fluid or gas; that is, a region where the fluid mostly spins around an imaginary axis line that forms a closed loop. The dominant flow in a vortex ring is said to be toroidal, more precisely poloidal. Vortex rings are plentiful in turbulent flows of liquids and gases, but are rarely noticed unless the motion of the fluid is revealed by suspended particles—as in the smoke rings which are often produced intentionally or accidentally by smokers. Fiery vortex rings are also a commonly produced trick by fire eaters. Visible vortex rings can also be formed by the firing of certain artillery, in mushroom clouds, and in microbursts. A vortex ring usually tends to move in a direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring and such that the inner edge of the ring moves faster forward than the outer edge. Within a stationary body of fluid, a vortex ring can travel for relatively long distance, carrying the spinning fluid with it.
Vortex Tube is a thermal device, which generates two streams at different temperature from a single injection. Injected into the vortex tube tangentially, the compressed gas is then divided into two parts and exhausted from the exits at temperatures lower and higher than the inlet gas, respectively. A vortex tube creates cold air and hot air by forcing compressed air through a generation chamber, which spins the air at a high rate of speed of 1,000,000 rpm into a vortex. The high-speed air heats up as it spins along the inner walls of the tube toward the control valve. Vortex technology uses no blades, getting energy from. wind through oscillation without gears, brakes nor oil.
Vortex Generator is an aerodynamic device used to delay flow separation, is in motion relative to the air, the VG creates a vortex
A vortex is believed to be a swirling center of energy that can produce a range of physical, emotional, and spiritual effects. Many people believe that the Sedona Vortexes are particularly powerful and can enhance meditation, self-discovery, and spiritual growth.
 Helix is a structure consisting of
something wound in a continuous series
of loops. An object having a
three-dimensional shape like that of a wire wound uniformly in a
single layer around a cylinder or cone,
as in a corkscrew or spiral staircase. A curve that
lies on the surface of a cylinder or cone and cuts the element at a
constant angle.
Helix is a shape like
a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with
tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important
in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices,
and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices.
The word helix comes from the Greek word "twisted, curved". A
"filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is called a
Helicoid, after the
plane and the catenoid, is the third minimal surface to be known.
Catenoid is a type
of surface, arising by rotating a catenary curve about an axis. It is a
minimal surface, meaning that it occupies the least area when bounded by
a closed space. Soap film attached to twin circular
rings will take the shape of a catenoid. Because they are members of the
same associate family of surfaces, a catenoid can be bent into a portion
of a helicoid, and vice versa.
Helix is a structure consisting of
something wound in a continuous series
of loops. An object having a
three-dimensional shape like that of a wire wound uniformly in a
single layer around a cylinder or cone,
as in a corkscrew or spiral staircase. A curve that
lies on the surface of a cylinder or cone and cuts the element at a
constant angle.
Helix is a shape like
a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with
tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important
in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices,
and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices.
The word helix comes from the Greek word "twisted, curved". A
"filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is called a
Helicoid, after the
plane and the catenoid, is the third minimal surface to be known.
Catenoid is a type
of surface, arising by rotating a catenary curve about an axis. It is a
minimal surface, meaning that it occupies the least area when bounded by
a closed space. Soap film attached to twin circular
rings will take the shape of a catenoid. Because they are members of the
same associate family of surfaces, a catenoid can be bent into a portion
of a helicoid, and vice versa.Orbital Planes - Tornado - Symmetry - Life and Math - Spirals - Fields
Unfolding is a developmental process. Develop or come to a promising stage. Spread out or open from a closed or folded state.
Fold is to bend or lay so that one part covers the other. An angular or rounded shape made by folding.
Folding is the process whereby a protein molecule assumes its intricate three-dimensional shape. Capable of being folded up and stored.
Manifold - Contraction - Expansion - Folds into the whole and then the whole unfolds.
Impeller is a rotor used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid, or decrease in case of turbines. Propeller.
The temperature of the Universe today is about 2.73 degrees above absolute zero in every part of the sky.
Thermal Equilibrium if no heat flows between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially and temporally uniform. E=MC^2.
The Universe has no center and no edge?
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived from the Greek isos (ἴσος, "equal") and tropos (τρόπος, "way"). Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix an, hence anisotropy. Anisotropy is also used to describe situations where properties vary systematically, dependent on direction. Isotropic radiation has the same intensity regardless of the direction of measurement, and an isotropic field exerts the same action regardless of how the test particle is oriented.
Anisotropy is the property of being directionally dependent, which implies different properties in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physical or mechanical properties (absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, tensile strength, etc.) An example of anisotropy is the light coming through a polarizer. Another is wood, which is easier to split along its grain than against it.
Cosmic Microwave Background is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or "relic radiation". The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost isotropic, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum.
Cosmic Variance is the statistical uncertainty inherent in observations of the universe at extreme distances.
Recombination refers to the epoch at which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms.[nb 1] Recombination occurred about 378,000 years after the Big Bang (at a redshift of z = 1100).
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP), was a spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) – the radiant heat remaining from the Big Bang.
The universe is infinitely large and infinitely small, there's even infinity within a confined space. There's black holes in various sizes, there's atoms, there's dark matter, dark energy, double torus...what an incredible machine...time does not stop, and it's not a constant, time can go extremely fast and go extremely slow....The mind is the interface, but not all of the connections and controls have been defined, at least not yet anyway.
Interface is a program that allows a user to interact with a system. Linking one device with another. Interfaces.
Time Travel - Wormhole Portal
How can atoms have so much space and be in constant motion and yet some how become a solid? Is it because there are 5 Sextillion Atoms in a single drop of water, so this 0.1 % of mass actually adds up to create something more solid? We have physical limitations but seem to have no mental limitations. We are an energy wave in constant motion and in constant renewal, but we can retain our memories. Is it just our current speed and frequency that is dictating our current limitations? Can the human mind adjust the speed and frequency in which we currently operate in?
The Wave of Life - Wavelength - Scaling Law - Finite Subdivision Rules - Math
Angular Momentum - Torque - Coriolis Effect
Density of a substance is its mass per unit volume.
Optical Resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged. Resolution Types.
Ratio - Pattern - Vacuum Singularity
Conservation of Mass - Conservation of Energy - Fields
Open System (Open to what? Closed to What?)
Rate is the ratio between two related quantities. Often it is a rate of change. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit of measurement. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit of time, or per unit of length or mass or another quantity. The most common type of rate is "per unit of time", such as speed, heart rate and flux. Ratios that have a non-time denominator include exchange rates, literacy rates and electric field (in volts/meter).
Rate Function is a function used to quantify the probabilities of rare events. It is required to have several properties which assist in the formulation of the large deviation principle. In some sense, the large deviation principle is an analogue of weak convergence of probability measures, but one which takes account of how well the rare events behave.
Volumetric Flow Rate is the volume of fluid which passes per unit time; usually represented by the symbol Q (sometimes V̇). The SI unit is m3/s (cubic metres per second). Another unit used is sccm or standard cubic centimeters per minute.
Telemetry is an automated communications process by which measurements and other data are collected at remote or inaccessible points and transmitted to receiving equipment for monitoring.
Dimensions
Dimension of a mathematical space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it – for example, the point at 5 on a number line. A surface such as a plane or the surface of a cylinder or sphere has a dimension of two because two coordinates are needed to specify a point on it – for example, both a latitude and longitude are required to locate a point on the surface of a sphere. The inside of a cube, a cylinder or a sphere is three-dimensional because three coordinates are needed to locate a point within these spaces.
Spatial Intelligence - Geometry - Manifolds - Structure Matrix - Holography - Layers - Infinity - Motion
Dimension is the magnitude of something in a particular direction, especially length, width or height. The shape or form to required dimensions. A construct whereby objects or individuals can be distinguished. One of three Cartesian coordinates that determine a position in space. Dimension in physics is the physical units of a quantity, expressed in terms of fundamental quantities like time, mass and length. Dimension in science fiction is an alternative universe or plane of existence. Vector.
Dimensional Analysis is the analysis of the relationships between different physical quantities by identifying their fundamental dimensions (such as length, mass, time, and electric charge) and units of measure (such as miles vs. kilometers, or pounds vs. kilograms vs. grams) and tracking these dimensions as calculations or comparisons are performed. Navigation - Motion.
1D: One Dimensional Space is where the position of each point on it can be described by a single number.
2D: Two Dimensional Space is a geometric model of the planar projection of the physical universe. The two dimensions are commonly called length and width. Both directions lie in the same plane. The horizontal or X dimension and the vertical or Y dimension, up or down, left or right, the image has only two dimensions, and if turned to the side becomes a line. 2D Computer Graphics (wiki) - 2D Geometric Model (wiki).
3D: Three Dimensional Space is a geometric setting in which three values called parameters are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informal meaning of the term dimension. 3D adds the depth Z dimension to the X and Y dimension. This third dimension allows for rotation and visualization from multiple perspectives. X, Y, and Z describes every point in three-dimensional space by means of three coordinates. Three coordinate axes are given, each perpendicular to the other two at the origin, the point at which they cross. Three-dimensional space is the simplest possible abstraction of the observation that one only needs three numbers called dimensions to describe the sizes or locations of objects in the everyday world. Example, the volume of a rectangular box is found by measuring and multiplying its length, width, and height, often labeled L, W, and H. When it comes to sizes, Length is the longest side of a shape. Width is the shorter side, side to side or left to right. Height is the vertical dimension or top to bottom. Depth is how deep something is, front to back. 3D Modeling - Torus - Cube.
4D: Four Dimensional Space is a geometric space with four dimensions. It typically is more specifically four-dimensional Euclidean space, generalizing the rules of three-dimensional Euclidean space. It has been studied by mathematicians and philosophers for over two centuries, both for its own interest and for the insights it offered into mathematics and related fields. Research using virtual reality finds that humans, in spite of living in a three-dimensional world, can, without special practice, make spatial judgments about line segments, embedded in four-dimensional space, based on their length (one dimensional) and the angle (two dimensional) between them. The researchers noted that "the participants in our study had minimal practice in these tasks, and it remains an open question whether it is possible to obtain more sustainable, definitive, and richer 4D representations with increased perceptual experience in 4D virtual environments". In another study, the ability of humans to orient themselves in 2D, 3D and 4D mazes has been tested. Each maze consisted of four path segments of random length and connected with orthogonal random bends, but without branches or loops (i.e. actually labyrinths). Time is the fourth dimension. To know where you are you have to know what time it is. To describe where you are in three-dimensional space using length, width and height, you also need to know what time it is. Time Dimension is the aspect of time added to the spatial dimensions. (Length, Width, Height, Time). 4D Toys: a box of Four-Dimensional Toys, and how objects bounce and roll in 4D (youtube) - A Beginner's Guide to the Fourth Dimension (youtube)
5D: Five Dimensional Space is one more than the usual three spatial dimensions and the fourth dimension of time used in relativitistic physics.
6D: Six Dimensional Space is any space that has six dimensions, six degrees of freedom, and that needs six pieces of data, or coordinates, to specify a location in this space.
7D: Seven Dimensional Space refers to a seven-dimensional vector space over any field, such as a seven-dimensional complex vector space, which has 14 real dimensions. It may also refer to a seven-dimensional manifold such as a 7-sphere, or a variety of other geometric constructions.
8D: Eight Dimensional Space refers to an eight-dimensional vector space over any field, such as an eight-dimensional complex vector space, which has 16 real dimensions. It may also refer to an eight-dimensional manifold such as an 8-sphere, or a variety of other geometric constructions. Crystal Lattice.
Dr Quantum - Flatland (youtube) - Tenth Dimension (youtube)
Number of Dimensions (string theory)
Non-Dimensional is something that can not be expressed or represented in terms of any particular unit of mass, length, or time, or nondimensional numbers with a nondimensional width to height ratio. Inter-Dimensional - Parallel Universe.
Nondimensionalization is the partial or full removal of physical dimensions from an equation involving physical quantities by a suitable substitution of variables. This technique can simplify and parameterize problems where measured units are involved. It is closely related to dimensional analysis. In some physical systems, the term scaling is used interchangeably with nondimensionalization, in order to suggest that certain quantities are better measured relative to some appropriate unit. These units refer to quantities intrinsic to the system, rather than units such as SI units. Nondimensionalization is not the same as converting extensive quantities in an equation to intensive quantities, since the latter procedure results in variables that still carry units. Nondimensionalization can also recover characteristic properties of a system. For example, if a system has an intrinsic resonance frequency, length, or time constant, nondimensionalization can recover these values. The technique is especially useful for systems that can be described by differential equations. One important use is in the analysis of control systems. One of the simplest characteristic units is the doubling time of a system experiencing exponential growth, or conversely the half-life of a system experiencing exponential decay; a more natural pair of characteristic units is mean age/mean lifetime, which correspond to base e rather than base 2. Many illustrative examples of nondimensionalization originate from simplifying differential equations. This is because a large body of physical problems can be formulated in terms of differential equations. Consider the following: List of dynamical systems and differential equations topics. List of partial differential equation topics. Differential equations of mathematical physics. Although nondimensionalization is well adapted for these problems, it is not restricted to them. An example of a non-differential-equation application is dimensional analysis; another example is normalization in statistics. Measuring devices are practical examples of nondimensionalization occurring in everyday life. Measuring devices are calibrated relative to some known unit. Subsequent measurements are made relative to this standard. Then, the absolute value of the measurement is recovered by scaling with respect to the standard.
Octonions are a normed division algebra over the real numbers, usually represented by the capital letter O, using boldface O or blackboard bold O {\displaystyle \mathbb {O} } \mathbb {O} . Octonions have eight dimensions; twice the number of dimensions of the quaternions, of which they are an extension. Along with the real numbers R, complex numbers C, and quaternions H, octonions complete the set of numbers capable of being added, subtracted, multiplied or divided; as such, they are believed by some researchers to have fundamental importance in physical theory. They are noncommutative and nonassociative, but satisfy a weaker form of associativity; namely, they are alternative. Octonions are not as well known as the quaternions and complex numbers, which are much more widely studied and used. Despite this, they have some interesting properties and are related to a number of exceptional structures in mathematics, among them the exceptional Lie groups. Additionally, octonions have applications in fields such as string theory, special relativity, and quantum logic. Applying the Cayley-Dickson construction to the octonions produces the sedenions.
Researchers create a one-dimensional gas out of light. Predictions about the transition into this exotic state of matter for the first time. The method used in the experiment by the researchers could be used for examining quantum effects.
Another Dimension is a belief that there are other series of planes of existence where the laws of nature differ. Almost all of the electromagnetic spectrum is invisible to us. And we didn't even know that it existed until recently. And the fact that we have no idea what 90% of outer space is made out of, is also an indicator of how little we know. Maybe this extra dimension or other dimension is too small to see or smaller than visible light.
Beings from another Dimension or Higher Dimensional Aliens or Transdimensional Entities. There is currently no conceivable way to physically travel to the 4th dimension or to a higher dimension. Because we only know life in 3D, our brains don't understand how to look for anything more. We move through space, either left or right, forward or backward, up or down. Everything around us, from the houses we live in to the objects we use in everyday life, has three dimensions, height, length, and width. The first dimension is a single point. The second dimension contains two axis, x & y. And from the third dimension, the 2nd has height and width, but not depth. We perceive the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd dimensions but we can't perceive anything past that. Three-dimensional beings such as humans with a 2D retina, can see all the sides and the insides of a 2D shape simultaneously, a 4D being could see all faces and the inside of a 3D shape at once with their 3D retina. So a 4-D being would seem like magic to us, or be like a god to us. This being would see everything in our world. It could even look inside your stomach and remove your breakfast without cutting through your skin, just like you could remove a dot inside a circle by moving it up into the third dimension, perpendicular to the circle, without breaking the circle. In everyday life, we inhabit a space of three dimensions. People have a spatial self-perception as beings in a three-dimensional space, but are visually restricted by one less dimension: the eye sees the world as a projection to two dimensions, on the surface of the retina. Although our brains can imagine objects only in 3 spatial dimensions, some concept of higher dimensions is occasionally possible. For example, a hypercube of 4 spatial dimensions may be appreciated by examining its 3-dimensional shadow.
4th Dimension explained by Carl Sagan (youtube) - Virtual Reality - Wormholes - Spacetime - Multiverse - Illusions - Voices
Understanding Gravity: The Nano-Scale search for Extra Dimensions. Scientists use high-sensitivity experiments to probe exotic gravitational force. Scientists have used a pulsed slow neutron beamline to probe the deviation of the inverse square law of gravity below the wavelength of 0.1 nm. The experiment achieved the highest sensitivity for a neutron experiment demonstrated to date, and is a significant step toward determining whether the space we live in is really limited to the three dimensions most are familiar with.
New Class of 2D Artificial Materials using atoms in a ferroelectric-like metal that contains barium titanate, strontium titanate and lanthanum titanate.
Coordinate System is a system which uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of a point or other geometric element on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is significant, and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by a letter, as in "the x-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and vice versa; this is the basis of analytic Geometry.
Celestial Coordinate System is a system for specifying positions of celestial objects: satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and so on. Coordinate systems can specify an object's position in three-dimensional space or plot merely its direction on a celestial sphere, if the object's distance is unknown or trivial. The coordinate systems are implemented in either spherical or rectangular coordinates. Spherical coordinates, projected on the celestial sphere, are analogous to the geographic coordinate system used on the surface of Earth. These differ in their choice of fundamental plane, which divides the celestial sphere into two equal hemispheres along a great circle. Rectangular coordinates, in appropriate units, are simply the cartesian equivalent of the spherical coordinates, with the same fundamental (x, y) plane and primary (x-axis) direction. Each coordinate system is named after its choice of fundamental plane. Navigating Space.
Cartesian Coordinate System is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference line is called a coordinate axis or just axis of the system, and the point where they meet is its origin, usually at ordered pair (0, 0). The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axis, expressed as signed distances from the origin.
Euclidean Space encompasses the two-dimensional Euclidean plane, the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, and certain other spaces. It is named after the Ancient Greek mathematician Euclid of Alexandria. The term "Euclidean" distinguishes these spaces from other types of spaces considered in modern geometry. Euclidean spaces also generalize to higher dimensions. Every point in three-dimensional Euclidean space is determined by three coordinates.
Topological Space may be defined as a set of points, along with a set of neighbourhoods for each point, satisfying a set of axioms relating points and neighbourhoods. The definition of a topological space relies only upon set theory and is the most general notion of a mathematical space that allows for the definition of concepts such as continuity, connectedness, and convergence. Other spaces, such as manifolds and metric spaces, are specializations of topological spaces with extra structures or constraints. Being so general, topological spaces are a central unifying notion and appear in virtually every branch of modern mathematics. The branch of mathematics that studies topological spaces in their own right is called point-set topology or general topology.
Manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, each point of an n-dimensional manifold has a neighborhood that is homeomorphic to the Euclidean space of dimension n. In this more precise terminology, a manifold is referred to as an n-manifold. One-dimensional manifolds include lines and circles, but not figure eights (because no neighborhood of their crossing point is homeomorphic to Euclidean 1-space). Two-dimensional manifolds are also called surfaces. Examples include the plane, the sphere, and the torus, which can all be embedded (formed without self-intersections) in three dimensional real space, but also the Klein bottle and real projective plane, which will always self-intersect when immersed in three-dimensional real space. Although a manifold locally resembles Euclidean space, meaning that every point has a neighbourhood homeomorphic to an open subset of Euclidean space, globally it may be not homeomorphic to Euclidean space. For example, the surface of the sphere is not homeomorphic to the Euclidean plane, because (among other properties) it has the global topological property of compactness that Euclidean space lacks, but in a region it can be charted by means of map projections of the region into the Euclidean plane (in the context of manifolds they are called charts). When a region appears in two neighbouring charts, the two representations do not coincide exactly and a transformation is needed to pass from one to the other, called a transition map. The concept of a manifold is central to many parts of geometry and modern mathematical physics because it allows complicated structures to be described and understood in terms of the simpler local topological properties of Euclidean space. Manifolds naturally arise as solution sets of systems of equations and as graphs of functions. Manifolds can be equipped with additional structure. One important class of manifolds is the class of differentiable manifolds; this differentiable structure allows calculus to be done on manifolds. A Riemannian metric on a manifold allows distances and angles to be measured. Symplectic manifolds serve as the phase spaces in the Hamiltonian formalism of classical mechanics, while four-dimensional Lorentzian manifolds model spacetime in general relativity. Submanifold (wiki).
Manifold is a collection of points forming a certain kind of set, such as those of a topologically closed surface or an analog of this in three or more dimensions. A pipe or chamber branching into several openings. A pipe that has several lateral outlets to or from other pipes. Many and varied; having many features or forms.
Torus - Expansion (contraction) - Fields
Calabi–Yau Manifold or a Calabi–Yau space, is a particular type of manifold which has properties, such as Ricci flatness, yielding applications in theoretical physics. Particularly in superstring theory, the extra dimensions of spacetime are sometimes conjectured to take the form of a 6-dimensional Calabi–Yau manifold, which led to the idea of mirror symmetry.
Curvature of Riemannian Manifolds of dimension at least two can be defined intrinsically without reference to a larger space.
Möbius Strip is a surface that can be formed by attaching the ends of a strip of paper together with a half-twist.
Klein Bottle is an example of a non-orientable surface; it is a two-dimensional manifold against which a system for determining a normal vector cannot be consistently defined. Informally, it is a one-sided surface which, if traveled upon, could be followed back to the point of origin while flipping the traveler upside down. Other related non-orientable objects include the Möbius strip and the real projective plane. While a Möbius strip is a surface with boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary. For comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary.
Pseudo-Riemannian Manifold or semi-Riemannian manifold, is a differentiable manifold with a metric tensor that is everywhere nondegenerate. This is a generalization of a Riemannian manifold in which the requirement of positive-definiteness is relaxed. Every tangent space of a pseudo-Riemannian manifold is a pseudo-Euclidean vector space. A special case used in general relativity is a four-dimensional Lorentzian manifold for modeling spacetime, where tangent vectors can be classified as timelike, null, and spacelike.
Roman Surface is a self-intersecting mapping of the real projective plane into three-dimensional space, with an unusually high degree of symmetry. This mapping is not an immersion of the projective plane; however, the figure resulting from removing six singular points is one.
Point in geometry refers usually to an element of some set called a space. More specifically, in Euclidean geometry, a point is a primitive notion upon which the geometry is built, meaning that a point cannot be defined in terms of previously defined objects. That is, a point is defined only by some properties, called axioms, that it must satisfy. In particular, the geometric points do not have any length, area, volume or any other dimensional attribute. A common interpretation is that the concept of a point is meant to capture the notion of a unique location in Euclidean space.
There is no up or down in space, only coordinates, and you need at least 3 identifiable reference points to know where you are, and at least 6 identifiable reference points to know where you're going, and also have a way to accurately measure the distances between every reference point in space, which is really difficult when everything is moving. Space Travel.
Jones Diagram opposite directions of an axis represent different quantities, unlike in a Cartesian graph where they represent positive or negative signs of the same quantity. The Jones diagram therefore represents four variables. Each quadrant shares the vertical axis with its horizontal neighbor, and the horizontal axis with the vertical neighbor. For example, the top left quadrant shares its vertical axis with the top right quadrant, and the horizontal axis with the bottom left quadrant. The overall system response is in quadrant I; the variables that contribute to it are in quadrants II through IV.
Quadrant Plane. The axes of a two-dimensional Cartesian system divide the plane into four infinite regions, called quadrants, each bounded by two half-axes.
Regular Grid is a tessellation of n-dimensional Euclidean space by congruent parallelotopes (e.g. bricks). Grids of this type appear on graph paper and may be used in finite element analysis as well as finite volume methods and finite difference methods. Since the derivatives of field variables can be conveniently expressed as finite differences, structured grids mainly appear in finite difference methods. Unstructured grids offer more flexibility than structured grids and hence are very useful in finite element and finite volume methods.
Grid Reference define locations on maps using Cartesian Coordinates. Grid lines on maps define the coordinate system, and are numbered to provide a unique reference to features.
Grid illusion is any kind of grid that deceives a person's vision. The two most common types of grid illusions are the Hermann grid illusion and the scintillating grid illusion. Grid Cell.
Spin - Trajectory - Action Physics - Relative?
Orientability is a property of surfaces in Euclidean space that measures whether it is possible to make a consistent choice of surface normal Vector at every point. A choice of surface normal allows one to use the right-hand rule to define a "clockwise" direction of loops in the surface, as needed by Stokes' theorem for instance. More generally, orientability of an abstract surface, or manifold, measures whether one can consistently choose a "clockwise" orientation for all loops in the manifold. Equivalently, a surface is orientable if a two-dimensional figure such as Small in the space cannot be moved (continuously) around the space and back to where it started so that it looks like its own mirror image.
Flower of Life (symmetry) - Shapes
Four-Dimensional Physics in Two Dimensions. Light passing through a two-dimensional waveguide array that flows through the device behaves precisely according to the predictions of the four-dimensional quantum Hall effect.
Grassmannian is a space which parameterizes all linear subspaces of a vector space V of given dimension r. For example, the Grassmannian Gr(1, V) is the space of lines through the origin in V, so it is the same as the projective space of one dimension lower than V.
Amplituhedron enables simplified calculation of particle interactions in some quantum field theories. In planar N = 4 supersymmetric Yang–Mills theory, also equivalent to the perturbative topological B model string theory in twistor space, an amplituhedron is defined as a mathematical space known as the positive Grassmannian. Symmetry.
Riemannian Geometry is the branch of differential geometry that studies Riemannian manifolds, smooth manifolds with a Riemannian metric, i.e. with an inner product on the tangent space at each point that varies smoothly from point to point. This gives, in particular, local notions of angle, length of curves, surface area, and volume. From those some other global quantities can be derived by integrating local contributions.
Magnetics - Electromagnetic
Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually exhibits electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions commonly called forces in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation. Electrodynamics is the branch of mechanics concerned with the interaction of electric currents with magnetic fields or with other electric currents. Mechanics is that area of science concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment.
 Electromagnetic Radiation
-
What are Magnets - North
Pole South Pole - Navigation
Electromagnetic Radiation
-
What are Magnets - North
Pole South Pole - NavigationMost materials feature balanced atoms whereby electrons at either end spin in opposite directions, which cancels out their magnetic forces, or in most solids, the electrons tend to line up in pairs so their magnetic moments cancel out. But in magnets, all of the electrons align evenly along their north and south poles, producing an intense magnetic force. When all of the atoms are facing the same direction, that metal will be magnetic.
Magnetosphere is the region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are controlled by that object's magnetic field. We live in a Magnetic Universe.
Earth's Magnetic Field (0.5 Gauss) - Sun Magnetic Field - Galaxy Magnetic Field - Human Body Magnetic Field - Fields - Black Holes - Expansion Contraction - Gravity
Tractor Beam is a device with the ability to attract one object to another from a distance.
EMP is the radiant energy released by certain electromagnetic processes. (EMR) -
Measuring Magnetism Tools - Sensing - Bio-Magnetics - Magnet Types
Visible Light is electromagnetic radiation, as is invisible light, such as radio, infrared, and X-rays. MRI.
Infrared is electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than those of visible light, and is therefore invisible, although it is sometimes loosely called Infrared Light. It extends from the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum at 700 nanometers (frequency 430 THz), to 1 mm (300 GHz) (although people can see infrared up to at least 1050 nm in experiments). Most of the thermal radiation emitted by objects near room temperature is infrared. Like all EMR, IR carries radiant energy, and behaves both like a wave and like its quantum particle, the photon. Measuring Infrared.
Magnetic Field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. Interplanetary Magnetic Field is the solar magnetic field carried by the solar wind among the planets of the Solar System. Fields.
 Electromagnetic Field or EMF is a physical
fields produced by
electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects
in the vicinity of the fields. The electromagnetic field extends
indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic
interaction. It is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the
others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction). The
field can be viewed as the combination of an electric field and a magnetic
field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges, and the
magnetic field by moving charges (currents); these two are often described
as the sources of the field. The way in which charges and currents
interact with the electromagnetic field is described by Maxwell's
equations and the Lorentz force law. The force created by the electric
field is much stronger than the force created by the magnetic field. From
a classical perspective in the history of electromagnetism, the
electromagnetic field can be regarded as a smooth, continuous field,
propagated in a wavelike manner; whereas from the perspective of quantum
field theory, the field is seen as quantized, being composed of individual
particles.
Electromagnetic Field or EMF is a physical
fields produced by
electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects
in the vicinity of the fields. The electromagnetic field extends
indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic
interaction. It is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the
others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction). The
field can be viewed as the combination of an electric field and a magnetic
field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges, and the
magnetic field by moving charges (currents); these two are often described
as the sources of the field. The way in which charges and currents
interact with the electromagnetic field is described by Maxwell's
equations and the Lorentz force law. The force created by the electric
field is much stronger than the force created by the magnetic field. From
a classical perspective in the history of electromagnetism, the
electromagnetic field can be regarded as a smooth, continuous field,
propagated in a wavelike manner; whereas from the perspective of quantum
field theory, the field is seen as quantized, being composed of individual
particles. Electromotive Force - Gyroscopes - Antigravity
Electric Field is a vector field that associates to each point in space the Coulomb's Law that would be experienced per unit of electric charge, by an infinitesimal test charge at that point. Electric fields converge and diverge at electric charges and can be induced by time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field combines with the magnetic field to form the electromagnetic field.
Lorentz Force or electromagnetic force is the combination of electric and magnetic force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields.
Electric Displacement Field is denoted by D, is a vector field that appears in Maxwell's equations. It accounts for the effects of free and bound charge within materials while its sources are the free charges only. "D" stands for "displacement", as in the related concept of displacement current in dielectrics. In free space, the electric displacement field is equivalent to flux density, a concept that lends understanding to Gauss's law. In SI, it is expressed in units of coulomb per metre squared (C m−2).
Vector Field is an assignment of a vector to each point in a subset of space. A vector field in the plane (for instance), can be visualised as: a collection of arrows with a given magnitude and direction, each attached to a point in the plane. Vector fields are often used to model, for example, the speed and direction of a moving fluid throughout space, or the strength and direction of some force, such as the magnetic or gravitational force, as it changes from point to point. Line of Force.
Fine-Structure Constant is a fundamental physical constant which quantifies the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles.
 Right-Hand Rule
is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation conventions for vectors
in three dimensions. Most of the various left and right-hand rules
arise from the fact that the three axes of 3-dimensional space have
two possible orientations. This can be seen by holding your hands outward
and together, palms up, with the fingers curled. If the curl of your
fingers represents a movement from the first or X axis to the second
or Y axis then the third or Z axis can point either along your left
thumb or right thumb. Left and right-hand rules arise when dealing with
co-ordinate axes, rotation, spirals, electromagnetic fields, mirror
images and enantiomers in mathematics and chemistry.
Right-Hand Rule
is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation conventions for vectors
in three dimensions. Most of the various left and right-hand rules
arise from the fact that the three axes of 3-dimensional space have
two possible orientations. This can be seen by holding your hands outward
and together, palms up, with the fingers curled. If the curl of your
fingers represents a movement from the first or X axis to the second
or Y axis then the third or Z axis can point either along your left
thumb or right thumb. Left and right-hand rules arise when dealing with
co-ordinate axes, rotation, spirals, electromagnetic fields, mirror
images and enantiomers in mathematics and chemistry.
Maxwell's Equations are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields. One important consequence of the equations is that they demonstrate how fluctuating electric and magnetic fields propagate at the speed of light. Known as electromagnetic radiation, these waves may occur at various wavelengths to produce a spectrum from radio waves to γ-rays.
 Poynting Vector represents the directional energy flux
or the energy
transfer per unit area per unit time of an electromagnetic field. The
SI unit of the Poynting vector is the watt per square metre (W/m2).
Poynting Vector represents the directional energy flux
or the energy
transfer per unit area per unit time of an electromagnetic field. The
SI unit of the Poynting vector is the watt per square metre (W/m2).
Magnetic Reconnection is a physical process in highly conducting plasmas in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection occurs on timescales intermediate between slow resistive diffusion of the magnetic field and fast Alfvénic timescales. The qualitative description of the reconnection process is such that magnetic field lines from different magnetic domains (defined by the field line connectivity) are spliced to one another, changing their patterns of connectivity with respect to the sources. It is a violation of an approximate conservation law in plasma physics, called the Alfvén's Theorem, and can concentrate mechanical or magnetic energy in both space and time. Solar flares, the largest explosions in the Solar System, may involve the reconnection of large systems of magnetic flux on the Sun, releasing, in minutes, energy that has been stored in the magnetic field over a period of hours to days. Magnetic reconnection in Earth's magnetosphere is one of the mechanisms responsible for the aurora, and it is important to the science of controlled nuclear fusion because it is one mechanism preventing magnetic confinement of the fusion fuel. Magnetic reconnection refers to the breaking and reconnecting of oppositely directed magnetic field lines in a plasma. In the process, magnetic field energy is converted to plasma kinetic and thermal energy. Reconnection is at the heart of many spectacular events in our solar system.
Discovering a previously unknown role for a source of Magnetic Fields.
Revealing the thermal heat dance of magnetic domains. Everyone knows that holding two magnets together will lead to one of two results: they stick together, or they push each other apart. From this perspective, magnetism seems simple, but scientists have struggled for decades to really understand how magnetism behaves on the smallest scales. On the near-atomic level, magnetism is made of many ever-shifting kingdoms -- called magnetic domains -- that create the magnetic properties of the material. While scientists know these domains exist, they are still looking for the reasons behind this behavior. A novel analysis technique called coherent correlation imaging is used to image the evolution of magnetic domains in time and space without any previous knowledge. The scientists could not see the "dance of the domains" during the measurement but only afterward, when they used the recorded data to rewind the tape.
Biermann Battery is a process by which a weak seed magnetic field can be generated from zero initial conditions. The relative motion between electrons and ions is driven by rotation.
Magnonics is an emerging field of modern magnetism, which can be considered a sub-field of modern solid state physics. Magnonics combines waves and magnetism, its main aim is to investigate the behaviour of spin waves in nano-structure elements. In essence, spin waves are a propagating re-ordering of the Magnetisation in a material and arise from the precession of magnetic moments. Magnetic moments arise from the orbital and spin moments of the electron, most often it is this spin moment that contributes to the net magnetic moment, which is a quantity that represents the magnetic strength and orientation of a magnet or other object that produces a magnetic field.
 Gravitoelectromagnetism refers to a set of formal analogies between
the equations for electromagnetism and
relativistic gravitation;
specifically: between
Maxwell's field equations and an approximation,
valid under certain conditions, to the Einstein field equations for
general relativity. Gravitomagnetism is a widely used term referring
specifically to the kinetic effects of gravity, in analogy to the magnetic
effects of moving electric charge. The most common version of GEM is valid
only far from isolated sources, and for slowly moving test particles. Gravitomagnetic field H due to (total)
angular momentum J.
Gravitoelectromagnetism refers to a set of formal analogies between
the equations for electromagnetism and
relativistic gravitation;
specifically: between
Maxwell's field equations and an approximation,
valid under certain conditions, to the Einstein field equations for
general relativity. Gravitomagnetism is a widely used term referring
specifically to the kinetic effects of gravity, in analogy to the magnetic
effects of moving electric charge. The most common version of GEM is valid
only far from isolated sources, and for slowly moving test particles. Gravitomagnetic field H due to (total)
angular momentum J.
Meissner Effect is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state. In the presence of an applied magnetic field, were cooled below their superconducting transition temperature, whereupon the samples cancelled nearly all interior magnetic fields. They detected this effect only indirectly because the magnetic flux is conserved by a superconductor: when the interior field decreases, the exterior field increases. The experiment demonstrated for the first time that superconductors were more than just perfect conductors and provided a uniquely defining property of the superconductor state. Rotating Super Conductor (feral fluid cooled for zero friction) 60,000 rpm). Anti Gravity (levitation)
Flux is a vector quantity, describing the magnitude and direction of the flow of a substance or property. In electromagnetism, flux is a scalar quantity, defined as the surface integral of the component of a vector field perpendicular to the surface at each point. As will be made clear, the easiest way to relate the two concepts is that the surface integral of a flux according to the first definition is a flux according to the second definition. Magnetic Flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B passing through that surface. Compressed Magnetic Flux Generator is a generator device of compressed magnetic flux.
Dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.
Electromagnetic Induction is the production of an electromotive force (i.e., voltage) across an electrical conductor due to its dynamic interaction with a magnetic field.
Action physics - Why don't magnets have an electrical charge?
Faraday's Law of Induction is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (EMF)—a phenomenon called electromagnetic induction. It is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors, generators and solenoids.
Solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. A coil whose length is substantially greater than its diameter, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a uniform magnetic field in a volume of space (where some experiment might be carried out) when an electric current is passed through it. A solenoid is a type of electromagnet when the purpose is to generate a controlled magnetic field. If the purpose of the solenoid is instead to impede changes in the electric current, a solenoid can be more specifically classified as an inductor rather than an electromagnet. Not all electromagnets and inductors are solenoids; for example, the first electromagnet, invented in 1824, had a horseshoe rather than a cylindrical solenoid shape.
Lenz's Law is a common way to understand how electromagnetic circuits obey Newton's third law and the conservation of energy. An induced electromotive force (emf) always gives rise to a current whose magnetic field opposes the original change in magnetic flux. Lenz's law is shown with the negative sign in Faraday's law of induction:
Unlocking new insights into in-plane magnetic field-induced hall effects. In-plane magnetic fields reveal new Hall effect behaviors in advanced materials, reshaping our understanding of electronic transport. In-plane magnetic fields are responsible for inducing anomalous Hall effect in certain films, report researchers. By studying how these fields change electronic structures, the team discovered a large in-plane anomalous Hall effect. These findings pave the way for new strategies for controlling electronic transport under magnetic fields, potentially advancing applications in magnetic sensors.
Copper's Surprising Reaction to Strong Magnets | Force Field Motion Dampening (youtube) Experiment with Lenz's Law And Faraday's Law of Induction to generate electricity and magnetic force fields in copper. Anti-Gravity.
Permittivity is the measure of resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium.
Permeability in electromagnetism is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. Hence, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Otherwise known as distributed inductance in Transmission Line Theory.
Saturation in magnetics is the state reached when an increase in applied external magnetic field H cannot increase the magnetization of the material further, so the total magnetic flux density B more or less levels off. (It continues to increase very slowly due to the vacuum permeability.) Saturation is a characteristic of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, cobalt and their alloys.
What Element is Attracted the most to a Magnet? (youtube) - Two words: Permeability, and flux saturation. Iron has the highest saturation density of any of the elements. Cobalt has a higher permeability. Wrap 20 turns of wire around the samples, to make solenoid electromagnets. Apply 1 amp to each magnet. The Cobalt will be the strongest, followed by nickel, then a close third place, will be iron. Now, increase the current, until core saturation occurs. every element will reach a maximum, after which, it will not become any stronger, no matter how much more current is applied. Iron will be the clear winner. All these samples were saturated in your direct contact pull test, with the spring scale. That chart will apply. The distance tests, are permeability. (the one where they were floated on water. The one with the magnet placed above the samples on the scale, may have saturated some cores, but not others, based on their permeability times their saturation level. Those giant Neodymium magnets you used in this test are no joke. They cast a large field, and can saturate those small samples, without direct contact. I hope this answers more questions, than it begs.
Coherence is when two wave sources are perfectly coherent if they have a constant phase difference and the same frequency. It is an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference.
Interference in wave propagation is a phenomenon in which two waves superpose to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude.
New discovery by scientists redefines magnetism. Discovery on the nanoscale of a new type of quasiparticle found in all magnetic materials, no matter their strength or temperature.
Current generated by the quantum Hall effect has additional magnetic properties. The quantum Hall effect, a fundamental effect in quantum mechanics, not only generates an electric but also a magnetic current. It arises from the motion of electrons on an orbit around the nuclei of atoms. These results can potentially be used to develop new types of inexpensive and energy-efficient devices. Hall effect is the production of a potential difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field perpendicular to the current.
Magnet Types
Magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet, which is a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. Child Dangers: Between 2002 and 2011, there were over 22,500 magnet-related injuries in those under 21. Most were from swallowing them, but 21 percent were nose-related.
Rare-Earth Magnet are strong permanent magnets made from alloys of rare-earth elements, elements in the lanthanide series, plus scandium and yttrium.
Permanent Magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. Permanent magnet is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties in the absence of an inducing field or current.
Temporary Magnets are those which act like a permanent magnet when they are within a strong magnetic field, but lose their magnetism when the magnetic field disappears.
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism, which is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. Law of Attraction.
Gauss's Law for Magnetism states that the magnetic field B has divergence equal to zero, that it is a solenoidal vector field. It is equivalent to the statement that magnetic monopoles do not exist. Rather than "magnetic charges", the basic entity for magnetism is the magnetic dipole, which is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the dimensions of the source are reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant.
Magnetic Susceptibility is one measure of the magnetic properties of a material. The susceptibility indicates whether a material is attracted into or repelled out of a magnetic field, which in turn has implications for practical applications. Quantitative measures of the magnetic susceptibility also provide insights into the structure of materials, providing insight into bonding and energy levels.
Ferrimagnetism material is one that has populations of atoms with opposing magnetic moments, as in antiferromagnetism; however, in ferrimagnetic materials, the opposing moments are unequal and a Spontaneous Magnetization remains. This happens when the populations consist of different materials or ions (such as Fe2+ and Fe3+).
Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets and stick together. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally occurring minerals, including some varieties of lodestone (magnetite is considered ferrimagnetic, rather than ferromagnetic). Making Ferro-Magnets Stronger by adding Non-Magnetic Element.
First observation of a native Ferroelectric Metal. A native metal with bistable and electrically switchable spontaneous polarization states—the hallmark of ferroelectricity. The study found coexistence of native metallicity and ferroelectricity in bulk crystalline tungsten ditelluride (WTe2) at room temperature. A van-der-Waals material that is both metallic and ferroelectric in its bulk crystalline form at room temperature has potential for nano-electronics applications.
Merons realized in synthetic antiferromagnets. Researchers have demonstrated the presence of merons in synthetic antiferromagnets and thus in materials that can be produced using standard deposition techniques.
Reflecting Antiferromagnetic Arrangements. An X-ray imaging technique could help scientists understand -- and ultimately control -- the magnetic structure of promising materials for the development of electronic devices that exploit electron spin.
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby certain materials are attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. (attracts but does not come in contact or stick.)
Diamagnetism materials create an induced magnetic field in a direction opposite to an externally applied magnetic field, and are repelled by the applied magnetic field. In contrast, the opposite behavior is exhibited by paramagnetic materials. (Silver and Gold).
Antiferromagnetism the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. Antiferromagnets outperform Ferromagnets in ultrafast, energy-efficient memory operations.
Neodymium Magnet is a type of rare-earth magnet, is a permanent magnet made from an alloy of neodymium, iron and boron to form the Nd2Fe14B tetragonal crystalline structure. Nodymium Rare Earth Block Magnet.
Amazing Magnets - Aec Magnetics
Magnet Fishing is searching in outdoor waters for ferromagnetic objects available to pull with a strong neodymium magnet. The hobby is a combination of environmentalism and treasure hunting. The magnets used are strong enough to remove large debris such as discarded bicycles, guns, safes, bombs, grenades, coins and car tire rims from bodies of water, but many who engage in the hobby are hoping to find rare and valuable items as well. It is thought magnet fishing was initially started by boaters using magnets to recover fallen keys from the water.
Electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of insulated wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole in the center of the coil. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet. The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field. Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.
Strongest Magnet in the World. The strongest magnet ever build is 22-foot tall and weights 34 tons. It was built in a research lab in Tallahassee and it produces a magnetic field of at least 45 Tesla. To understand how powerful this is you have to know that the strength of a magnetic field is measured in Gauss (G) or Tesla (T). National High Magnetic Field Laboratory (MagLab).
New world record for the strongest steady magnetic field. On August 12, the hybrid magnet of the Steady High Magnetic Field Facility or SHMFF in Hefei, China, generated the world’s highest steady magnetic field by a working magnet measuring 45.22 teslas (T). In comparison, Earth’s magnetic field at 0° latitude and 0° longitude only has a strength of 0.000032 teslas. It surpassed the 45-tesla prior world record set by a hybrid magnet in 1999 at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory of the United States.
Samarium Cobalt Magnet is a type of rare earth magnet, is a strong permanent magnet made of an alloy of samarium and cobalt.
Alnico is a family of iron alloys which in addition to iron are composed primarily of aluminium (Al), nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co), hence al-ni-co. They also include copper, and sometimes titanium. Alnico alloys are ferromagnetic, with a high coercivity (resistance to loss of magnetism) and are used to make permanent magnets. Before the development of rare-earth magnets in the 1970s, they were the strongest type of permanent magnet.
Ferrite Magnet is a type of ceramic compound composed of iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3) combined chemically with one or more additional metallic elements. They are both electrically nonconductive and ferrimagnetic, meaning they can be magnetized or attracted to a magnet. Ferrites can be divided into two families based on their magnetic coercivity, their resistance to being demagnetized. Hard ferrites have high coercivity, hence they are difficult to demagnetize. They are used to make magnets, for devices such as refrigerator magnets, loudspeakers and small electric motors. Soft ferrites have low coercivity. They are used in the electronics industry to make ferrite cores for inductors and transformers, and in various microwave components. Ferrite compounds have extremely low cost, being made of iron oxide (i.e. rusted iron), and also have excellent corrosion resistance. They are very stable and difficult to demagnetize, and can be made with both high and low coercive forces.
Atomically Thin Magnets. Researchers have become the first to control atomically thin magnets with an electric field, a breakthrough that provides a blueprint for producing exceptionally powerful and efficient data storage in computer chips, among other applications. (Two-dimensional chromium-triiodide magnets)
Single-Molecule Magnet are a class of metalorganic compounds that show superparamagnetic behavior below a certain blocking temperature at the molecular scale. In this temperature range, SMMs exhibit magnetic hysteresis of purely molecular origin. Contrary to conventional bulk magnets and molecule-based magnets, collective long-range magnetic ordering of magnetic moments is not necessary.
Nanomagnet is a nanoscopic scale system that presents spontaneous magnetic order or magnetization at zero applied magnetic field or remanence. The small size of nanomagnets prevents the formation of magnetic domains. The magnetization dynamics of sufficiently small nanomagnets at low temperatures, typically single-molecule magnets, presents quantum phenomena, such as macroscopic spin tunnelling. At larger temperatures, the magnetization undergoes random thermal fluctuations or superparamagnetism which present a limit for the use of nanomagnets for permanent information storage.
Researchers develop manual for engineering spin dynamics in nanomagnets. Manual can help debug and design nanomagnet devices. Despite their small size, nanomagnets -- found in most spintronic applications -- reveal rich dynamics of spin excitations, or "magnons," the quantum-mechanical units of spin fluctuations. Due to its nanoscale confinement, a nanomagnet can be considered to be a zero-dimensional system with a discrete magnon spectrum, similar to the spectrum of an atom.
Altermagnetism is a type of persistent magnetic state in ideal crystals. Altermagnetic structures are collinear and crystal-symmetry compensated, resulting in zero net magnetisation. Unlike in an ordinary collinear antiferromagnet, another magnetic state with zero net magnetization, the electronic bands in an altermagnet are not Kramers degenerate, but instead depend on the wavevector in a spin-dependent way. Related to this feature, key experimental observations were published in 2024. It has been speculated that altermagnetism may have applications in the field of spintronics.
Altermagnetism proves its place on the magnetic family tree. Experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS prove the existence of a new type of magnetism, with broad implications for technology and research. Altermagnets have a special combination of the arrangement of spins and crystal symmetries. The spins alternate, as in antiferromagnets, resulting in no net magnetisation. Yet, rather than simply cancelling out, the symmetries give an electronic band structure with strong spin polarization that flips in direction as you pass through the material's energy bands -- hence the name altermagnets. This results in highly useful properties more resemblant of ferromagnets, as well as some completely new properties.
Vacuum in optical cavity can change material's magnetic state without laser excitation. Researchers in Germany and the USA have produced the first theoretical demonstration that the magnetic state of an atomically thin material, ?-RuCl3, can be controlled solely by placing it into an optical cavity. Crucially, the cavity vacuum fluctuations alone are sufficient to change the material's magnetic order from a zigzag antiferromagnet into a ferromagnet.
2-D Platinum Magnet. University of Groningen physicists have induced magnetism in platinum with an electric field created by a paramagnetic ionic liquid. As only the surface of the platinum is affected, this creates a switchable 2D ferromagnet.
Degaussing is the process of decreasing or eliminating a remnant magnetic field.
Lodestone is a naturally magnetized piece of the mineral magnetite. They are naturally-occurring magnets, which can attract iron.
Iron is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from Latin: ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is by mass the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. Its abundance in rocky planets like Earth is due to its abundant production by fusion in high-mass stars, where it is the last element to be produced with release of energy before the violent collapse of a supernova, which scatters the iron into space. Iron Oxide are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. All together, there are sixteen known iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. Iron (III) Chloride is an industrial scale commodity chemical compound, with the formula FeCl3 and with iron in the +3 oxidation state. The colour of iron(III) chloride crystals depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red. Anhydrous iron(III) chloride is deliquescent, forming hydrated hydrogen chloride mists in moist air. It is rarely observed in its natural form, the mineral molysite, known mainly from some fumaroles.
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores. With the chemical formula is Fe3O4, it is one of the oxides of iron. Magnetite is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself.
Tetrataenite is a native metal found in meteorites with the composition FeNi. It is one of the mineral phases found in meteoric iron.
Rock Magnetism is the study of the magnetic properties of rocks, sediments and soils.
Exotic Elements vs. Magnet | Part 5/5 | Platinum Group! (youtube)
Professor Eric Laithwaite: The Circle of Magnetism - 1968 (youtube) - Imperial College London demonstrates some of the most difficult concepts in electricity & magnetism.
Magnetic Domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction.
Magnetic Moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the torque it will experience in an external magnetic field. A loop of electric current, a bar magnet, an electron, a molecule, and a planet all have magnetic moments. The magnetic moment may be considered to be a vector having a magnitude and direction. The direction of the magnetic moment points from the south to north pole of the magnet. The magnetic field produced by the magnet is proportional to its magnetic moment. More precisely, the term magnetic moment normally refers to a system's magnetic dipole moment, which produces the first term in the multipole expansion of a general magnetic field. The dipole component of an object's magnetic field is symmetric about the direction of its magnetic dipole moment, and decreases as the inverse cube of the distance from the object.
Bio-Electromagnetism is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological entities.
The DEEPEST Secrets of Magnetism, first time explained & CENTER OF LIGHT at the Inertia Plane (youtube)
Ferrofluid is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.(portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid). Ferrocell Complete Systems
Monster Magnet meets Magnetic Fluid..Neodymium Magnet and Ferrofluid (youtube)
Spirograph is a geometric drawing toy that produces mathematical roulette curves of the variety technically known as hypotrochoids and epitrochoids.
 Torus - Black Holes
- Fields
Torus - Black Holes
- FieldsToroflux 3D Flow Ring Kinectic Spring (amazon)
Hyperboloid is a surface that may be generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is a surface that may be obtained from a paraboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. A hyperboloid is a quadric surface, that is a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, a hyperboloid is characterized by not being a cone or a cylinder, having a center of symmetry, and intersecting many planes into hyperbolas. A hyperboloid has also three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry, and three pairwise perpendicular planes of symmetry.
Hypotrochoid is a roulette traced by a point attached to a circle of radius r rolling around the inside of a fixed circle of radius R, where the point is a distance d from the center of the interior circle.
Algebraic Structure is a set (called carrier set or underlying set) with one or more finitary operations defined on it that satisfies a list of axioms. Examples of algebraic structures include groups, rings, fields , and lattices. More complex structures can be defined by introducing multiple operations, different underlying sets, or by altering the defining axioms. Examples of more complex algebraic structures include vector spaces, modules, and algebras.
Topology is concerned with the properties of space that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, crumpling and bending, but not tearing or gluing. This can be studied by considering a collection of subsets, called open sets, that satisfy certain properties, turning the given set into what is known as a topological space. Important topological properties include connectedness and compactness.
Topography Map - Surface - Shape of the Universe
Algebraic Topology is a branch of mathematics that uses tools from abstract algebra to study topological spaces. The basic goal is to find algebraic invariants that classify topological spaces up to homeomorphism, though usually most classify up to homotopy equivalence.
Topological Space is defined as a set of points, along with a set of neighborhoods for each point, satisfying a set of axioms relating points and neighborhoods. The definition of a topological space relies only upon set theory and is the most general notion of a mathematical space that allows for the definition of concepts such as continuity, connectedness, and convergence. Other spaces, such as manifolds and metric spaces, are specializations of topological spaces with extra structures or constraints.
Topological Property is a property of a topological space which is invariant under homeomorphisms. Shapes.
Synthetic Magnetic State in Solids JILA’s record-setting atomic clock, in which strontium atoms are trapped in a laser grid known as an optical lattice.
Magnetorheological Fluid is a type of smart fluid in a carrier fluid, usually a type of oil. When subjected to a magnetic field, the fluid greatly increases its apparent viscosity, to the point of becoming a viscoelastic solid. Importantly, the yield stress of the fluid when in its active ("on") state can be controlled very accurately by varying the magnetic field intensity. The upshot is that the fluid's ability to transmit force can be controlled with an electromagnet, which gives rise to its many possible control-based applications.
Poles - North Pole - South Pole
 North Pole is a wandering point on the surface of Earth's Northern
Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically
downwards, in other words, if a
magnetic compass needle is allowed to
rotate about a horizontal axis, it will point straight down. There is
only one location where this occurs, near (but distinct from) the
Geographic North Pole and the
Geomagnetic North Pole. Spins Counter Clock Wise
causing matter to contract.
North Pole is a wandering point on the surface of Earth's Northern
Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically
downwards, in other words, if a
magnetic compass needle is allowed to
rotate about a horizontal axis, it will point straight down. There is
only one location where this occurs, near (but distinct from) the
Geographic North Pole and the
Geomagnetic North Pole. Spins Counter Clock Wise
causing matter to contract.
Earth's Rotation is Counter Clock Wise, which is the same direction the core spins. Orbit.
South Pole is the wandering point on Earth's Southern Hemisphere where the geomagnetic field lines are directed vertically upwards. It should not be confused with the South Geomagnetic Pole described later. Energy Spins Clock Wise and causes matter to expand.
Polarizability is the ability to form instantaneous dipoles. It is a property of matter. Polarizabilities determine the dynamical response of a bound system to external fields, and provide insight into a molecule's internal structure. In a solid, polarizability is defined as the dipole moment per unit volume of the crystal cell. LCR meters give the measurements needed to calculate polarizability. Chemical Polarity.
Polarization in waves is a parameter applying to waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillation. Electromagnetic waves such as light exhibit multiple polarizations, as do many other types of waves such as gravitational waves and sound waves in solids. On the other hand, sound waves in a gas or liquid only oscillate in the wave's direction of propagation, and the oscillation of ocean waves is always in the vertical direction. In these cases one doesn't normally speak of "polarization" since the oscillation's direction is not in question. Balance.
Dipole is an electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some (usually small) distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret. A magnetic dipole is a closed circulation of electric current. A simple example of this is a single loop of wire with some constant current through it.
Electric Dipole Moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system, that is, a measure of the system's overall polarity. The electric field strength of the dipole is proportional to the magnitude of dipole moment. The SI units for electric dipole moment are Coulomb-meter (C m), however the most commonly used unit is the Debye (D).
Magnetic Monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole, either a north pole without a south pole or vice versa.
Electrical Polarity is the term used to describe the direction of current flow in an electrical circuit. Current flows from the positive pole to the negative pole. (electrons flows from negative to positive.
Orbital Pole is either point at the ends of an imaginary line segment that runs through the center of an orbit (of a revolving body like a planet) and is perpendicular to the orbital plane. Projected onto the celestial sphere, orbital poles are similar in concept to celestial poles, but are based on the body's orbit instead of its equator. The north orbital pole of a revolving body is defined by the right-hand rule. If the fingers of the right hand are curved along the direction of orbital motion, with the thumb extended and oriented to be parallel to the orbital axis, then the direction the thumb points is defined to be the orbital north. The poles of Earth's orbit are referred to as the ecliptic poles. For the remaining planets, the orbital pole in ecliptic coordinates is given by the longitude of the ascending node (☊) and inclination (i): l = ☊ - 90°, b = 90° - i.
Celestial Pole is the point on the celestial sphere directly above either of the earth's geographic poles, around which the stars and planets appear to rotate during the course of the night. The north celestial pole is currently within one degree of the star Polaris. Ecliptic.
The Truth About Toilet Swirl - Northern Hemisphere (youtube)
ENLIGHTENED MAGNETISM, PART 1 (youtube)
Polarity mutual inductance for a device with mutual inductance designates the relative instantaneous current directions of such device's winding leads.
Chemical Polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multipole moment.
Video 1 Uncovering the Missing Secrets of Magnetism (video channel)
"Quartz" crystals at the Earth's core power its Magnetic Field.
Superconductor is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic flux fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature.
Research reveals novel quantum state in strange insulating materials. Experiments show how electrons in Mott insulators with strong spin-orbit coupling arrange themselves to make the materials magnetic at low temperatures. The work could help zero in on a more complete quantum theory of magnetism.
Electromagnetic Spectrum - Electrical Generator
Extremely Low Frequency is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. In atmospheric science, an alternative definition is usually given, from 3 Hz to 3 kHz. In the related magnetosphere science, the lower frequency electromagnetic oscillations (pulsations occurring below ~3 Hz) are considered to lie in the ULF range, which is thus also defined differently from the ITU radio bands.
Radiation - Electronic Warfare - Effects of Nuclear Explosions
Edward Leedskalnin Magnetic Current Research - Edward Leedskalnin (January 12, 1887 – December 7, 1951)
Electricity - Light
Ley Line are apparent alignments of land forms, places of ancient religious significance or culture, often including man-made structures. They are ancient, straight 'paths' or routes in the landscape which are believed to have spiritual significance.
Tuned Mass Damper also known as a harmonic absorber, is a device mounted in structures to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations. Their application can prevent discomfort, damage, or outright structural failure. They are frequently used in power transmission, automobiles, and buildings.
Neural Oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.
Phase-Locked Loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal.
Dirac Equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin-1/2 massive particles such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. It was validated by accounting for the fine details of the hydrogen spectrum in a completely rigorous way.
Gravity
Michelson-Morley Experiment was performed over the spring and summer of 1887 by Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and published in November of the same year. It compared the speed of light in perpendicular directions, in an attempt to detect the relative motion of matter through the stationary luminiferous aether ("aether wind"). The result was negative, in that the expected difference between the speed of light in the direction of movement through the presumed aether, and the speed at right angles, was found not to exist; this result is generally considered to be the first strong evidence against the then-prevalent aether theory, and initiated a line of research that eventually led to special relativity, which rules out a stationary aether. The experiment has been referred to as "the moving-off point for the theoretical aspects of the Second Scientific Revolution"
Large Underground Xenon experiment (LUX) aims to directly detect weakly interacting massive particle (WIMP) dark matter interactions with ordinary matter on Earth. Despite the wealth of (gravitational) evidence supporting the existence of non-baryonic dark matter in the Universe, dark matter particles in our galaxy have never been directly detected in an experiment. LUX utilizes a 370 kg liquid xenon detection mass in a time-projection chamber (TPC) to identify individual particle interactions, searching for faint dark matter interactions with unprecedented sensitivity.
Measuring Electromagnetic Radiation
 Geomagnetic Storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's
magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic
field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the
solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar
wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and
transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions
cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by
increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in
electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.
Geomagnetic Storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's
magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic
field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the
solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar
wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and
transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions
cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by
increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in
electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.Bose-Einstein Condensate is a state of matter of a dilute gas of bosons cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero. Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point microscopic quantum phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent. A BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density, about one-hundred-thousandth the density of normal air, to ultra-low temperatures.
Coherence two wave sources are perfectly coherent if they have a constant phase difference and the same frequency. It is an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference. It contains several distinct concepts, which are limiting cases that never quite occur in reality but allow an understanding of the physics of waves, and has become a very important concept in quantum physics. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a single wave, or between several waves or wave packets.
Phase Waves is the position of a point in time (an instant) on a waveform cycle. A complete cycle is defined as the interval required for the waveform to return to its arbitrary initial value.
Frequencies - Electric Field
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point.
Spectral Density is any signal that can be represented as an amplitude that varies in time has a corresponding frequency spectrum. This includes familiar entities such as visible light (perceived as color), musical notes (perceived as pitch), radio/TV (specified by their frequency, or sometimes wavelength) and even the regular rotation of the earth. Torus.
Harmonic in its strictest sense describes any member of the harmonic series. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music and acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, etc. It is typically applied to repeating signals, such as sinusoidal waves. A harmonic of such a wave is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the frequency of the original wave, known as the fundamental frequency. The original wave is also called 1st harmonic, the following harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz.
Resonance is a phenomenon in which a vibrating system or external force drives another system to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific preferential frequency. Sound.
Overtone is any frequency greater than the fundamental frequency of a sound.
Tone Generator - Function Generator
Impedance of Free Space is a physical constant relating the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields of electromagnetic radiation travelling through free space.
Lavitrón la magia de los imanes (youtube)
Logarithm - Heliosphere
The Electric Universe - HD Documentary 2015 (youtube) - Primer Fields - What is Space made of?
Magnetoquasistatic Field is a class of electromagnetic field in which a slowly oscillating magnetic field is dominant. A magnetoquasistatic field is typically generated by low-frequency induction from a magnetic dipole or a current loop. The magnetic near-field of such an emitter behaves differently from the more commonly used far-field electromagnetic radiation. At low frequencies the rate of change of the instantaneous field strength with each cycle is relatively slow, giving rise to the name "magneto-quasistatic". The near field or quasistatic region typically extends no more than a wavelength from the antenna, and within this region the electric and magnetic fields are approximately decoupled. Magnetic Field Emitter.
Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) Mission (NSSA) - Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission (wiki)
SQUID or superconducting quantum interference device, is a very sensitive magnetometer used to measure extremely subtle magnetic fields, based on superconducting loops containing Josephson junctions. SQUIDs are sensitive enough to measure fields as low as 5 a T (5×10−18 T) with a few days of averaged measurements. Their noise levels are as low as 3 fT·Hz−½. For comparison, a typical refrigerator magnet produces 0.01 tesla (10−2 T), and some processes in animals produce very small magnetic fields between 10−9 T and 10−6 T. Recently invented SERF atomic magnetometers are potentially more sensitive and do not require cryogenic refrigeration but are orders of magnitude larger in size (~1 cm3) and must be operated in a near-zero magnetic field.
Magnetic Sense - Biological Compass
 Passive Electrolocation in Fish is a process where certain species of
fish or aquatic amphibians can
detect electric fields using specialized
electroreceptors to detect and to locate the source of an external
electric field in its environment creating the electric field. These
external electric fields can be produced from animate sources such as: DC
fields produced by any bioelectrical process in a living organism. DC
fields produced from wounded or damaged organism. Electric fields produced
by actions of the nerves or muscles of fish.
Electric fields emitted by
specially developed electric organs from fish or to inanimate sources such
as the electric fields induced by movement of a conducting organism
through the earth's magnetic field, or from atmospheric electricity. These
external fields the fish identifies are low or high frequency, weak
electric signals that the fish uses to detect prey, locate other fish,
avoid predators, and navigate in the Earth’s magnetic field.
Passive Electrolocation in Fish is a process where certain species of
fish or aquatic amphibians can
detect electric fields using specialized
electroreceptors to detect and to locate the source of an external
electric field in its environment creating the electric field. These
external electric fields can be produced from animate sources such as: DC
fields produced by any bioelectrical process in a living organism. DC
fields produced from wounded or damaged organism. Electric fields produced
by actions of the nerves or muscles of fish.
Electric fields emitted by
specially developed electric organs from fish or to inanimate sources such
as the electric fields induced by movement of a conducting organism
through the earth's magnetic field, or from atmospheric electricity. These
external fields the fish identifies are low or high frequency, weak
electric signals that the fish uses to detect prey, locate other fish,
avoid predators, and navigate in the Earth’s magnetic field.
Animals that Navigate using Magnetism
Magnetoception is the ability to detect magnetic fields, which is principally useful in providing a sense of direction when detecting the Earth’s magnetic field. Unlike most birds, humans do not have a strong magentoception, however, experiments have demonstrated that we do tend to have some sense of magnetic fields. The mechanism for this is not completely understood; it is theorized that this has something to do with deposits of ferric iron in our noses. This would make sense if that is correct as humans who are given magnetic implants have been shown to have a much stronger magnetoception than humans without. Fast Triplet, the triplet referring to the spin state of the electron pair. Animals that sense Earth's magnetic field include sea turtles, birds, fish and lobsters. Sea turtles, for example, can use the ability for navigation to return to the beach where they were born.
Sense of Direction - Brain Cells for Spatial Reasoning - Sense of Time - Human Body Magnetic Field
Animal Navigation is the ability of many animals to find their way accurately without maps or instruments. Birds such as the Arctic tern, insects such as the monarch butterfly and fish such as the salmon regularly migrate thousands of miles to and from their breeding grounds, and many other species navigate effectively over shorter distances.
Study challenges long-held theories on how migratory birds navigate. Migratory birds are known for their ability to traverse thousands of kilometres to reach their breeding or wintering grounds. Research found that these birds, in this case, Eurasian reed warblers (Acrocephalus scirpaceus) are using only the Earth's magnetic inclination and declination to determine their position and direction. This challenges the long-held belief that all components of the Earth's magnetic field, especially total intensity, are essential for accurate navigation. Magnetic Sense of Birds.
Cryptochrome are a class of flavoproteins that are sensitive to blue light. They are found in plants and animals. Cryptochromes are involved in the circadian rhythms of plants and animals, and possibly also in the sensing of magnetic fields in a number of species. The name cryptochrome was proposed as a portmanteau combining the cryptic nature of the photoreceptor, and the cryptogamic organisms on which many blue-light studies were carried out.
Flavoprotein are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin that are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including, but by no means limited to, bioluminescence, removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, DNA repair, and apoptosis. The spectroscopic properties of the flavin cofactor make it a natural reporter for changes occurring within the active site; this makes flavoproteins one of the most-studied enzyme families.
Cry4 protein belongs to a group of proteins called cryptochromes. Normally they regulate the biological clock, but have also been considered significant for the magnetic sense. Cry4 is an ideal magnetoreceptor as the level of the protein in the eyes is constant.
Magnetotactic Bacteria are a polyphyletic group of bacteria that orient themselves along the magnetic field lines of Earth's magnetic field. To perform this task, these bacteria have organelles called magnetosomes that contain magnetic crystals. The biological phenomenon of microorganisms tending to move in response to the environment's magnetic characteristics is known as magnetotaxis, which is a process implemented by a diverse group of gram negative bacteria that involves orienting and coordinating movement in response to Earth's magnetic field.
Jual Magnet - Toko Magnet - Fermi Lab - Higgs Boson - T-Shirts
Caterpillars can detect their predators by the static electricity they emit. Caterpillars respond defensively to electric fields similar to those emitted by their natural predators, scientists have found. Experts showed that caterpillar hairs move in response to electric fields and are most sensitive to the frequencies that correspond to the wingbeats frequencies of other insects, indicating that their hairs could be tuned to pick up the electrical cues of their predators.
Evidence for a Human Geomagnetic Sense. Scientists develop a robust experiment that shows human brain waves respond to changes in Earth-strength magnetic fields. Human Body Magnetic Field.
Bio-Magnetic - Bio-Electric
Volume Conduction a term used in bio-electro-magnetism, can be defined as the transmission of electric or magnetic fields from an electric primary current source through biological tissue towards measurement sensors.
Bioelectromagnetics is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic fields and biological entities. Areas of study include electrical or electromagnetic fields produced by living cells, tissues or organisms, including bioluminescent bacteria; for example, the cell membrane potential and the electric currents that flow in nerves and muscles, as a result of action potentials. Others include animal navigation utilizing the geomagnetic field; potential effects of man-made sources of electromagnetic fields like mobile phones; and developing new therapies to treat various conditions. The term can also refer to the ability of living cells, tissues, and organisms to produce electrical fields and the response of cells to electromagnetic fields.
Biomagnetism is the phenomenon of magnetic fields produced by living organisms; it is a subset of bioelectromagnetism. In contrast, organisms' use of magnetism in navigation is magnetoception and the study of the magnetic fields' effects on organisms is magnetobiology.
Biofields List (wiki) - Bio-Electronics
Team Maps Magnetic Fields of Bacterial Cells, Nano-objects for the first time
Bioelectrogenesis is the generation of electricity by living organisms, a phenomenon that belongs to the science of electrophysiology. In biological cells, electrochemically active transmembrane ion channel and transporter proteins, such as the sodium-potassium pump, make electricity generation possible by maintaining a voltage imbalance from an electrical potential difference between the intracellular and extracellular space. The sodium-potassium pump simultaneously releases three Na ions away from, and influxes two K ions towards, the intracellular space. This generates an electrical potential gradient from the uneven charge separation created. The process consumes metabolic energy in the form of ATP. Electrogenic is something that produces a change in the electrical potential of a cell.
Bioelectricity refers to the regulation of cell, tissue, and organ-level patterning and behavior as the result of endogenous electrically-mediated signaling. Cells and tissues of all types use ion fluxes to communicate electrically. The charge carrier in bioelectricity is the ion (charged atom), and an electric current and field is generated whenever a net ion flux occur. Endogenous electric currents and fields, ion fluxes, and differences in resting potential across tissues comprise an ancient and highly conserved communicating and signaling system. It functions alongside (in series and in parallel to) biochemical factors, transcriptional networks, and other physical forces to regulate the cell behavior and large-scale patterning during embryogenesis, regeneration, cancer, and many other processes. Human Magnetic Field.
Gravity - Gravitation
Gravitation is a natural phenomenon by which all things with mass can move toward one another, including planets, stars and galaxies. Since energy and mass are equivalent, all forms of energy, including light, also cause gravitation and are under the influence of it.
Magnetism - Anti-Gravity - Levitation - Vacuum - Black Holes - Space - Gravito - Superconductor
Gravitate is to move toward something due to the pull of gravitation. To be attracted to something.
Gravity will accelerate any object at a rate of 32 feet per second per second. (fps 2 ), which means the velocity it's moving at is increasing by 32 feet per second every second. After two seconds, Object A is falling at 64 feet per second. 9.7536 m / s2.
Equations for a falling body describes the resultant trajectories when objects move owing to a constant gravitational force under normal Earth-bound conditions. For example, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to F = mg, where m is the mass of the body. This assumption is reasonable for objects falling to earth over the relatively short vertical distances of our everyday experience, but is untrue over larger distances, such as spacecraft trajectories. Please note that in this article any resistance from air (drag) is neglected.
 Gravitational Constant is an empirical physical constant involved in
the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of
universal gravitation and in Albert Einstein's general theory of
relativity. Its measured value is approximately 6.674×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2.
(also known as the universal gravitational constant, or as Newton's
constant, denoted by the letter G).
Gravitational Constant is an empirical physical constant involved in
the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of
universal gravitation and in Albert Einstein's general theory of
relativity. Its measured value is approximately 6.674×10−11 m3⋅kg−1⋅s−2.
(also known as the universal gravitational constant, or as Newton's
constant, denoted by the letter G).Equivalence Principle in Gravity is the inertial mass and gravitational mass are the same thing. Then, gravitational force is proportional to inertial mass, and the proportionality is independent of the kind of matter. Equivalence principle is the hypothesis that the observed equivalence of gravitational and inertial mass is a consequence of nature.
Gravity exists everywhere in the universe — without it, everything would simply fly apart and cease to exist. The reason astronauts on the space station look weightless is because both the space station and the astronauts are in a continuous state of free fall toward the earth. Because objects of any mass fall at the same speed, the space station, and the astronauts fall together, creating the illusion of zero gravity.
Gravitational Collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the centre of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formation in the universe. Over time an initial, relatively smooth distribution of matter will collapse to form pockets of higher density, typically creating a hierarchy of condensed structures such as clusters of galaxies, stellar groups, stars and planets. A star is born through the gradual gravitational collapse of a cloud of interstellar matter. The compression caused by the collapse raises the temperature until thermonuclear fusion occurs at the center of the star, at which point the collapse gradually comes to a halt as the outward thermal pressure balances the gravitational forces. The star then exists in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Once all its energy sources are exhausted, a star will again collapse until it reaches a new equilibrium state.
Great Attractor is a region of gravitational attraction in intergalactic space and the apparent central gravitational point of the Laniakea Supercluster of galaxies that includes the Milky Way galaxy, as well as about 100,000 other galaxies. The observed attraction suggests a localized concentration of mass having the order of 1016 solar masses. The attraction is observable by its effect on the motion of galaxies and their associated clusters over a region of hundreds of millions of light-years across the universe. Neighboring galaxies are being pulled off course at over one million miles per hour. These galaxies are observable above and below the Zone of Avoidance; all are redshifted in accordance with the Hubble flow, indicating that they are receding relative to the Milky Way and to each other, but the variations in their redshifts are large enough and regular enough to reveal that they are slightly drawn towards the attraction. The variations in their redshifts are known as peculiar velocities, and cover a range from about +700 km/s to −700 km/s, depending on the angular deviation from the direction to the Great Attractor. The Great Attractor itself is moving towards the Shapley Supercluster. The Dipole Repeller.
Center of Gravity of an object is the point at which weight is evenly dispersed and all sides are in balance. Center of Gravity is the average location of the weight of an object. A human's center of gravity can change as he takes on different positions, but in many other objects, it's a fixed location. (a Donut has no center of gravity).
Center of Mass of a distribution of mass in space or the balance point is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may be applied to cause a linear acceleration without an angular acceleration. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass. It is a hypothetical point where the entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualise its motion. In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton's laws of motion. In the case of a single rigid body, the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body, and if the body has uniform density, it will be located at the centroid. The center of mass may be located outside the physical body, as is sometimes the case for hollow or open-shaped objects, such as a horseshoe. In the case of a distribution of separate bodies, such as the planets of the Solar System, the center of mass may not correspond to the position of any individual member of the system. The center of mass is a useful reference point for calculations in mechanics that involve masses distributed in space, such as the linear and angular momentum of planetary bodies and rigid body dynamics. In orbital mechanics, the equations of motion of planets are formulated as point masses located at the centers of mass. The center of mass frame is an inertial frame in which the center of mass of a system is at rest with respect to the origin of the coordinate system.
A 'Cosmic Glitch' in Gravity. When we try to understand gravity on a cosmic scale, at the scale of galaxy clusters and beyond, we encounter apparent inconsistencies with the predictions of general relativity.
Plumb Bob or Plumb-Line is a weight with a pointed tip on the bottom, suspended from a string and used as a vertical reference line. It is a precursor to the spirit level and used to establish a vertical or horizontal datum. The instrument has been used since at least the time of ancient Egypt to ensure that constructions are "plumb", or vertical. It is also used in surveying, to establish the nadir with respect to gravity of a point in space. It is used with a variety of instruments (including levels, theodolites, and steel tapes) to set the instrument exactly over a fixed survey marker or to transcribe positions onto the ground for placing a marker.
Rockets need to travel 11 kilometers or 7 miles per second, or over 40,000 kilometers per hour or 25,000 miles per hour, to enter Low Earth Orbit. Then you would need to travel 370,000 miles or 600,000 kilometers from the Earth in order to be free from Earths Gravitational Pull. Then you would need to travel 39.5 astronomical units or 3,670,050,000 miles or 5,906,380,000 kilometers from the Suns Magnetic pull, which is far beyond the orbit of Pluto.
Escape Velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape from the gravitational influence of a massive body. The escape velocity from Earth is about 11.186 km/s (6.951 mi/s; 40,270 km/h; 25,020 mph) at the surface. More generally, escape velocity is the speed at which the sum of an object's kinetic energy and its gravitational potential energy is equal to zero; an object which has achieved escape velocity is neither on the surface, nor in a closed orbit (of any radius). With escape velocity in a direction pointing away from the ground of a massive body, the object will move away from the body, slowing forever and approaching, but never reaching, zero speed. Once escape velocity is achieved, no further impulse need be applied for it to continue in its escape. In other words, if given escape velocity, the object will move away from the other body, continually slowing, and will asymptotically approach zero speed as the object's distance approaches infinity, never to return. Note that the minimum escape velocity assumes that there is no friction (e.g., atmospheric drag), which would increase the required instantaneous velocity to escape the gravititational influence, and that there will be no future sources of additional velocity (e.g., thrust), which would reduce the required instantaneous velocity.
Standard Gravity is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined by standard as 9.80665 m/s2, which is exactly 35.30394 km/(h·s) (about 32.174 ft/s2, or 21.937 mph/s).
Gravity Current is a primarily horizontal flow in a gravitational field that is driven by a density difference in a fluid or fluids and is constrained to flow horizontally by, for instance, a ceiling. Typically, the density difference is small enough for the Boussinesq approximation to be valid. Gravity currents can be thought of as either finite in volume, such as the pyroclastic flow from a volcano eruption, or continuously supplied from a source, such as warm air leaving the open doorway of a house in winter. Other examples include dust storms, turbidity currents, avalanches, discharge from wastewater or industrial processes into rivers, or river discharge into the ocean. Gravity currents are typically much longer than they are tall. Flows that are primarily vertical are known as plumes. As a result, it can be shown (using dimensional analysis) that vertical velocities are generally much smaller than horizontal velocities in the current; the pressure distribution is thus approximately hydrostatic, apart from near the leading edge. Gravity currents may be simulated by the shallow water equations, with special dispensation for the leading edge which behaves as a discontinuity. When a gravity current propagates along a plane of neutral buoyancy within a stratified ambient fluid, it is known as a gravity current intrusion.
Gravity Hole is a spot where Earth's gravitational pull is weaker, its mass is lower than normal, and the sea level dips by over 328 feet (100 meters). Gravity holes happen as the Earth gravitational field is not uniform due to variations in density and mass distribution. There are some areas which are denser than the others and this variation in the density create differences in the gravitational attractions, that forms geoids.
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation states that a particle attracts every other particle in the universe using a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Gravitational Potential at a location is equal to the work (energy transferred) per unit mass that would be needed to move an object to that location from a fixed reference location. It is analogous to the electric potential with mass playing the role of charge. The reference location, where the potential is zero, is by convention infinitely far away from any mass, resulting in a negative potential at any finite distance. In mathematics, the gravitational potential is also known as the Newtonian potential and is fundamental in the study of potential theory. It may also be used for solving the electrostatic and magnetostatic fields generated by uniformly charged or polarized ellipsoidal bodies.
Micro-G Environment is more or less synonymous with the terms weightlessness and zero-g, but with an emphasis on the fact that g-forces are never exactly zero—just very small (on the ISS, for example, the small g-forces come from tidal effects, gravity from objects other than the Earth, such as astronauts, the spacecraft, and the Sun, and, occasionally, air resistance). The symbol for microgravity, µg, was used on the insignias of Space Shuttle flights STS-87 and STS-107, because these flights were devoted to microgravity research in low Earth orbit.
Zero Gravity does not exist (very low gravity)
Reduced-Gravity Aircraft is a type of fixed-wing aircraft that provides brief near-weightless environments for training astronauts, conducting research and making gravity-free movie shots. Versions of such airplanes were operated by the NASA Reduced Gravity Research Program., and one is currently operated by the Human Spaceflight and Robotic Exploration Programmes of the European Space Agency. The unofficial nickname "vomit comet" became popular among those who experienced their operation. Parabolic Flight.
Weightlessness is the complete or near-complete absence of the sensation of weight. This is also termed zero-g, although the more correct term is "zero g-force". It occurs in the absence of any contact forces upon objects including the human body.
G-Force is a measurement of the type of acceleration that causes weight.
ZARM Bremen Drop Tower offers the opportunity for short-term experiments under high-quality microgravity conditions and is the only laboratory of this kind in Europe. Inside a Drop Tower Creating Zero Gravity on Earth (youtube). Zero-G Experiments on Earth: The Bremen Drop Tower (youtube) - The Bremen Drop Tower.
Artificial Gravity is the creation of an inertial force that mimics the effects of a gravitational force, usually by rotation. Artificial gravity, or rotational gravity, is thus the appearance of a centrifugal force in a rotating frame of reference (the transmission of centripetal acceleration via normal force in the non-rotating frame of reference), as opposed to the force experienced in linear acceleration, which by the equivalence principle is indistinguishable from gravity. In a more general sense, "artificial gravity" may also refer to the effect of linear acceleration, e.g. by means of a rocket engine. Rotational simulated gravity has been used in simulations to help astronauts train for extreme conditions. Rotational simulated gravity has been proposed as a solution in human spaceflight to the adverse health effects caused by prolonged weightlessness. However, there are no current practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans due to concerns about the size and cost of a spacecraft necessary to produce a useful centripetal force comparable to the gravitational field strength on Earth (g).
Gravity is 0.1% stronger in the northern United States than in the southern United States.
Orthometric Height of a point is the distance H along a plumb line from the point to the geoid, which is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravity and rotation alone, in the absence of other influences such as winds and tides.
Gravitational Wave are ripples in the curvature of spacetime that propagate as waves at the speed of light, generated in certain gravitational interactions that propagate outward from their source.
Speed of Gravity refers to the speed of a gravitational wave, which, as predicted by general relativity and confirmed by observation of the GW170817 neutron star merger, is the same speed as the speed of light (c).
Gravitational Energy s the gravitational potential energy a body with mass has in relation to another massive object. It is potential energy associated with the gravitational field. Gravitational energy is dependent on the masses of two bodies, their distance apart and the gravitational constant (G).
Gravitational Lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels towards the observer.
Einstein Field Equations is the set of 10 equations in Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity that describes the fundamental interaction of gravitation as a result of spacetime being curved by mass and energy.
Supercomputer shows 'Chameleon Theory' could change how we think about gravity. Chameleon Theory changes behaviour according to the environment.
Field Equation is a partial differential equation which determines the dynamics of a physical field, specifically the time evolution and spatial distribution of the field. The solutions to the equation are mathematical functions which correspond directly to the field, as a functions of time and space. Since the field equation is a partial differential equation, there are families of solutions which represent a variety of physical possibilities. Usually, there is not just a single equation, but a set of coupled equations which must be solved simultaneously. Field equations are not ordinary differential equations since a field depends on space and time, which requires at least two variables.
Inverse-Square Law is any physical law stating that a specified physical quantity or intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity.
Gravitation Physics Book (amazon)
General Relativity generalizes special relativity and Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time, or spacetime. In particular, the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of partial differential equations.
Curved Space
Equivalence Principle is any of several related concepts dealing with the equivalence of gravitational and inertial mass, and to Albert Einstein's observation that the gravitational "force" as experienced locally while standing on a massive body (such as the Earth) is actually the same as the pseudo-force experienced by an observer in a non-inertial (accelerated) frame of reference.
Quantum Gravity is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics, and where quantum effects cannot be ignored, such as in the vicinity of black holes or similar compact astrophysical objects where the effects of gravity are strong. Three of the four fundamental forces of physics are described within the framework of quantum mechanics and quantum field theory. The current understanding of the fourth force, gravity, is based on Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which is formulated within the entirely different framework of classical physics. However, that description is incomplete: describing the gravitational field of a black hole in the general theory of relativity, physical quantities such as the spacetime curvature diverge at the center of the black hole. This signals the break down of the general theory of relativity and the need for a theory that goes beyond general relativity into the quantum. At distances very close to the center of the black hole (closer than the Planck length), quantum fluctuations of spacetime are expected to play an important role. To describe these quantum effects a theory of quantum gravity is needed. Such a theory should allow the description to be extended closer to the center and might even allow an understanding of physics at the center of a black hole. On more formal grounds one can argue that a classical system cannot consistently be coupled to a quantum one.
Scientists test for Quantum Nature of Gravity. Research at the south pole studied the mysterious quantum structure of space and time. A new study reports on a deep new probe into the interface between the theories of gravity and quantum mechanics, using ultra-high energy neutrino particles detected by a particle detector set deep into the Antarctic glacier at the south pole.
Physicists develop novel test of the Holographic Principle. In the quest toward finding the correct theory of quantum gravity, physicists have been testing the holographic principle which, they say, is a key property of any valid theory of quantum gravity.
Causal Sets program is an approach to quantum gravity. Its founding principles are that spacetime is fundamentally discrete (a collection of discrete spacetime points, called the elements of the causal set) and that spacetime events are related by a partial order. This partial order has the physical meaning of the causality relations between spacetime events.
Causal Structure of an arbitrary (possibly curved) Lorentzian manifold is made more complicated by the presence of curvature. Discussions of the causal structure for such manifolds must be phrased in terms of smooth curves joining pairs of points. Conditions on the tangent vectors of the curves then define the causal relationships.
Experiment to test quantum gravity just got a bit less complicated. A well-known consequence of the quantum theory is the phenomenon called quantum superposition: in certain situations, quantum states can have two different values at the same time. Take an electron that is irradiated with laser light. Quantum theory says that it can either absorb or not absorb the photon energy from the light. Absorbing the energy would alter the electron's spin, a magnetic moment that can be either up or down. The result of quantum superposition is that the spin is both up and down. These quantum effects take place in tiny objects, such as electrons. By targeting an electron in a specially constructed miniature diamond, it is possible to create superposition in a much larger object. The diamond is small enough to sustain this superposition, but also large enough to feel the pull of gravity. This characteristic is what the experiment exploits: placing two of these diamonds next to each other in freefall and, therefore, cancelling out external gravity. This means that they only interact through the gravity between them. And that is where another quantum phenomenon comes in. Quantum entanglement means that when two or more particles are generated in close proximity, their quantum states are linked. In the case of the diamonds, if one is spin up, the other, entangled diamond should be spin down. So, the experiment is designed to determine whether quantum entanglement occurs in the pair during freefall, when the force of the gravity between the diamonds is the only way that they interact.
Loop Quantum Gravity is a theory of quantum gravity, which aims to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity, incorporating matter of the Standard Model into the framework established for the pure quantum gravity case. It is an attempt to develop a quantum theory of gravity based directly on Einstein's geometric formulation rather than the treatment of gravity as a force. As a theory LQG postulates that the structure of space and time is composed of finite loops woven into an extremely fine fabric or network. These networks of loops are called spin networks. The evolution of a spin network, or spin foam, has a scale above the order of a Planck length, approximately 10−35 meters, and smaller scales are meaningless. Consequently, not just matter, but space itself, prefers an atomic structure. The areas of research, which involves about 30 research groups worldwide, share the basic physical assumptions and the mathematical description of quantum space. Research has evolved in two directions: the more traditional canonical loop quantum gravity, and the newer covariant loop quantum gravity, called spin foam theory. The most well-developed theory that has been advanced as a direct result of loop quantum gravity is called loop quantum cosmology (LQC). LQC advances the study of the early universe, incorporating the concept of the Big Bang into the broader theory of the Big Bounce, which envisions the Big Bang as the beginning of a period of expansion that follows a period of contraction, which one could talk of as the Big Crunch.
Graviton is the hypothetical quantum of gravity, an elementary particle that mediates the force of gravity. There is no complete quantum field theory of gravitons due to an outstanding mathematical problem with renormalization in general relativity. In string theory, believed to be a consistent theory of quantum gravity, the graviton is a massless state of a fundamental string. If it exists, the graviton is expected to be massless because the gravitational force is very long range and appears to propagate at the speed of light. The graviton must be a spin-2 boson because the source of gravitation is the stress–energy tensor, a second-order tensor (compared with electromagnetism's spin-1 photon, the source of which is the four-current, a first-order tensor). Additionally, it can be shown that any massless spin-2 field would give rise to a force indistinguishable from gravitation, because a massless spin-2 field would couple to the stress–energy tensor in the same way that gravitational interactions do. This result suggests that, if a massless spin-2 particle is discovered, it must be the graviton.
Perturbation in astronomy is the complex motion of a massive body subject to forces other than the gravitational attraction of a single other massive body. The other forces can include a third (fourth, fifth, etc.) body, resistance, as from an atmosphere, and the off-center attraction of an oblate or otherwise misshapen body.
Our Surprising Magnetic Galaxy. The first 3D map of magnetic fields in our galaxy explains star-forming regions. A team of astronomers has created the first-ever map of magnetic field structures within a spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy. Previous studies on galactic magnetic fields only gave a very general picture, but the new study reveals that magnetic fields in the spiral arms of our galaxy break away from this general picture significantly and are tilted away from the galactic average by a high degree. The findings suggest magnetic fields strongly impact star-forming regions which means they played a part in the creation of our own solar system. Polar.
Anti-Gravity - Levitation
Anti-Gravity is an idea of creating a place or object that is free from the force of gravity.
Levitation is the process by which an object is held aloft, without mechanical support, in a stable position. Levitation is accomplished by providing an upward force that counteracts the pull of gravity in relation to gravity on earth, plus a smaller stabilizing force that pushes the object toward a home position whenever it is a small distance away from that home position. The force can be a fundamental force such as magnetic or electrostatic, or it can be a reactive force such as optical, buoyant, aerodynamic, or hydrodynamic. Levitation excludes floating at the surface of a liquid because the liquid provides direct mechanical support. Levitation excludes hovering flight by insects, hummingbirds, helicopters, rockets, and balloons because the object provides its own counter-gravity force.
Vacuum Energy - Zero Point Energy -Gyroscopes - Space Travel - Expansion
Levitate is to cause to rise in the air or be suspended in the air and float, as if in defiance of gravity.
Superconducting Quantum Levitation on a 3 Möbius Strip (youtube)
Levitating a Superconductor: Boaz Almog (video and interactive text) - How can a super-thin 3-inch disk levitate something 70,000 times its own weight? Superconductors.
Anti-Gravity Project - Jeff Lucas Astrophotographer - Published on Oct 26, 2018 (youtube) - Lenz's, Ohm's Law and Nikola Tesla about how I think anti-gravity works. When it comes to building anti-gravity, everyone is building it wrong, its upside down, its not the number of magnets, it how much E = I/R ~ direct current you can apply to magnets to create levitation repulsive force, polarities e.g. North to North, South to South.
Meissner Effect - Gravito - Gravito-Electromagnetism - Magnetodynamics
Gravity control refers to the idea of manipulating or counteracting gravitational forces. Altering the mass distribution of objects could, in theory, affect gravitational fields.
Quantum Levitation Kits - Meta-Materials - Superconductor
Magnetic Levitation or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force and any other forces. The two primary issues involved in magnetic levitation are lifting forces: providing an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity, and stability: ensuring that the system does not spontaneously slide or flip into a configuration where the lift is neutralized. Magnetic levitation is used for maglev trains, contactless melting, magnetic bearings, and for product display purposes.
Spin-Stabilized Magnetic Levitation is a phenomenon of magnetic levitation whereby a spinning magnet or array of magnets is levitated via magnetic forces above another magnet or array of magnets, and stabilised by gyroscopic effect due to a spin that is neither too fast, nor too slow to allow for a necessary precession.
Electrostatic Levitation is the process of using an electric field to levitate a charged object and counteract the effects of gravity.
Acoustic Levitation is a method for suspending matter in air against gravity using acoustic radiation pressure from high intensity sound waves. Acoustic Radiation Force (wiki)
Scientists Levitate Particles with Sound to find out how they cluster together. Scientists have used sound waves to levitate particles, revealing new insights about how materials cluster together in the absence of gravity -- principles which underlie everything from how molecules assemble to the very early stages of planet formation from space dust.
Light and sound waves reveal negative pressure. Negative pressure is a rare and challenging-to-detect phenomenon in physics. Using liquid-filled optical fibers and sound waves, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light.
Aerodynamic Levitation is the use of gas pressure to levitate materials so that they are no longer in physical contact with any container. In scientific experiments this removes contamination and nucleation issues associated with physical contact with a container.
Electrogravitics is claimed to be an unconventional type of effect or anti-gravity force created by an electric field's effect on a mass.
Gravity's Effect On Antimatter Revealed. Researchers have observed individual atoms of anti-hydrogen fall under the effects of gravity. In confirming antimatter and regular matter are gravitationally attracted, the finding rules out gravitational repulsion as the reason why antimatter is largely missing from the observable universe.
Telekinesis is the ability to move objects using only your mind. It's a hypothetical psychic ability allowing a person to influence a physical system without physical interaction.
Levitron is a brand of levitating toys and gifts in science and educational markets.
United States Gravity Control Propulsion Research publicized goals were to develop and discover technologies and theories for the manipulation of gravity or gravity-like fields for propulsion. (anti-gravity, anti-gravitation, baricentric, counterbary, electrogravitics (eGrav), G-projects, gravitics, gravity control, and gravity propulsion). Space Travel.
Halbach Array is a special arrangement of permanent magnets that augments the magnetic field on one side of the array while cancelling the field to near zero on the other side. This is achieved by having a spatially rotating pattern of magnetisation. The rotating pattern of permanent magnets (on the front face; on the left, up, right, down) can be continued indefinitely and have the same effect. The effect of this arrangement is roughly similar to many horseshoe magnets placed adjacent to each other, with similar poles touching.
Gravitational Singularity is a location in space-time where the gravitational field of a celestial body becomes infinite in a way that does not depend on the coordinate system.
Quantum Gravity is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe the force of gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics, and where quantum effects cannot be ignored. Quantum Gravity.
Casimir Effect is physical forces arising from a quantized field.
Loop Quantum Gravity is a theory that attempts to describe the quantum properties of the universe and gravity. It is also a theory of quantum spacetime because, according to general relativity, gravity is a manifestation of the geometry of spacetime. LQG is an attempt to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity. Quantum Space.
Quantum Locking occurs when a superconductor becomes trapped within a magnetic field. When this happens, the superconductor will be locked in space and will not move without an outside force. 0 reactions. Now, this is possible due to the Meissner effect.
Quantum Locking Will Blow Your Mind—How Does it Work? (youtubr)
Flux Pinning is the phenomenon where a superconductor is pinned in space above a magnet. The superconductor must be a type-II superconductor because type-I superconductors cannot be penetrated by magnetic fields. Some type-I superconductors can experience the effects of flux pinning if they are thin enough. If the material's thickness is comparable to the London penetration depth, the magnetic field can pass through the material. The act of magnetic penetration is what makes flux pinning possible. At higher magnetic fields (above Hc1 and below Hc2) the superconductor allows magnetic flux to enter in quantized packets surrounded by a superconducting current vortex (see Quantum vortex). These sites of penetration are known as flux tubes. The number of flux tubes per unit area is proportional to the magnetic field with a constant of proportionality equal to the magnetic flux quantum. On a simple 76 millimeter diameter, 1-micrometer thick disk, next to a magnetic field of 28 kA/m, there are approximately 100 billion flux tubes that hold 70,000 times the superconductor's weight. At lower temperatures the flux tubes are pinned in place and cannot move. This pinning is what holds the superconductor in place thereby allowing it to levitate. This phenomenon is closely related to the Meissner effect, though with one crucial difference — the Meissner effect shields the superconductor from all magnetic fields causing repulsion, unlike the pinned state of the superconductor disk which pins flux, and the superconductor in place. (quantum pinning).
Eddy Current are loops of electrical current induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field in the conductor according to Faraday's law of induction. Eddy currents flow in closed loops within conductors, in planes perpendicular to the magnetic field. (Eddy currents are also called Foucault's currents). Friction.
Researchers make sand that flows uphill. Engineering researchers have discovered that sand can actually flow uphill. A corresponding video shows what happens when torque and an attractive force is applied to each grain -- the grains flow uphill, up walls, and up and down stairs.
Cooper Pair is a pair of electrons or other fermions bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner, an arbitrarily small attraction between electrons in a metal can cause a paired state of electrons to have a lower energy than the Fermi energy, which implies that the pair is bound. In conventional superconductors, this attraction is due to the electron–phonon interaction. The Cooper pair state is responsible for superconductivity.
Speed of Gravity refers to the speed of a gravitational wave, which is the same speed as the speed of light.
Quantum Entanglement is a physical phenomenon that occurs when pairs or groups of particles are generated or interact in ways such that the quantum state of each particle cannot be described independently of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance – instead, a quantum state must be described for the system as a whole. Entanglement.
Quantum Teleportation is a process by which quantum information (e.g. the exact state of an atom or photon) can be transmitted (exactly, in principle) from one location to another, with the help of classical communication and previously shared quantum entanglement between the sending and receiving location. Because it depends on classical communication, which can proceed no faster than the speed of light, it cannot currently be used for faster-than-light transport or communication of classical bits. While it has proven possible to teleport one or more qubits of information between two (entangled) atoms, this has not yet been achieved between molecules or anything larger. Teleportation.
Strange Matters (2015) (video 1:47)
Aegis uses a beam of antiprotons from the Antiproton Decelerator to measure the value of Earth's gravitational acceleration.
Gbar - Gravitational Behaviour of Antihydrogen at Rest.
Difference between Sound Waves and Electromagnetic Waves.
The Ability to Cancel Magnetic Fields has benefits in quantum technology, biomedicine and neurology. This is achieved through creating a device comprised of a careful arrangement of electrical wires. This creates additional fields and so counteracts the effects of the unwanted magnetic field.
Anti-Matter - Exotic Matter - Magnetics
Acoustic Tractor Beams use the Power of Sound to hold particles in mid-air, and unlike magnetic levitation, they can grab most solids or liquids even small insects. Acoustic tractor beam could pave the way for levitating humans.
Defying Gravity is from the musical called Wicked, an original broadway cast recording 2003) (youtube) - Something has changed within me, Something is not the same, I'm through with playing by the rules, Of someone else's game, Too late for second-guessing, Too late to go back to sleep, It's time to trust my instincts, Close my eyes and leap, It's time to try defying gravity, I think I'll try defying gravity, Kiss me goodbye, I'm defying gravity, And you won't bring me down, I'm through accepting limits, 'Cause someone says they're so, Some things I cannot change, But till I try, I'll never know, Too long I've been afraid of, Losing love, I guess I've lost, Well, if that's love, it comes at much too high a cost, I'd sooner buy defying gravity, Kiss me goodbye, I'm defying gravity, I think I'll try defying gravity, And you won't bring me down, Unlimited (unlimited), My future is (my future is) unlimited (unlimited), And I've just had a vision, almost like a prophecy, I know, it sounds truly crazy, And true, the vision's hazy, But I swear, someday I'll be, Flying so high (defying gravity), Kiss me goodbye (defying gravity), So if you care to find me, Look to the western sky, As someone told me lately, "Everyone deserves the chance to fly", I'm defying gravity, And you won't bring me down, Bring me down,Bring me down.
Wicked is a musical with music and lyrics by Stephen Schwartz and book by Winnie Holzman. The show is told from the perspective of the witches of the Land of Oz. Wicked tells the story of two unlikely friends, Elphaba (the Wicked Witch of the West) and Galinda (later Glinda the Good Witch), whose relationship struggles through their opposing personalities and viewpoints, same love interest, reactions to the Wizard's corrupt government, and, ultimately, Elphaba's fall from grace.
Contraction - Expansion
Contraction is the process or result of becoming smaller or pressed together. The act of decreasing. Matter contracts as the temperature or energy decreases.
Length Contraction is the phenomenon that a moving object's length is measured to be shorter than its proper length, which is the length as measured in the object's own rest frame. Length contraction is only in the direction in which the body is travelling. For standard objects, this effect is negligible at everyday speeds, and can be ignored for all regular purposes, only becoming significant as the object approaches the speed of light relative to the observer. Time Dilation.
Gravitational Collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of mass.
Torus (folding, unfolding) - Implosion - Motion - Cavitation - Black Holes Contracting - Contraction of a Dark Matter - Dark Energy - Negative Energy - Conservation of Mass - Material Science
Length Contraction is the phenomenon of a decrease in length of an object as measured by an observer who is traveling at any non-zero velocity relative to the object. Lorentz contraction is the phenomenon that a moving object's length is measured to be shorter than its proper length, which is the length as measured in the object's own rest frame. Relativity.
Compression is the application of balanced inward ("pushing") forces to different points on a material or structure, that is, forces with no net sum or torque directed so as to reduce its size in one or more directions. It is contrasted with tension or traction, the application of balanced outward ("pulling") forces; and with shearing forces, directed so as to displace layers of the material parallel to each other. The compressive strength of materials and structures is an important engineering consideration.
Compressibility is a measure of the relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure (or mean stress) change.
Big Crunch is a theory that space will eventually stop expanding and then reverse and collapse.
The Contraction and Expansion of Magnetic Fields - Contraction Operator Theory - Tensor Contraction - Tensor
*
Expansion is the act of increasing something in size, volume, quantity or scope. Adding information or detail. A discussion that provides additional information. Expansion in mathematics is a function expressed as a sum or product of terms. Matter expands as the temperature or energy increases.
Expansion is a polytope operation where facets are separated and moved radially apart, and new facets are formed at separated elements (vertices, edges, etc.). Equivalently this operation can be imagined by keeping facets in the same position but reducing their size. Vacuum.
Cosmological Constant states that the whole universe is not only expanding but the expansion is speeding up. The only way for that to happen is if there's a strong, steady push coming from everywhere at once. Gravity wants to pull everything together, like when magnets stick together. But the cosmological constant wants to push everything apart, like invisible super-powered air pushing the walls of the balloon away from each other. The cosmological constant is fine-tuned to 120 decimal places.
Entropy - Dark Matter - Conservation - Symmetry
Boyle's Law is an experimental gas law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to increase as the volume of the container decreases.
Metric Expansion of Space is the increase of the distance between two distant parts of the universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. This is different from other examples of expansions and explosions in that, as far as observations can ascertain, it is a property of the entirety of the universe rather than a phenomenon that can be contained and observed from the outside. Torus.
Inflation in cosmology is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from 10−36 seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singularity to sometime between 10−33 and 10−32 seconds after the singularity. Following the inflationary period, the Universe continues to expand, but at a less rapid rate. Faster than the Speed of Light.
Expansion of the Universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not expand "into" anything and does not require space to exist "outside" it. Technically, neither space nor objects in space move. Instead it is the metric governing the size and geometry of spacetime itself that changes in scale. Although light and objects within spacetime cannot travel faster than the speed of light, this limitation does not restrict the metric itself. To an observer it appears that space is expanding and all but the nearest galaxies are receding into the distance. During the inflationary epoch about 10−32 of a second after the Big Bang, the universe suddenly expanded, and its volume increased by a factor of at least 1078 (an expansion of distance by a factor of at least 1026 in each of the three dimensions), equivalent to expanding an object 1 nanometer (10−9 m, about half the width of a molecule of DNA) in length to one approximately 10.6 light years (about 1017 m or 62 trillion miles) long. A much slower and gradual expansion of space continued after this, until at around 9.8 billion years after the Big Bang (4 billion years ago) it began to gradually expand more quickly, and is still doing so. The metric expansion of space is of a kind completely different from the expansions and explosions seen in daily life. It also seems to be a property of the universe as a whole rather than a phenomenon that applies just to one part of the universe or can be observed from "outside" of it. The universe is expanding into what? When something expands in a sealed container that is filled completely, then where does the space come from as it expands?
Taylor Expansion is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point.
Expansion and Contraction (youtube) - Expansion and Contraction (PDF) - Contraction of Dark Matter (PDF)
Adiabatic Process is one that occurs without transfer of heat or matter between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings. In an adiabatic process, energy is transferred only as work. The adiabatic process provides a rigorous conceptual basis for the theory used to expound the first law of thermodynamics, and as such it is a key concept in thermodynamics.
Friedmann Equations are a set of equations in physical cosmology that govern the expansion of space in homogeneous and isotropic models of the universe within the context of general relativity. Steady State.
Repulsive Gravity, in the context of Einstein's theory of General Relativity, refers to a gravitational force that pushes objects away from each other instead of pulling them together. This concept is explored in the context of dark energy, the cosmological constant, and the expansion of the universe. While not a common everyday experience, it's a key concept in understanding the large-scale structure and dynamics of the universe.
Negative Pressure refers to a situation where the air pressure within a space is lower than the surrounding pressure. This is often used in the context of negative pressure rooms, which are designed to prevent contaminated air from escaping into other areas. For example, in hospitals, negative pressure rooms are used to isolate patients with airborne illnesses and prevent the spread of infection.
Negative Energy is a concept used in physics to explain the nature of certain fields, including the gravitational field and various quantum field effects.
Inflation Field is a hypothetical scalar field which is conjectured to have driven cosmic inflation in the very early universe.
Older galaxies may only seem to be moving faster, because in the past, time was faster? If a Galaxy is 13.2 billion light years away, how do we know if it's moving away from us, towards us, or if it's even still there? If you are receiving light that's over 13 billion years old, that means you're seeing the past. And in the past, almost everything was expanding and moving away. So I would not say that the Universe is accelerating, but you can say that the Universe was accelerating? If the universe is expanding, then why is the milky way going to collide with another galaxy? The Light from the sun takes 8 minutes to reach us, if it went out 7 minutes ago we wouldn't know it for another minute. Is space in motion just like the planets and the stars? Does space move too? If so, in what direction?
Redshift is a phenomenon where electromagnetic radiation such as light from an object undergoes an increase in wavelength. Whether or not the radiation is visible, "redshift" means an increase in wavelength, equivalent to a decrease in wave frequency and photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light. Neither the emitted nor perceived light is necessarily red; instead, the term refers to the human perception of longer wavelengths as red, which is at the section of the visible spectrum with the longest wavelengths. Examples of redshifting are a gamma ray perceived as an X-ray, or initially visible light perceived as radio waves. The opposite of a redshift is a blueshift, where wavelengths shorten and energy increases. However, redshift is a more common term and sometimes blueshift is referred to as negative redshift. There are three main causes of redshifts in astronomy and cosmology: Objects move apart (or closer together) in space. This is an example of the Doppler effect. Space itself is expanding, causing objects to become separated without changing their positions in space. This is known as cosmological redshift. All sufficiently distant light sources (generally more than a few million light-years away) show redshift corresponding to the rate of increase in their distance from Earth, known as Hubble's law. Gravitational redshift is a relativistic effect observed due to strong gravitational fields, which distort spacetime and exert a force on light and other particles.
Hubble's Law is the observation in physical cosmology that: Objects observed in deep space—extragalactic space, 10 megaparsecs (Mpc) or more—are found to have a redshift, interpreted as a relative velocity away from Earth; This Doppler shift-measured velocity of various galaxies receding from the Earth is approximately proportional to their distance from the Earth for galaxies up to a few hundred megaparsecs away. Hubble's law is considered the first observational basis for the expansion of the universe and today serves as one of the pieces of evidence most often cited in support of the Big Bang model. The motion of astronomical objects due solely to this expansion is known as the Hubble flow.
Radiating is to extend or spread outward from a center or focus or inward towards a center. Send out rays or waves. Experience a feeling of well-being or happiness, as from good health or an intense emotion.
Our universe is continually contracting and expanding, and humans are somewhere in between the contraction and the radiating.
Space is just weird, everything seems to be in a constant state of Flux...What is here? What is there? Where does it go?
Conservation of Energy - Torus - Thermodynamics
Embryos are also turning themselves upside down and inside out. Embryo folds inwards into a cup-like shape.
Gastrulation is a phase early in the embryonic development of most animals, during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a trilaminar ("three-layered") structure known as the gastrula. These three germ layers are known as the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Trinity.
Chromosomal Inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end. An inversion occurs when a single chromosome undergoes breakage and rearrangement within itself. Inversions are of two types: paracentric and pericentric.
Volvox embryo turning itself inside out (youtube)
How to Turn a Sphere Inside Out (youtube)
Inversion is the act of turning something inside out. Turning upside down; setting on end. Abnormal condition in which an organ is turned inward or inside out (as when the upper part of the uterus is pulled into the cervical canal after childbirth). A chemical process in which the direction of optical rotation of a substance is reversed from dextrorotatory to levorotary or vice versa. Inversion in genetics is a kind of mutation in which the order of the genes in a section of a chromosome is reversed. The reversal of the normal order of words. A counterpoint or a variation of a melody or part in which ascending intervals are replaced by descending intervals and vice versa. When the layer of air near the earth is cooler than an overlying layer.
Morphogenesis - Metamorphosis
Impermanence doctrine asserts that all of conditioned existence, without exception, is "transient, evanescent, inconstant". All temporal things, whether material or mental, are compounded objects in a continuous change of condition, subject to decline and destruction. The concept of impermanence is also found in various schools of Hinduism and Jainism and is one of the essential doctrines and a part of three marks of existence in Buddhism. Trinity.
Quantum Tunneling
Macrocosm and Microcosm refers to a vision of cosmos where the part (microcosm) reflects the whole (macrocosm) and vice versa.
Is space made up of Extremely Tiny Micro Black Holes? And when these tiny holes need to group together, they form A Black Hole, which helps stars, planets and galaxies form?
Is space a type of superconductor? - Lightning
Is gravity just electromagnetic energy? Is gravity just a product of matter, and not related to Space?
"Everything is moving relative to everything else." "Things appear to be the same to every observers frame of reference."
The Universe looks like one large experiment, trying all kind of things. Not every planet has life, not every star gives life, but you can still learn something from all these different outcomes. We are literally standing on one of these successful experiments.
The universe was not made to be able to figure out, it's encrypted. If you could figure it out, then people would exploit it, just like when people exploit laws to commit crimes here on earth.
Space is Alive. Is Space a living entity? With out space there would be no life, no universe. Dark Matter, dark energy, maybe space is not dark at all. Space is the giver of life. Without darkness there is no light? Since space is everywhere, maybe space is God? If space is a living organism, then maybe praying does help. Maybe someone hears our prayers because space is connected to everything in the Universe. But we must speak our prayers, and not just think them.
Cosmic Web is composed of interconnecting filaments of clustered galaxies and gases stretched out across the universe. A giant cosmic web of invisible gas weaves throughout the universe, providing the scaffolding out of which galaxies were born. There may be several hundred billion galaxies in the observable universe based on new data from New Horizons, which is an interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. New Horizons spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow, which became a mission to 486958 Arrokoth. It is the fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. New Frontiers program is a series of space exploration missions being conducted by NASA with the purpose of furthering our understanding of the Solar System.
Big Bang
If the Universe was created about 13.7 Billion years ago, was it the first time or second time? When the Universe first began, was dark matter present then? Was dark energy present then? What is space? What are we expanding into?
Big Bang is a theory of the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model describes how the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure and Hubble's Law.
What came first, space or energy? Is energy a product of space, or is energy the force that creates space, or is space something that is used as a medium for energy? Either way, one of those things came first or at the same time. Then after you have space and energy, you would create a black hole, then create a star, and then create the planets. And the space you created needed to expand in order for more atoms and particles to be added, And then you would experiment with different size stars and black holes and planets and different configurations of matter. And the purpose was to create a planet that could sustain life for as long as the star and the planet allowed life to have a sustainable environment, which is usually around 2 billion years, that's if everything goes as planned. So what came first, a black hole or a star? Maybe the Big Bang was from the first star exploding that was in a seemingly empty space or universe. And from that first really big star explosion, more stars were made from its remains, and then planets started to form soon after. So first there had to be basic elements for making a star. Then the first star exploded, which created a big bang since the universe was really small in the beginning. This big bang created new elements along with dark energy and dark matter, and at the same time, expanding the universe's shell. I believe the universe is round, since that is a common shape that matter likes to use. If something is 14 billions light years away, it's not really a distance, because the light is 14 billion light years old, and we have no idea where that star or cluster of stars is now, especially when using our current time measurement system in 2022. What came first, the idea or the person who had an idea?
An Alternative to the Big Bang Theory? - Arp's Cosmology (youtube) - Halton Arp had a unique view on what Quasars are, together with Hoyle, Narlikar and Burbidge have they found an alternative to the Big Bang which can make sense of Quasars?
Big History is an academic discipline which examines history from the Big Bang to the present. Big History resists specialization, and searches for universal patterns or trends. It examines long time frames using a multidisciplinary approach based on combining numerous disciplines from science and the humanities, and explores human existence in the context of this bigger picture. It integrates studies of the cosmos, Earth, life, and humanity using empirical evidence to explore cause-and-effect relations, and is taught at universities and primary and secondary schools often using web-based interactive presentations. Tree of Life.
Vast bubble of galaxies discovered, given Hawaiian name. The immense bubble is 820 million light years from Earth and believed to be a fossil-like remnant of the birth of the universe. A University of Hawaiʻi-led discovery of an immense bubble 820 million light years from Earth is believed to be a fossil-like remnant of the birth of the universe. Astronomer Brent Tully from the UH Institute for Astronomy and his team unexpectedly found the bubble within a web of galaxies. The entity has been given the name Hoʻoleilana, a term drawn from the Kumulipo, a Hawaiian creation chant evoking the origin of structure. The new findings published in The Astrophysical Journal, mention these massive structures are predicted by the Big Bang theory, as the result of 3D ripples found in the material of the early universe, known as Baryon Acoustic Oscillations, which are fluctuations in the density of the visible baryonic matter (normal matter) of the universe, caused by acoustic density waves in the primordial plasma of the early universe.
Fire Investigation is the analysis of fire-related incidents. After firefighters extinguish a fire, an investigation is launched to determine the origin and cause of the fire or explosion. Investigations of such incidents require a systematic approach and knowledge of basic fire science. (Or the knowledge of life before life even existed. All you heard was a noise before you even knew what sound was, or before you even knew what time was, or anything else for that matter. Not to say that measurements of background radiation is not important, because it is. The question is Do you Know enough?).
Background Radiation is a measure of the ionizing Radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources. Background radiation originates from a variety of sources, both natural and artificial. These include cosmic radiation and environmental radioactivity from such as naturally occurring radioactive materials including radon and radium, and man-made fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents.
Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation was in 1964, US physicist Arno Allan Penzias and radio-astronomer Robert Woodrow Wilson discovered the CMB, estimating its temperature as 3.5 K, as they experimented with the Holmdel Horn Antenna.
The Big Bang Never Happened (youtube) - Big Bang never Happened
Big Bounce is a hypothetical scientific model of the formation of the known universe. It was originally suggested as a property of the cyclic model or oscillatory universe interpretation of the Big Bang where the first cosmological event was the result of the collapse of a previous universe; however, it is also a consequence of applying loop quantum gravity techniques to Big Bang cosmology and this need not be cyclic.
Conformal Cyclic Cosmology the universe iterates through infinite cycle.
Recombination in cosmology refers to the epoch at which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms. Recombination occurred about 378,000 years after the Big Bang (at a redshift of z = 1100). The word "recombination" is misleading, since the big bang theory doesn't posit that protons and electrons had been combined before, but the name exists for historical reasons since it was named before the Big Bang hypothesis became the primary theory of the creation of the universe.
Primordial Fluctuations are density variations in the early universe which are considered the seeds of all structure in the universe. Currently, the most widely accepted explanation for their origin is in the context of cosmic inflation. According to the inflationary paradigm, the exponential growth of the scale factor during inflation caused quantum fluctuations of the inflaton field to be stretched to macroscopic scales, and, upon leaving the horizon, to "freeze in". At the later stages of radiation- and matter-domination, these fluctuations re-entered the horizon, and thus set the initial conditions for structure formation. The statistical properties of the primordial fluctuations can be inferred from observations of anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background and from measurements of the distribution of matter, e.g., galaxy redshift surveys. Since the fluctuations are believed to arise from inflation, such measurements can also set constraints on parameters within inflationary theory.
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations are fluctuations in the density of the visible baryonic matter (normal matter) of the universe, caused by acoustic density waves in the primordial plasma of the early universe. In the same way that supernovae provide a "standard candle" for astronomical observations, BAO matter clustering provides a "standard ruler" for length scale in cosmology. The length of this standard ruler is given by the maximum distance the acoustic waves could travel in the primordial plasma before the plasma cooled to the point where it became neutral atoms (the epoch of recombination), which stopped the expansion of the plasma density waves, "freezing" them into place. The length of this standard ruler (~490 million light years in today's universe) can be measured by looking at the large scale structure of matter using astronomical surveys. BAO measurements help cosmologists understand more about the nature of dark energy (which causes the acceleration of the expansion of the universe) by constraining cosmological parameters.
Universe The Cosmology Quest (youtube)
Conspiracy Local (youtube)
The Electric Universe - HD Documentary 2015 (youtube)
Everything and Nothing with Jim Al-Khalili BBC
Not long ago, the center of the Milky Way exploded. Researchers find evidence of a cataclysmic flare that punched so far out of the galaxy its impact was felt 200,000 light years away. A titanic, expanding beam of energy sprang from close to the supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way just 3.5 million years ago, sending a cone-shaped burst of radiation through both poles of the galaxy and out into deep space.
Universe Theory's - What we know so far
Spatial Intelligence - Digital Physics
Nebular Hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System. It suggests that the Solar System formed from nebulous material.
Morphs Collaboration was a coordinated study to determine the morphologies of galaxies in distant clusters and to investigate the evolution of galaxies as a function of environment and epoch. Eleven clusters were examined and a detailed ground-based and space-based study was carried out.
Maybe the Big Bang is the reason why we're flying through the universe? Formation and evolution of the Solar System. Maybe the Big Bang was needed to create motion, which is needed to create energy and gravity?
Superconductor - Electromagnetism - Light - Atoms
Interstellar Medium is the matter that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field.
Vacuum Energy is an underlying background energy that exists in space throughout the entire Universe. One contribution to the vacuum energy may be from virtual particles which are thought to be particle pairs that blink into existence and then annihilate in a timespan too short to observe. Their behavior is codified in Heisenberg's energy–time uncertainty principle. Still, the exact effect of such fleeting bits of energy is difficult to quantify. The vacuum energy is a special case of zero-point energy that relates to the quantum vacuum.
 If atoms get their
energy from space, then where does space get its energy from? Is the sun pushing
through space, or being pulled through space, or just falling through
space? Will space expand into an equilibrium and just live off the
energy that comes from the motion of particles?
If atoms get their
energy from space, then where does space get its energy from? Is the sun pushing
through space, or being pulled through space, or just falling through
space? Will space expand into an equilibrium and just live off the
energy that comes from the motion of particles?It's good to know that there are still a lot of things that you just can't comprehend or think about for too long because it breaks your brain. When you can't find a logical answer to something or have an explanation for something, and when you're completely at a loss for words and you have no idea how to proceed, It's like you're frozen in time and you're completely lost in a void. All you can do is go back to the reality that you know, and try not to think about that void of empty space, or the perceived empty space? Maybe the space is created by my lack of knowledge and information, so it may be the space between my ears? But on the good side, these brain breaking exercises are not that bad and could actually be beneficial to you. Like wondering what's outside the universe. Does outer space have an end? And if it does, what's on the other side? These are the kind of things that you don't want to think about for too long because they seem to have no end. But it's good to have these types of questions around, it can help exercise your brain a little. When the brain has an infinite number of choices to choose from, the brain may choose something at random, and then you will have to determine whether it's worth the time and effort to continue, which is usually no. There's no reason to think about something that is extremely difficult, especially when there are better things to think about. You need balance. And you certainly don't want to pretend to have an answer, because then you will never find an answer. So I occasionally go back to the void, just to take a peak, maybe something changed. Nope, I still don't see anything in 2020. Maybe I should work more on my consciousness, and not depend so much on my eyes. Illusions are real, so how will I know the difference?
No Man's Land is an indeterminate or undefined place or state. No Man's Land can also mean a land that is unoccupied or is under dispute between parties who leave it unoccupied out of fear or uncertainty. A land or area that is un-owned or uninhabited, or undesirable. A disputed ground between the front lines or trenches of two opposing armies. Ignorance.
When I look at the universe, it doesn't make me feel small, because the universe has many more things that are much smaller than me than it does have things that are much bigger than me. I'm not sure if I'm in the middle or in between, but I'm definitely some where, and I'm definitely connected to everything big and small. So where do we go from here? I guess we begin by understanding and learning about what being "here" actually means. We might just find out that being there or being anywhere is still being here. Not to say that there's no differences in locations, because every place is a little different and some places can be extremely different in many ways, but everything shares the same thing, the place we call here. Light Quotes - Life Quotes.
